Слайд 2
Endoscopic surgery
it is area of the surgery, allowing to execute radical operations
or diagnostic procedures without a wide dissection of integument or through dot punctures of tissues (laparoscopic, thoracoscopic, rhinoscopic, arthroscopic operations), or through natural physiological apertures (FGDS, colonoscopy, bronchoscopy, cystoscopy, etc.)

Слайд 3
Development of endoscopic surgery
Hippocrat (460-375 up to AD) - has described carrying
out of the proctoscopy;
Abdul Quasim (936-1013) - investigated neck of uterus using a glass mirror reflector;
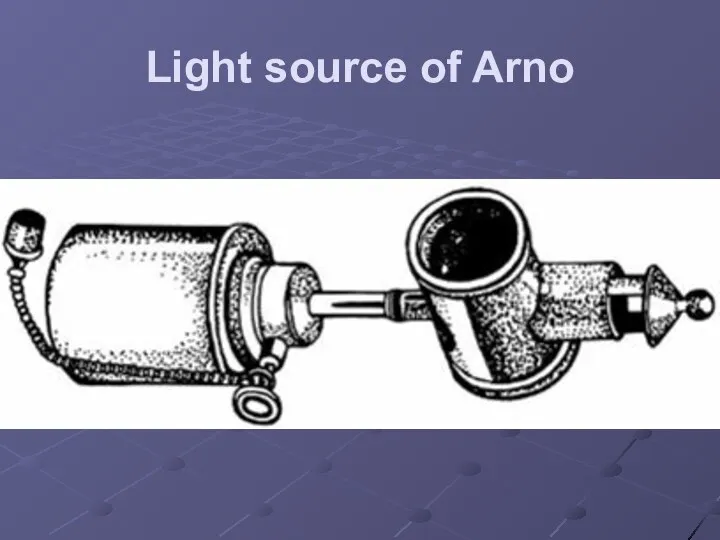
R.P. Arnaud (1651-1723) - has created the first extracorporal source of light for the medical purposes;
Phillip Bozini (1773-1809) - has created endoscope which design has been named "LICHTLEITER";
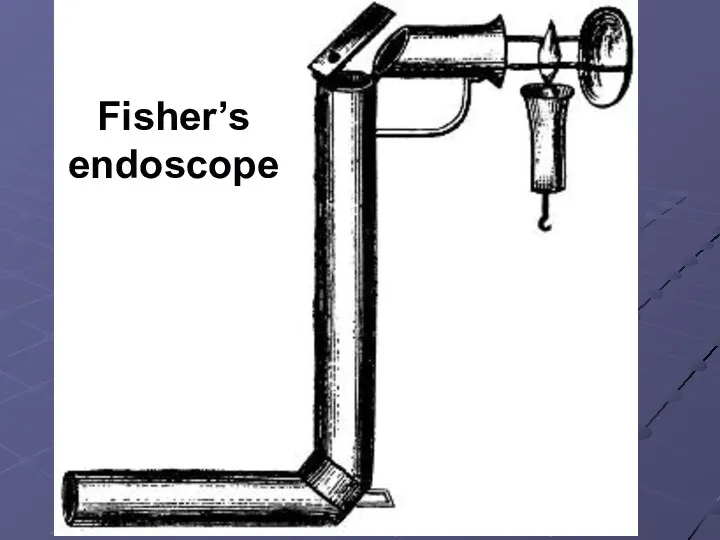
John Fisher, 1827 – has created one of the first endoscops;
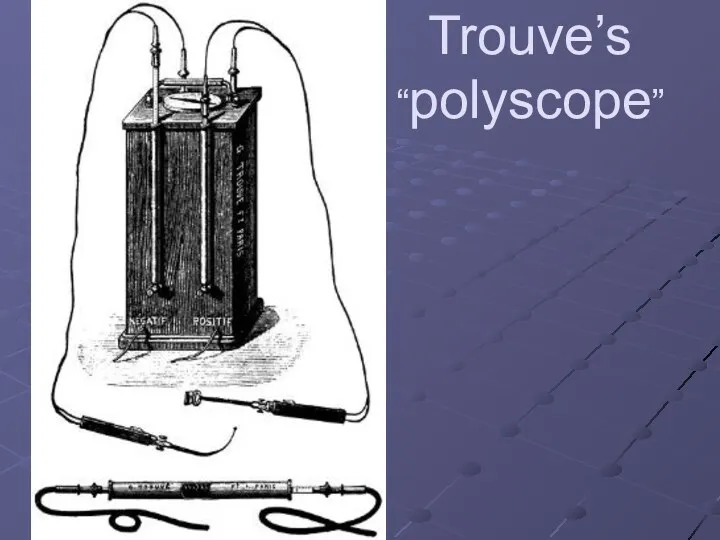
Gustave Trouve in 1873 in has designed "polyscope", intended for gastroscopy and cystoscopy, brightness of a luminescence of a platinum wire in which was adjusted with a help of a rheostat.

