Содержание
- 2. AGENDA Quantitative research in Management: methodology. Introduction to IBM SPSS – September 6 Data visualization. Descriptive
- 3. DESCRIBING DATA: «FIRST SIGHT ON THE DATA» Graphical description E.g., histograms (to identify outlines – «выбросы»)
- 4. GRAPHICAL DESCRIPTION pie chart bar charts scatterplots and bubbles - used for comparison of two variables
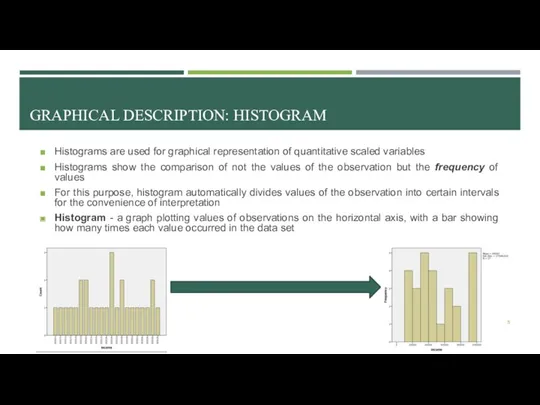
- 5. GRAPHICAL DESCRIPTION: HISTOGRAM Histograms are used for graphical representation of quantitative scaled variables Histograms show the
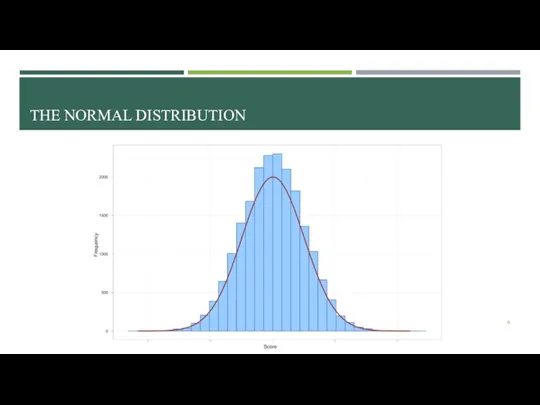
- 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
- 7. GRAPHICAL DESCRIPTION: HISTOGRAMS AND NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The ‘Normal’ distribution Bell («колокол») shaped Symmetrical around the center
- 8. TEST OF NORMALITY: HOW TO TEST IF THE DATA IS NORMALLY DISTRIBUTED? 1st way: To look
- 9. TEST OF NORMALITY: HOW TO TEST IF THE DATA IS NORMALLY DISTRIBUTED? 2nd way: To conduct
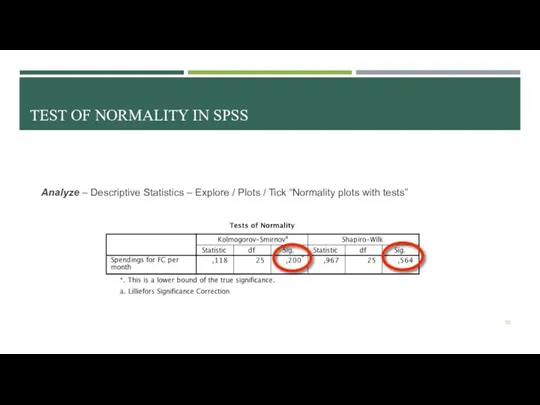
- 10. TEST OF NORMALITY IN SPSS Analyze – Descriptive Statistics – Explore / Plots / Tick “Normality
- 11. TEST OF NORMALITY: CONDUCTION H0: sample is not normally distributed H1: sample is normally distributed We
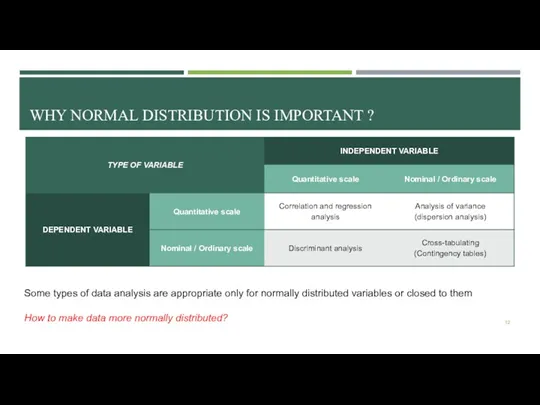
- 12. WHY NORMAL DISTRIBUTION IS IMPORTANT ? Some types of data analysis are appropriate only for normally
- 13. DESCRIBING DATA: «FIRST SIGHT ON THE DATA» Graphical description E.g., histograms (to identify outlines – «выбросы»)
- 14. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Analysis of the basic statistical parameters in order to get acquainted with the data,
- 15. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: MAIN INDICATORS Mode «мода» Median «медиана» Range «размах» Minimum Maximum Mean (=average) «среднее» Standard
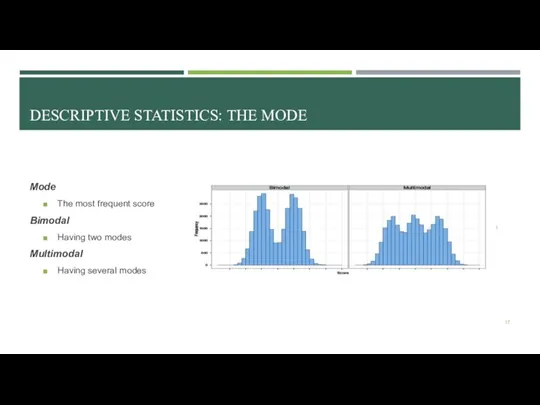
- 16. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: THE MODE Mode – the most frequent observation, typical observation, represents most frequent category
- 17. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: THE MODE Mode The most frequent score Bimodal Having two modes Multimodal Having several
- 18. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: THE MEDIAN Median – the value that is in the middle: half of the
