Содержание
- 2. Economic Systems Why are economies around the world growing more market oriented? How much can an
- 3. Objectives Economic Questions and Economic Systems Identify three questions that all economic systems must answer. Describe
- 4. Economic Questions and Economic Systems economic system pure market economy pure centrally planned economy mixed economy
- 5. Three Economic Questions All economies must answer these three questions: 1. What goods and services will
- 6. Economic System An economic system is the set of mechanisms and institutions that resolves the what,
- 7. Pure Market Economy All resources are privately owned Coordination of economic activity is based on the
- 8. Invisible Hand of Markets According to economist Adam Smith (1723–1790), market forces coordinate production as if
- 9. Problems with Pure Market Economies Difficulty enforcing property rights Some people have few resources to sell
- 10. Pure Centrally Planned Economy All resources government-owned Production coordinated by the central plans of government Sometimes
- 11. Problems with Centrally Planned Economies Consumers get low priority Little freedom of choice Central planning can
- 12. Mixed Economy United States is a mixed economy Also considered a market economy Government regulates the
- 13. Transitional Economy A transitional economy is in the process of shifting orientation from central planning to
- 14. Traditional Economy A traditional economy is shaped largely by custom or religion. Family relations also play
- 15. Production Possibilities Frontier Describe the production possibilities frontier and explain its shape. Explain what causes the
- 16. Production Possibilities Frontier production possibilities frontier (PPF) efficiency law of increasing opportunity cost economic growth Key
- 17. Efficiency and Production Possibilities Frontier PPF model Shows possible combinations of 2 types of goods that
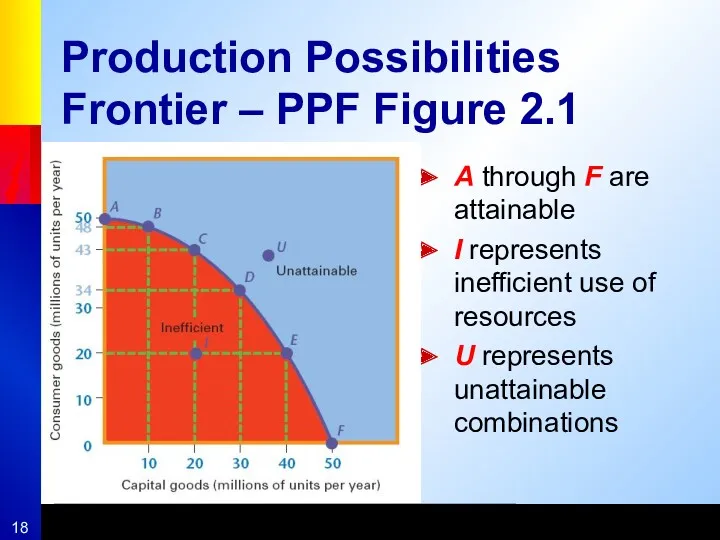
- 18. Production Possibilities Frontier – PPF Figure 2.1 A through F are attainable I represents inefficient use
- 19. Efficiency and Production Possibilities Frontier The resources in an economy are not all perfectly adaptable Law
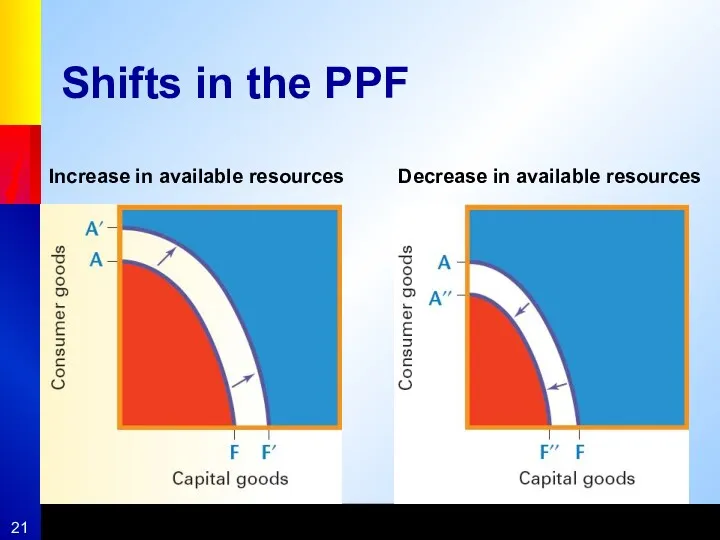
- 20. Shifts in the PPF Economic Growth – an expansion in the economies ability to produce Changes
- 21. Shifts in the PPF
- 22. Comparative Advantage Explain the law of comparative advantage Understand the gains from specialization and exchange. Objectives
- 23. Comparative Advantage absolute advantage law of comparative advantage specialization barter money division of labor Key Terms
- 24. Comparative Advantage Absolute advantage – being able to do something using fewer resources than other producers
- 25. Specialization Specialization – when individual workers focus on single tasks Gains from specialization More efficient and
- 26. Specialization Most people consume little of what they produce and produce little of what they consume!
- 28. Скачать презентацию




















 Микроэкономика. Множество производственных возможностей
Микроэкономика. Множество производственных возможностей Еңбек күшінің географиялық ерекшеліктері
Еңбек күшінің географиялық ерекшеліктері Деятельность в области стандартизации
Деятельность в области стандартизации Виды рынков. Конкуренция и монополия
Виды рынков. Конкуренция и монополия Внешняя торговля России
Внешняя торговля России Категории качества. Эволюция развития и изменения понятия качество
Категории качества. Эволюция развития и изменения понятия качество Держава в системі макроекономічного регулювання
Держава в системі макроекономічного регулювання Спрос, предложение и рыночное равновесие
Спрос, предложение и рыночное равновесие Транснациональные корпорации в мировом хозяйстве (TNC’s)
Транснациональные корпорации в мировом хозяйстве (TNC’s) Анализ рынка
Анализ рынка Национальная экономика как система. Тема 8. Дисциплина экономическая теория
Национальная экономика как система. Тема 8. Дисциплина экономическая теория Экономическое обоснование инженерного решения
Экономическое обоснование инженерного решения Всемирная торговая организация
Всемирная торговая организация Information Technology in the Digital Economy
Information Technology in the Digital Economy Обеспечение операционной деятельности производственной мощностью
Обеспечение операционной деятельности производственной мощностью Збереження енергетичних ресурсів. Три напрямки розв’язання проблеми майбутнього енергетичного голоду
Збереження енергетичних ресурсів. Три напрямки розв’язання проблеми майбутнього енергетичного голоду Природные ресурсы и их рациональное использование
Природные ресурсы и их рациональное использование Место и значение дисциплины Экономика предприятия в экономической науке
Место и значение дисциплины Экономика предприятия в экономической науке Формы, цели и задачи международных экономических организаций. Этапы развития МЭОР
Формы, цели и задачи международных экономических организаций. Этапы развития МЭОР 10 principles of economics
10 principles of economics Основные фонды предприятия
Основные фонды предприятия Экономические стратегии в домохозяйстве на примере конкретных стран
Экономические стратегии в домохозяйстве на примере конкретных стран Развитие общества: экономика и сотрудничество. Задания
Развитие общества: экономика и сотрудничество. Задания Предложение товаров на рынке
Предложение товаров на рынке Индонезия. Экономика Индонезии
Индонезия. Экономика Индонезии Европейский Союз. Крупнейшие политические интеграционные объединения
Европейский Союз. Крупнейшие политические интеграционные объединения Структура издержек предприятия
Структура издержек предприятия Введение в микроэкономику
Введение в микроэкономику