Содержание
- 2. The Meaning of Competition A perfectly competitive market has the following characteristics: There are many buyers
- 3. The Meaning of Competition As a result of its characteristics, the perfectly competitive market has the
- 4. The Meaning of Competition Buyers and sellers in competitive markets are said to be price takers.
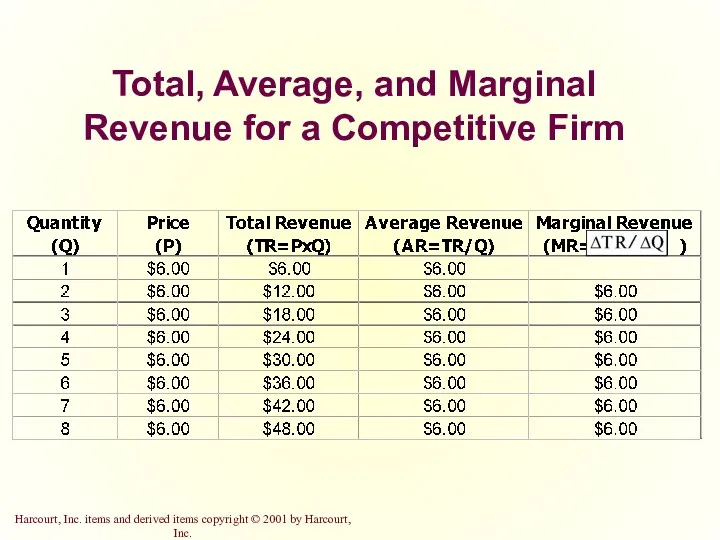
- 5. Revenue of a Competitive Firm Total revenue for a firm is the selling price times the
- 6. Revenue of a Competitive Firm Total revenue is proportional to the amount of output.
- 7. Revenue of a Competitive Firm Average revenue tells us how much revenue a firm receives for
- 8. Revenue of a Competitive Firm In perfect competition, average revenue equals the price of the good.
- 9. Revenue of a Competitive Firm Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue from an additional
- 10. Revenue of a Competitive Firm For competitive firms, marginal revenue equals the price of the good.
- 11. Total, Average, and Marginal Revenue for a Competitive Firm
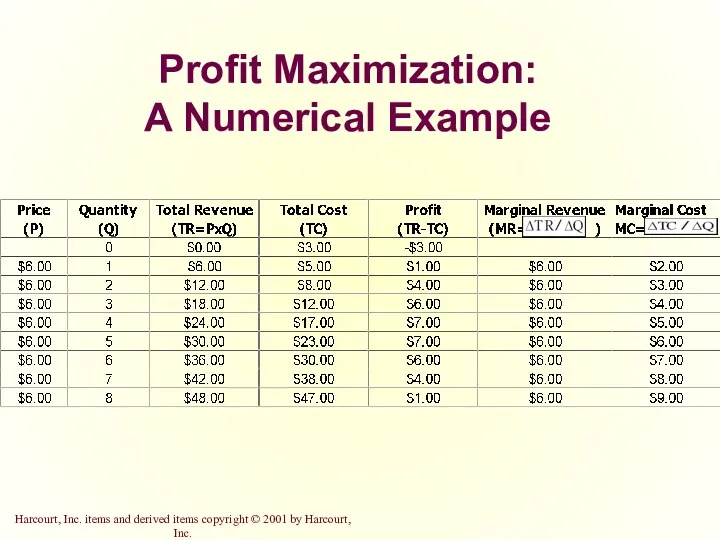
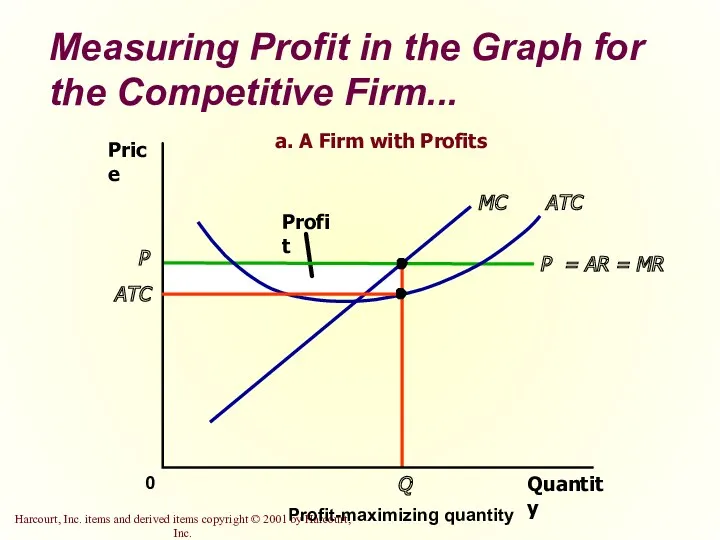
- 12. Profit Maximization for the Competitive Firm The goal of a competitive firm is to maximize profit.
