Содержание
- 2. THIS CHAPTER WILL HELP YOU UNDERSTAND: LO 1 What we mean by a company’s strategy. LO
- 3. A company’s strategy is the set of actions that its managers take to outperform the company’s
- 4. WHAT DO WE MEAN BY STRATEGY ? What is our present situation? Business environment and industry
- 5. WHAT IS STRATEGY ABOUT? Strategy is all about How: How to attract and please customers. How
- 6. Strategy is about competing differently from rivals—doing what competitors don’t do or, even better, doing what
- 7. WHY BOTHER WITH STRATEGY? A firm needs a strategy to specify what actions are going to
- 8. STRATEGY AND COMPETITORS Strategy is about competing differently from rivals— Doing what they do not do
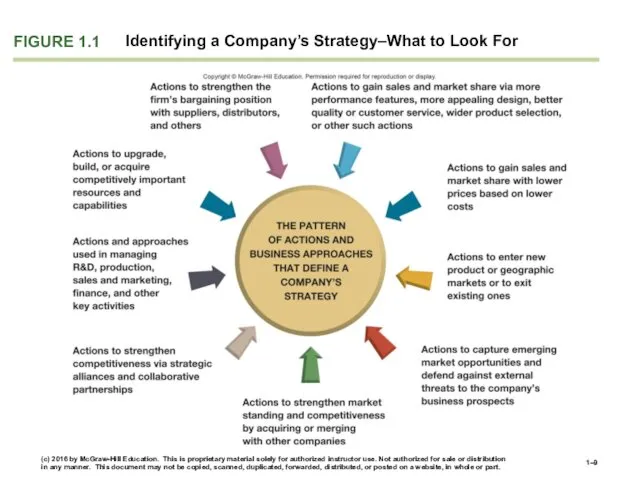
- 9. FIGURE 1.1 Identifying a Company’s Strategy–What to Look For (c) 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is
- 10. (c) 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized
- 11. STRATEGY AND THE QUEST FOR COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE Competitive Advantage Requires meeting customer needs either more effectively
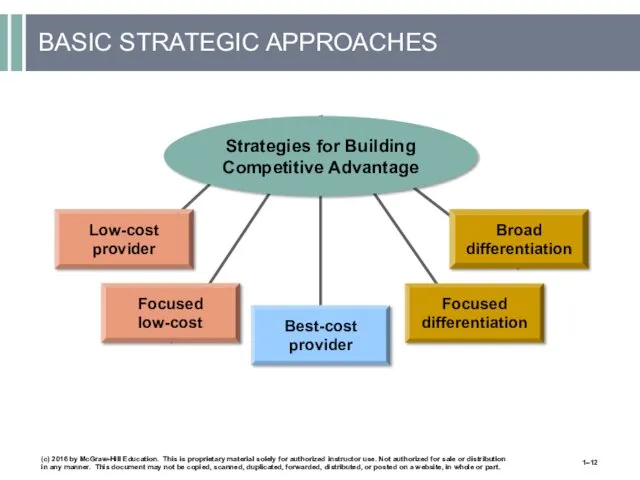
- 12. BASIC STRATEGIC APPROACHES (c) 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor
- 13. STRATEGIC APPROACHES Building a competitive advantage by: Striving to become the industry’s low-cost provider (efficiency). Outcompeting
- 14. A firm achieves a competitive advantage when it provides buyers with superior value compared to rival
- 15. GAINING SUSTAINABLE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE How to create a sustainable competitive advantage: Develop valuable expertise and competitive
- 16. WHY A COMPANY’S STRATEGY EVOLVES OVER TIME Managers modify strategy in response to: Changing market conditions
