Содержание
- 2. Accounting Learning Objectives – Chapter 4 Prepare the financial statements including the classified balance sheet Use
- 3. Accounting Learning Objectives – Chapter 4 4. Prepare the post-closing trial balance 5. Describe the accounting
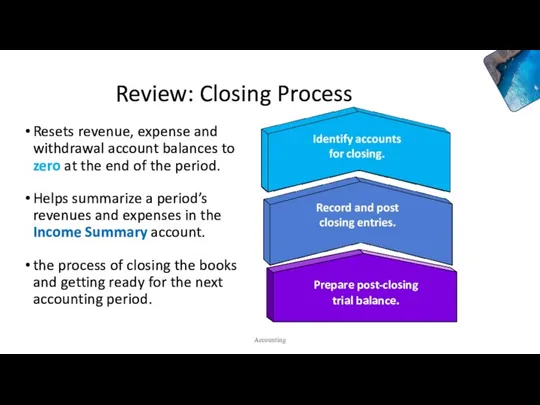
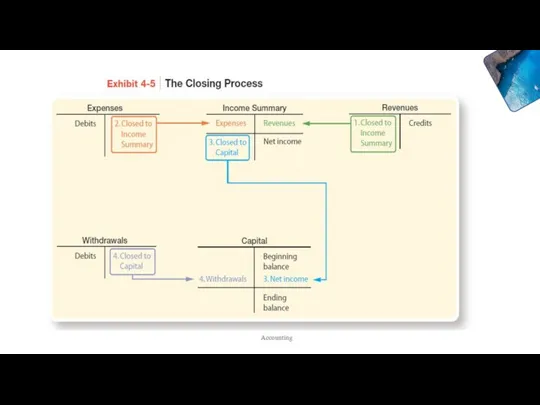
- 4. Review: Closing Process Resets revenue, expense and withdrawal account balances to zero at the end of
- 5. Accounting
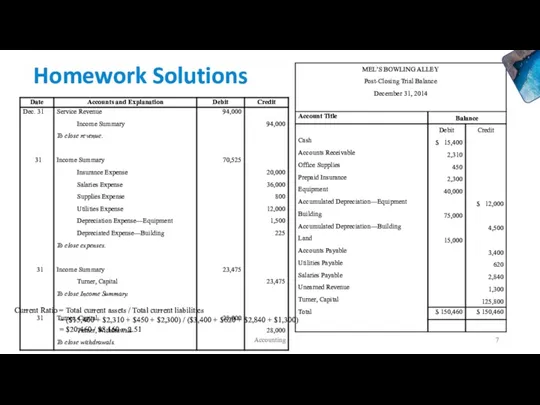
- 6. Review: Homework Accounting
- 7. Homework Solutions Accounting Current Ratio = Total current assets / Total current liabilities = ($15,400 +
- 8. Review: Current Ratio The most commonly used ratio is the Current Ratio. It is a measure
- 9. Learning Objective 1 Prepare the financial statements including the classified balance sheet Accounting
- 10. Adjusted Trial Balance (T/B) Accounting The financial statements come from the Adjusted Trial Balance. Each account
- 11. How do we prepare Financial Statements? Accounting The financial statements should be prepared in the following
