Содержание
- 2. Session 1: Types of language classroom question and correction techniques
- 3. Questions relating to issues in this session? Why are questions crucial in all learning ? What
- 4. Teachers typically ask between 300-400 questions per day Questioning is crucial in: managing the class engaging
- 5. EFL: Types of questions
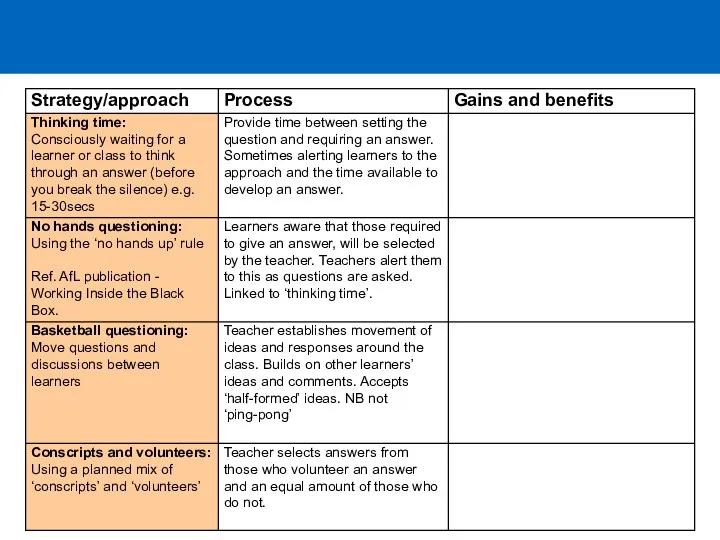
- 6. Language teacher questions convergent question hypothetical question probing question procedural question display question divergent question concept
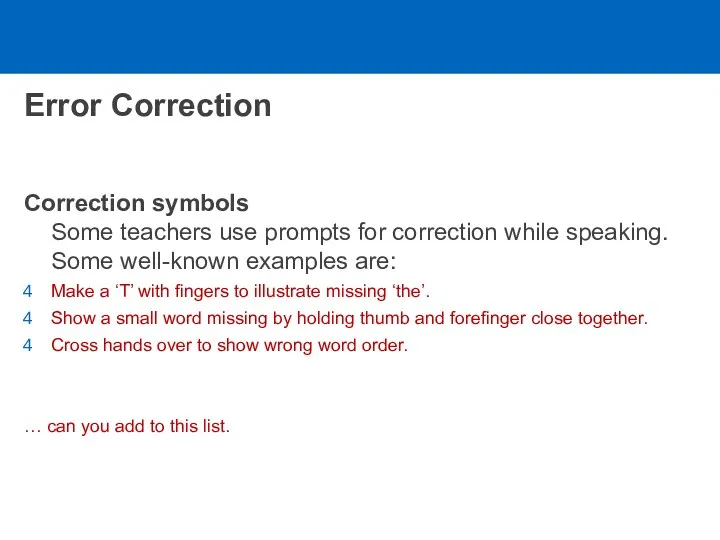
- 10. Error Correction Correction symbols Some teachers use prompts for correction while speaking. Some well-known examples are:
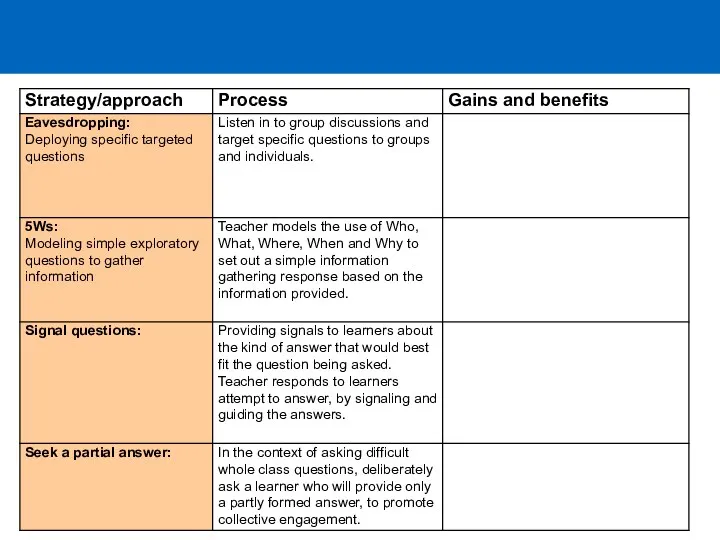
- 11. Returning to our question… How can we categorise types of classroom question? Give a concrete example
- 12. Session 2: Using story input
- 13. Questions relating to issues in this session Why do young learners find stories so engaging? How
- 14. Tiddler ‘story’ [W] Listening to an animal story with illustrations e.g. ‘Tiddler’. Teacher reads the story
- 15. Key class phases in story activity Pre: pre-teaching/eliciting vocabulary introducing characters story-telling setting: mat, props, hats,
- 16. Bike stories: Curious George and other bikes [W] Learners turn illustrations of a bike story ‘My
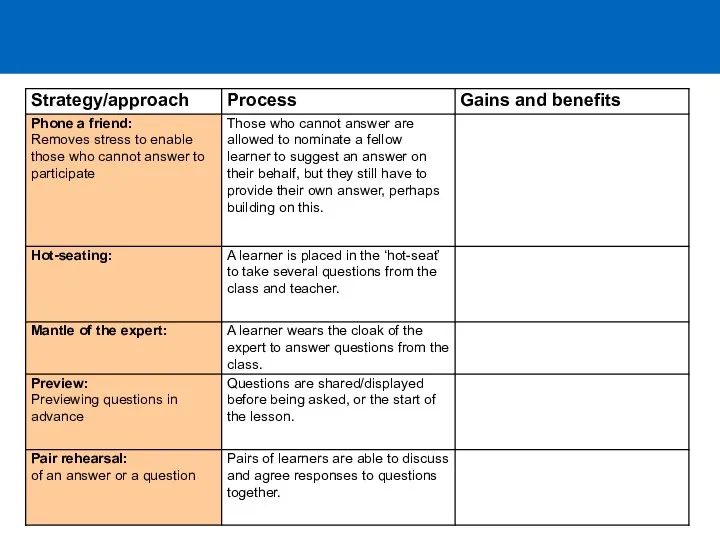
- 17. Returning to our question How can Ts modify language when storytelling? Discuss with another delegate features
- 18. Session 3: Craft activities and display
- 19. Questions related to issues in the session What are the different learning style/mode preferences typically exhibited
- 20. Audio, visual and kinaesthetic learners Learning styles are simply different preferences in the ways of learning.