Слайд 4
George Kelling (1901) – for the first time has made a laparoscopy in
experiment on a dog;
D.O.Ott (1901) – has informed about "ventroscopy" inspection of a abdominal cavity by means of a candle, a frontal mirror and a tube;
Heinz Kalk (1928 г) - has developed a technique laparoscopic puncture biopsy of a liver, and in 1939 has published the work based on research of 200 patients;
Janos Veress (1938) - has invented a needle with spring mandrin. For today is most widely used tool for imposing of pneumoperitoneum;
Raul Palmer (1947) - has offered ways of definition of position of a needle widely used now for insufflation (Palmer-test);
Kurt Semm - with the colleagues and pupils have developed methodics of the majority laparoscopic interventions on organs of a small pelvis, have created enormous amount laparoscopic tools and devices
De Kok in 1977 for the first time has executed laparoscopic appendectomy;
E. Muhe (1985 г) - has executed the first laparoscopic cholecystectomy;
U.I. Gallinger (1991 г) for the first time in Russia has executed laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the Science Centre of surgery of Russian Academy of Medical Science.

Слайд 5
Слайд 6
Слайд 7

Слайд 8

Слайд 9
Слайд 10

Слайд 11

Слайд 12

Слайд 13

Слайд 14

Слайд 15

Слайд 16
Advantages of endosurgery in comparison with traditional operations
Slight trauma of tissues
Short
hospital period
Decrease of disability terms
Cosmetic effect
Decrease of frequency and weight of complications
Economic efficiency

Слайд 17
Complications
General lethality come to 0,5 %, and frequency of complications – 10 %;
Wound
infection – meets in 1-2 % of cases;
Damage of internal organs;
Pneumomediastinum, subcutaneous emphysema;
Pneumothorax;
Development of a gas embolism
Electrosurgical damages;
Cardiovascular collapse;
Postoperative pain in a right shoulder;
Damage of vessels and nerves of a forward belly wall;
Hernias of an abdominal wall.

Слайд 18
Relative contraindications
Heavy accompanying pathology of cardiovascular and respiratory systems
- Obstructive diseases
of lungs
- Cardiovascular insufficiency of 2-3 degrees
- Old myocardial infarction
- The transferred operations on heart and large vessels
- The congenital and acquired heart diseases
Diffuse peritonitis
Heavy coagulopathy
Adiposity of 3-4 degrees
Late terms of pregnancy
Portal hypertensia
Insufficient qualification of the operator

Слайд 19
The minimal set for carrying out endoscopic operations
a) Needles for imposing pneumoperitoneum;
b) trocars with clamps and adapters;
c) Tools for suture of trocar apertures;
d) Manipulators: dissectors, cissors, clips, retractors;
e) The equipment for irrigation and aspiration;
f) Tools for coagulation;
i) Suture materials and tools for endoscopic suture;
j) Devices for ligation vessels and ducts.

