Содержание
- 2. Control system: - Multi Purpose Controller - Control Network - Main Operating Panel - Local Operating
- 3. Control Systems Bridge Ctr System Engine Ctr System
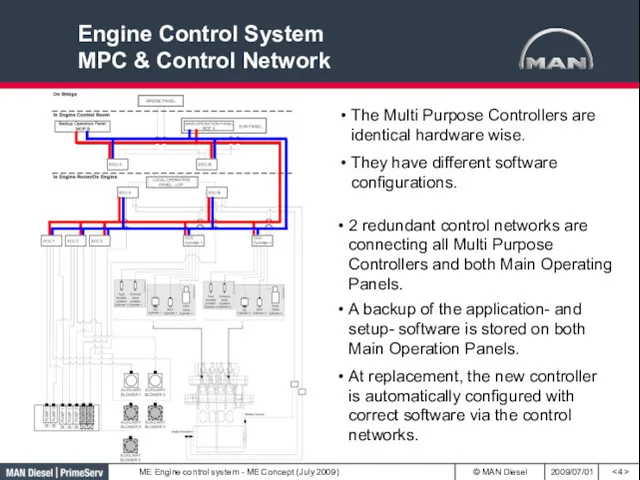
- 4. Engine Control System MPC & Control Network 2 redundant control networks are connecting all Multi Purpose
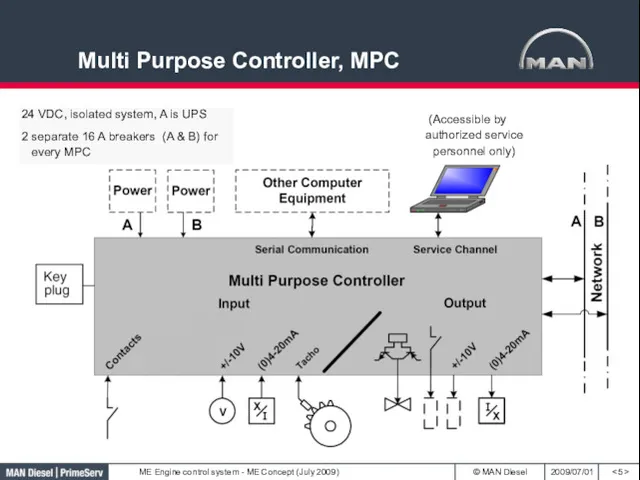
- 5. Multi Purpose Controller, MPC 24 VDC, isolated system, A is UPS 2 separate 16 A breakers
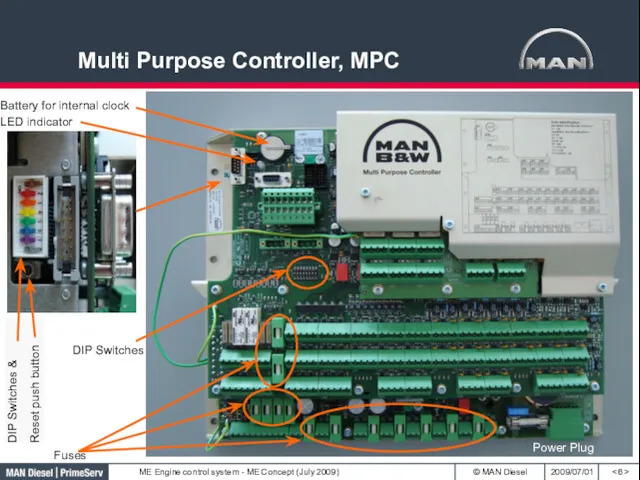
- 6. Multi Purpose Controller, MPC DIP Switches DIP Switches & Reset push button Power Plug
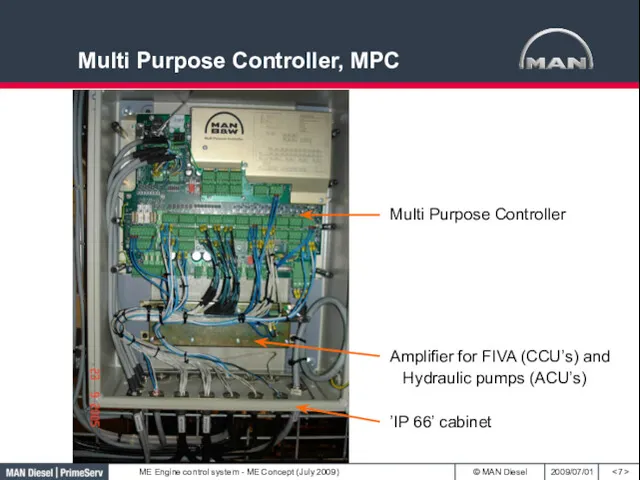
- 7. Multi Purpose Controller, MPC Amplifier for FIVA (CCU’s) and Hydraulic pumps (ACU’s) Multi Purpose Controller ’IP
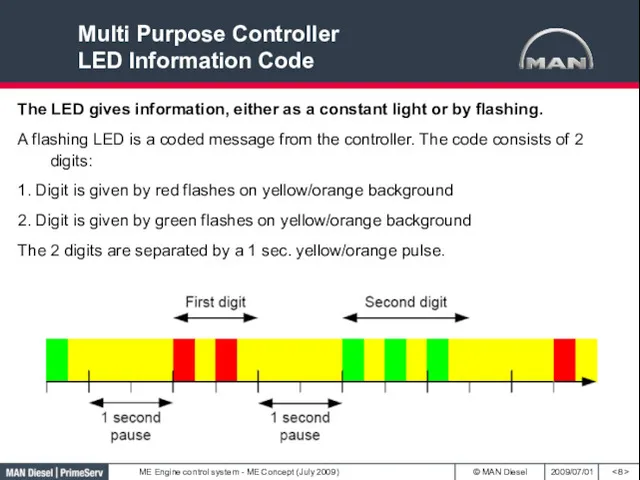