- 13. Profit Maximization: A Numerical Example
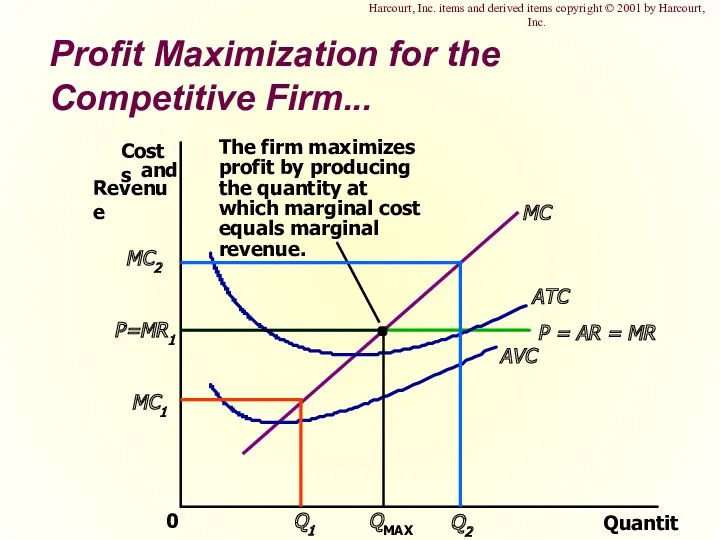
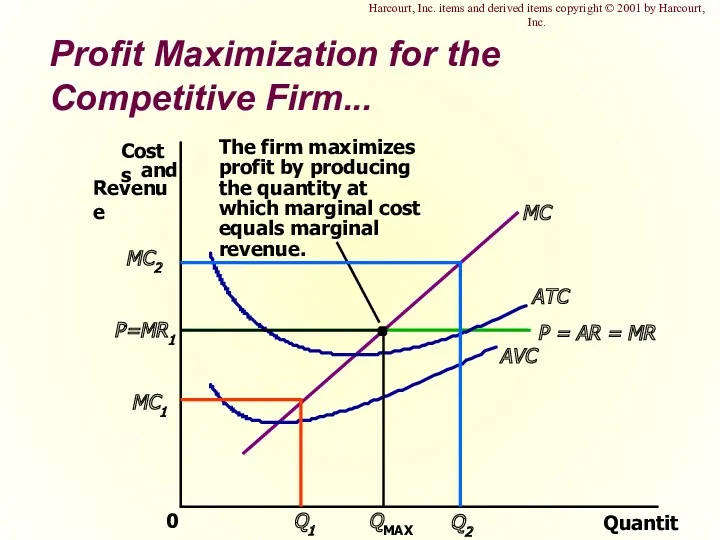
- 14. Profit Maximization for the Competitive Firm... Quantity 0 ATC AVC Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items
- 15. Profit Maximization for the Competitive Firm Profit maximization occurs at the quantity where marginal revenue equals
- 16. Profit Maximization for the Competitive Firm When MR > MC increase Q When MR When
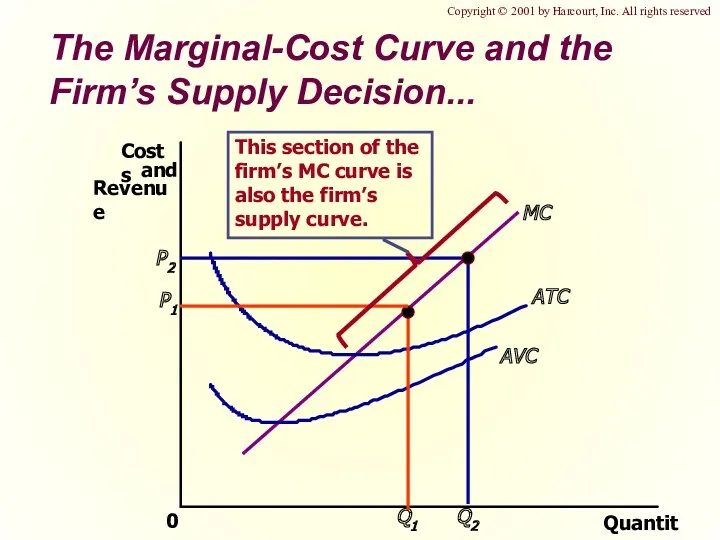
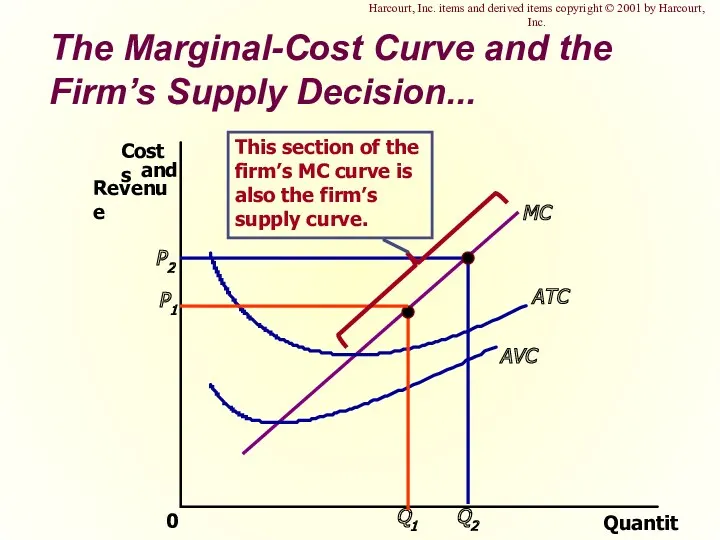
- 17. The Marginal-Cost Curve and the Firm’s Supply Decision... Quantity 0 MC ATC AVC Copyright © 2001
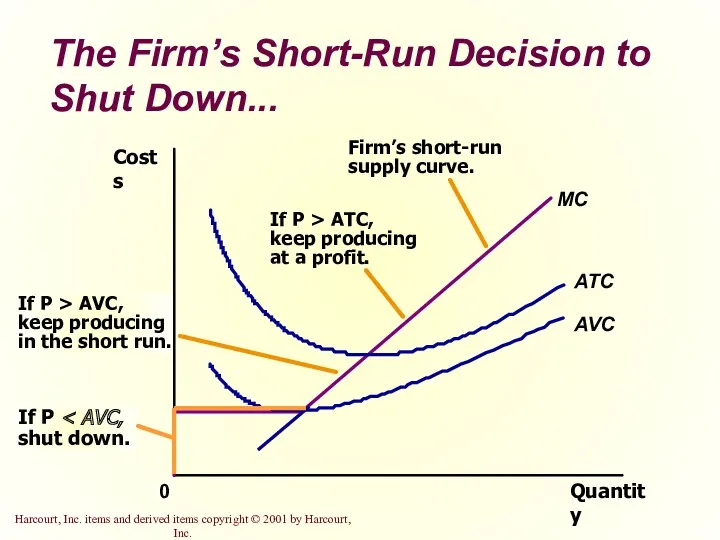
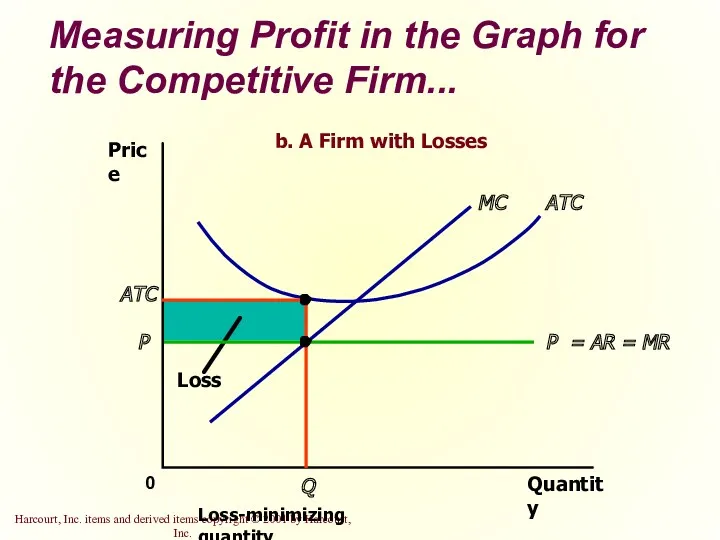
- 18. The Firm’s Short-Run Decision to Shut Down A shutdown refers to a short-run decision not to
- 19. The Firm’s Short-Run Decision to Shut Down The firm considers its sunk costs when deciding to
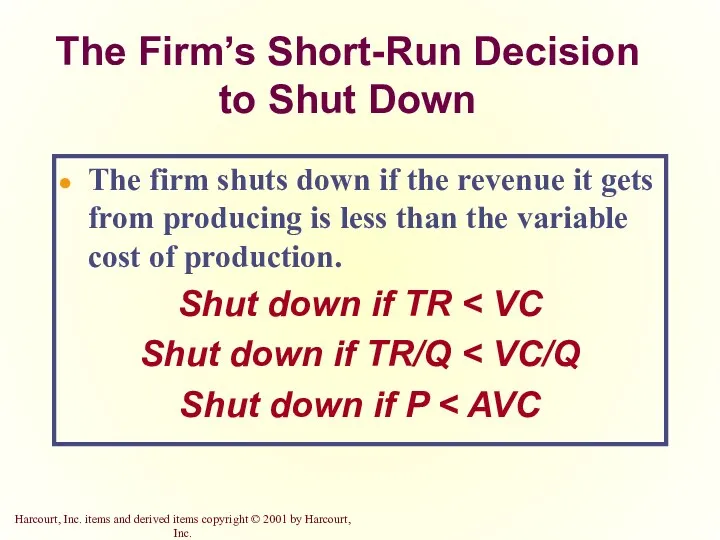
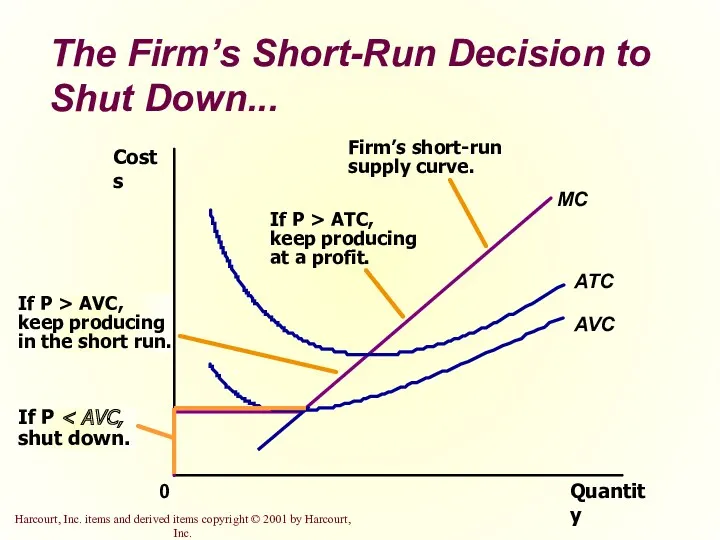
- 20. The Firm’s Short-Run Decision to Shut Down The firm shuts down if the revenue it gets
