Содержание
- 2. Agenda Test Design and Implementation process Example Test Case Management tools Zephyr for Jira
- 3. Test Design Process
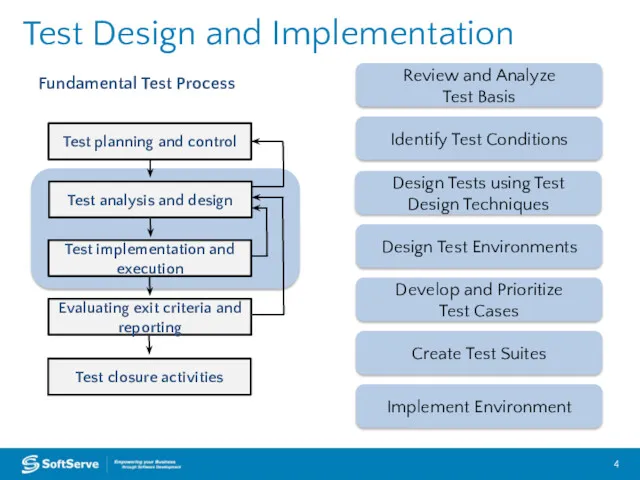
- 4. Test Design and Implementation Test planning and control Test analysis and design Test implementation and execution
- 5. Why Test Cases? Testing efficiency: be ready to test once the code is ready Early bug
- 6. Example Driving test is an analogy for testing. We will use it to illustrate the Test
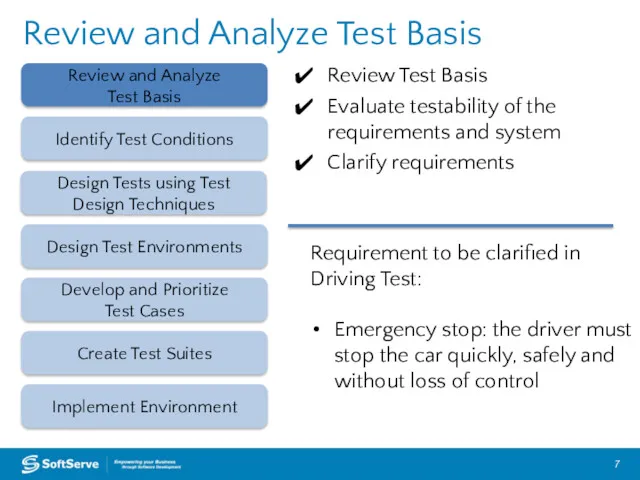
- 7. Review and Analyze Test Basis Review Test Basis Evaluate testability of the requirements and system Clarify
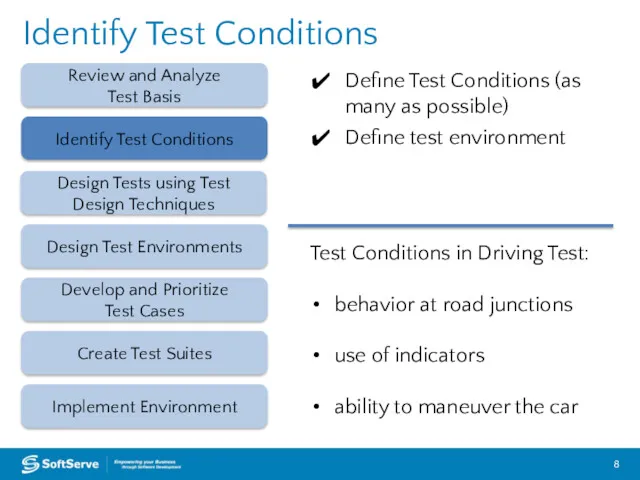
- 8. Identify Test Conditions Review and Analyze Test Basis Design Test Environments Create Test Suites Implement Environment
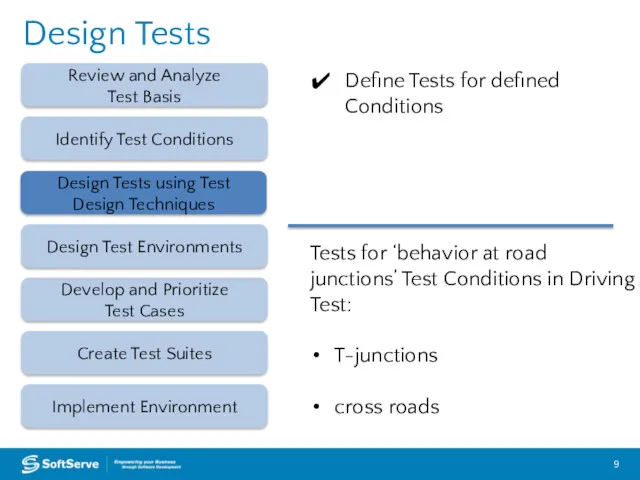
- 9. Design Tests Review and Analyze Test Basis Design Test Environments Create Test Suites Implement Environment Identify