- 8. Multi Purpose Controller LED Information Code The LED gives information, either as a constant light or
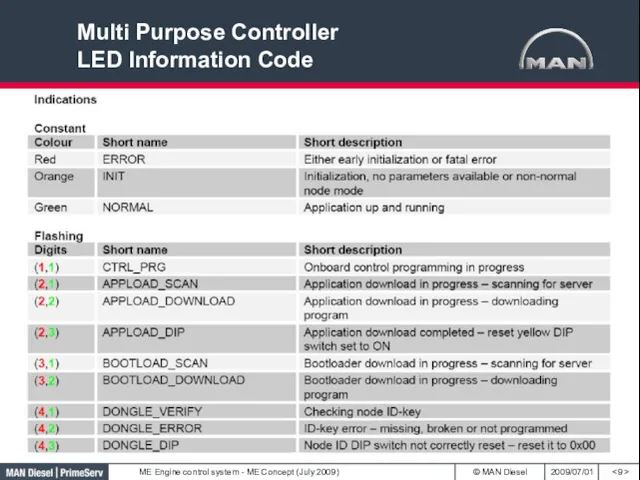
- 9. Multi Purpose Controller LED Information Code
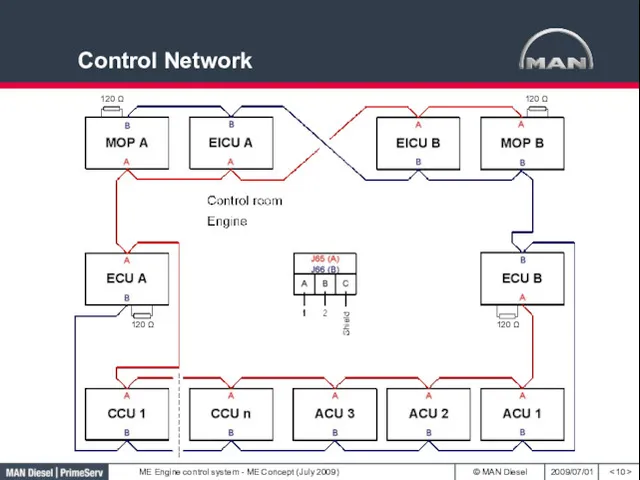
- 10. Control Network 120 Ω 120 Ω 120 Ω 120 Ω
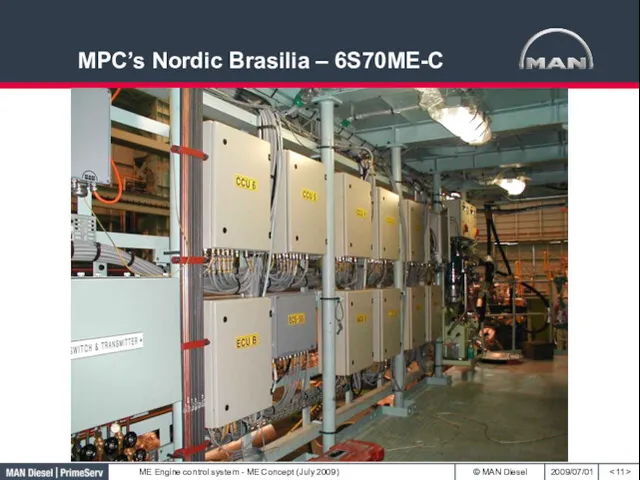
- 11. MPC’s Nordic Brasilia – 6S70ME-C
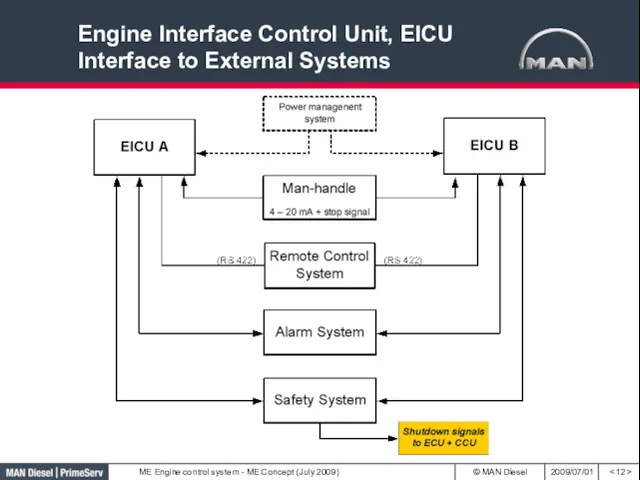
- 12. Engine Interface Control Unit, EICU Interface to External Systems
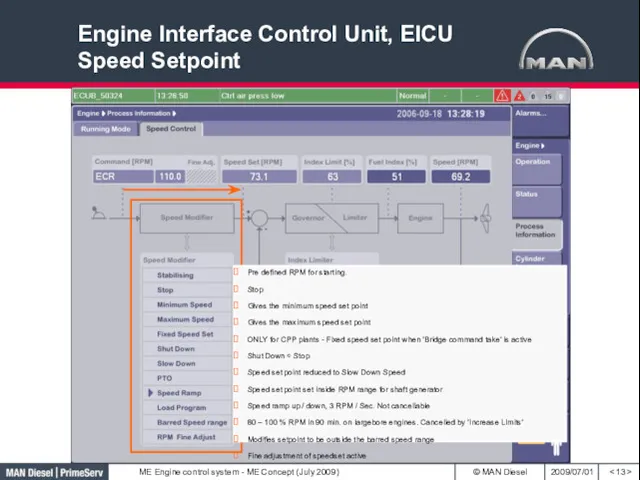
- 13. Engine Interface Control Unit, EICU Speed Setpoint Pre defined RPM for starting. Stop Gives the minimum
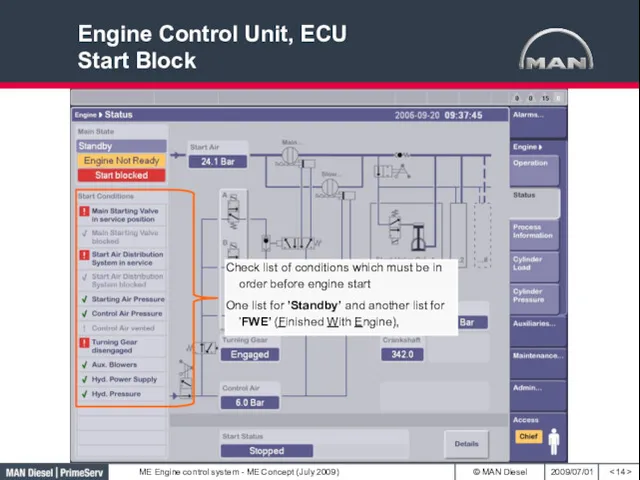
- 14. Engine Control Unit, ECU Start Block
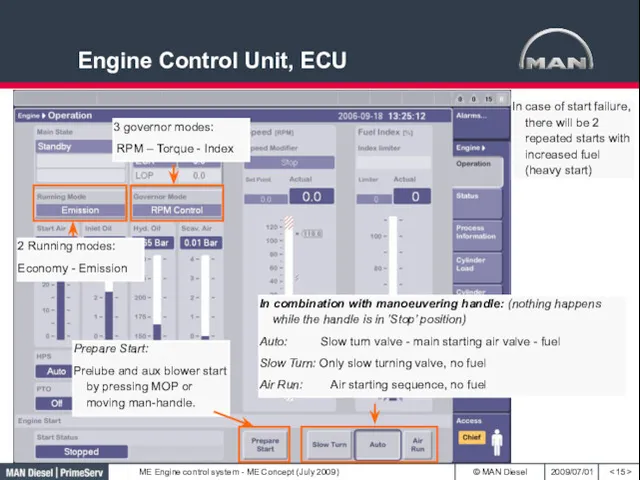
- 15. Engine Control Unit, ECU 3 governor modes: RPM – Torque - Index 2 Running modes: Economy