- 17. Changing circumstances and ongoing management efforts to improve the strategy cause a company’s strategy to evolve
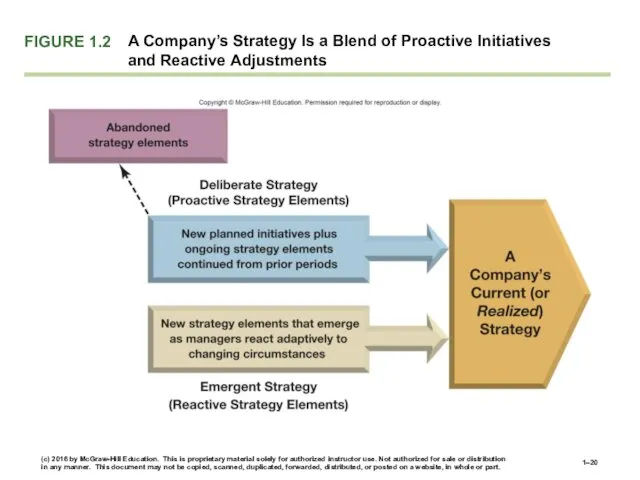
- 18. THE EVOLVING NATURE OF A FIRM’S STRATEGY Realized (current) strategy is a blend of: Proactive (deliberate)
- 19. A company’s deliberate strategy consists of proactive strategy elements that are both planned and realized as
- 20. FIGURE 1.2 A Company’s Strategy Is a Blend of Proactive Initiatives and Reactive Adjustments (c) 2016
- 21. Just for Fun: Using the terms shown in Exhibit 1.2, explain why U.S. football teams get
- 22. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN A FIRM’S STRATEGY AND ITS BUSINESS MODEL (c) 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education. This
- 23. A COMPANY’S STRATEGY AND ITS BUSINESS MODEL How the business will make money : By providing
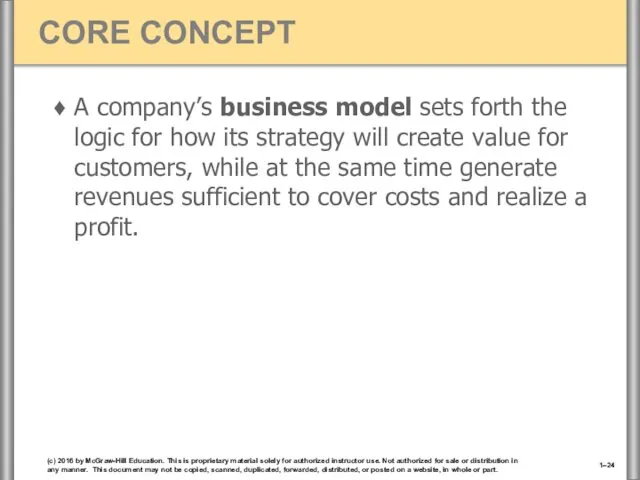
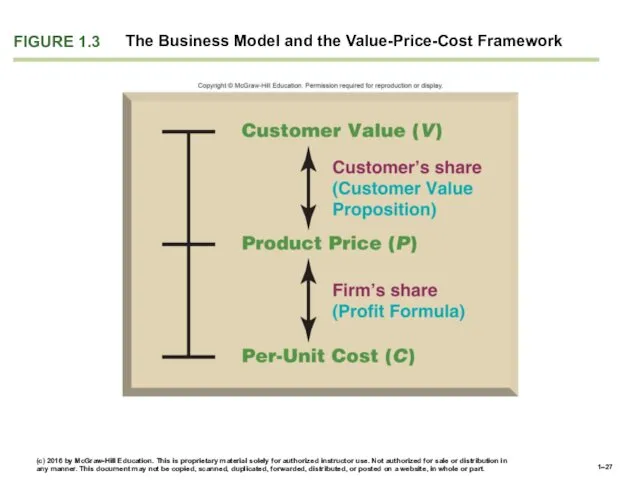
- 24. A company’s business model sets forth the logic for how its strategy will create value for
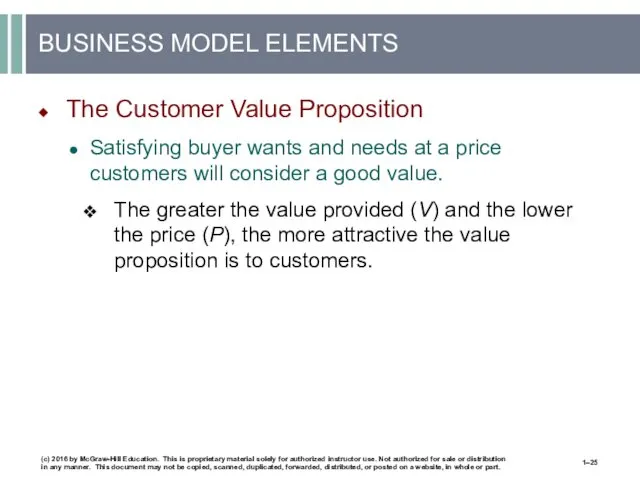
- 25. BUSINESS MODEL ELEMENTS The Customer Value Proposition Satisfying buyer wants and needs at a price customers
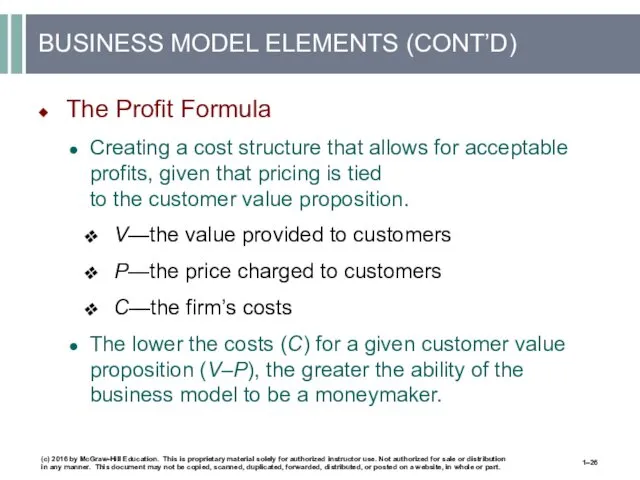
- 26. BUSINESS MODEL ELEMENTS (CONT’D) The Profit Formula Creating a cost structure that allows for acceptable profits,
- 27. FIGURE 1.3 The Business Model and the Value-Price-Cost Framework
- 28. Amazon's continuing lack of profitability has begun to concern its long-term investors. What internal and external
- 29. (c) 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized
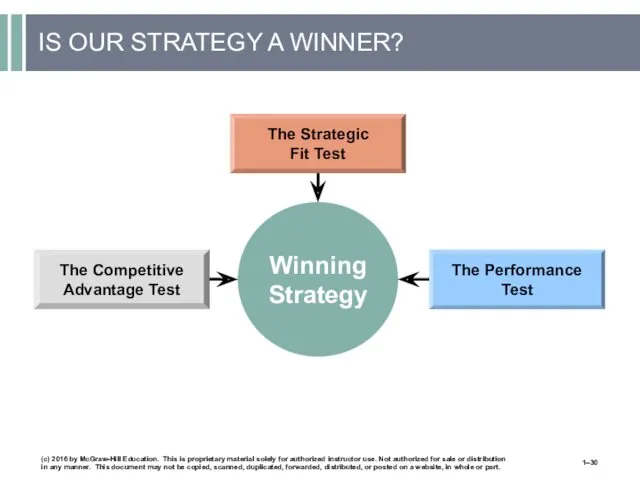
