Содержание
- 2. 9- The foreign exchange market Foreign exchange market: A market for converting the currency of one
- 3. 9- Types of Forex Risk Transactions Risk: risk that contract value Will change due to forex
- 4. 9- Functions of the foreign exchange market Two functions: Converting currencies Reducing risk
- 5. 9- Currency conversion Companies receiving payment in foreign currencies need to convert these payments to their
- 6. 9- Reducing risk Insuring against foreign exchange risk Spot exchange rate: rate of currency exchange on
- 7. Economic Exposure WSJ, Feb 1, 2011, p. B2 Nissan Presses Export Brakes “…a move in the
- 8. 9- Foreign Exchange Quotes See any reputable financial site Note that quotes change every second. Yahoo
- 9. How much more would you have paid by waiting? 50,000€ × $1.287 = $64,359.00 50,000€ ×
- 10. 9- Important terminology: Direct and Indirect Rates Direct Rates: units of home currency per one unit
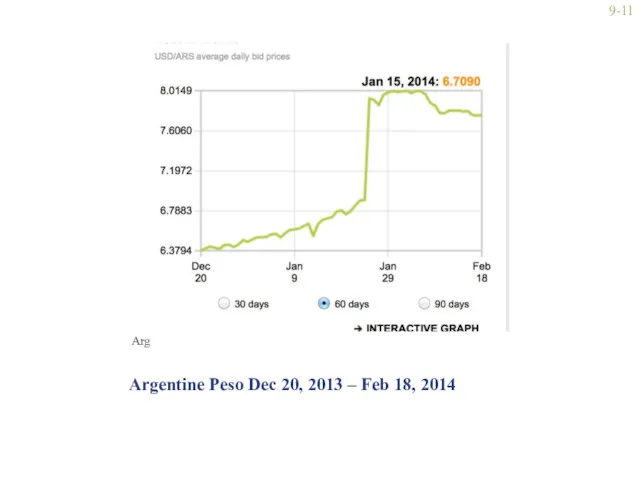
- 11. Argentine Peso Dec 20, 2013 – Feb 18, 2014 Arg 9-
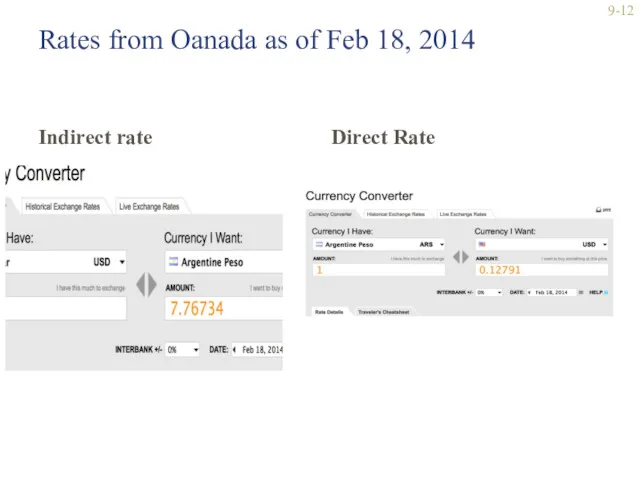
- 12. Rates from Oanada as of Feb 18, 2014 Indirect rate Direct Rate 9-
- 13. 9- The foreign exchange market (FX) Global network of banks, brokers and foreign exchange dealers connected
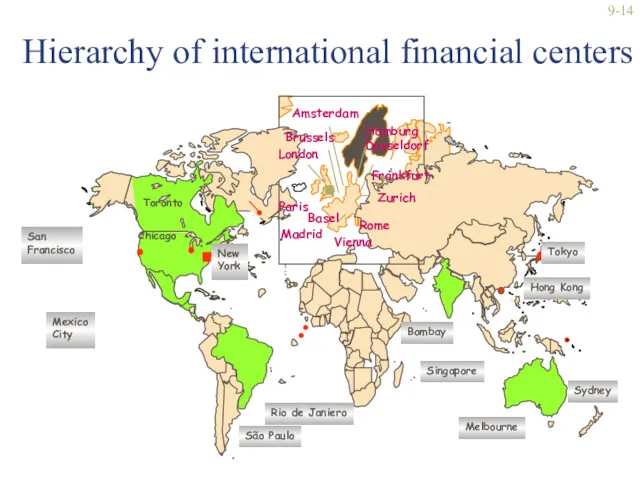
- 14. 9- Hierarchy of international financial centers Note: Size of dots (squares) indicates cities’ relative importance
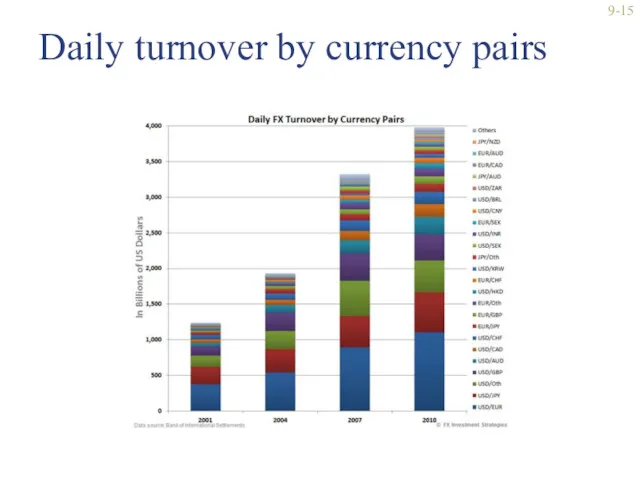
- 15. Daily turnover by currency pairs 9-
- 16. 9- Economic theories of exchange rate determination “Floating” Exchange rates are determined by the demand and
- 17. 9- Law of one price In competitive markets free of transportation costs and trade barriers, identical
- 18. 9- Purchasing power parity By comparing the prices of identical products in different currencies, it should
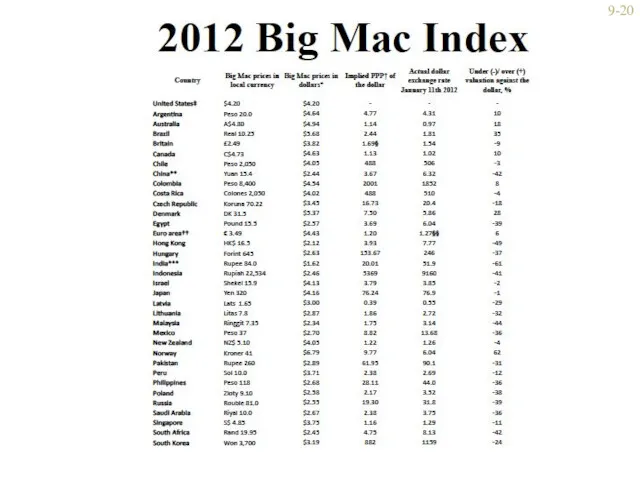
- 19. http://www.economist.com/content/big-mac-index Why? 9-
- 20. 9-
- 21. 9- Where the numbers from from. Take price in $ and divide into local price. [81
- 22. 9- Money supply and inflation PPP theory predicts that changes in relative prices will result in