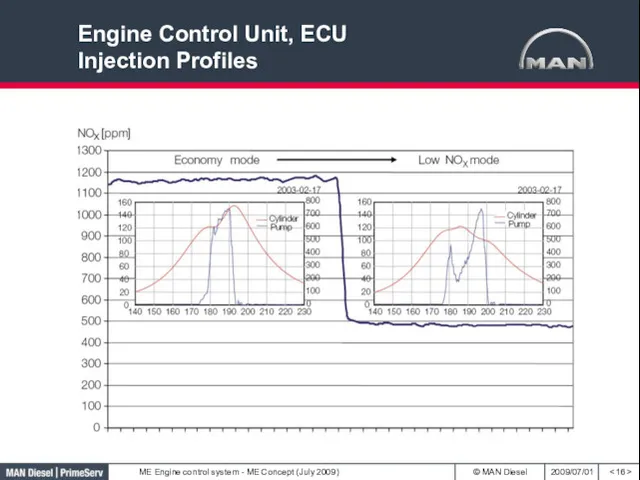
- 16. Engine Control Unit, ECU Injection Profiles
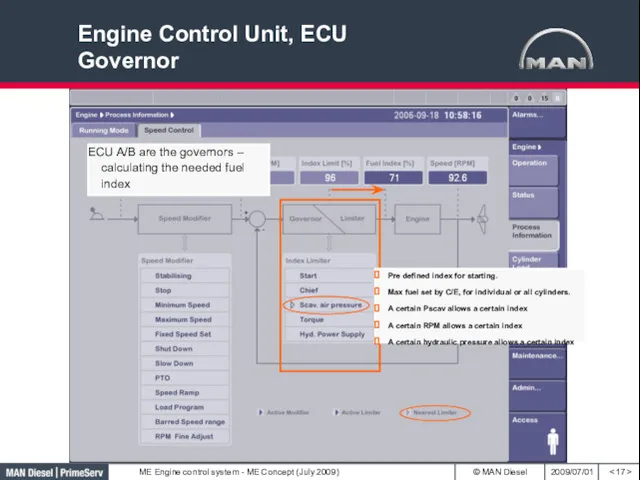
- 17. Engine Control Unit, ECU Governor Pre defined index for starting. Max fuel set by C/E, for
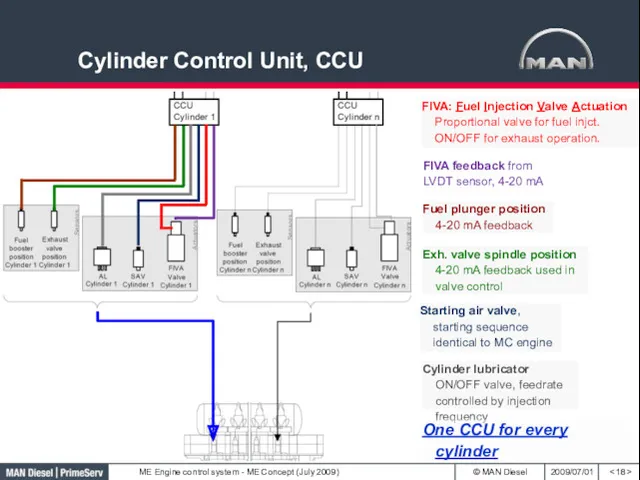
- 18. Cylinder Control Unit, CCU Fuel plunger position 4-20 mA feedback Exh. valve spindle position 4-20 mA
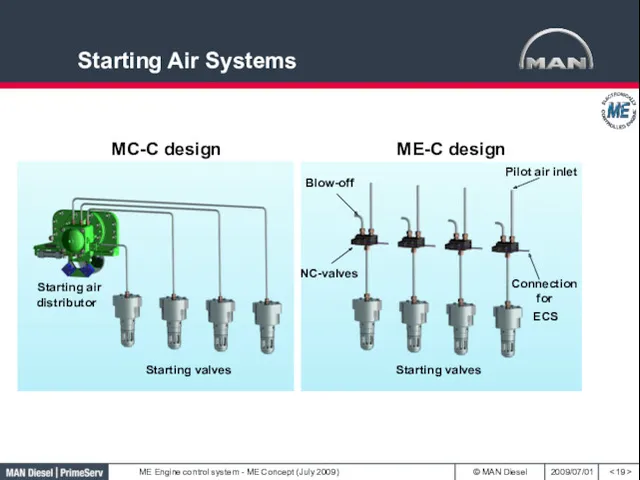
- 19. Starting Air Systems
- 20. Starting- and Pilot Air Valve
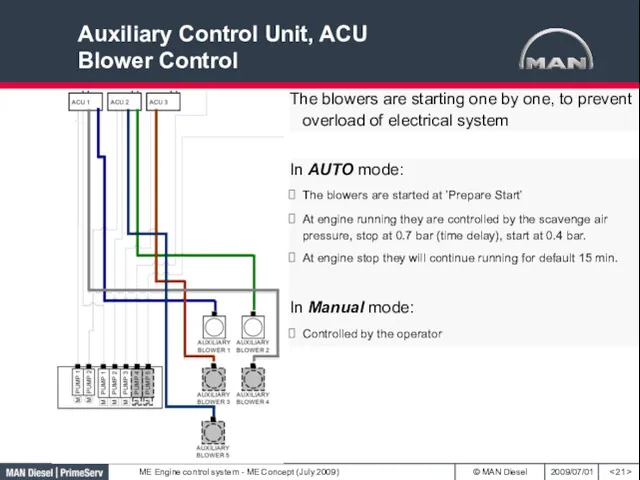
- 21. Auxiliary Control Unit, ACU Blower Control The blowers are starting one by one, to prevent overload
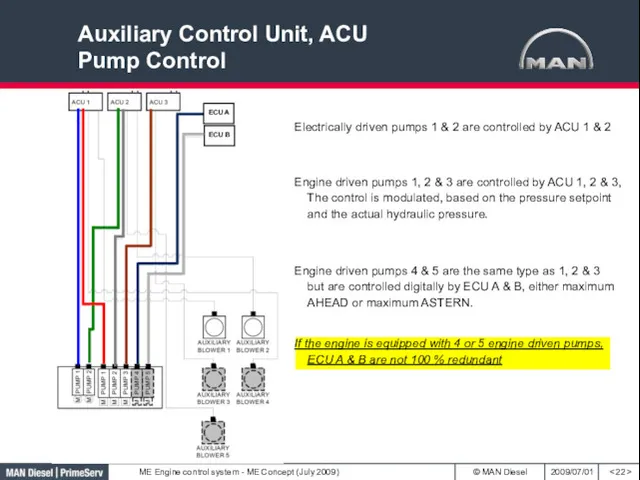
- 22. Auxiliary Control Unit, ACU Pump Control Electrically driven pumps 1 & 2 are controlled by ACU
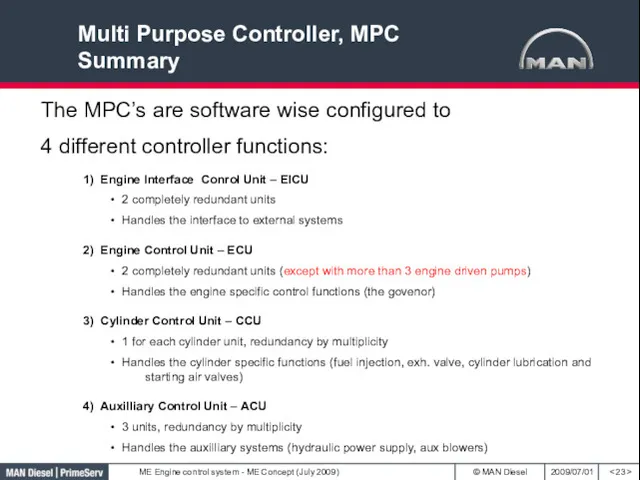