- 21. Audio learners like teachers that: use role plays as part of their teaching encourage classroom discussions
- 22. Visual learners like teachers that: use pictures and videos draw on the board ask learners to
- 23. Kinaesthetic learners like teachers that: encourage good note-taking (when watching videos, listening to explanations or going
- 24. What’s in a task? visual learners auditory learners kinaesthetic learners Look at the activities. Sort them
- 25. Making finger/potato/hand puppets a simple hand [bag] puppet www.youtube.com/watch?v=BnFdE7lbaBE
- 26. Making a traditional hat www.youtube.com/watch?v=nzmAf5xjQBo
- 27. Display Display as stimulus - designed to arouse interest in a particular concept or theme; cross-curricular
- 28. Key elements in display imagination: think big and out of the box effort: think planning and
- 29. Primary Display Internet inspiration Find ‘display’ images from real classrooms that might be used to inspire
- 30. Returning to our earlier questions What was the main motivational ‘purpose’ behind each display found on
- 31. Session 4: Cross-curricular learning
- 32. Questions related to this session Why use content/activities from other subjects ? Can curricular concepts be
- 33. Collaborative teaching http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o0u16p4wyoE
- 34. Science [P] Listening to instructions for cutting out, vehicle outlines, making body of vehicle and showing
- 35. Cross-curricular primary tasks Maths Listening, measuring and completing a graph about how long learner’s step is.
- 36. Simple Maths/Science focuses within the English Curriculum Halving and doubling bingo Sink or swim Making representations
- 38. Скачать презентацию