Слайд 20
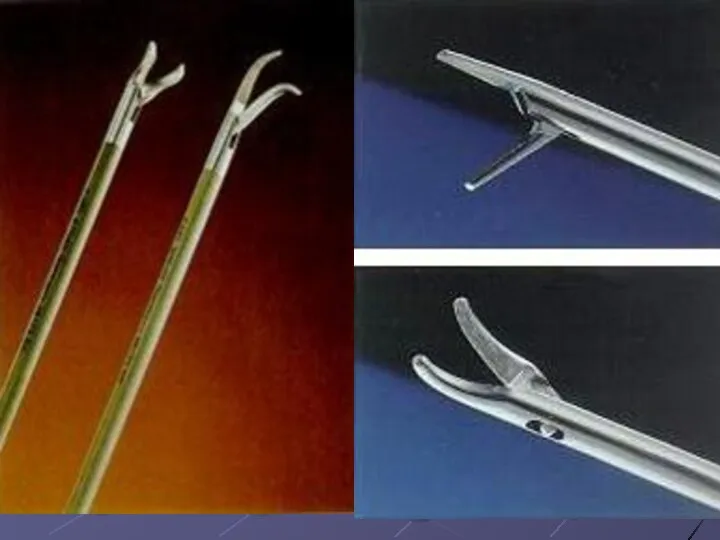
The general requirements to endoscopic tools
а) Handiness: the handle of the tool
should not complicate manipulations, at long operation there should not be a weariness of a wirst;
б) Sensitivity: the tool should provide the maximal sensitivity as the surgeon is deprived at endoscopic manipulations of tactile sensitivity;
в) Electroisolation: isolating layer should reach up to branches of the tool and to be strong enough;
г) Presence of the rotary mechanism providing rotation of a working part of the tool on 360 degrees around of a longitudinal axis.

Слайд 21
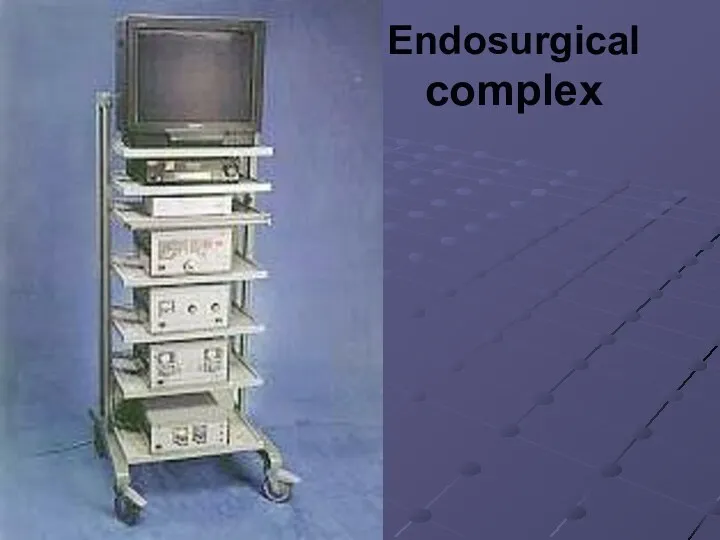
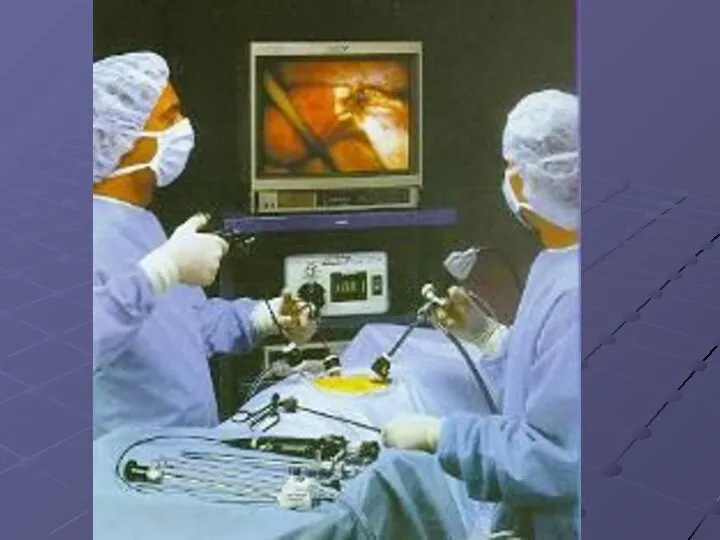
Essentially the complex will consist of the following blocks:
a) A videocamera;
b)
A video monitor;
c) The illuminator - the electronic device having a powerful lamp (xenon or halogen);
d) Laparoscope with an optical path;
e) Insufflator - it is intended for submission of carbonic gas in a abdominal cavity at imposing and maintenance of pneumoperitoneum;
f) Aquapurator - it is intended for washing and evacuation of liquid contents of a abdominal cavity;
i) Electrocoagulator;
j) The rack - handcart.