- 23. Multi Purpose Controller, MPC Summary The MPC’s are software wise configured to 4 different controller functions:
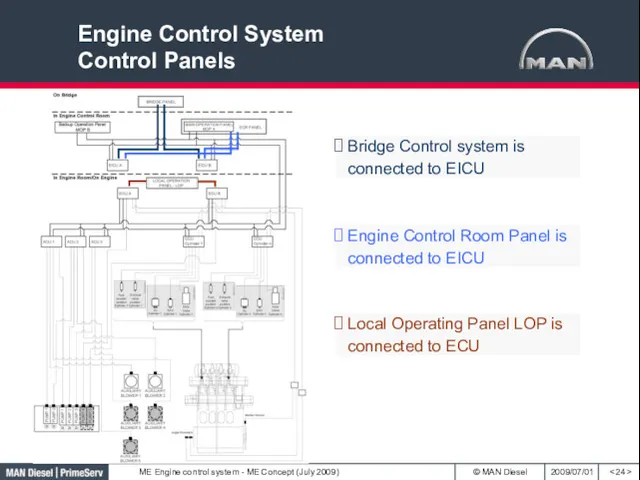
- 24. Engine Control System Control Panels Bridge Control system is connected to EICU Engine Control Room Panel
- 25. Main Operating Panel, MOP
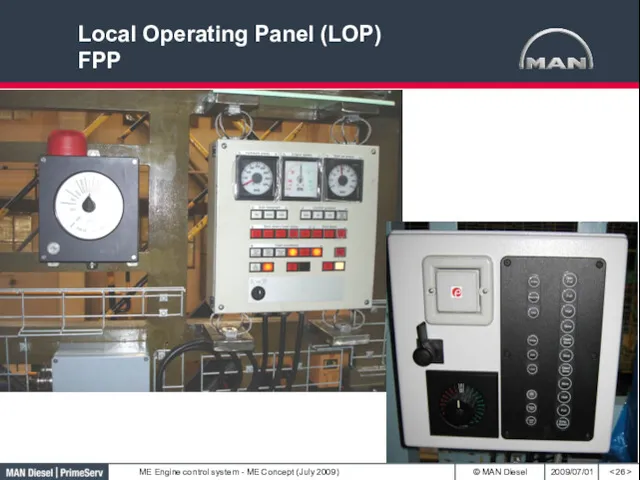
- 26. Local Operating Panel (LOP) FPP
- 27. Local Operating Panel (LOP) CPP
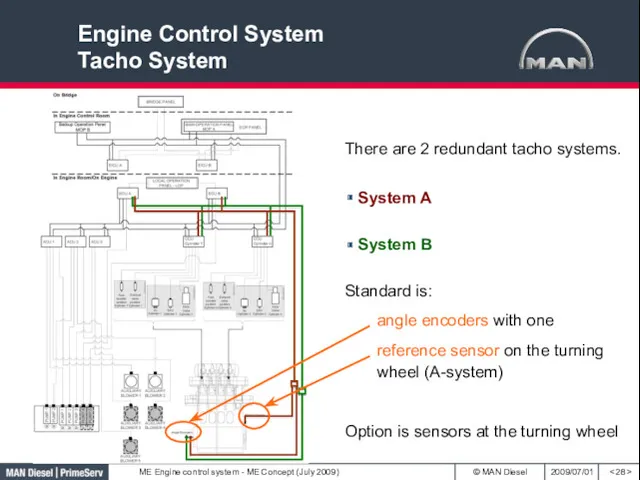
- 28. Engine Control System Tacho System There are 2 redundant tacho systems. System B System A Standard
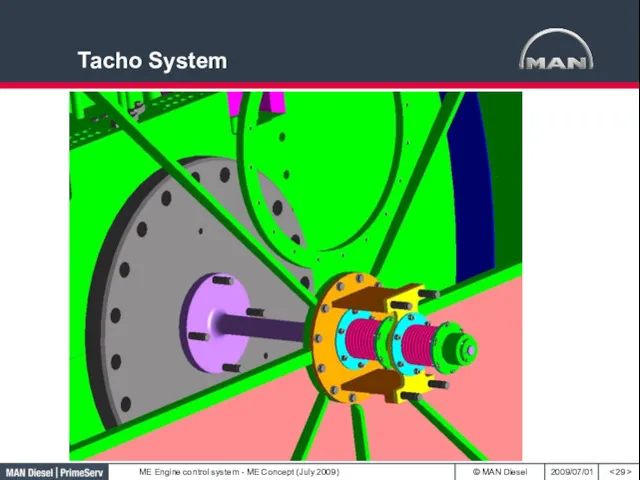
- 29. Tacho System
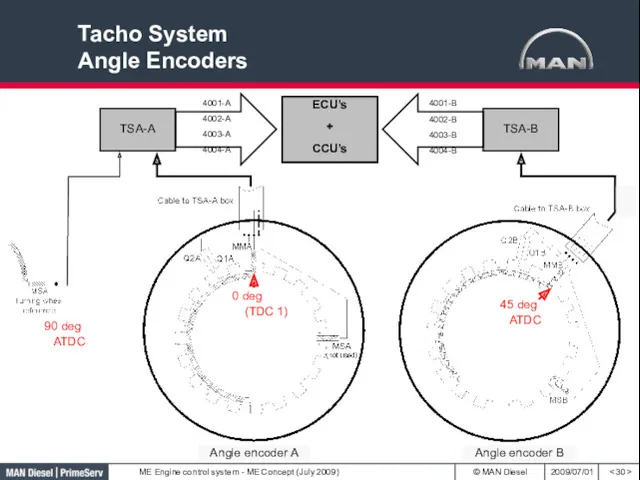
- 30. Tacho System Angle Encoders 90 deg ATDC Angle encoder A Angle encoder B
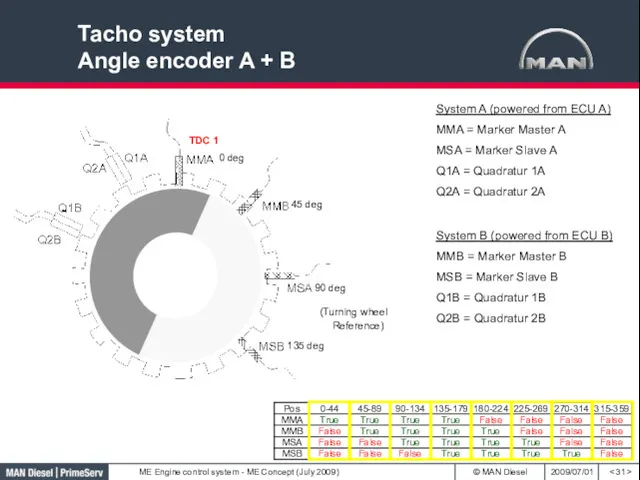
- 31. Tacho system Angle encoder A + B System A (powered from ECU A) MMA = Marker
