Содержание
- 2. Pedagogics (pedagogy) Pedagogics is a science about specially organized, goal-oriented, and systematic forming of a human
- 3. Meaning of the word The word comes from the Ancient Greek word literally meaning "to lead
- 4. Development of ancient pedagogics Aristotle (384– 322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student
- 5. Medieval European Education In medieval Western Europe, education was typically a charge of the church: the
- 6. With the Renaissance, education of boys (and some girls) in classics and mathematics became widespread. After
- 7. Education in the Ukraine The Kyiv-Mohyla Academy, the school's predecessor, was established in 1632. Alumni of
- 8. Hryhorii Skovoroda Hryhorii Skovoroda (1722–1794) was a Ukrainian philosopher, poet, teacher and composer who made important
- 9. 2. Pedagogics as a science Pedagogy as an independent experimental field of study began at the
- 10. Jan Amos Comenius After Bacon’s theories, Jan Amos Comenius (1592-1670), Czech scientist, wrote his work ‘The
- 11. 3. The basic categories of pedagogics are
- 12. Personality formation Personality formation is a process of shaping an individual by means of goal-oriented influence
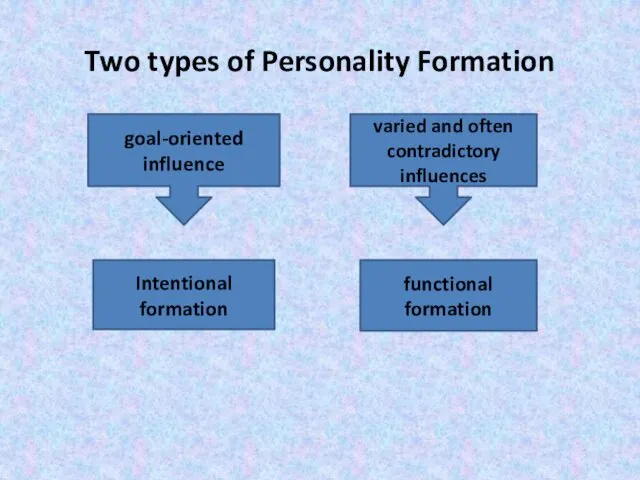
- 13. Two types of Personality Formation goal-oriented influence varied and often contradictory influences Intentional formation functional formation
- 14. Upbringing Upbringing is a purposeful, systematic shaping of a personality in preparation for active participation in
- 15. 4.Education Education is a process and result of the acquisition of systematized knowledge and skills
- 16. Education (continuation) Associated with education are the transfer from one generation to the next of knowledge
- 17. Education (continuation) Education is essential to preparing for life and work. It is the basic means
- 18. Four Types of education:
- 19. Formal education Formal education can be defined as a hierarchically structured and chronologically graded education system.
- 20. Adult education As the name suggests, adult education refers to a practice of educating adults. There
- 21. Alternative education This type of education is actually an alternative approach to traditional or mainstream education.
- 22. Special education There are some students who require special learning needs, which are addressed through special
- 23. Four Stages in formal education: Nursery education Often referred to as preschool education, nursery education is
- 24. Primary education Elementary or primary education refers to a first few years of structured, formal education.
- 25. Secondary education It is the final stage of school education that is offered during a child’s
- 26. Higher education Tertiary or higher education is a non-compulsory educational level, which comprises of undergraduate and
- 27. Instruction Instruction is the process of transmitting and acquiring knowledge, skills, and work habits; the basic
- 28. Instruction (continuation) Although the main way of obtaining an education is through instruction in various kinds
- 29. Instruction (continuation) The goals of education and upbringing are realized through instruction. In addition to specially
- 30. 5.Upbringing Upbringing is closely linked with instruction; many of its most important tasks are accomplished through
- 31. Self-upbringing At a certain point in the spiritual development of a personality there arises a need
- 32. The Main Types of Upbringing The main types of upbringing are family (or domestic) and social
- 33. Family Upbringing Family Upbringing the systematic, purposeful influence of the adult members of a family and
- 34. Family Upbringing (continuation) Among the main aspects of family upbringing are constant but unobtrusive guidance of
- 35. Family Upbringing (continuation) Another important part of family upbringing is the formation of higher moral qualities
- 36. Family Upbringing (continuation) Family upbringing also involves acquainting children with works of literature and art and
- 37. Social upbringing Social upbringing is the process by which an individual acquires specific knowledge and values
- 39. Скачать презентацию



































 Родительское собрание Первый раз в первый класс
Родительское собрание Первый раз в первый класс Урок математики в 5 классе коррекционной школы 8 вида по теме Решение сложных примеров. Даты и числа из истории Успенского района
Урок математики в 5 классе коррекционной школы 8 вида по теме Решение сложных примеров. Даты и числа из истории Успенского района Поём на мотив песен (для дошкольников, Вера)
Поём на мотив песен (для дошкольников, Вера) Здоровое поколение - здоровая Россия!
Здоровое поколение - здоровая Россия! Концепция развития дополнительного образования детей
Концепция развития дополнительного образования детей Балеринки - снежинки
Балеринки - снежинки Что такое педагогическая технология? Лекция 1
Что такое педагогическая технология? Лекция 1 Помоги Маше собрать первоцветы. Интерактивная игра
Помоги Маше собрать первоцветы. Интерактивная игра Стартовые позиции в системе работы по формированию общеучебных умений младших школьников
Стартовые позиции в системе работы по формированию общеучебных умений младших школьников Духовно-нравственное воспитание как основа гармоничного развития личности.
Духовно-нравственное воспитание как основа гармоничного развития личности. Формирование элементарных математических представлений в подготовительной группе: внутри - снаружи. Слева. Справа
Формирование элементарных математических представлений в подготовительной группе: внутри - снаружи. Слева. Справа Конкурсно-игровая программа с элементом театрализации Здравствуй, лето!
Конкурсно-игровая программа с элементом театрализации Здравствуй, лето! План работы тьютора с обучающимся с умственной отсталостью
План работы тьютора с обучающимся с умственной отсталостью Лидер и успех
Лидер и успех Презентация к занятию Путешествие в страну Доброты и Вежливости
Презентация к занятию Путешествие в страну Доброты и Вежливости Родительское собрание. (1-5 класс)
Родительское собрание. (1-5 класс) Современный урок немецкого языка в свете требований ФГОС
Современный урок немецкого языка в свете требований ФГОС Рисование осенних листьев
Рисование осенних листьев Упражнения Как хорошо я знаю правила чтения!
Упражнения Как хорошо я знаю правила чтения! Волшебные превращения комочка пластилина
Волшебные превращения комочка пластилина Эффективность работы по качественному массовому среднему образованию.
Эффективность работы по качественному массовому среднему образованию. Наглядно-информационная форма взаимодействия с родителями
Наглядно-информационная форма взаимодействия с родителями Чего на ёлке не бывает
Чего на ёлке не бывает Доклад Коррекция поведения. Воспитание личностных качеств.
Доклад Коррекция поведения. Воспитание личностных качеств. Духовно- нравственное воспитание
Духовно- нравственное воспитание Технологии работы с детьми с аутизмом в коррекционной деятельности
Технологии работы с детьми с аутизмом в коррекционной деятельности Лучшая семейная сосиска
Лучшая семейная сосиска Сабаққа қойылатын талаптар, құзыреттілікке жеткізетін мақсат-міндеттері анықталған сабақтың жоспарын құру
Сабаққа қойылатын талаптар, құзыреттілікке жеткізетін мақсат-міндеттері анықталған сабақтың жоспарын құру