Слайд 22
Слайд 23
Слайд 24

Слайд 25

Слайд 26

Слайд 27

Слайд 28
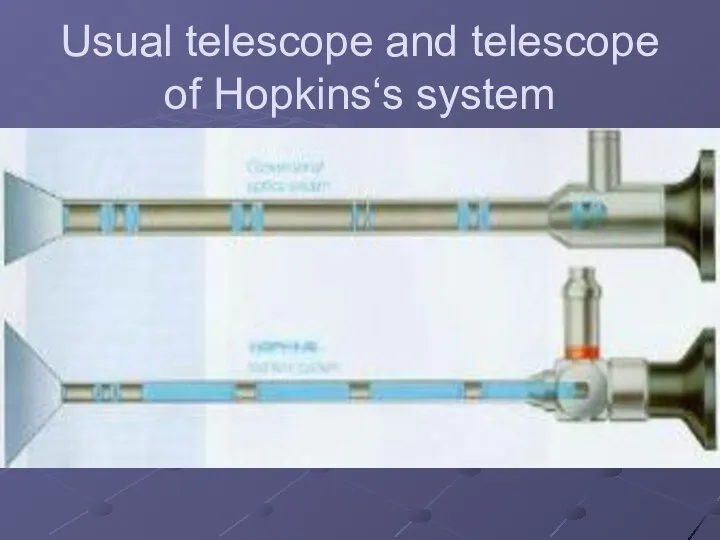
Usual telescope and telescope of Hopkins‘s system
Слайд 29