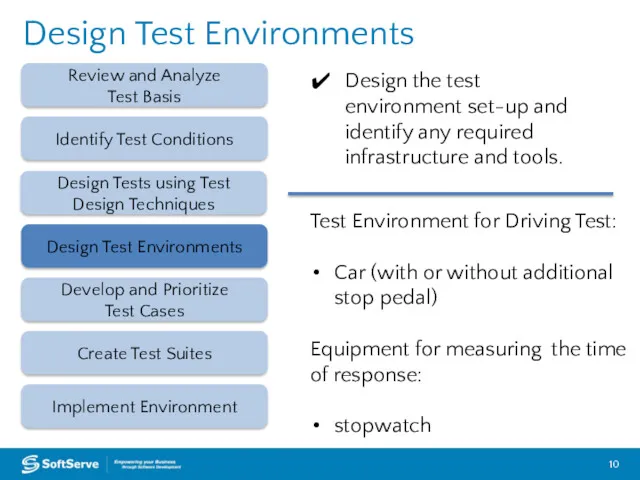
- 10. Design Test Environments Review and Analyze Test Basis Design Test Environments Create Test Suites Implement Environment
- 11. Test Case for test condition 'junctions' in Driving Test: take the route down Mayfield Road to
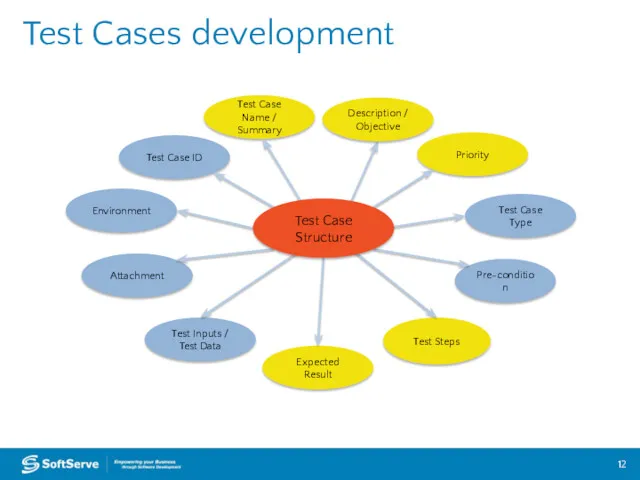
- 12. Test Cases development Attachment Test Case Name / Summary Description / Objective Priority Test Steps Expected
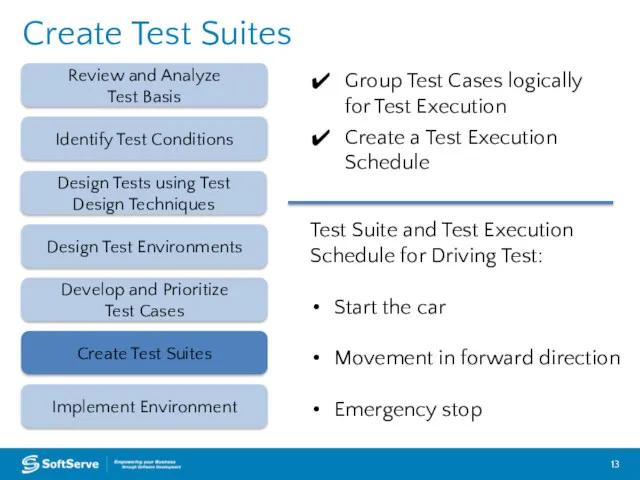
- 13. Create Test Suites Review and Analyze Test Basis Design Test Environments Create Test Suites Implement Environment
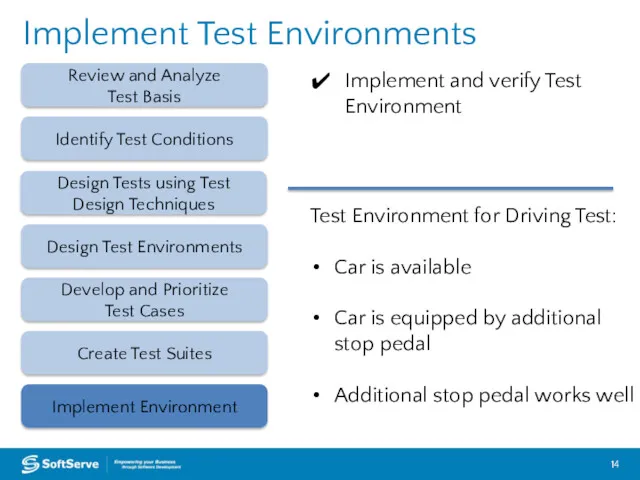
- 14. Implement Test Environments Review and Analyze Test Basis Design Test Environments Create Test Suites Implement Environment
- 15. Test Design and Implementation Example
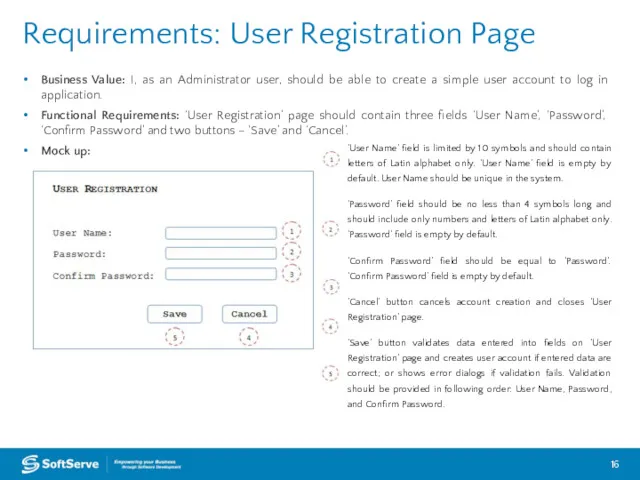