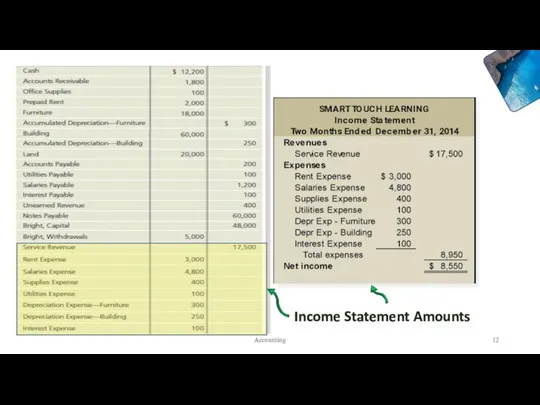
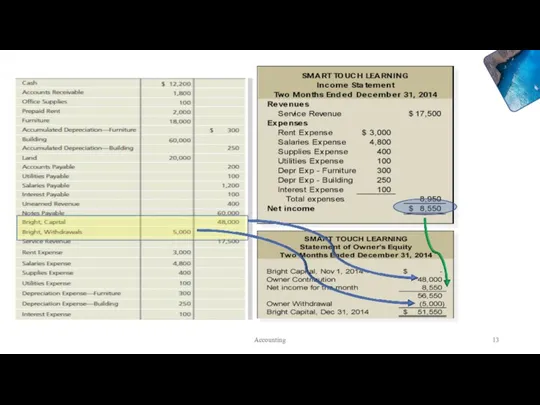
- 12. Income Statement Amounts Accounting
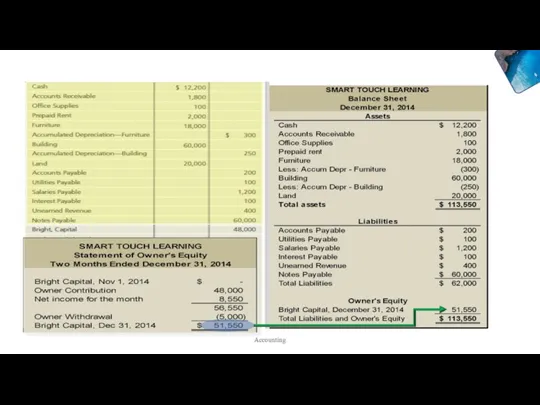
- 13. Accounting
- 14. Accounting
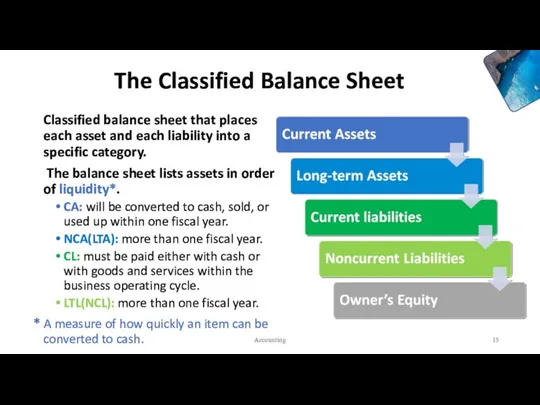
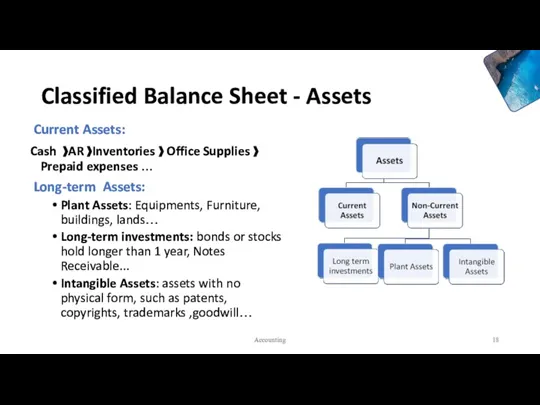
- 15. The Classified Balance Sheet Classified balance sheet that places each asset and each liability into a
- 16. The Classified Balance Sheet Accounting
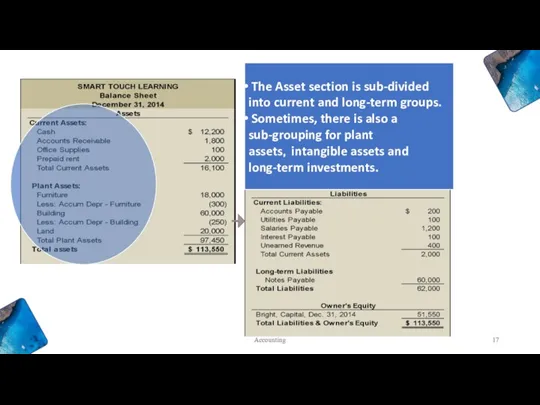
- 17. The Asset section is sub-divided into current and long-term groups. Sometimes, there is also a sub-grouping
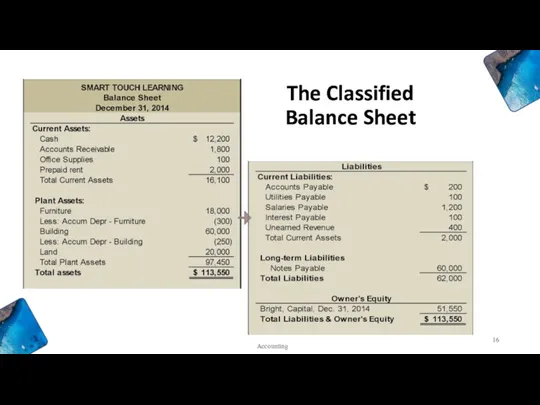
- 18. Classified Balance Sheet - Assets Current Assets: Cash 》AR 》Inventories 》 Office Supplies 》Prepaid expenses …
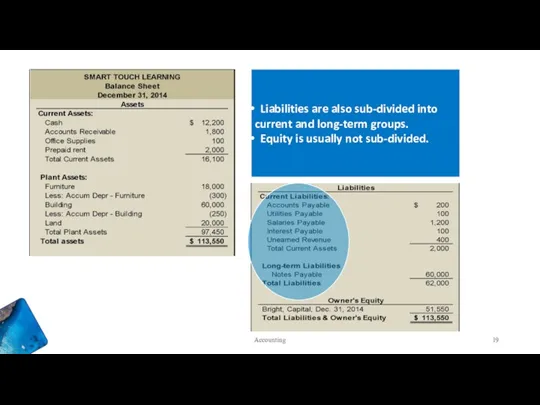
- 19. Liabilities are also sub-divided into current and long-term groups. Equity is usually not sub-divided. Accounting
- 20. Accounting
- 21. Accounting
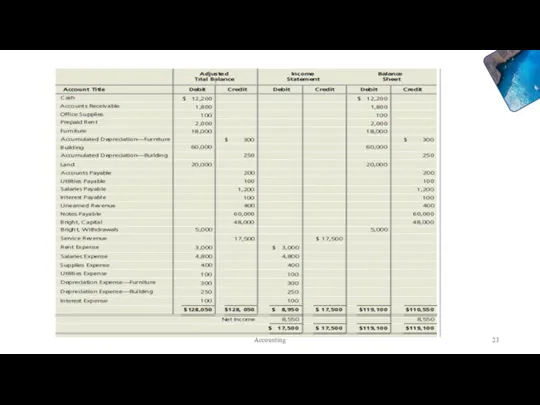
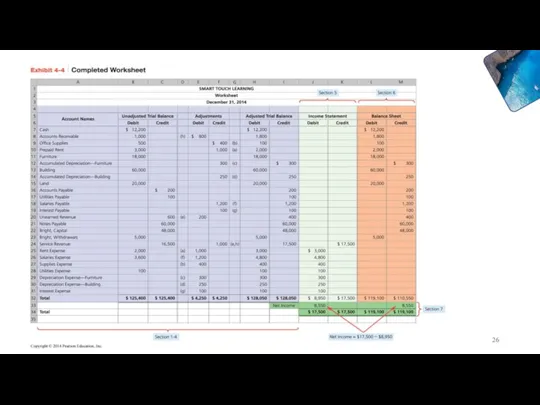
- 22. Learning Objective 2 Use the worksheet to prepare financial statements Accounting
