Содержание
- 2. IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL LEARN: about the issues macroeconomists study about the tools macroeconomists use
- 3. Important issues in macroeconomics What causes recessions? What is “government stimulus” and why might it help?
- 4. Important issues in macroeconomics Why does the cost of living keep rising? Why are so many
- 5. microeconomics Examines the functioning of individual industries and the behavior of individual decision-making units—firms and households.
- 6. Three of the major concerns of macroeconomics are Output growth Unemployment Inflation and deflation Macroeconomic Concerns
- 7. Macroeconomic Concerns business cycle The cycle of short-term ups and downs in the economy. aggregate output
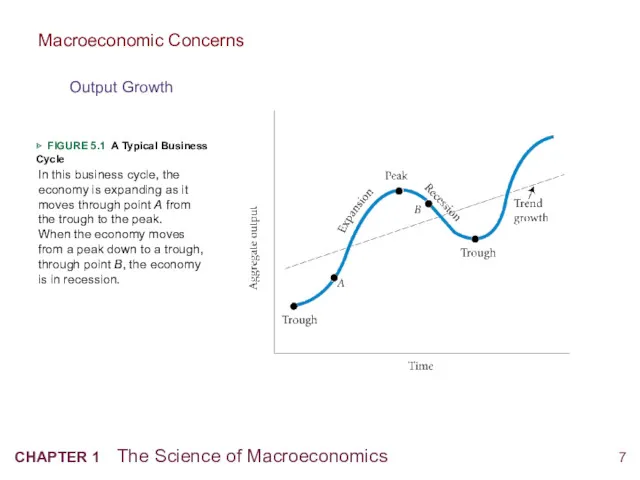
- 8. ▶ FIGURE 5.1 A Typical Business Cycle In this business cycle, the economy is expanding as
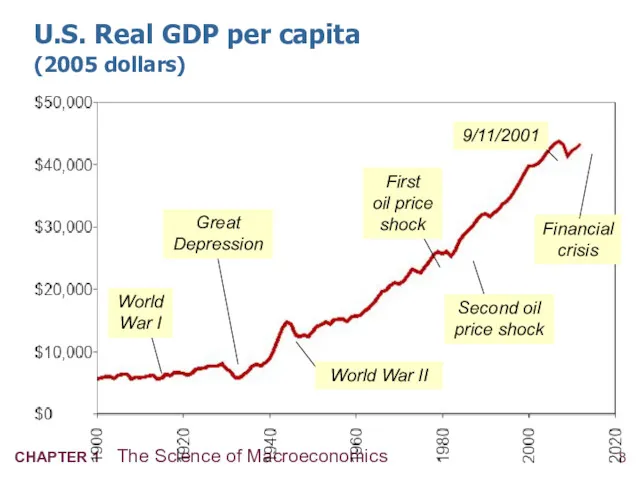
- 9. U.S. Real GDP per capita (2005 dollars) Great Depression World War II First oil price shock
- 10. Macroeconomic Concerns Unemployment unemployment rate The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed.
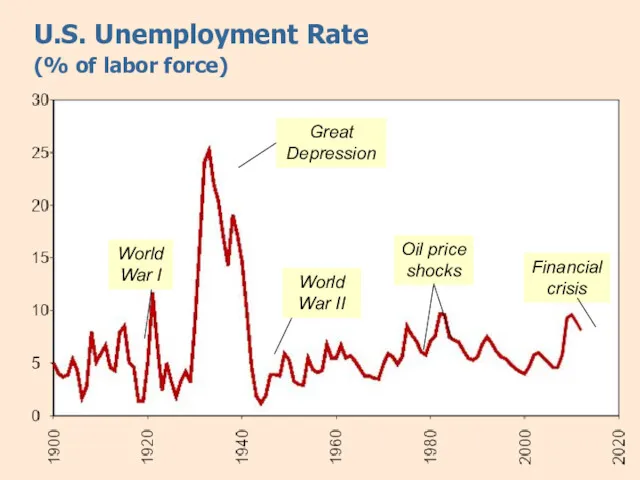
- 11. U.S. Unemployment Rate (% of labor force) Great Depression Financial crisis World War II World War
- 12. Macroeconomic Concerns Inflation and Deflation inflation An increase in the overall price level. hyperinflation A period
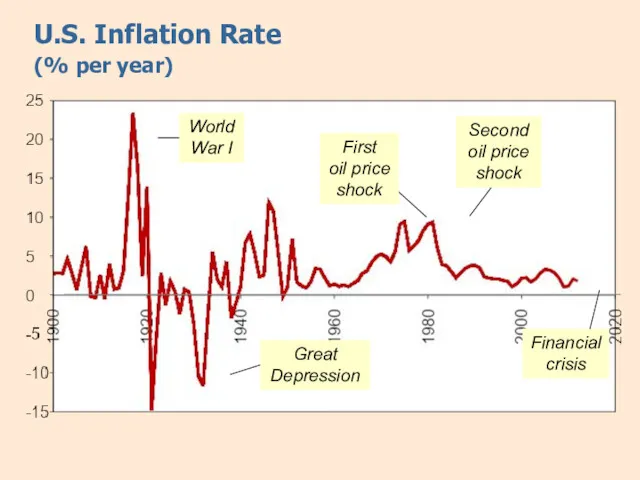