- 21. The Firm’s Short-Run Decision to Shut Down... Quantity ATC AVC 0 Costs
- 22. The Firm’s Short-Run Decision to Shut Down The portion of the marginal-cost curve that lies above
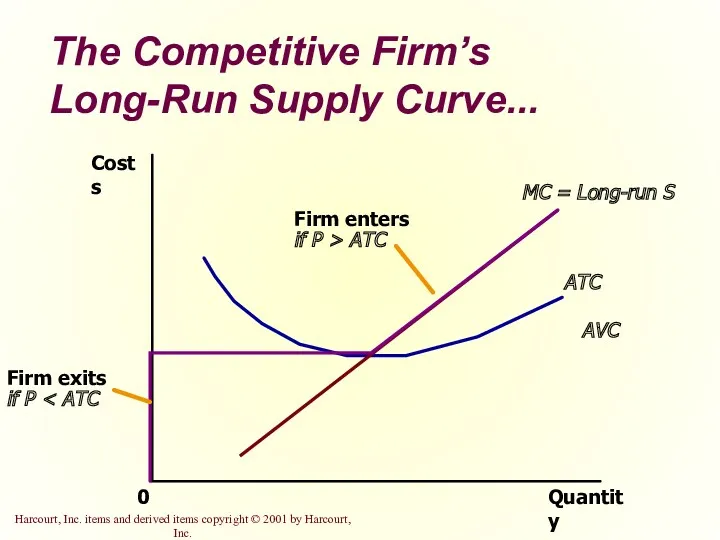
- 23. The Firm’s Long-Run Decision to Exit or Enter a Market In the long-run, the firm exits
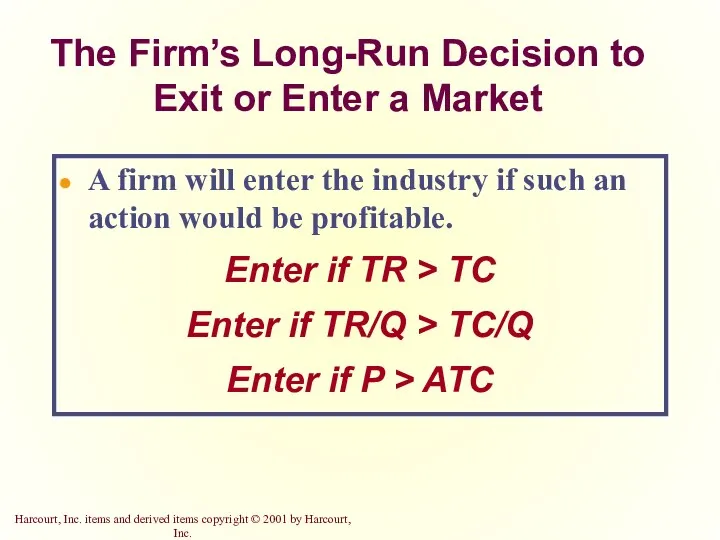
- 24. The Firm’s Long-Run Decision to Exit or Enter a Market A firm will enter the industry
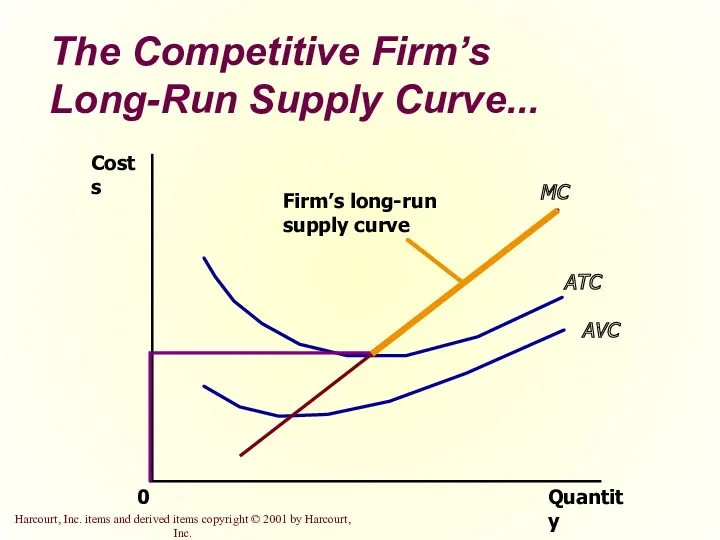
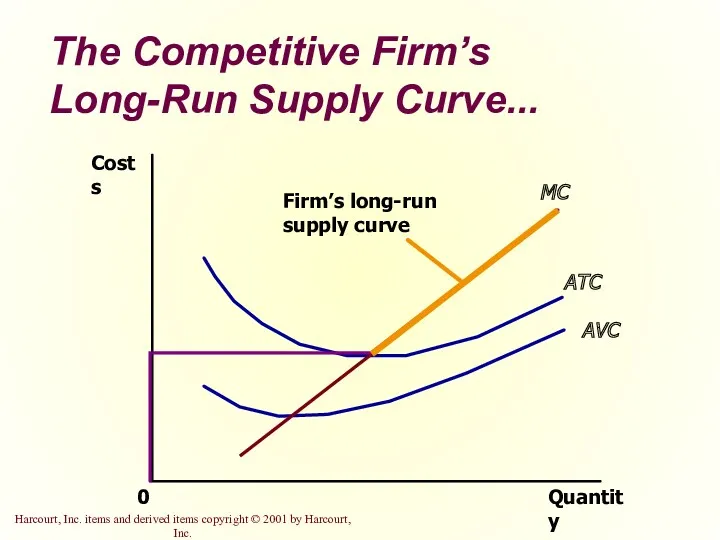
- 25. The Competitive Firm’s Long-Run Supply Curve... Quantity MC = Long-run S ATC AVC 0 Costs
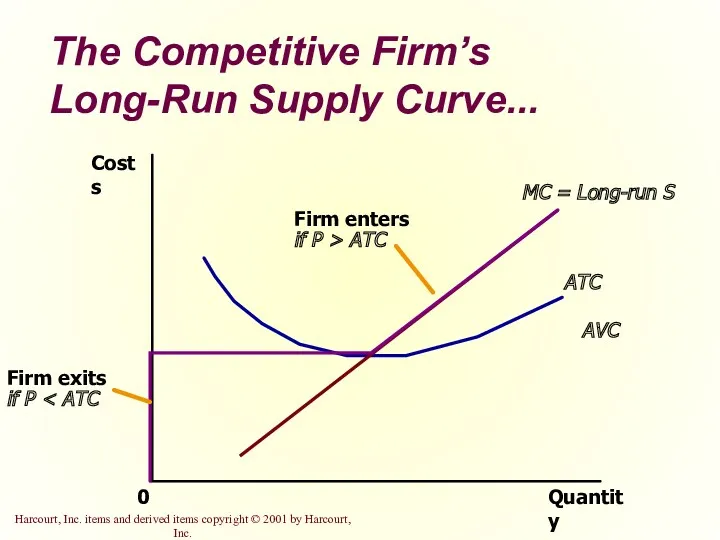
- 26. The Competitive Firm’s Long-Run Supply Curve The competitive firm’s long-run supply curve is the portion of
- 27. The Competitive Firm’s Long-Run Supply Curve... Quantity MC ATC AVC 0 Costs
- 28. The Firm’s Short-Run and Long-Run Supply Curves Short-Run Supply Curve The portion of its marginal cost
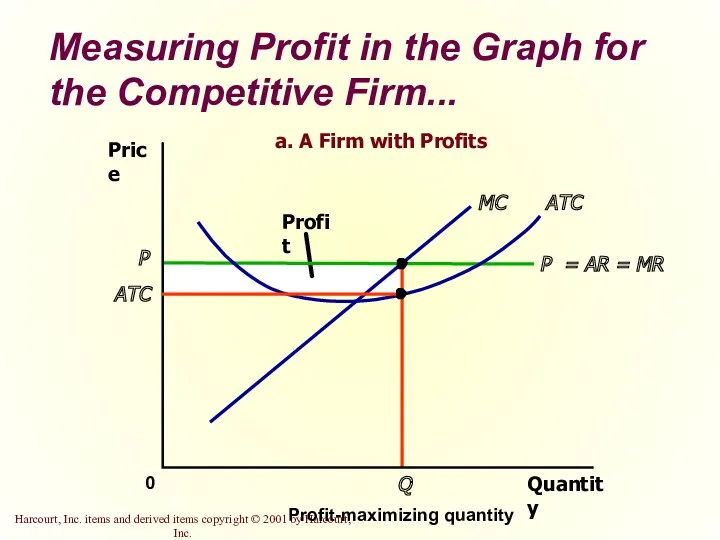
- 29. Measuring Profit in the Graph for the Competitive Firm... Quantity 0 Price P = AR =
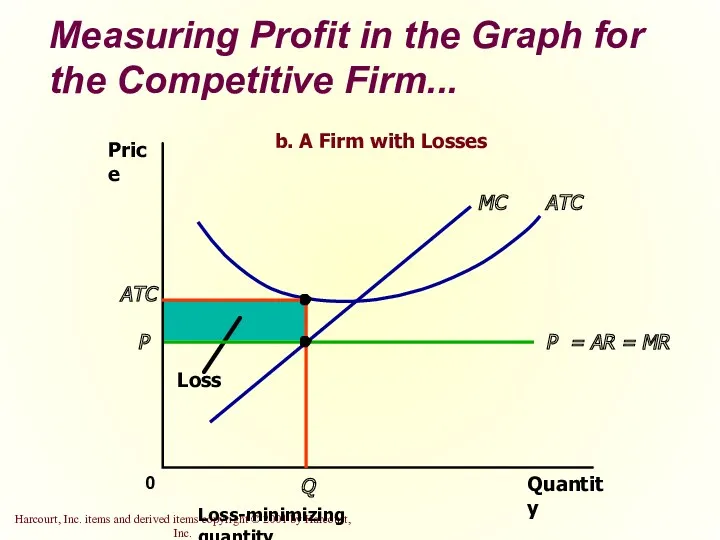
