Содержание
- 2. 1-2 FINANCIAL SYSTEM 9/8/2021 FINANCIAL SYSTEM Elena Rogova, Professor, erogova@hse.ru
- 3. The financial system is the collection of institutions that facilitate the flow of funds between lenders
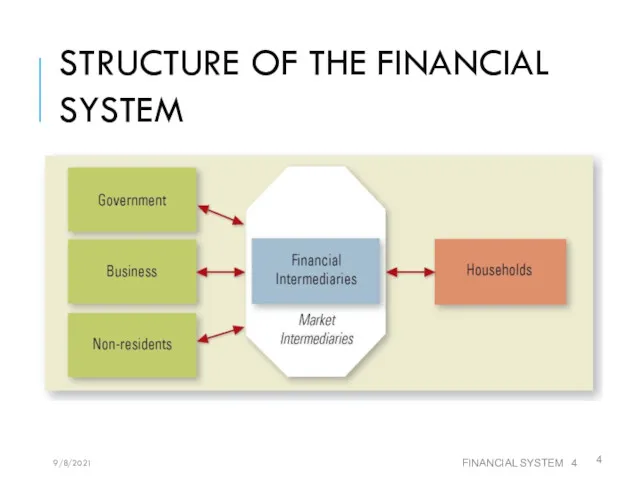
- 4. STRUCTURE OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM FINANCIAL SYSTEM 9/8/2021
- 5. THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM: SAVINGS AND INVESTMENTS When people earn income, they typically don’t want to consume
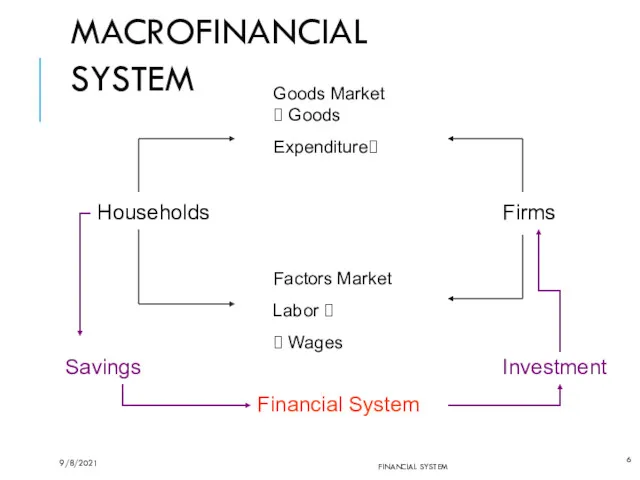
- 6. MACROFINANCIAL SYSTEM FINANCIAL SYSTEM Households Firms Goods Market ? Goods Expenditure? Factors Market Labor ? ?
- 7. WHAT DOES THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM DO? FINANCIAL SYSTEM The financial system serves multiple purposes: It helps
- 8. FINANCIAL MARKETS Markets in which funds are transferred from people who have an excess of available
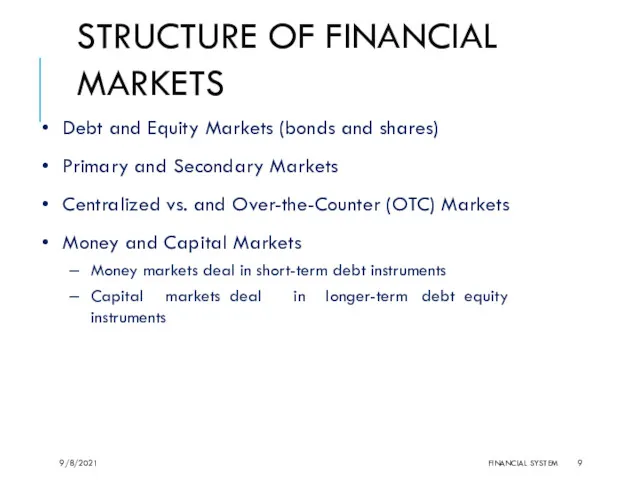
- 9. STRUCTURE OF FINANCIAL MARKETS Debt and Equity Markets (bonds and shares) Primary and Secondary Markets Centralized
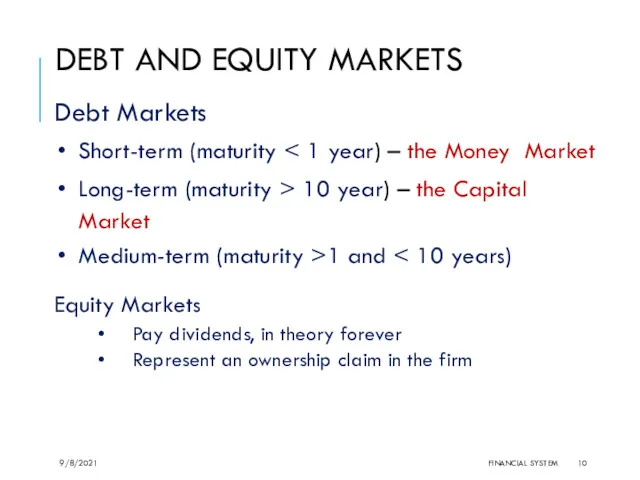
- 10. DEBT AND EQUITY MARKETS Debt Markets Short-term (maturity Long-term (maturity > 10 year) – the Capital
- 11. DEBT INSTRUMENT A contractual agreement by the borrower to pay the holder of the instrument fixed
- 12. COMMON STOCK Claims to share in the net income and the assets of the business Often
- 13. PRIMARY MARKET New security, bond or stock, issues sold to initial buyers by the corporation or
- 14. SECONDARY MARKET Securities previously issued are bought and sold Even though firms don’t get any money,
- 15. TYPES OF SECONDARY MARKETS Exchanges or Auction Markets Secondary markets that involve a bidding process that
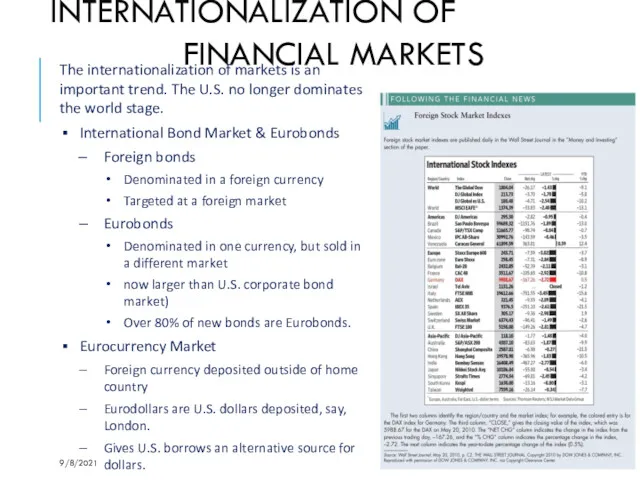
- 16. INTERNATIONALIZATION OF FINANCIAL MARKETS The internationalization of markets is an important trend. The U.S. no longer
- 17. BANKING AND FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS Financial Intermediaries - institutions that borrow funds from people who have saved
- 18. TYPES OF FIS Depository Institutions Insurance Companies Securities Firms and Investment Banks Mutual Funds Finance Companies
- 19. DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS Commercial Banks: accept deposits and make loans to consumers and businesses. Savings Associations Qualified