- 13. U.S. Inflation Rate (% per year) Great Depression First oil price shock Second oil price shock
- 14. Understanding how the macroeconomy works can be challenging because a great deal is going on at
- 15. Economic models …are simplified versions of a more complex reality irrelevant details are stripped away …are
- 16. Endogenous vs. exogenous variables The values of endogenous variables are determined in the model. The values
- 17. Example of a model: Supply & demand for new cars shows how various events affect price
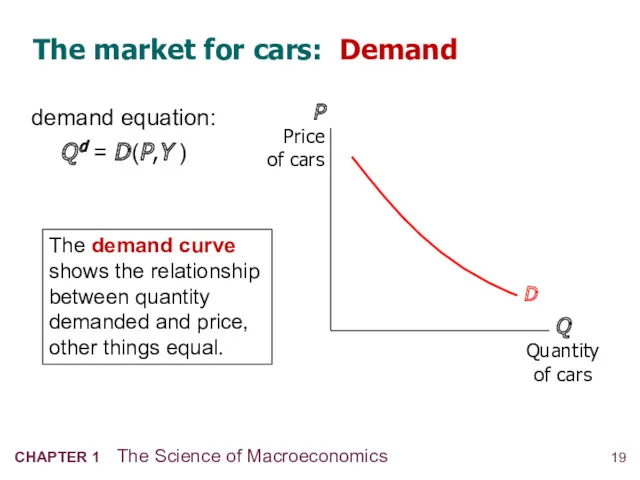
- 18. The demand for cars demand equation: Q d = D (P,Y ) shows that the quantity
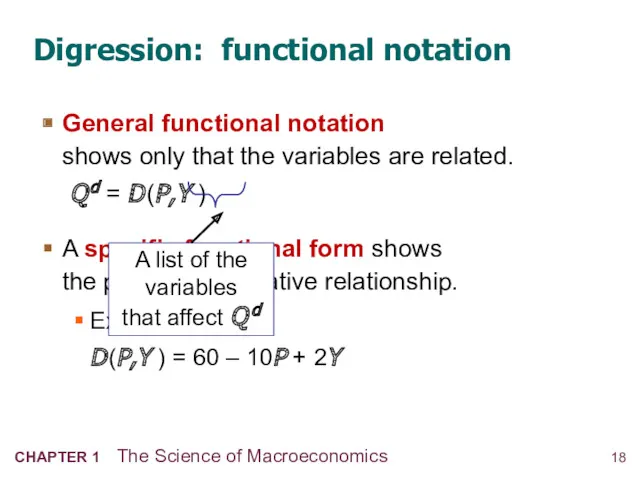
- 19. Digression: functional notation General functional notation shows only that the variables are related. Q d =
- 20. The market for cars: Demand Q Quantity of cars P Price of cars The demand curve
- 21. The market for cars: Supply supply equation: Q s = S (P,PS )
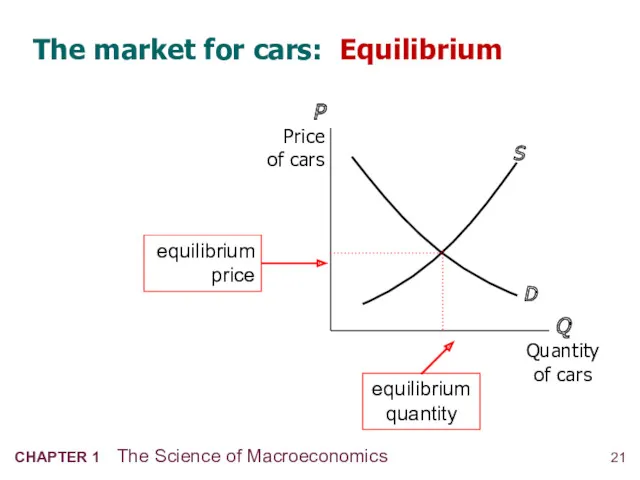
- 22. The market for cars: Equilibrium
- 23. The effects of an increase in income An increase in income increases the quantity of cars
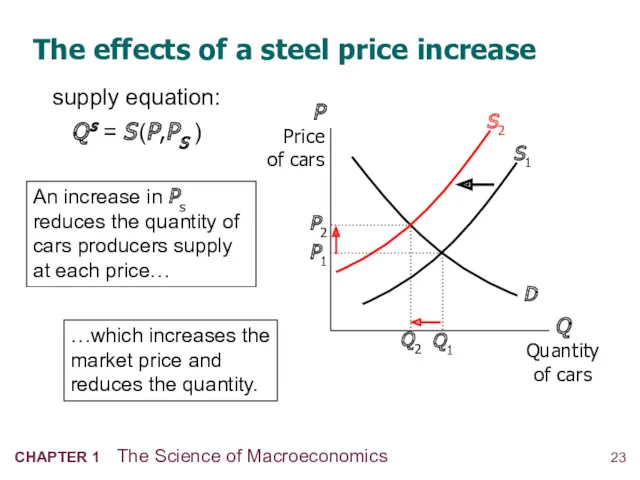
- 24. The effects of a steel price increase An increase in Ps reduces the quantity of cars
- 25. NOW YOU TRY Supply and Demand 1. Write down demand and supply equations for smartphones; include
- 26. The use of multiple models No one model can address all the issues we care about.