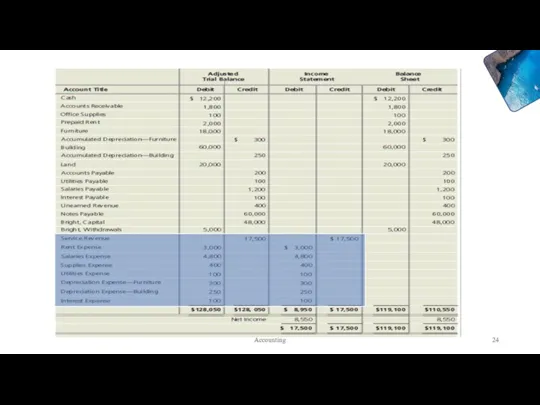
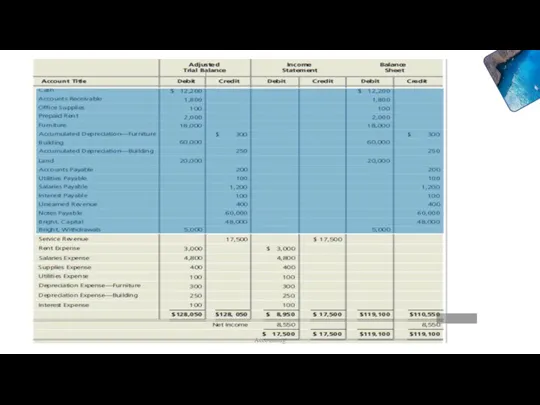
- 23. Accounting
- 24. Accounting
- 25. 4- Accounting
- 26. Accounting
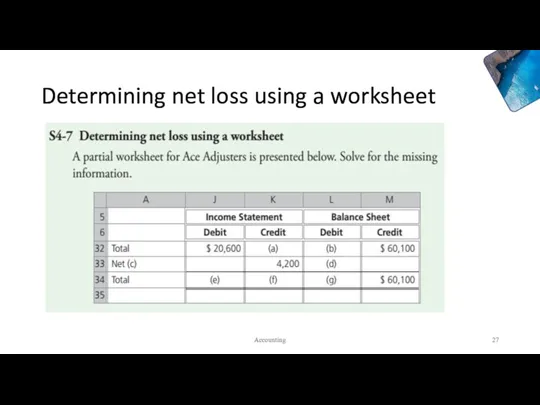
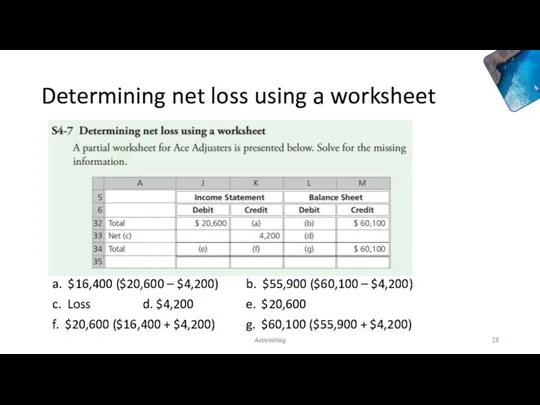
- 27. Determining net loss using a worksheet Accounting
- 28. Determining net loss using a worksheet a. $16,400 ($20,600 – $4,200) b. $55,900 ($60,100 – $4,200)
- 29. Learning Objective 5 Describe the accounting cycle Accounting
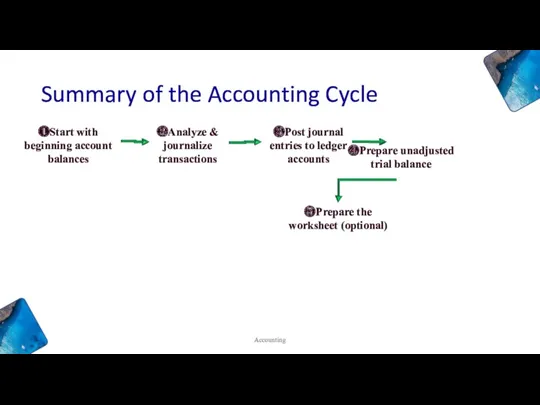
- 30. Summary of the Accounting Cycle Accounting ❷Analyze & journalize transactions ❸Post journal entries to ledger accounts
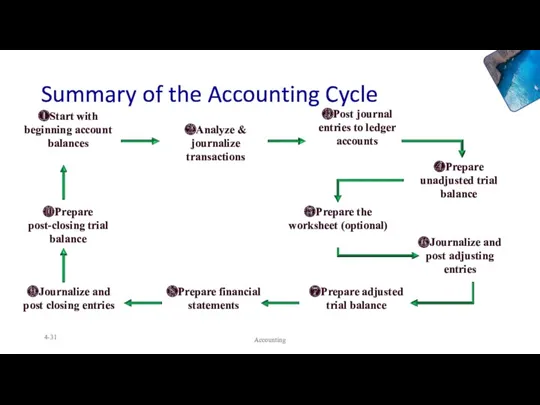
- 31. Summary of the Accounting Cycle Accounting 4- ❷Analyze & journalize transactions ❸Post journal entries to ledger
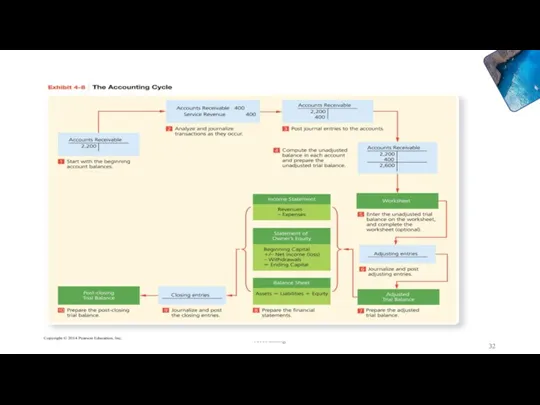
- 32. Accounting
- 33. Identify steps in the accounting cycle Accounting
- 34. Identify steps in the accounting cycle Accounting 6 2 8 1 5 3 4 7
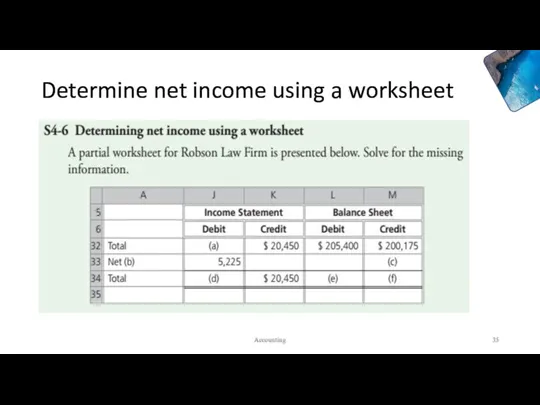
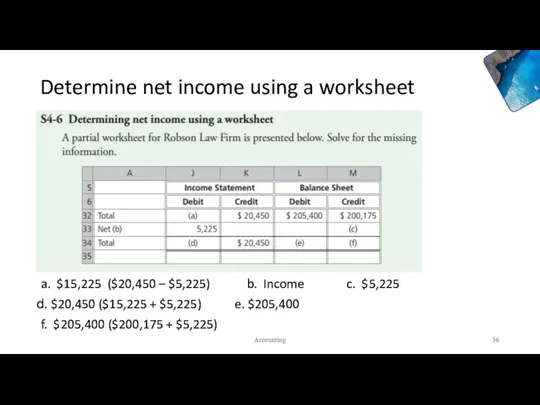