- 16. Requirements: User Registration Page Business Value: I, as an Administrator user, should be able to create
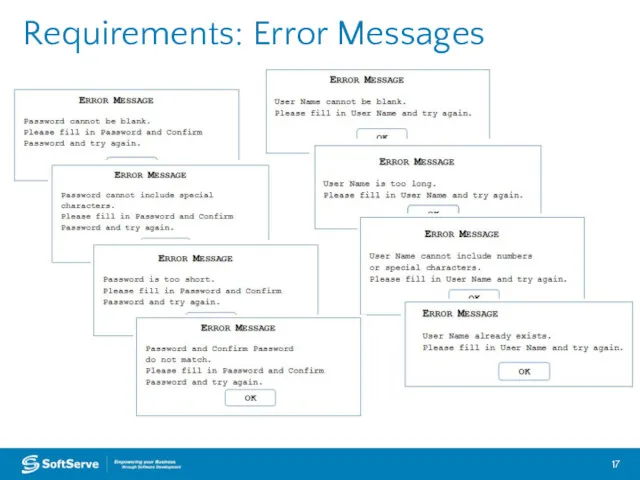
- 17. Requirements: Error Messages
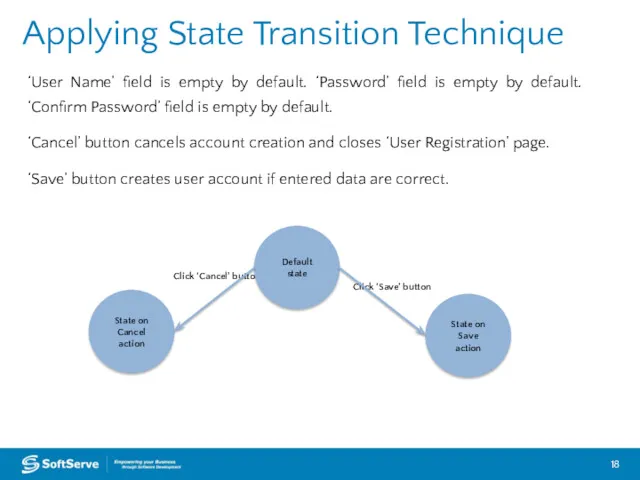
- 18. Click ‘Save’ button Click ‘Cancel’ button Applying State Transition Technique State on Cancel action State on
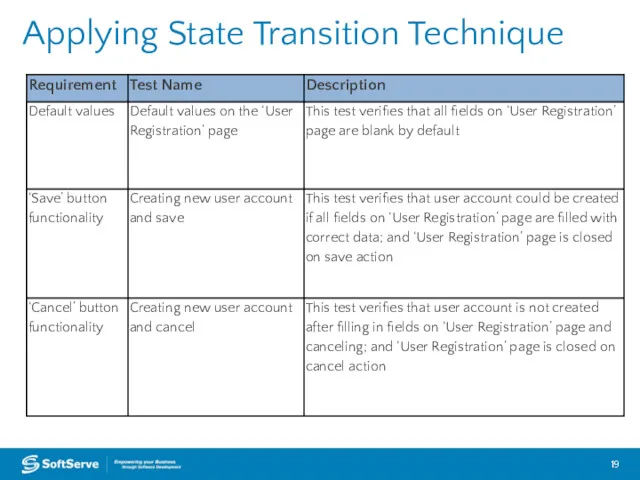
- 19. Applying State Transition Technique
- 20. Applying State Transition Technique State on Save action Default state Click ‘Save’ button Validate Password Click
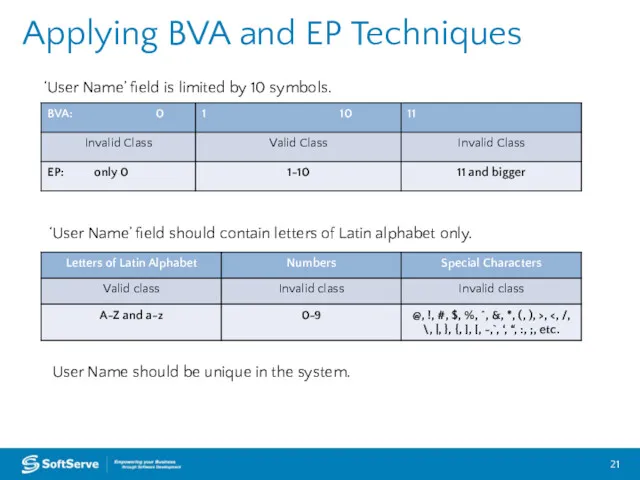
- 21. Applying BVA and EP Techniques ‘User Name’ field is limited by 10 symbols. ‘User Name’ field
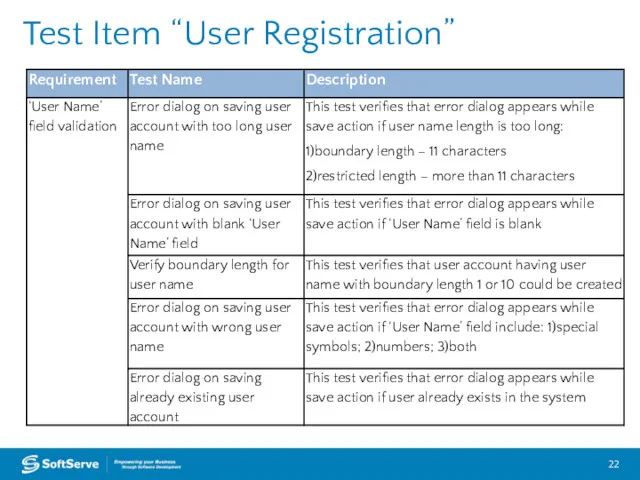
- 22. Test Item “User Registration”
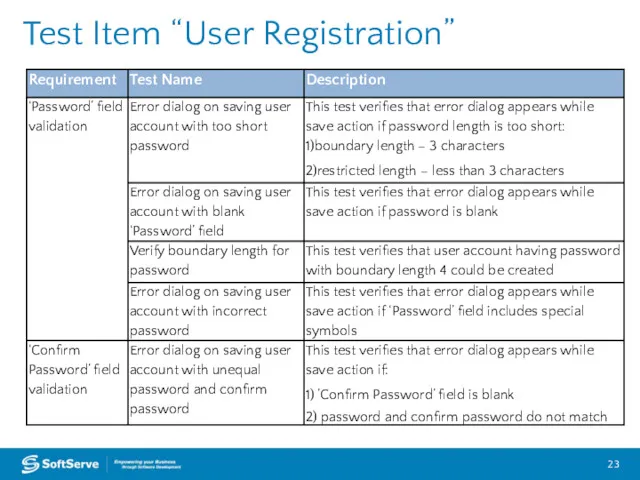
- 23. Test Item “User Registration”
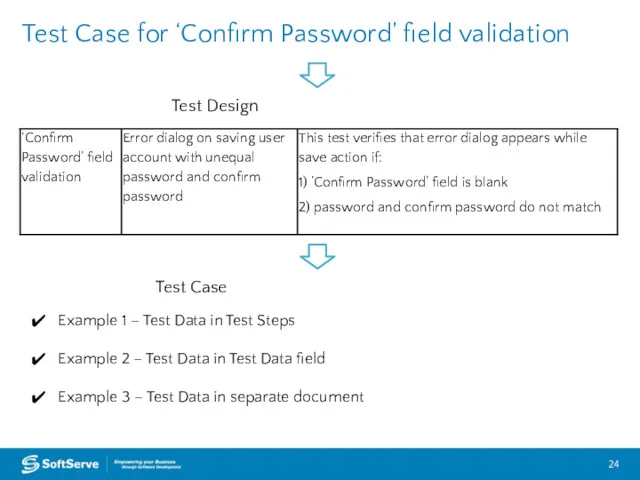
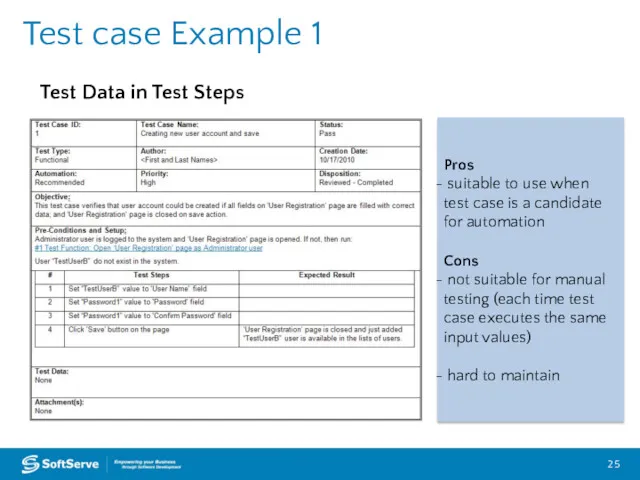