Слайд 30

Слайд 31
Слайд 32
Слайд 33
Points of a puncture for imposing a pneumoperitoneum
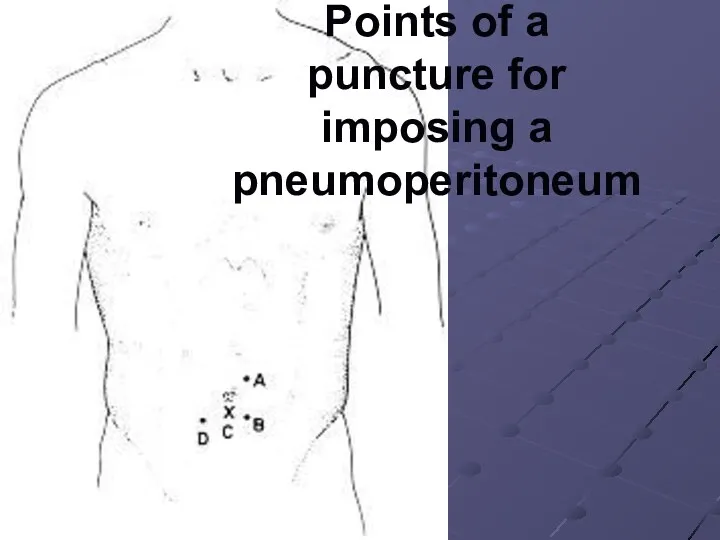
Слайд 34
Puncture through the back fornix of vagina
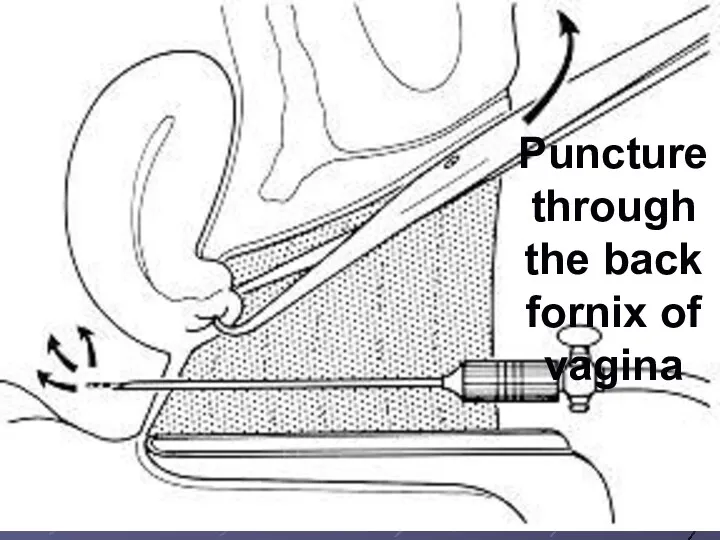
Слайд 35
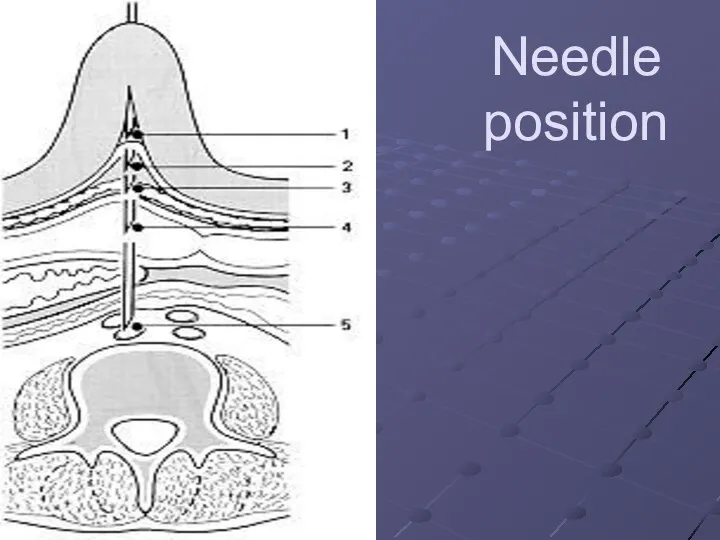
Слайд 36
Слайд 37