- 19. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: RANGE, MINIMUM, MAXIMUM Range The smallest / lowest score (minimum) subtracted from the largest
- 20. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: THE MEAN Mean The sum of scores divided by number of scores
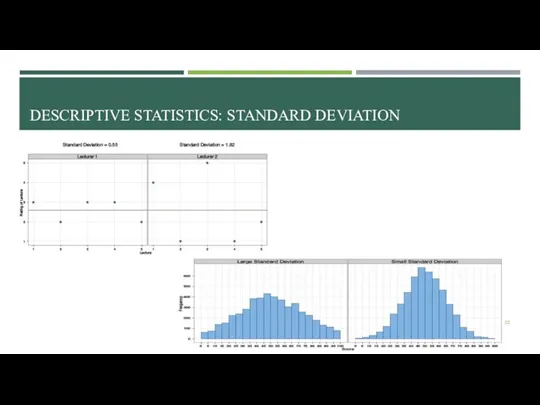
- 21. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: STANDARD DEVIATION Standard deviation the most common indicator of the dispersion of values of
- 22. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: STANDARD DEVIATION
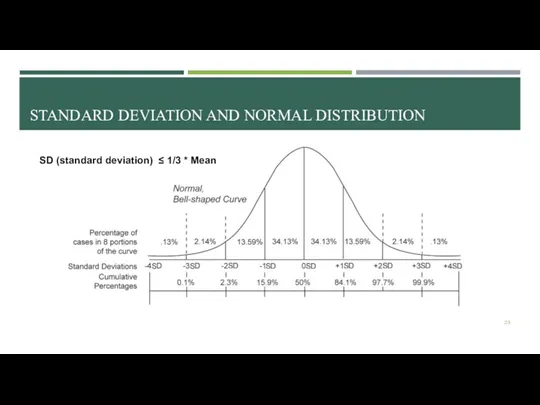
- 23. STANDARD DEVIATION AND NORMAL DISTRIBUTION SD (standard deviation) ≤ 1/3 * Mean
- 24. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS IN SPSS Analyze – Descriptive statistics – Frequencies OR Analyze – Descriptive statistics –
- 25. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS FOR VARIABLES IN DIFFERENT SCALES Nominal – mode Ordinal – mode + median, mean,
- 26. CROSS-TABULATING (CONTINGENCY TABLES)
- 27. CROSS-TABULATING Contingency tables (or cross tables) are usually constructed in the case when two qualitative (nominal
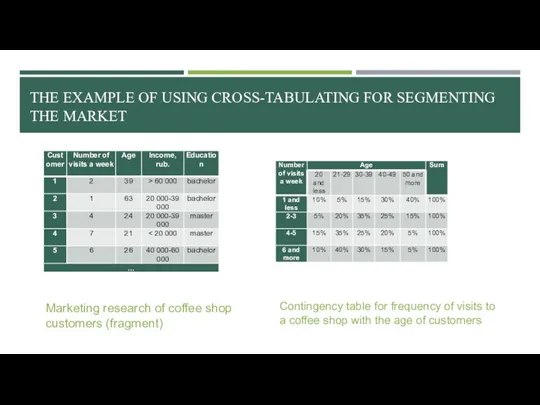
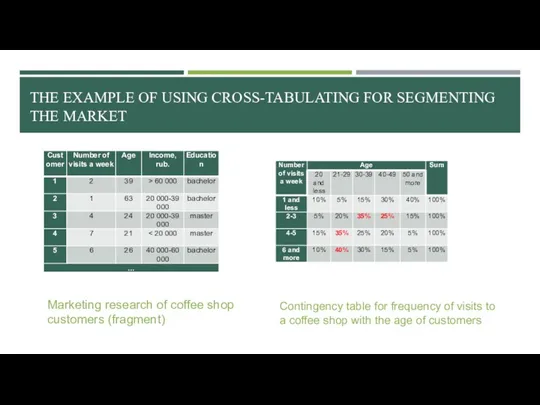
- 28. THE EXAMPLE OF USING CROSS-TABULATING FOR SEGMENTING THE MARKET Marketing research of coffee shop customers (fragment)
- 29. THE EXAMPLE OF USING CROSS-TABULATING FOR SEGMENTING THE MARKET Marketing research of coffee shop customers (fragment)
- 30. CONTINGENCY TABLES: VISUALIZATION Put the independent variable on columns and the dependent variable on rows Percentages
- 31. Pearson Chi-Square test is a nonparametric method that allows to check the presence or absence of
- 32. EXAMPLE №2: CROSS-TABULATING Is there any connection between family status and the fact of keeping any
- 33. CROSS-TABULATING IN SPSS Analyze – Descriptive statistics – Crosstabs Choose dependent and independent variables, identify the
- 34. WHAT TO DO WITH THE QUANTITATIVE DATA?..
- 36. Скачать презентацию






















 Комиссарские мероприятия на целине и в подготовительный период
Комиссарские мероприятия на целине и в подготовительный период Бренд-менеджмент (управление торговой маркой). Кобрендинг
Бренд-менеджмент (управление торговой маркой). Кобрендинг Менеджмент. Поняття та сутність