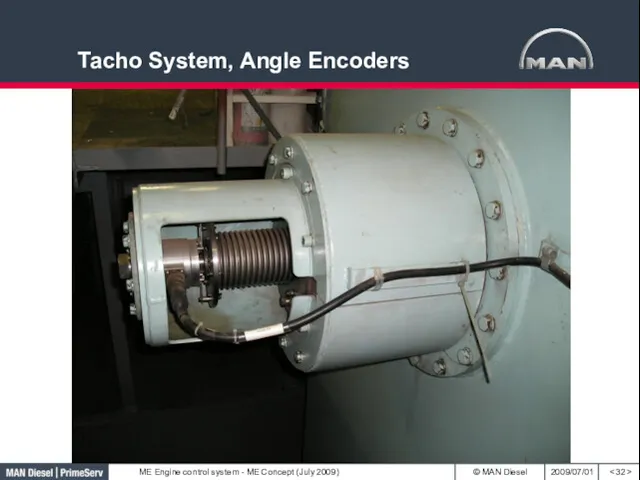
- 32. Tacho System, Angle Encoders
- 33. Tacho System Amplifier Boxes, TSA
- 34. Tacho System, Semicircular Ring
- 35. Tacho System, Master Slave A, MSA, on AFT end of Engine
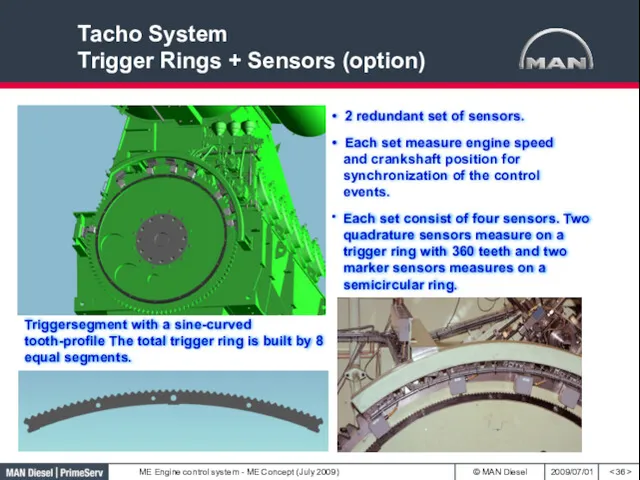
- 36. Tacho System Trigger Rings + Sensors (option) Triggersegment with a sine-curved tooth-profile The total trigger ring
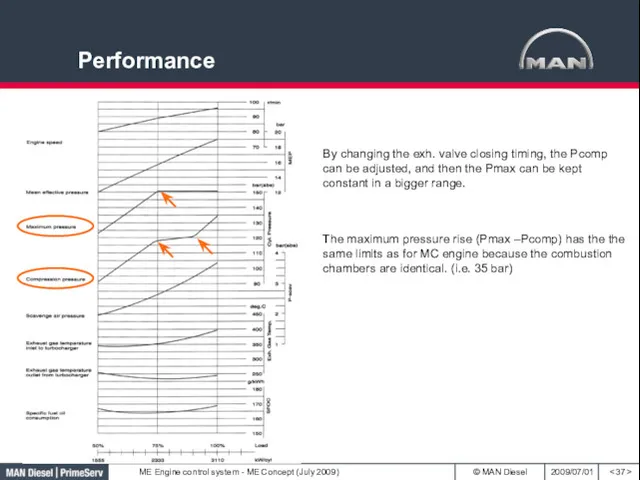
- 37. Performance By changing the exh. valve closing timing, the Pcomp can be adjusted, and then the
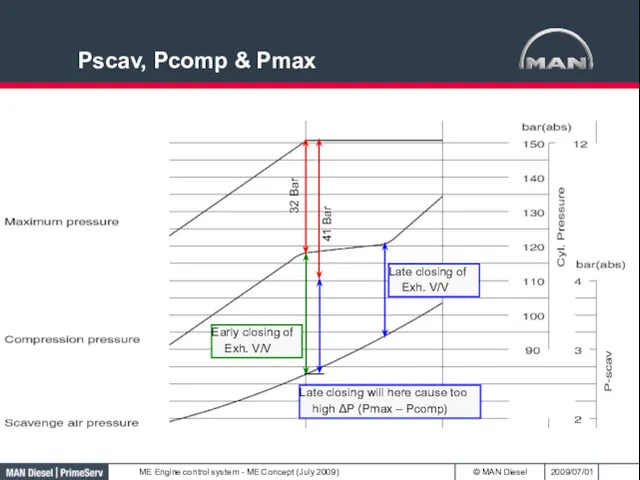
- 38. Pscav, Pcomp & Pmax
- 40. Скачать презентацию







 Сказочки-шумелки. Зима в лесу
Сказочки-шумелки. Зима в лесу Контроль условий, процессов и результатов образовательной деятельности
