Содержание
- 2. COOKING VEGGIES CHANGES THE FOLLOWING: TEXTURE FLAVOR COLOR NUTRIENTS
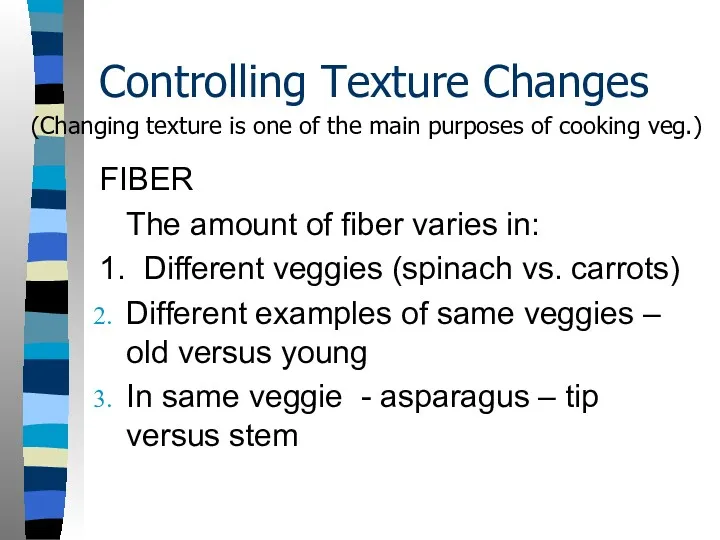
- 3. Controlling Texture Changes FIBER The amount of fiber varies in: 1. Different veggies (spinach vs. carrots)
- 6. TOUGH TENDER
- 7. FIBER IS MADE FIRMER BY: ACIDS – lemon jc., vinegar, tomato SUGARS – strengthen cell structure
- 8. FIBER IS SOFTENED BY: HEAT ALKALIS – bad for green veggies!
- 10. STARCH Dry legumes, rice, pasta need water so starch granules can absorb, swell, soften. Moist starchy
- 13. GUIDELINES FOR COOKING: Don’t overcook! Cook close to service time Shock to cool quickly and reheat
- 14. CONTROLLING FLAVOR CHANGES Cook for short time – quickly Boil water first, than add veggies Minimize
- 15. COOKING, CONT’D Flavor Changes: Cooking changes the flavor which is desirable as long as you don’t
- 18. CONTROLLING NUTRIENT LOSSES Hi temps Long cooking times Leaching Alkalis (baking soda, hard water) Plant enzymes
- 19. H2o – A LITTLE OR A LOT? Use just enough to cover Using a little increases
- 20. QUALITY IN COOKED VEGGIES Color Appearance on plate Texture Flavor Seasonings Sauces Attractive combinations
- 22. HANDLING VEGETABLES WASHING Wash thoroughly Cold water; veg. sink Scrub root veggies Leafy veggies: several times
- 23. PEELING AND CUTTING Not too much peel! Uniform pieces Cut close to service; retain moisture Veggies
- 24. PROCESSED VEGGIES
- 25. FROZEN VEGGIES Temperature – 0 degrees Large ice crystals – no good Signs of leakage –
- 26. CANNED VEGGIES No puffed or swollen cans Drained weight is important Check the grade: US Grade
- 28. Скачать презентацию
























 Articles
Articles Drugs in the Republic of Belarus
Drugs in the Republic of Belarus Способы выражения будущего времени
Способы выражения будущего времени Время. Предлоги времени в английском языке
Время. Предлоги времени в английском языке Генерация электрических колебаний. Лекция 11
Генерация электрических колебаний. Лекция 11 Australia
Australia Modal werbs. Lobular pneumonia
Modal werbs. Lobular pneumonia Metonymy
Metonymy Домашнее задание. (Урок 35)
Домашнее задание. (Урок 35) Smoke-as a social problem among 6th year students KazNMU
Smoke-as a social problem among 6th year students KazNMU Halloween - animated presentation (vocabulary)
Halloween - animated presentation (vocabulary) This Is Halloween
This Is Halloween Password game. Fun activities games
Password game. Fun activities games Aethetic education as leading direction of national pedagogy
Aethetic education as leading direction of national pedagogy The present simple. Diapositiva
The present simple. Diapositiva Healthy food
Healthy food School supplies
School supplies Direct speech
Direct speech Have Fun with English Club
Have Fun with English Club Past perfect tense
Past perfect tense Индия
Индия Перевод из прямой речи в косвенную
Перевод из прямой речи в косвенную Great Russian scientists
Great Russian scientists Thanks for victory
Thanks for victory Reported speech. Косвенная речь
Reported speech. Косвенная речь The Beatles
The Beatles Where is the monster
Where is the monster Chall-2-KET exam work on mistakes
Chall-2-KET exam work on mistakes