- 20. Banks convert deposits to loans and thereby increase access to capital by serving as a financial
- 21. CENTRAL BANKS AS MACRO REGULATORS THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM: The Federal Reserve system- One bank that
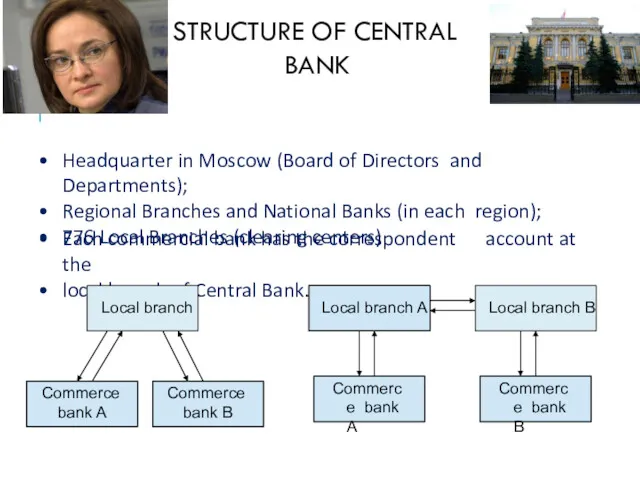
- 22. STRUCTURE OF CENTRAL BANK Headquarter in Moscow (Board of Directors and Departments); Regional Branches and National
- 23. COMMERCIAL BANKING 2/19/2020 Regulated by Lаw on Banks and Banking Activities (1993) Banks may provide all
- 24. INSURANCE COMPANIES 2/19/2020 Insurers sell policies and collect premiums from customers based on the pricing of
- 25. Financial innovations: create new financial products with payoffs desired by the customers (product innovations), provide new
- 26. HOW FINANCIAL INNOVATIONS IMPROVE ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE Completing markets: expanding opportunities for risk-sharing risk-pooling hedging Inter-temporal or
- 27. FINANCIAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS Payments system for the exchange of goods. Mechanism for the pooling of funds
- 28. PAYMENTS SYSTEM Decreasing the cost of processing payments for transactions –E.g. SWIFT, CHIPS Increasing the speed
- 29. Mechanism for the pooling of funds to create large-scale indivisible enterprises. – Creating a mechanism for
- 30. RESOURCES TRANSFER THROUGH TIME AND SPACE Investors need ways of transferring savings from the present (when
- 31. RISK MANAGEMENT Reducing the risk by selling the source of it. In general, adjusting a portfolio
- 32. INFORMATION FOR DECENTRALIZED DECISION-MAKING Decision makers need information about demand and supply and prices in their
- 33. MANAGING AGENCY COSTS Investors and Issuers may be unwilling to trade because of concerns as to
- 34. THE IMPACT OF GOVERNMENT ON FINANCIAL MARKETS The primary role of government is to promote competition,
- 35. HOW GOVERNMENTS AFFECT FINANCIAL MARKETS (1) As a legislator, by setting/ enforcing rules and restrictions on
- 36. These activities can have potential costs that can be classified as follows: direct costs to participants,
- 37. THE DYNAMIC OF FINANCIAL INNOVATION Aggregate Trading Volume expands secularly Trading is increasingly dominated by institutions