- 30. IS OUR STRATEGY A WINNER? (c) 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for
- 31. WHAT MAKES A STRATEGY A WINNER? A winning strategy must pass three tests: The Fit Test
- 32. WHY CRAFTING AND EXECUTING STRATEGY ARE IMPORTANT TASKS Strategy provides: A prescription for doing business. A
- 33. How well a company performs is directly attributable to the caliber of its strategy and the
- 34. Google’s web browser-based Chrome operating system and its online applications suite are now challenging Microsoft’s long-term
- 36. Скачать презентацию

























 Автоматизированные системы управления складом и транспортом
Автоматизированные системы управления складом и транспортом Теория продаж. Установление контакта
Теория продаж. Установление контакта Авиакомпания SCAT
Авиакомпания SCAT Закономерности, принципы и методы управления персоналом
Закономерности, принципы и методы управления персоналом Теоретико-методологические основы социологии управления
Теоретико-методологические основы социологии управления Кодекс поведения государственных служащих. Игра
Кодекс поведения государственных служащих. Игра Effective team 2019
Effective team 2019 Школа принятия управленческих решений. Преимущество и недостатки
Школа принятия управленческих решений. Преимущество и недостатки Типология управленческих решений и требования, предъявляемые к ним
Типология управленческих решений и требования, предъявляемые к ним Управление процессами труда в гостиничном предприятии
Управление процессами труда в гостиничном предприятии Групповая дифференциация и лидерство
Групповая дифференциация и лидерство Internal control and deontology - Chapter 9 External audit
Internal control and deontology - Chapter 9 External audit Введение в теорию управления. Развитие управленческой мысли