- 35. Determine net income using a worksheet Accounting
- 36. Determine net income using a worksheet a. $15,225 ($20,450 – $5,225) b. Income c. $5,225 $20,450
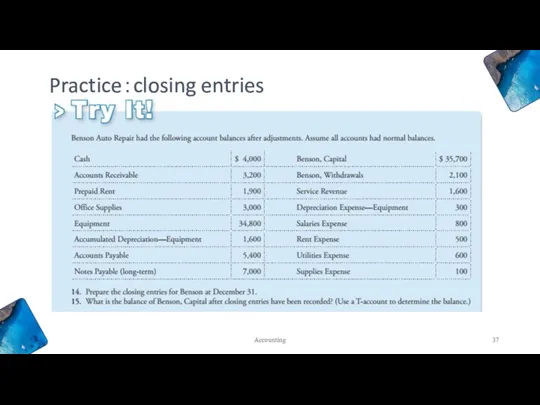
- 37. Accounting Practice:closing entries
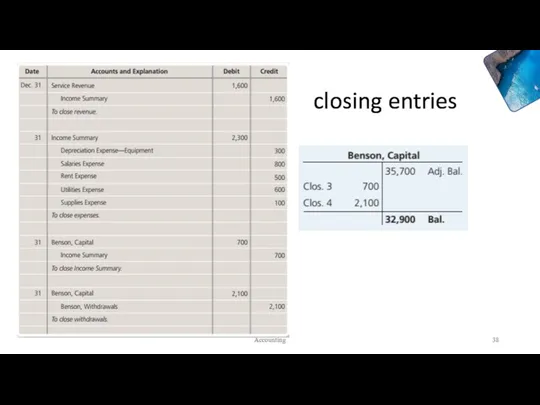
- 38. closing entries Accounting
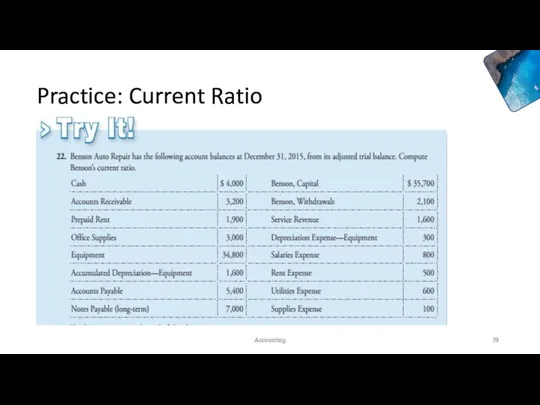
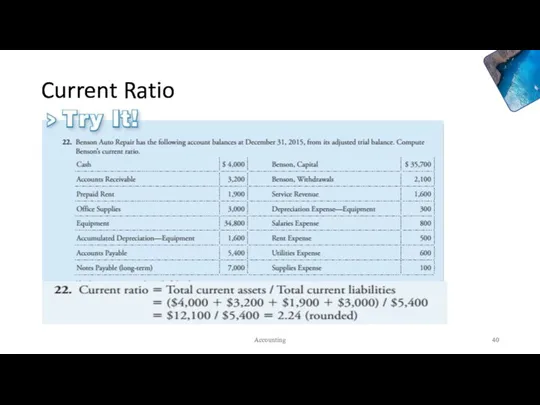
- 39. Practice: Current Ratio Accounting
- 40. Current Ratio A rule of thumb: A strong current ratio is 1.50. A current ratio of
- 41. Summary problem Accounting
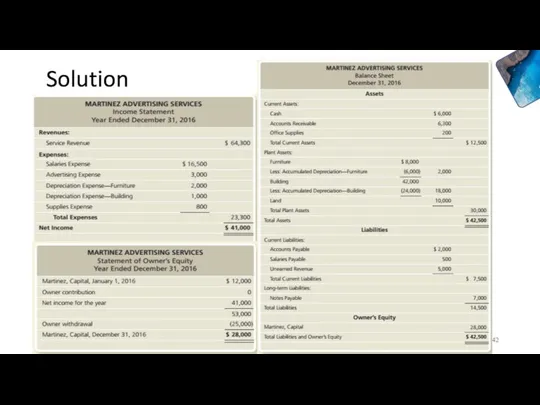
- 42. Solution Accounting
- 43. Solution Accounting
- 45. Скачать презентацию















 ПриватБанк и Payoneer
ПриватБанк и Payoneer Стандарти державного фінансового аудиту
Стандарти державного фінансового аудиту Денежная система: черты денежных систем в России и в мире, характеристика основных элементов
Денежная система: черты денежных систем в России и в мире, характеристика основных элементов Лекция Тема 4 . Повышение эффективности хозяйственной деятельности фирмы (организации (предприятия))