- 23. 9- Interest rates and exchange rates Theory says that nominal interest rates reflect expectations about future
- 24. 9- Interest Rate Parity Forward rate premium or discount will be equal to but opposite in
- 25. 9- FWD premium and Discount Using direct rates: [[Fwd-spot]/spot] X 12/N x100 = % premium or
- 26. 9- Covered Interest Arbitrage Arbitrage and Foreign Exchange In economics, arbitrage is the practice of taking
- 27. 9- Covered Interest Arbitrage
- 28. 9-
- 29. 9- Cross Rates When there is no quote between two currencies You need to use a
- 30. 9-
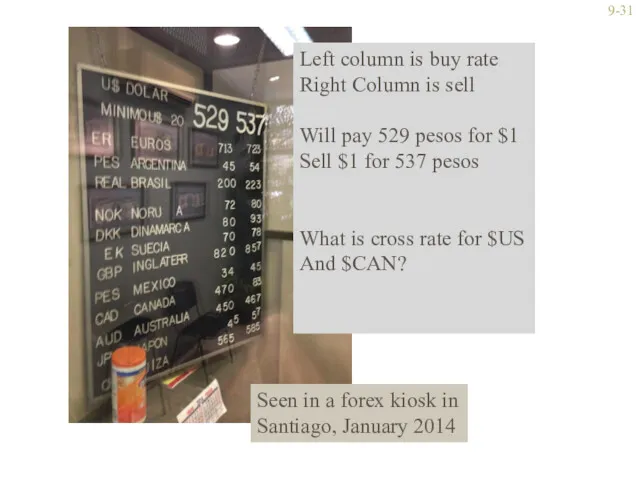
- 31. 9- Left column is buy rate Right Column is sell Will pay 529 pesos for $1
- 32. Assume $US and $Can are at 1$US=$C1.08. You have $C1,000,000 at your disposal. What would you
- 33. 9- Investor psychology and bandwagon effects Evidence suggests that neither PPP nor the International Fisher Effect
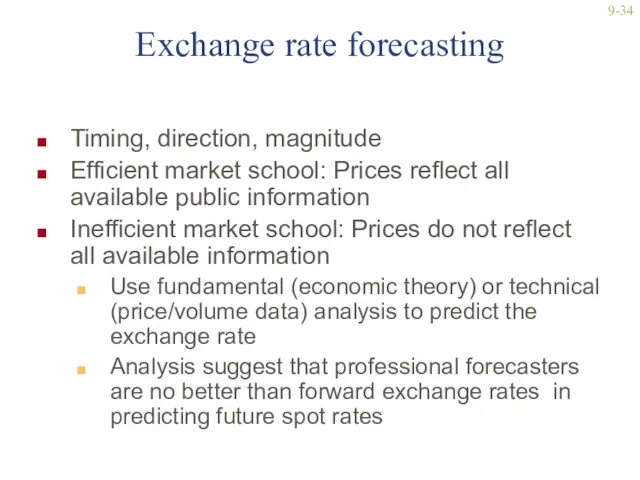
- 34. 9- Exchange rate forecasting Timing, direction, magnitude Efficient market school: Prices reflect all available public information
- 35. 9- Approaches to forecasting Fundamental analysis Draws on economic theory to construct sophisticated econometric models for
- 36. 9- Currency convertibility Political decision. Many countries have some kind of restrictions Governments limit convertibility to
- 37. 9- Counter trade Barter-like agreements where goods/services are traded for goods/services Helps firms avoid convertibility issue
- 38. 9- Managerial implications Exchange rates influence the profitability of trade and investment deals International businesses must
- 40. Скачать презентацию


















![9- FWD premium and Discount Using direct rates: [[Fwd-spot]/spot] X](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/138526/slide-24.jpg)











 Оценка качества кредитного портфеля в современной банковской практике
Оценка качества кредитного портфеля в современной банковской практике Базисные условия поставки. Инкотермс-2010
Базисные условия поставки. Инкотермс-2010 Как увеличить денежный поток