- 24. Test Case for ‘Confirm Password’ field validation Test Design Test Case Example 1 – Test Data
- 25. Test case Example 1 Pros suitable to use when test case is a candidate for automation
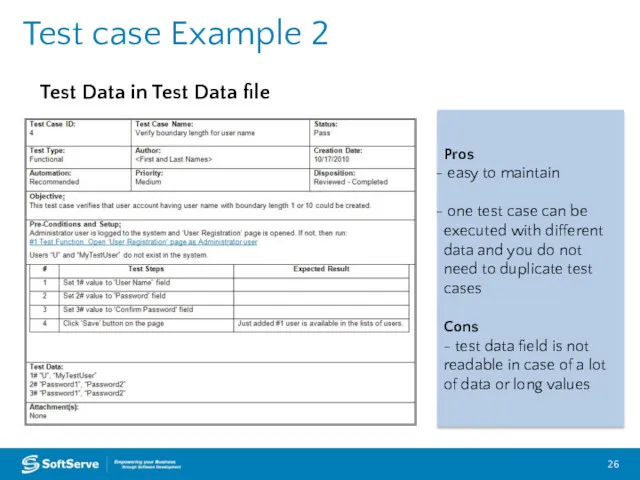
- 26. Test case Example 2 Pros easy to maintain one test case can be executed with different
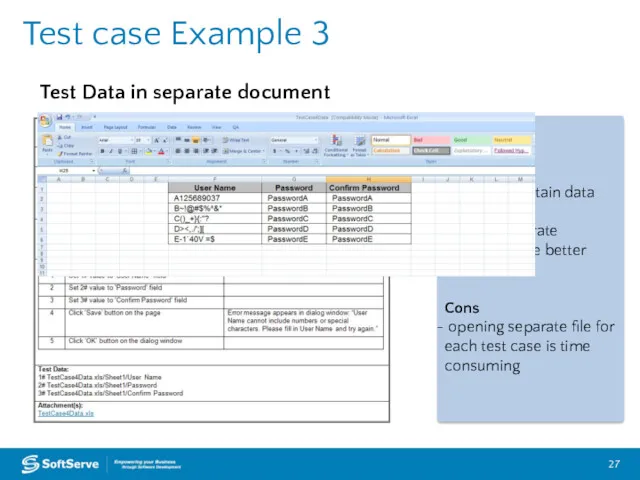
- 27. Test case Example 3 Pros easy to maintain data data in separate document are better structured
- 28. Tips and Tricks Write test cases for all requirements Write test cases with necessary detail level
- 29. Test Case Management Tools: Zephyr for Jira
- 30. Test Case Management Tools Test Case Management Tool – A tool that provides support to the
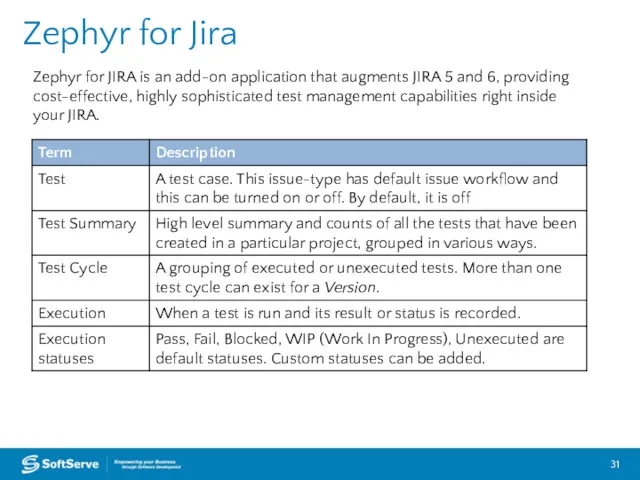
- 31. Zephyr for Jira Zephyr for JIRA is an add-on application that augments JIRA 5 and 6,
- 32. Major features include: Create, view, edit and clone tests Link to stories, tasks, requirements etc. Plan