- 39. Скачать презентацию




























 Формирование бюджета Москвы
Формирование бюджета Москвы Заработная плата
Заработная плата Фінансовий механізм управління прибутком підприємства. Тема 5
Фінансовий механізм управління прибутком підприємства. Тема 5 Бюджетная система России
Бюджетная система России Анализ рисков
Анализ рисков Исламский банкинг
Исламский банкинг Виды бюджетов, их место и роль в системе бюджетирования. (Тема 3)
Виды бюджетов, их место и роль в системе бюджетирования. (Тема 3) Бухгалтерский учет межбанковских расчетов. (Тема 4)
Бухгалтерский учет межбанковских расчетов. (Тема 4) Торговые поручения клиента. Виды, характеристика, особенности. Торговля акциями
Торговые поручения клиента. Виды, характеристика, особенности. Торговля акциями Полномочия Федерального казначейства как контрольного органа. Другие федеральные органы, осуществляющие финансовый контроль
Полномочия Федерального казначейства как контрольного органа. Другие федеральные органы, осуществляющие финансовый контроль Операционный отчет
Операционный отчет Страхование ответсвенности
Страхование ответсвенности Роль и содержание финансовой отчетности
Роль и содержание финансовой отчетности Формы и методы проектного финансирования
Формы и методы проектного финансирования Аналіз власного капіталу банку
Аналіз власного капіталу банку Налоги и налогообложение. (Темы 18-21)
Налоги и налогообложение. (Темы 18-21) Инвестиционный фонд
Инвестиционный фонд Порядок работы в ПУР КС ГИИС Электронный бюджет при проведении расходных операций
Порядок работы в ПУР КС ГИИС Электронный бюджет при проведении расходных операций A számok minden titkot kifecsegnek
A számok minden titkot kifecsegnek Фондовый рынок
Фондовый рынок Продукты компании Ваши деньги
Продукты компании Ваши деньги О мерах государственной поддержки малых форм хозяйствования
О мерах государственной поддержки малых форм хозяйствования Нормирование и оплата труда Технология. 11 класс
Нормирование и оплата труда Технология. 11 класс Понятие валютных отношений и валютной системы
Понятие валютных отношений и валютной системы Сельская ипотека. АО Россельхозбанк
Сельская ипотека. АО Россельхозбанк Деньги в нашей жизни
Деньги в нашей жизни Кредит, ссуда, ипотека, заем
Кредит, ссуда, ипотека, заем Структура государственного долга Украины
Структура государственного долга Украины