Как увеличить денежный поток Внебюджетные фонды в финансовой системе государства
Внебюджетные фонды в финансовой системе государства Негосударственные пенсионные фонды
Негосударственные пенсионные фонды Федеральное казначейство РФ. Вопросы технологического обеспечения передачи полномочий по ведению бюджетного учета
Федеральное казначейство РФ. Вопросы технологического обеспечения передачи полномочий по ведению бюджетного учета Ақша. Шығу тарихы
Ақша. Шығу тарихы Оборотные средства организации (предприятия) и их эффективность
Оборотные средства организации (предприятия) и их эффективность Финансовые методы повышения стоимости компании
Финансовые методы повышения стоимости компании Режимы налогообложения. Задание 6
Режимы налогообложения. Задание 6 Экономическая сущность и классификация инвестиций. Темы 1-4
Экономическая сущность и классификация инвестиций. Темы 1-4 Аудиторский контроль
Аудиторский контроль Зарплатный проект. Пакетная линейка карт
Зарплатный проект. Пакетная линейка карт Range market. Торговля в боковом тренде
Range market. Торговля в боковом тренде Основы социального страхования
Основы социального страхования Программы накопительного страхования жизни
Программы накопительного страхования жизни Innovations in Insurance
Innovations in Insurance История фальшивых денег, как избежать подделки
История фальшивых денег, как избежать подделки Правове положення комерційних банків. (Тема 3)
Правове положення комерційних банків. (Тема 3) Бухучет и налоги в 2020 году: отчетная революция
Бухучет и налоги в 2020 году: отчетная революция Семейный бюджет. Бюджет школьника
Семейный бюджет. Бюджет школьника Государственные ипотечные программы, реализуемые ГП НО НИКА
Государственные ипотечные программы, реализуемые ГП НО НИКА Управление денежными потоками по инвестиционной деятельности
Управление денежными потоками по инвестиционной деятельности Nauka o organizacji. Konsorcjum
Nauka o organizacji. Konsorcjum Зарплатный проект в рамках Пакетов решений Alfa Smart
Зарплатный проект в рамках Пакетов решений Alfa Smart Акционерное общество
Акционерное общество Daň z přidané hodnoty
Daň z přidané hodnoty Криптотрейдинг с нуля
Криптотрейдинг с нуля