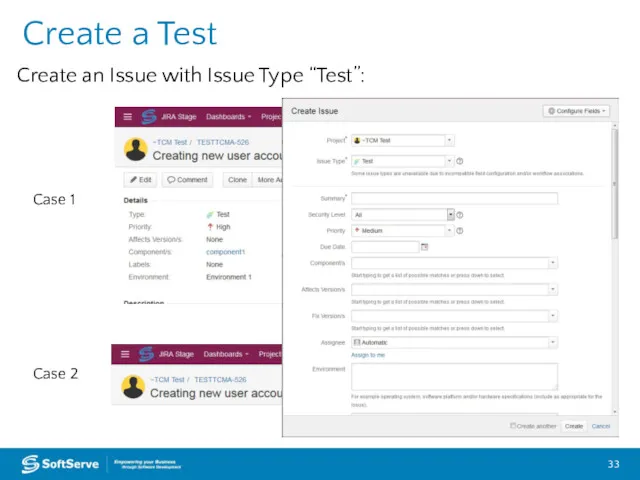
- 33. Create a Test Case 1 Case 2 Create an Issue with Issue Type “Test”:
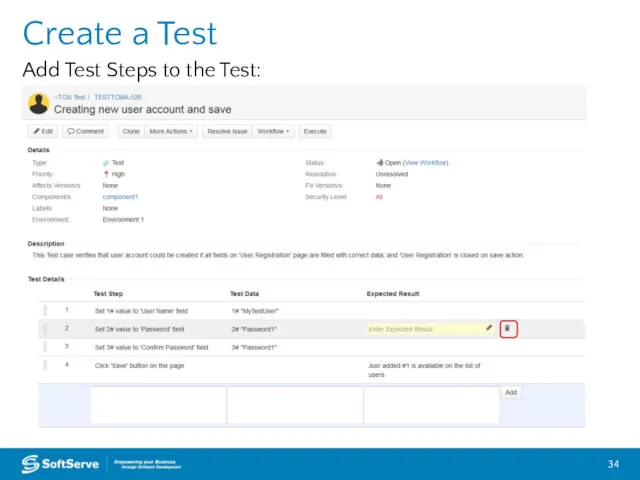
- 34. Create a Test Add Test Steps to the Test:
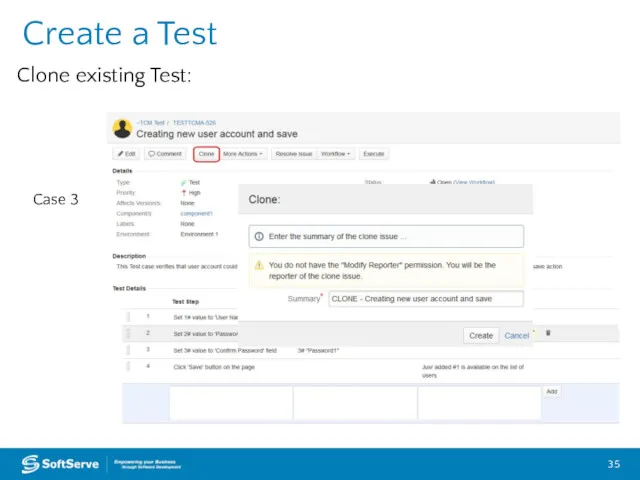
- 35. Create a Test Case 3 Clone existing Test:
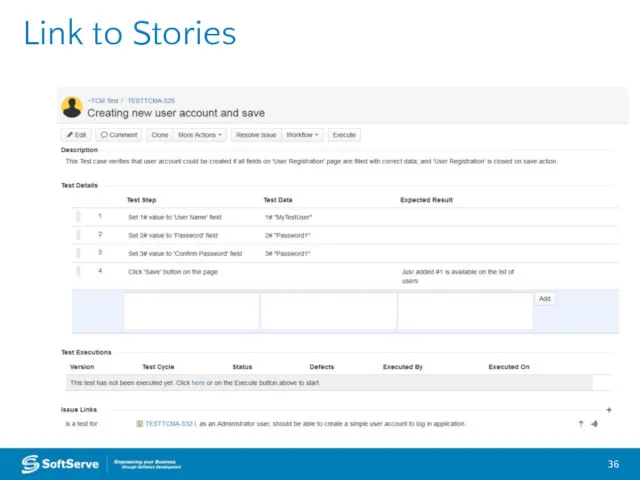
- 36. Link to Stories
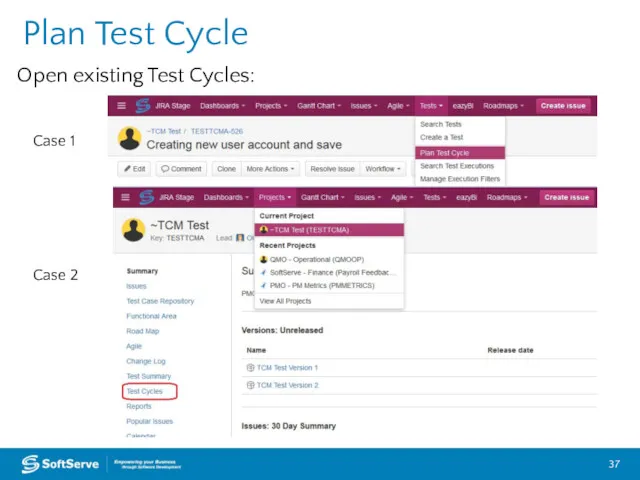
- 37. Plan Test Cycle Case 1 Case 2 Open existing Test Cycles:
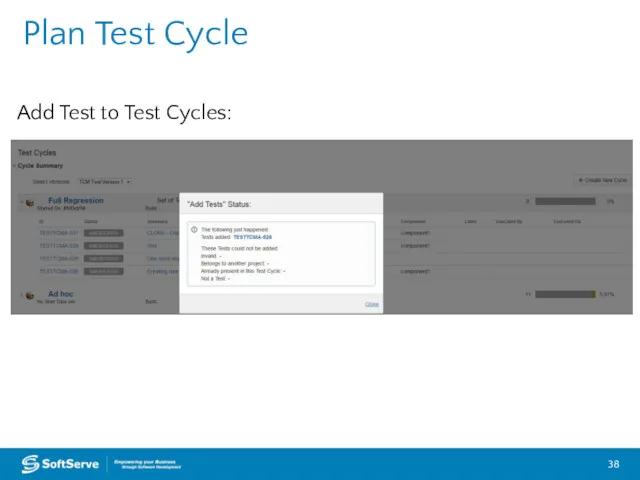
- 38. Plan Test Cycle Add Test to Test Cycles:
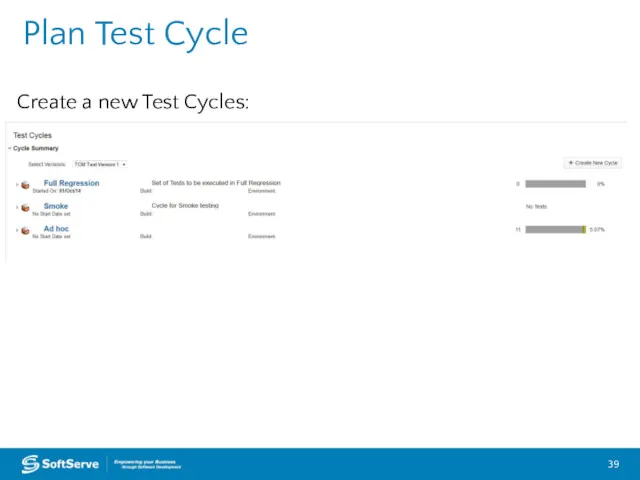
- 39. Plan Test Cycle Create a new Test Cycles:
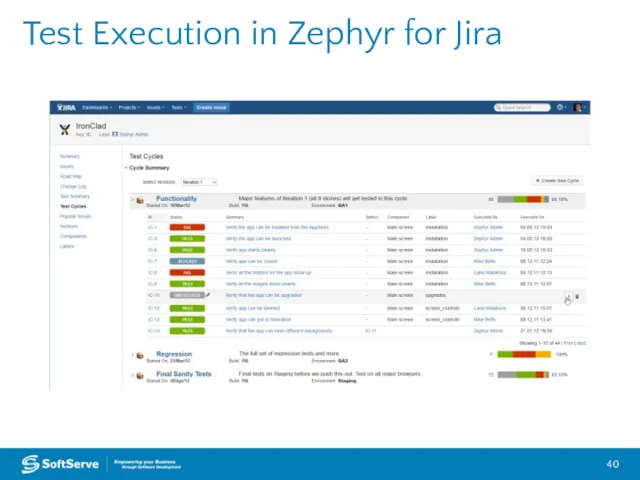
- 40. Test Execution in Zephyr for Jira
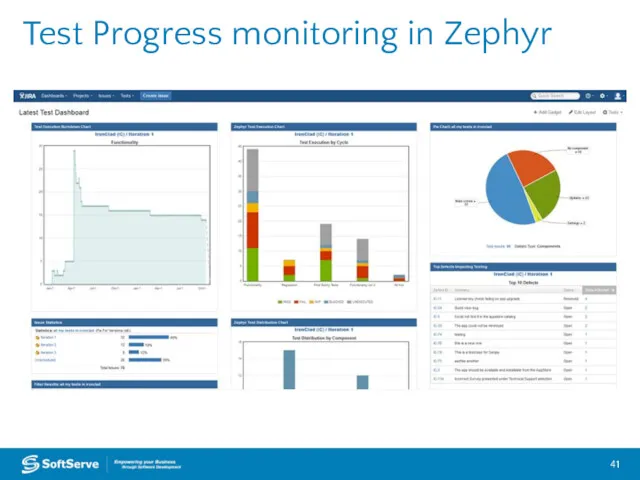
- 41. Test Progress monitoring in Zephyr
- 43. Скачать презентацию











 Группы в организациях