![Tiddler ‘story’ [W] Listening to an animal story with illustrations](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/347992/slide-13.jpg)

![Bike stories: Curious George and other bikes [W] Learners turn](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/347992/slide-15.jpg)







![Making finger/potato/hand puppets a simple hand [bag] puppet www.youtube.com/watch?v=BnFdE7lbaBE](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/347992/slide-24.jpg)





![Science [P] Listening to instructions for cutting out, vehicle outlines,](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/347992/slide-33.jpg)


 Научно-обоснованная концепция модернизации содержания и технологий преподавания предметной области Иностранные языки
Научно-обоснованная концепция модернизации содержания и технологий преподавания предметной области Иностранные языки Газета Пятнашки. МБОУ СОШ № 15 город Новочеркасск
Газета Пятнашки. МБОУ СОШ № 15 город Новочеркасск КАК ЛЮДИ НАУЧИЛИСЬ СЧИТАТЬ
КАК ЛЮДИ НАУЧИЛИСЬ СЧИТАТЬ Конспект
Конспект презентация на выпускной вечер 11 класс
презентация на выпускной вечер 11 класс Художественная культура
Художественная культура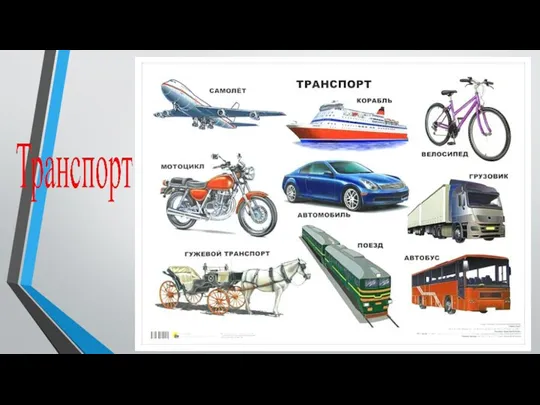 презентация развития речи в 3-м коррекционном классе по теме Городской транспорт
презентация развития речи в 3-м коррекционном классе по теме Городской транспорт Современные системы художественного образования детей
Современные системы художественного образования детей Виробнича практика в Anex tour
Виробнича практика в Anex tour Самый умный....
Самый умный.... Обучение чтению. (Часть 2)
Обучение чтению. (Часть 2) Выбор после 9 класса и ОГЭ
Выбор после 9 класса и ОГЭ Методические материалы начинающему педагогу по разработке образовательной программы
Методические материалы начинающему педагогу по разработке образовательной программы Методический семинар. Организация познавательной деятельности, как условие социальной самоидентификации учащихся
Методический семинар. Организация познавательной деятельности, как условие социальной самоидентификации учащихся Жасмин встречает друзей! Автоматизация звука ж
Жасмин встречает друзей! Автоматизация звука ж Детский центр Разумники. 2 смена лагеря Оранжевая планета Я и природа
Детский центр Разумники. 2 смена лагеря Оранжевая планета Я и природа Родителям о детской речи
Родителям о детской речи Классный час Интернет-зависимость
Классный час Интернет-зависимость Professional and communicative competence of the teachers of high school. New pedagogical thinking of high school teacher
Professional and communicative competence of the teachers of high school. New pedagogical thinking of high school teacher Простейшие виды швов. Урок технологии 3 класс
Простейшие виды швов. Урок технологии 3 класс Основные особенности нового закона Об образовании в Российской Федерации
Основные особенности нового закона Об образовании в Российской Федерации Успехи воспитанников
Успехи воспитанников Формирование предикативной лексики у детей старшего дошкольного возраста с тяжелыми нарушениями речи
Формирование предикативной лексики у детей старшего дошкольного возраста с тяжелыми нарушениями речи Презентация Толерантность - путь к миру.
Презентация Толерантность - путь к миру. Личностно - ориентированное обучение
Личностно - ориентированное обучение Классный час Моя семья
Классный час Моя семья Проект я – громадянин України
Проект я – громадянин України Презентация к уроку СБО, 7 класс по теме Универмаги. Специализированные магазины, их отделы
Презентация к уроку СБО, 7 класс по теме Универмаги. Специализированные магазины, их отделы