Лекция Тема 4 . Повышение эффективности хозяйственной деятельности фирмы (организации (предприятия)) Компания TeleTrade
Компания TeleTrade Тчет по проекту: содержательный, финансовый, публичный
Тчет по проекту: содержательный, финансовый, публичный Сравнительный подход к оценке стоимости
Сравнительный подход к оценке стоимости Supply and demand botanov
Supply and demand botanov Формирование методики оценки экономической эффективности инвестиционных проектов
Формирование методики оценки экономической эффективности инвестиционных проектов Зарплатный МТС Банк
Зарплатный МТС Банк Система показателей экономической эффективности бизнес-планирования
Система показателей экономической эффективности бизнес-планирования Ценообразование. Тема 7
Ценообразование. Тема 7 Финансовый контроль на предприятии (на материалах международный аэропорт Казань)
Финансовый контроль на предприятии (на материалах международный аэропорт Казань) Материальное обеспечение инвалидов
Материальное обеспечение инвалидов Экологический сбор
Экологический сбор Критерии анализа деловой активности предприятия. (Тема 6)
Критерии анализа деловой активности предприятия. (Тема 6) Рынок долгового капитала. (4)
Рынок долгового капитала. (4) Учетная политика для целей налогообложения
Учетная политика для целей налогообложения Бухгалтерская финансовая отчетность
Бухгалтерская финансовая отчетность SCP-анализ
SCP-анализ ВКР Направления улучшения использования оборотных средств предприятия
ВКР Направления улучшения использования оборотных средств предприятия Бухгалтерский учет и анализ финансовых результатов на примере ООО Гермес
Бухгалтерский учет и анализ финансовых результатов на примере ООО Гермес Актуализация нормативной базы по вопросам наличного денежного обращения
Актуализация нормативной базы по вопросам наличного денежного обращения Деньги и денежный рынок
Деньги и денежный рынок Выявление проблем в области клиентоориентированности
Выявление проблем в области клиентоориентированности Криптовалюты- деньги будущего
Криптовалюты- деньги будущего Кәсіпорындағы еңбекақы төлеу
Кәсіпорындағы еңбекақы төлеу Кәсіпорынның табыстылығын диверсификациялау мәселелері
Кәсіпорынның табыстылығын диверсификациялау мәселелері