Группы в организациях Система безопасности в гостиничном бизнесе
Система безопасности в гостиничном бизнесе Репутация. Фактор деловой репутации, как компонент нематериальных ресурсов
Репутация. Фактор деловой репутации, как компонент нематериальных ресурсов Создание единого центра управления станциями
Создание единого центра управления станциями Эффективный руководитель
Эффективный руководитель Организационное обеспечение информационной безопасности: Организация охраны объектов
Организационное обеспечение информационной безопасности: Организация охраны объектов Связь информационных систем и уровней управления на предприятии
Связь информационных систем и уровней управления на предприятии Профессиональный и личностный рост
Профессиональный и личностный рост Проблемно-ситуативный анализ или case-study. (Лекция 3)
Проблемно-ситуативный анализ или case-study. (Лекция 3) Управление персоналом на авиапредприятиях
Управление персоналом на авиапредприятиях Оптимизация зонирования складских помещений Артпласт
Оптимизация зонирования складских помещений Артпласт Организация поточного и автоматизированного производства
Организация поточного и автоматизированного производства Інформаційні системи та технології в інформаційно-комунікаційному менеджменті. (Тема 2)
Інформаційні системи та технології в інформаційно-комунікаційному менеджменті. (Тема 2) Планирование и прогнозирование развития образования. Тема 4
Планирование и прогнозирование развития образования. Тема 4 Понятие и виды деловой карьеры
Понятие и виды деловой карьеры Организационные структуры управления
Организационные структуры управления Складской технологический процесс. Операции по отпуску товаров
Складской технологический процесс. Операции по отпуску товаров Культура управленческого труда
Культура управленческого труда Основные технологии перевозки грузов
Основные технологии перевозки грузов Корпоративна культура та засоби її створення
Корпоративна культура та засоби її створення Организация туристской индустрии. Инфраструктура туризма
Организация туристской индустрии. Инфраструктура туризма Стратегические модели менеджмента
Стратегические модели менеджмента Роль внутреннего аудита в корпоративном управлении компании
Роль внутреннего аудита в корпоративном управлении компании Управление рисками
Управление рисками Способы предоставления продукции на контроль и методы сбора выборочной совокупности
Способы предоставления продукции на контроль и методы сбора выборочной совокупности Проект организации и управления зоны технического обслуживания №1 специализированного АТП
Проект организации и управления зоны технического обслуживания №1 специализированного АТП Лидерство
Лидерство Жизненный (личный) проект. Признаки жизненного проекта
Жизненный (личный) проект. Признаки жизненного проекта