- 30. Measuring Profit in the Graph for the Competitive Firm... Quantity 0 Price P = AR =
- 31. Supply in a Competitive Market Market supply equals the sum of the quantities supplied by the
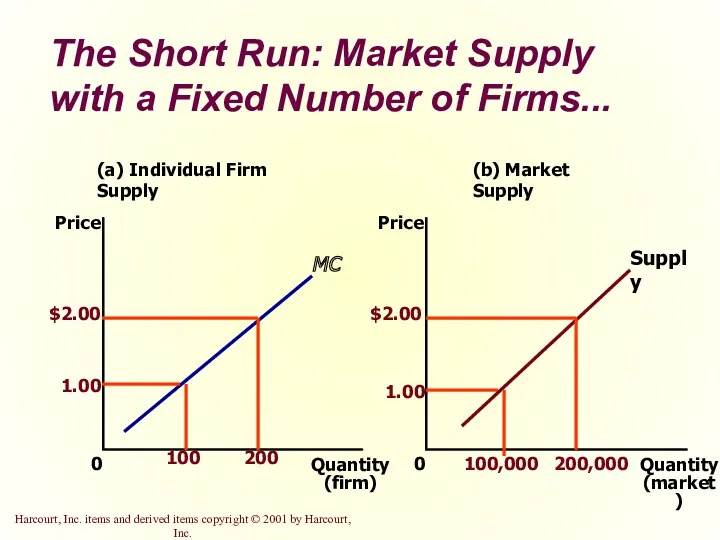
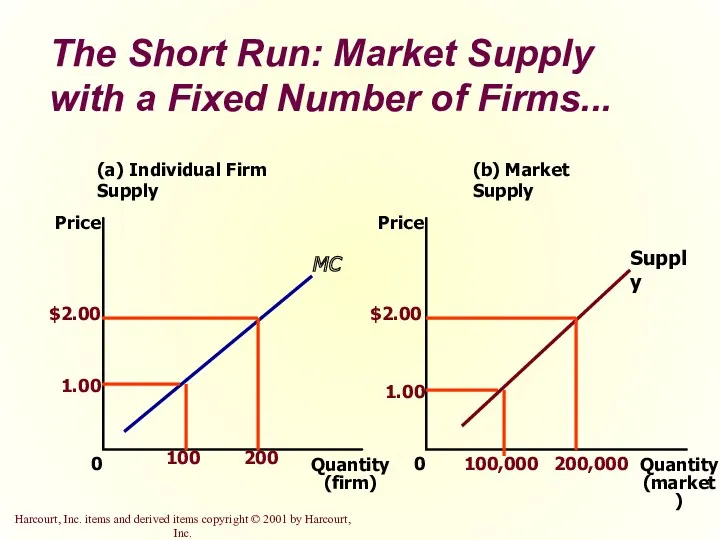
- 32. The Short Run: Market Supply with a Fixed Number of Firms For any given price, each
- 33. The Short Run: Market Supply with a Fixed Number of Firms... (a) Individual Firm Supply Quantity
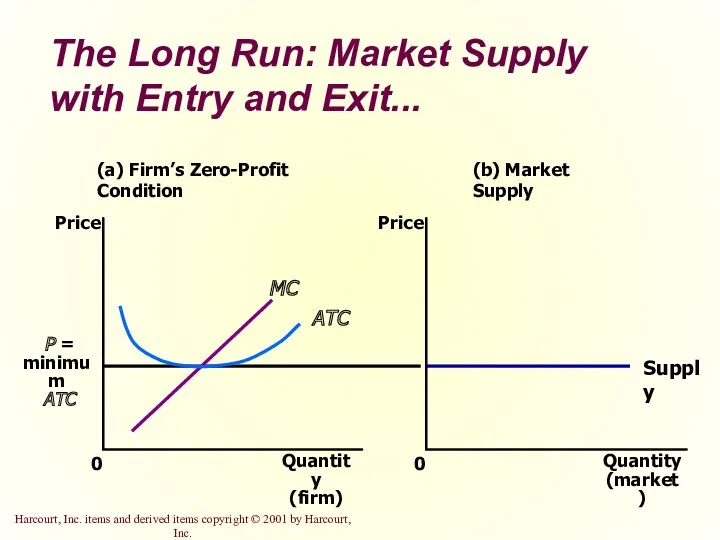
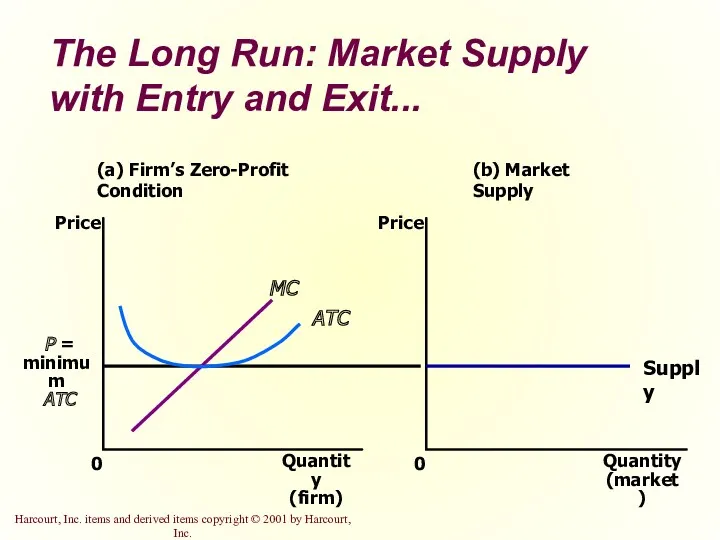
- 34. The Long Run: Market Supply with Entry and Exit Firms will enter or exit the market
- 35. The Long Run: Market Supply with Entry and Exit... (a) Firm’s Zero-Profit Condition Quantity (firm) 0
- 36. The Long Run: Market Supply with Entry and Exit At the end of the process of
- 37. Firms Stay in Business with Zero Profit Profit equals total revenue minus total cost. Total cost
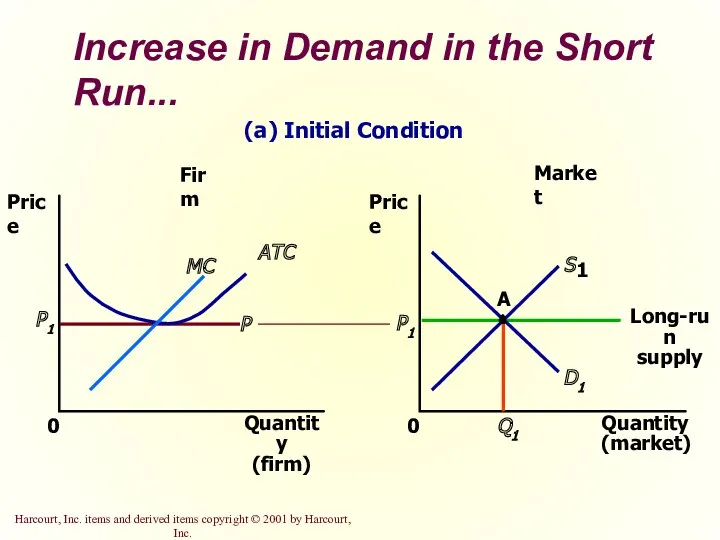
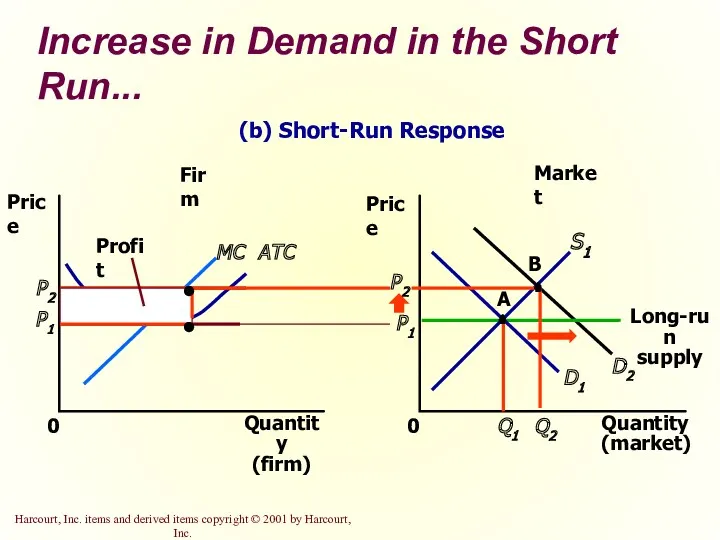
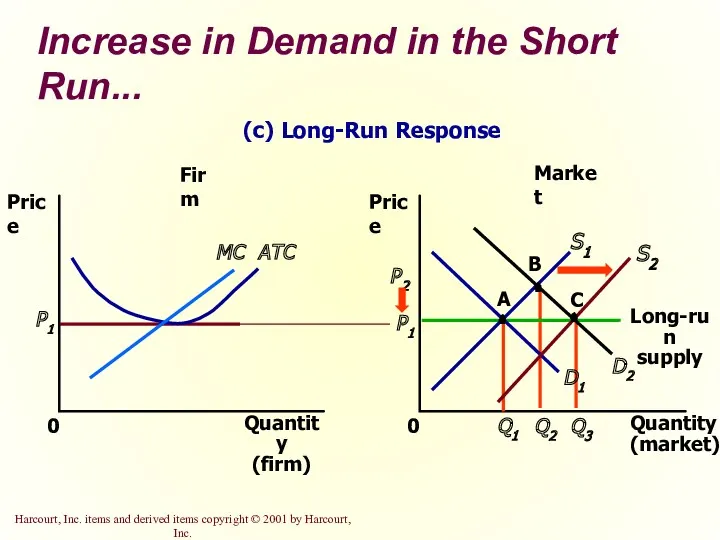
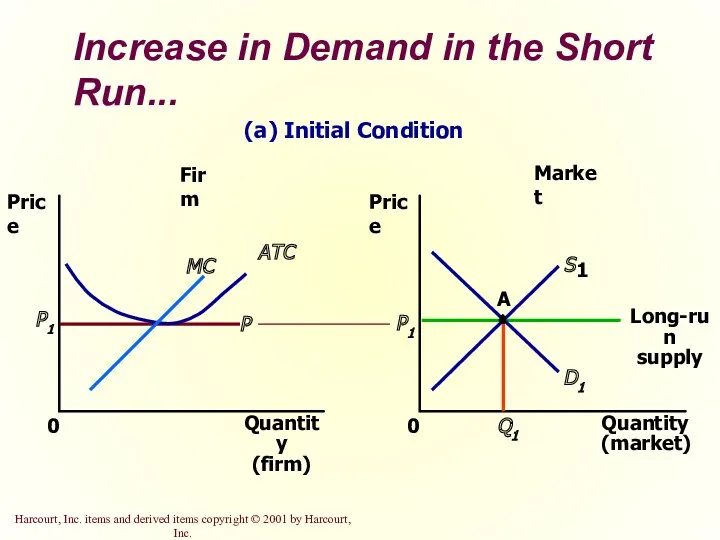
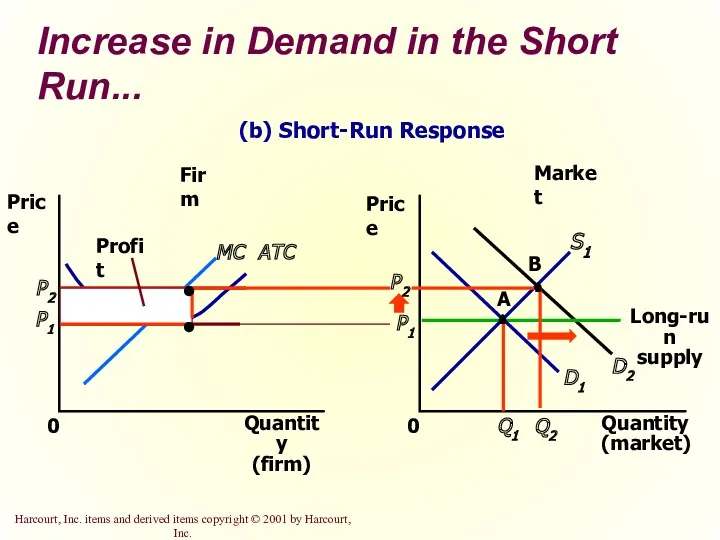