Слайд 38
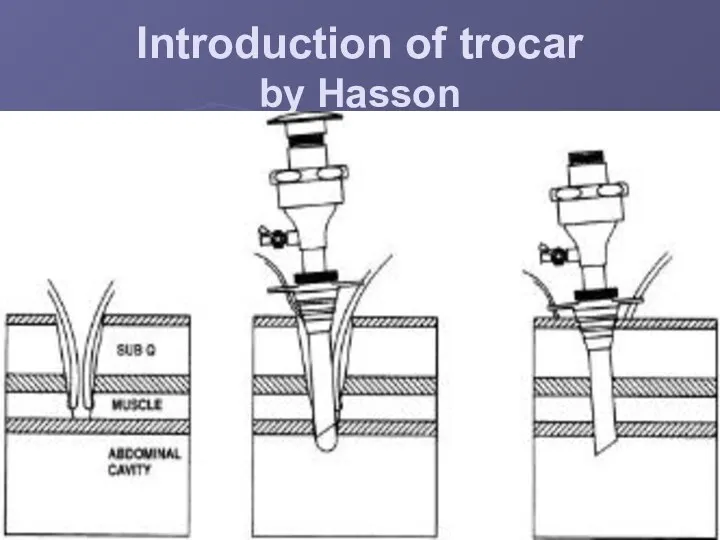
Introduction of trocar
by Hasson
Слайд 39
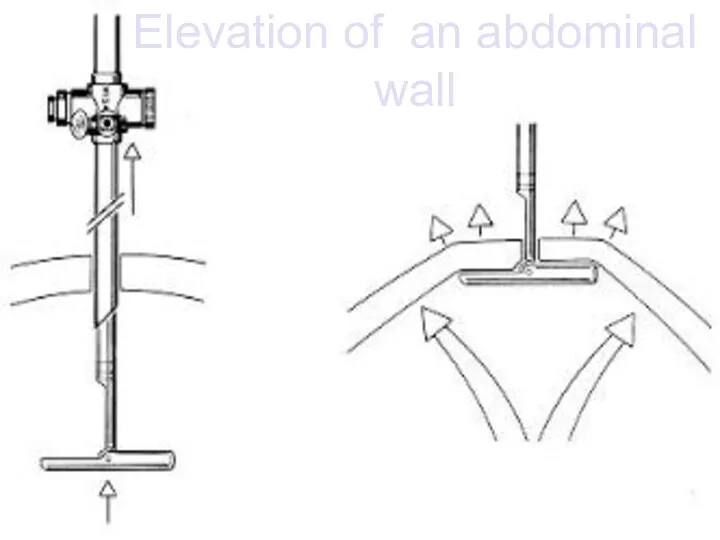
Elevation of an abdominal wall
Слайд 40
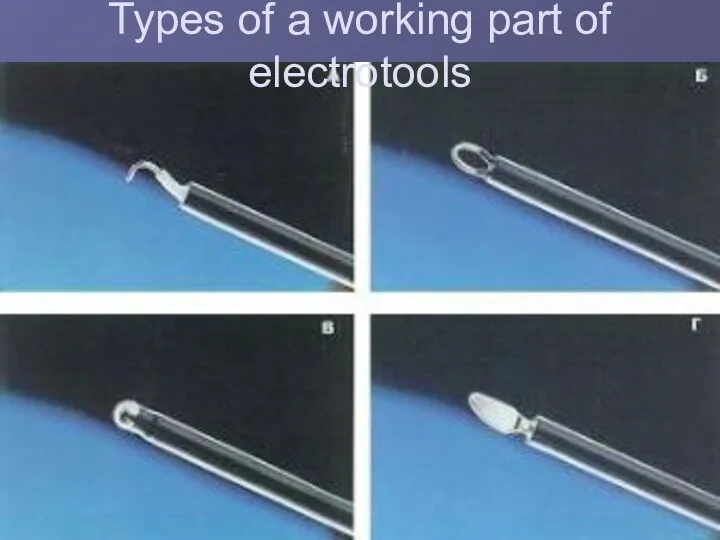
Types of a working part of electrotools
Слайд 41