- 27. The use of multiple models So we will learn different models for studying different issues (e.g.,
- 28. Prices: flexible vs. sticky Market clearing: An assumption that prices are flexible, adjust to equate supply
- 29. Prices: flexible vs. sticky The economy’s behavior depends partly on whether prices are sticky or flexible:
- 30. Outline of this book: Introductory material (Chaps. 1, 2) Classical Theory (Chaps. 3–7) How the economy
- 31. Outline of this book: Macroeconomic theory (Chaps. 15–17) Macroeconomic dynamics, models of consumer behavior, theories of
- 32. CHAPTER SUMMARY Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, including growth in incomes
- 34. Скачать презентацию






















 Основные принципы формирования внешнеторговых цен, таможенные пошлины (тарифы), порядок определения таможенной стоимости
Основные принципы формирования внешнеторговых цен, таможенные пошлины (тарифы), порядок определения таможенной стоимости Классификация природных ресурсов
Классификация природных ресурсов Доход, прибыль и рентабельность предприятия
Доход, прибыль и рентабельность предприятия Экономические отношения. Экономические системы. (Тема 3)
Экономические отношения. Экономические системы. (Тема 3) Региональная экономика. Приграничные и приморские регионы. Лекция 17
Региональная экономика. Приграничные и приморские регионы. Лекция 17 Общественное производство . Рынок природных ресурсов . Рынок труда . Рынок капитала
Общественное производство . Рынок природных ресурсов . Рынок труда . Рынок капитала Олигополия. Модели олигополии
Олигополия. Модели олигополии Как устроена мировая экономика. 10 класс
Как устроена мировая экономика. 10 класс Random walk theory and GBM
Random walk theory and GBM Преступления в сфере экономической деятельности. Тема 26
Преступления в сфере экономической деятельности. Тема 26 АСЕАН. Ассоциация государств Юго-Восточной Азии
АСЕАН. Ассоциация государств Юго-Восточной Азии Международные экономические организации
Международные экономические организации Международные корпорации
Международные корпорации The Mathematics of demand functions
The Mathematics of demand functions Ценообразование в организации
Ценообразование в организации Экономика организации
Экономика организации Кәсіпорынның табысы мен пайдасы
Кәсіпорынның табысы мен пайдасы Зовнішньоекономічна діяльність та її роль у розвитку національної економіки
Зовнішньоекономічна діяльність та її роль у розвитку національної економіки Меркантилизм. (Занятие 4)
Меркантилизм. (Занятие 4) Основы бизнес-планирования
Основы бизнес-планирования Семейный бюджет
Семейный бюджет Транспорт и сфера услуг
Транспорт и сфера услуг Предпринимательская деятельность. Технология. 9 класс
Предпринимательская деятельность. Технология. 9 класс Макроэкономика. Национальный продукт и его измерение
Макроэкономика. Национальный продукт и его измерение Экономика труда, как наука
Экономика труда, как наука Методы научно-технического прогнозирования. Метод паттерн
Методы научно-технического прогнозирования. Метод паттерн Особонности товарооборота. Тема 15
Особонности товарооборота. Тема 15 Транспорттағы метеорологиялық болжамдардың экономикалық тиімділігі
Транспорттағы метеорологиялық болжамдардың экономикалық тиімділігі