- 38. Increase in Demand in the Short Run An increase in demand raises price and quantity in
- 39. Increase in Demand in the Short Run... Market Firm Quantity (firm) 0 Price MC ATC P1
- 40. Increase in Demand in the Short Run... Market Firm Quantity (firm) 0 Price MC ATC P1
- 41. Increase in Demand in the Short Run... Market Firm Quantity (firm) 0 Price MC ATC P1
- 42. Why the Long-Run Supply Curve Might Slope Upward Some resources used in production may be available
- 43. Marginal Firm The marginal firm is the firm that would exit the market if the price
- 44. Summary Because a competitive firm is a price taker, its revenue is proportional to the amount
- 45. Summary To maximize profit a firm chooses the quantity of output such that marginal revenue equals
- 46. Summary In the short run when a firm cannot recover its fixed costs, the firm will
- 47. Summary In a market with free entry and exit, profits are driven to zero in the
- 49. Profit Maximization for the Competitive Firm... Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by
- 50. The Marginal-Cost Curve and the Firm’s Supply Decision... Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright ©
- 51. The Firm’s Short-Run Decision to Shut Down...
- 52. The Competitive Firm’s Long-Run Supply Curve...
- 53. The Competitive Firm’s Long-Run Supply Curve...
- 54. Measuring Profit in the Graph for the Competitive Firm...
- 55. Measuring Profit in the Graph for the Competitive Firm...
- 56. The Short Run: Market Supply with a Fixed Number of Firms...
- 57. The Long Run: Market Supply with Entry and Exit...
- 58. Increase in Demand in the Short Run...
- 59. Increase in Demand in the Short Run...
- 61. Скачать презентацию































 ОАО Протон-Пм
ОАО Протон-Пм Отчет о проделанной работе МУП ЖКХ Управляющая компания Гурьевского городского округа в 2017 году
Отчет о проделанной работе МУП ЖКХ Управляющая компания Гурьевского городского округа в 2017 году World Tourism Market. Introduction to the market and international tourism
World Tourism Market. Introduction to the market and international tourism Экономические взгляды Джона Бейтса Кларка
Экономические взгляды Джона Бейтса Кларка ИННОВАЦИИ. ПЕРСПЕКТИВЫ ИННОВАЦИОННОГО РАЗВИТИЯ РОССИИ