Слайд 42

Слайд 43
Слайд 44
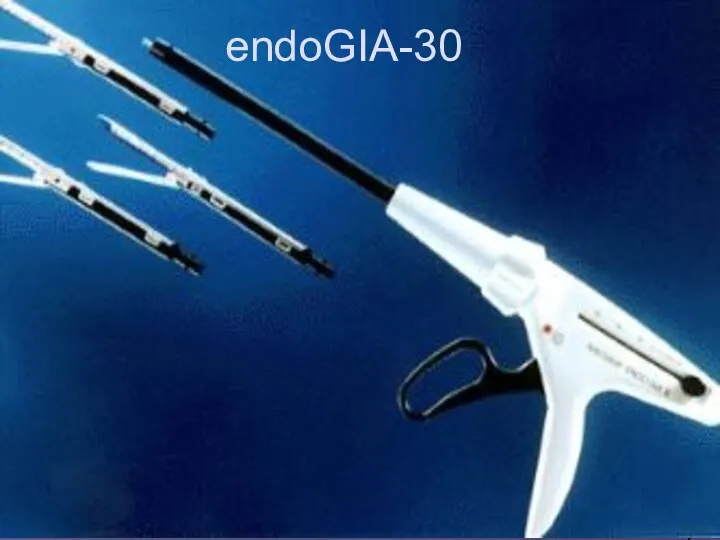
Слайд 45
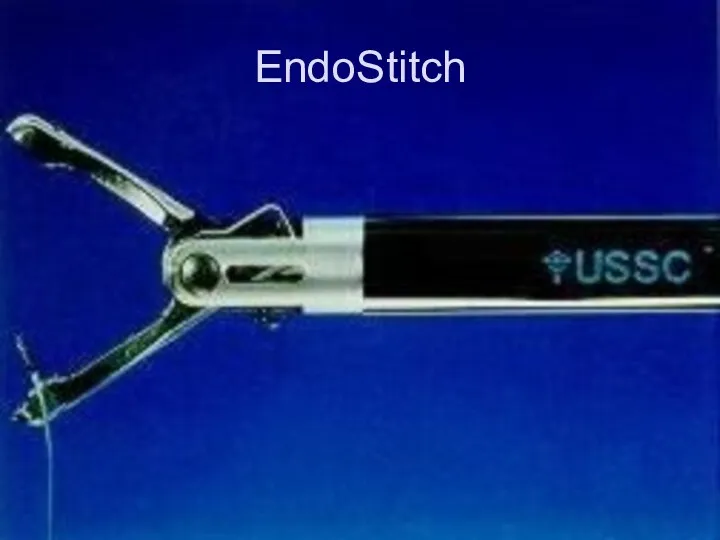
Слайд 46
Introduction of an atraumatic needles
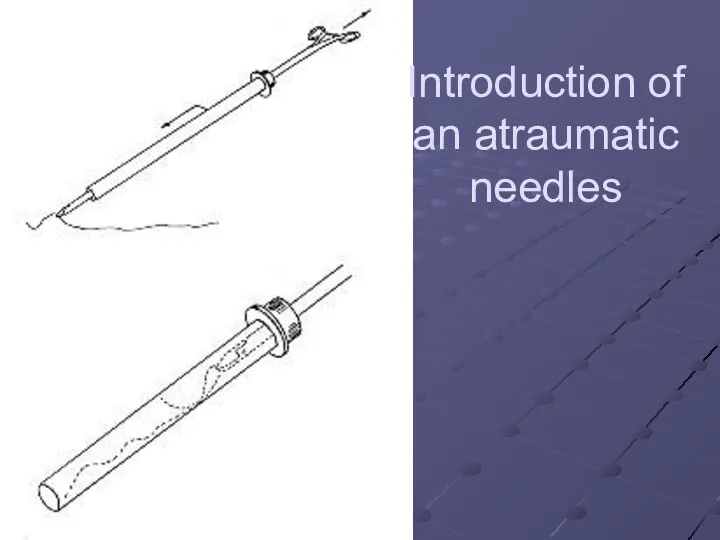
Слайд 47
The scheme of Reder’s knot
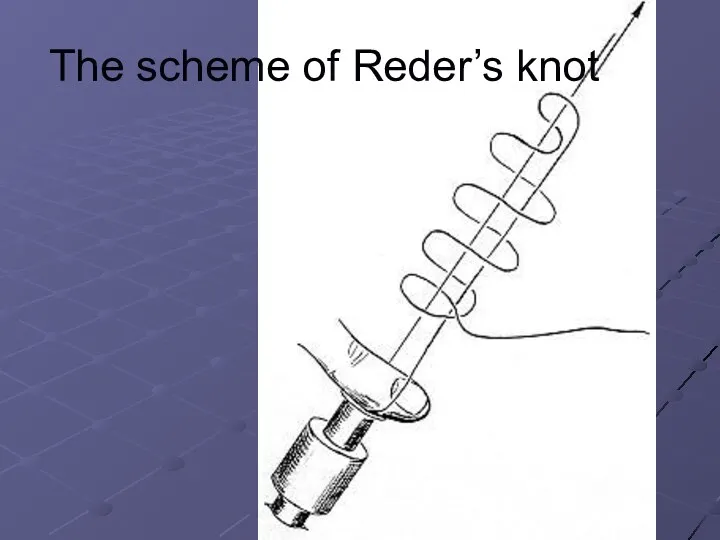














