Менеджмент. Поняття та сутність Определение системы. Классы систем
Определение системы. Классы систем Общая характеристика направления Менеджмент. Тема 1
Общая характеристика направления Менеджмент. Тема 1 Анализ элементов корпоративной культуры в отеле Чеховъ г. Екатеринбург
Анализ элементов корпоративной культуры в отеле Чеховъ г. Екатеринбург Международные речные перевозки грузов
Международные речные перевозки грузов Кадры организации
Кадры организации Курт Левин. Модели управления изменениями
Курт Левин. Модели управления изменениями Координация и контроль как функции управления
Координация и контроль как функции управления Эффективность управления организацией
Эффективность управления организацией Международные стандарты серии ИСО 9000 по управлению качеством и обеспечению качества
Международные стандарты серии ИСО 9000 по управлению качеством и обеспечению качества Организация туристской индустрии
Организация туристской индустрии Мотивация трудовой деятельности
Мотивация трудовой деятельности Лидерство в системе менеджмента
Лидерство в системе менеджмента Work Systems Design
Work Systems Design Стратегия голубого океана (Blue ocean strategy – BOS)
Стратегия голубого океана (Blue ocean strategy – BOS) Схема организации Главного управления МЧС России по Республике Тыва
Схема организации Главного управления МЧС России по Республике Тыва Топтың түрлері. (эталон, негізгі, қосалқы топтар). Топтық шешімдер қабылдау
Топтың түрлері. (эталон, негізгі, қосалқы топтар). Топтық шешімдер қабылдау Упаковка и тара. Маркировка грузов
Упаковка и тара. Маркировка грузов Портрет менеджера. Основные качества менеджера
Портрет менеджера. Основные качества менеджера Формы деловых коммуникаций
Формы деловых коммуникаций Приглашение на первую встречу. Рекрутирование
Приглашение на первую встречу. Рекрутирование Модели принятия решений
Модели принятия решений Классификация предприятий по типу инновационного поведения
Классификация предприятий по типу инновационного поведения Формирование базисных стратегий продукта
Формирование базисных стратегий продукта Прийняття управлінських рішень
Прийняття управлінських рішень Особенности оформления основных видов управленческих документов
Особенности оформления основных видов управленческих документов