ИННОВАЦИИ. ПЕРСПЕКТИВЫ ИННОВАЦИОННОГО РАЗВИТИЯ РОССИИ Сущность этики бизнеса
Сущность этики бизнеса Сценарий экономической игры
Сценарий экономической игры Экономика предприятия НГК. Практикум Расчет сметы затрат и калькуляция затрат на производство нефтепродуктов
Экономика предприятия НГК. Практикум Расчет сметы затрат и калькуляция затрат на производство нефтепродуктов Проблемы республики Тыва
Проблемы республики Тыва Планирование и прогнозирование промышленности
Планирование и прогнозирование промышленности Экономическая эффективность отраслевых производств
Экономическая эффективность отраслевых производств Основы функционирования рыночной экономики
Основы функционирования рыночной экономики Экономические системы
Экономические системы Внешняя среда туристской организации
Внешняя среда туристской организации Цели и задачи экономической оценки нефтегазовых проектов
Цели и задачи экономической оценки нефтегазовых проектов The data of macroeconomics
The data of macroeconomics Основы теории производства и издержек
Основы теории производства и издержек Порядок расчета продажной цены на готовую продукцию
Порядок расчета продажной цены на готовую продукцию Теория и анализ отраслевых рынков. Характеристика основных рыночных структур
Теория и анализ отраслевых рынков. Характеристика основных рыночных структур Проект социально-экономического развития территорий Тульской области на основе родовых поместий
Проект социально-экономического развития территорий Тульской области на основе родовых поместий Өнім өндіру мен өткізу шығындары
Өнім өндіру мен өткізу шығындары Оценка конкурентоспособности Краснодарского края
Оценка конкурентоспособности Краснодарского края Глобальные проблемы человечества. Международный терроризм
Глобальные проблемы человечества. Международный терроризм Современные формы международной торговли
Современные формы международной торговли Современные особенности развития мирового хозяйства
Современные особенности развития мирового хозяйства Информационные ресурсы в экономических исследованиях
Информационные ресурсы в экономических исследованиях Устойчивое развитие в условиях глобализации
Устойчивое развитие в условиях глобализации Логистиканың өндіріс үрдісі
Логистиканың өндіріс үрдісі