Введение в теорию управления. Развитие управленческой мысли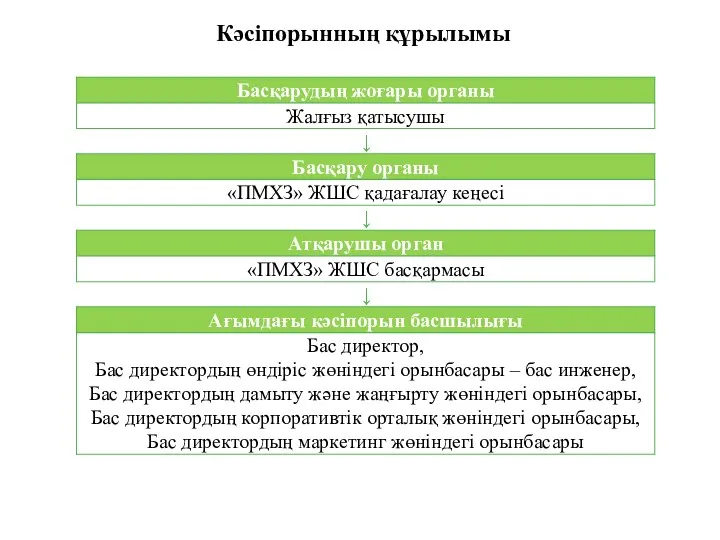 Кәсіпорынның құрылымы
Кәсіпорынның құрылымы Анализ существующих решений проблематики, выявление ключевых достоинств и недостатков
Анализ существующих решений проблематики, выявление ключевых достоинств и недостатков Кадровый потенциал и направления его совершенствования
Кадровый потенциал и направления его совершенствования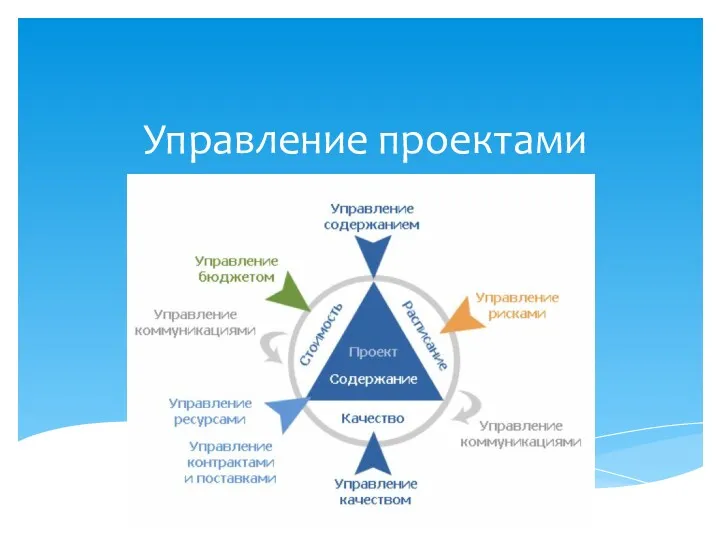 Управление проектами
Управление проектами Managing risks
Managing risks Основы менеджмента
Основы менеджмента Структура и основной сортамент продукции ОАО ММК. Численность кадрового состава
Структура и основной сортамент продукции ОАО ММК. Численность кадрового состава Системы мотивации и стимулирования трудовой деятельности
Системы мотивации и стимулирования трудовой деятельности Принципы организации деятельности СМИ. (Тема 2)
Принципы организации деятельности СМИ. (Тема 2) Кадрове забезпечення системи управління персоналом підприємства. ДР Запорожець
Кадрове забезпечення системи управління персоналом підприємства. ДР Запорожець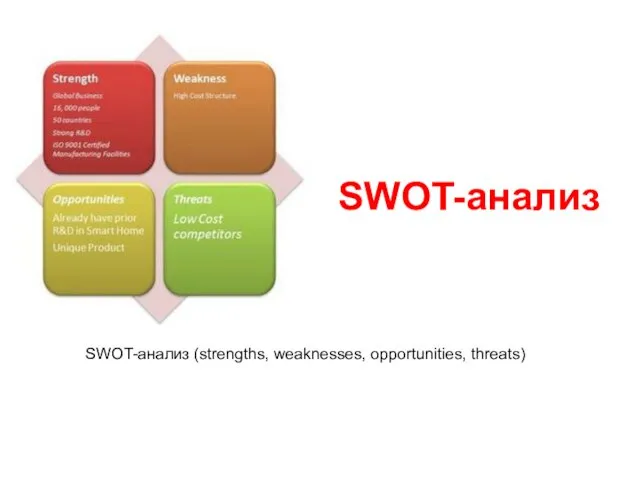 SWOT-анализ (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats)
SWOT-анализ (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) Анализ и совершенствование системы мотивации деятельности персонала (на примере ПАО Сбербанк)
Анализ и совершенствование системы мотивации деятельности персонала (на примере ПАО Сбербанк) Философия управления персоналом
Философия управления персоналом Управление проектами. Управление содержанием проекта
Управление проектами. Управление содержанием проекта Самоорганизация для достижения результатов
Самоорганизация для достижения результатов