Контроль условий, процессов и результатов образовательной деятельности Презентация- игра Гербы городов Липецкой области
Презентация- игра Гербы городов Липецкой области Презентация. Развитие мелкой моторики с помощью дидактических игр в разных областях образовательной деятельности.
Презентация. Развитие мелкой моторики с помощью дидактических игр в разных областях образовательной деятельности. Мастер-класс Силуэты
Мастер-класс Силуэты Наши права и обязанности
Наши права и обязанности Лоскутное шитье
Лоскутное шитье Проблемы управления политикой спроса
Проблемы управления политикой спроса Человеческий капитал ТЭК. Роль ТЭК в экономике страны
Человеческий капитал ТЭК. Роль ТЭК в экономике страны Познавательный проект Славяне
Познавательный проект Славяне Внеклассное занятие Легенды и мифы Санкт-Петербурга 2 класс
Внеклассное занятие Легенды и мифы Санкт-Петербурга 2 класс Ценовая эластичность спроса. Эластичность спроса и доход производителей
Ценовая эластичность спроса. Эластичность спроса и доход производителей Инвестиционная деятельность предприятия ПАО КАМАЗ Автомобильный завод
Инвестиционная деятельность предприятия ПАО КАМАЗ Автомобильный завод Что должен уметь ребенок 3-4 лет
Что должен уметь ребенок 3-4 лет Прямоугольная система координат
Прямоугольная система координат Хирургиядағы ақпаратты-компьютерлік технологиялар телемедицинасы
Хирургиядағы ақпаратты-компьютерлік технологиялар телемедицинасы Расстройства аутистического спектра
Расстройства аутистического спектра Наркомания
Наркомания Етика та естетика. Етика ділових відносин. Етикет
Етика та естетика. Етика ділових відносин. Етикет АСК 2 урок Природные особенности Смоленской области
АСК 2 урок Природные особенности Смоленской области Организация различных видов деятельности и общения детей. Практика
Организация различных видов деятельности и общения детей. Практика Презентация От Коперника до наших дней
Презентация От Коперника до наших дней презентация к родительскому собранию Агрессия детей, ее причины и предупреждение
презентация к родительскому собранию Агрессия детей, ее причины и предупреждение Проект Живая азбука
Проект Живая азбука Дружат дети всей Земли Диск
Дружат дети всей Земли Диск Презентация. Роль ИКТ в формировании познавательной сферы обучающихся, развитие логического мышления
Презентация. Роль ИКТ в формировании познавательной сферы обучающихся, развитие логического мышления Педагогические технологии
Педагогические технологии Тест по теме СОСТОЯНИЯ ВЕЩЕСТВА, 5 класс
Тест по теме СОСТОЯНИЯ ВЕЩЕСТВА, 5 класс