 Нанохимия и нанотехнологии. Методы и средства исследования нанообъектов. (Лекция 3)
Нанохимия и нанотехнологии. Методы и средства исследования нанообъектов. (Лекция 3) Первое и второе начало термодинамики
Первое и второе начало термодинамики Изучение треков заряженных частиц. Лабораторная работа № 7
Изучение треков заряженных частиц. Лабораторная работа № 7 Оценивание закономерностей окислительного изнашивания
Оценивание закономерностей окислительного изнашивания Строительная механика. Теория определения перемещений деформируемых систем. (Часть 1. Лекция 1)
Строительная механика. Теория определения перемещений деформируемых систем. (Часть 1. Лекция 1) Выбор реакторных устройств
Выбор реакторных устройств Спин, проекция на вектор n
Спин, проекция на вектор n Методы формирования уравнений электрического равновесия цепи
Методы формирования уравнений электрического равновесия цепи Электродвижущая сила. Закон Ома для полной цепи
Электродвижущая сила. Закон Ома для полной цепи Деятельностный подход в преподавании физики, как средство повышения качества знаний учащихся
Деятельностный подход в преподавании физики, как средство повышения качества знаний учащихся Тепловые двигатели и их влияние на окружающую среду
Тепловые двигатели и их влияние на окружающую среду Электрический ток. (лекция 2)
Электрический ток. (лекция 2) Physical chemistry of nanostructured systems
Physical chemistry of nanostructured systems Конструирование элементов ременных и цепных передач
Конструирование элементов ременных и цепных передач Роль фізичної та астрономічної наук у формуванні наукового світогляду сучасної людини
Роль фізичної та астрономічної наук у формуванні наукового світогляду сучасної людини Удельная теплота. Тест
Удельная теплота. Тест Расчет статически неопределимых балок на изгиб
Расчет статически неопределимых балок на изгиб Момент инерции
Момент инерции Кинематика
Кинематика Предохранительный клапан
Предохранительный клапан Введение в динамику. Законы и аксиомы динамики материальной точки. Основное уравнение динамики
Введение в динамику. Законы и аксиомы динамики материальной точки. Основное уравнение динамики Презентация к уроку по теме Механическая работа 7 класс
Презентация к уроку по теме Механическая работа 7 класс Сила тока. Амперметр
Сила тока. Амперметр Теплообмен излучением между телами, разделённой прозрачной средой. Коэффициент облучённости. Теплообмен между телами
Теплообмен излучением между телами, разделённой прозрачной средой. Коэффициент облучённости. Теплообмен между телами Основы кинематики. Раздел механики, в котором описывается движение тел, но не анализируются его причины
Основы кинематики. Раздел механики, в котором описывается движение тел, но не анализируются его причины Выходные устройства авиационных двигателей. (Тема 7)
Выходные устройства авиационных двигателей. (Тема 7)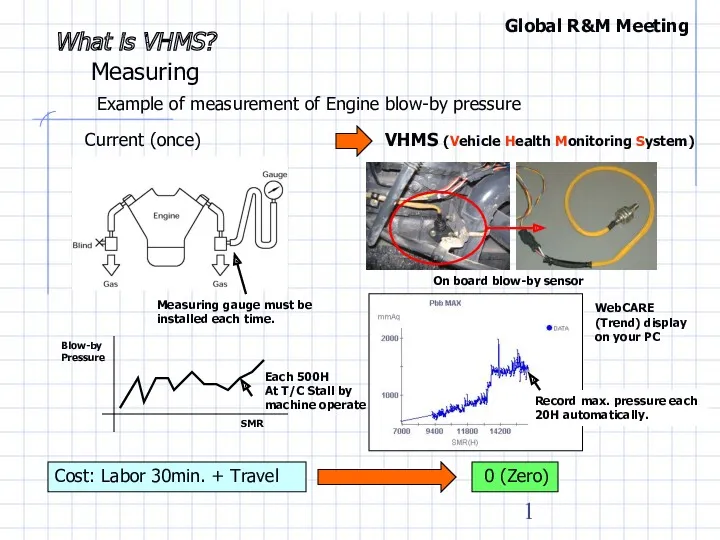 Summary of effective use 6
Summary of effective use 6 Сообщающиеся сосуды и их применение
Сообщающиеся сосуды и их применение