Содержание
- 2. Success Criteria Name and classify alcohols. Explain some physical properties of alcohols. Write oxidation products of
- 3. Keywords Alcohol Aldehyde Carboxylic acid Primary alcohol Secondary alcohol Tertiary alcohol Distillation Reflux ALCOHOLS
- 4. Video Clip Activity
- 5. What are alcohols? Alcohols are a homologous series of organic compounds with the general formula CnH2n+1OH
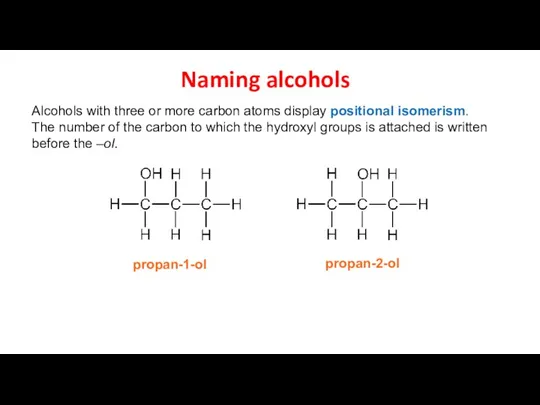
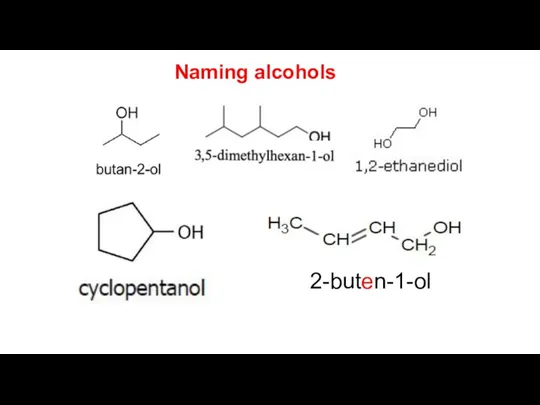
- 6. Naming alcohols Alcohols with three or more carbon atoms display positional isomerism. The number of the
- 7. 2-buten-1-ol Naming alcohols
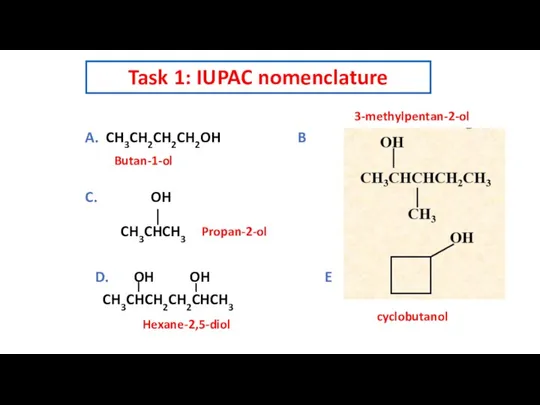
- 8. Task 1: IUPAC nomenclature A. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH B C. OH CH3CHCH3 D. OH OH E CH3CHCH2CH2CHCH3 Butan-1-ol
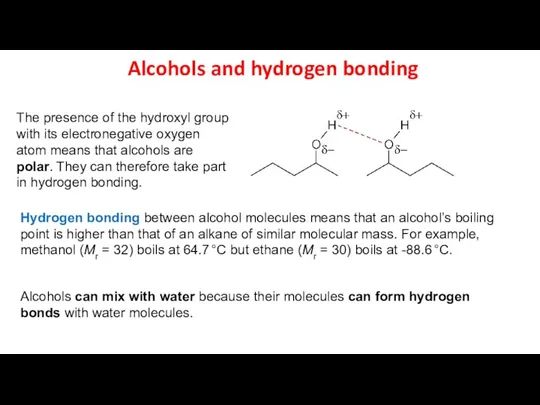
- 9. Alcohols and hydrogen bonding The presence of the hydroxyl group with its electronegative oxygen atom means
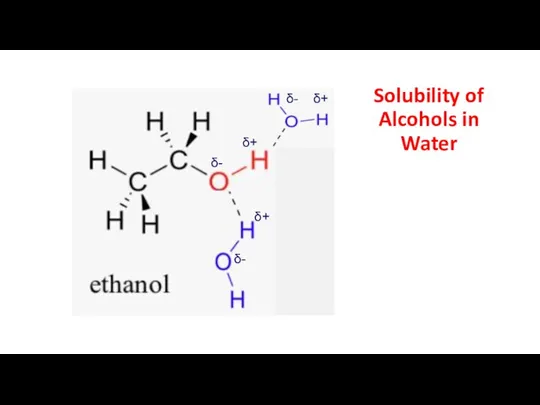
- 10. Solubility of Alcohols in Water δ- δ+ δ+ δ+ δ- δ-
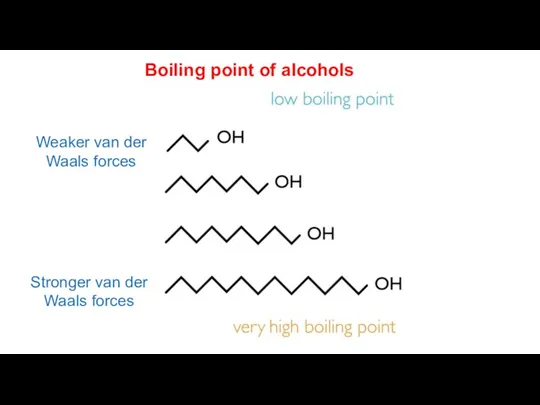
- 11. Stronger van der Waals forces Weaker van der Waals forces Boiling point of alcohols
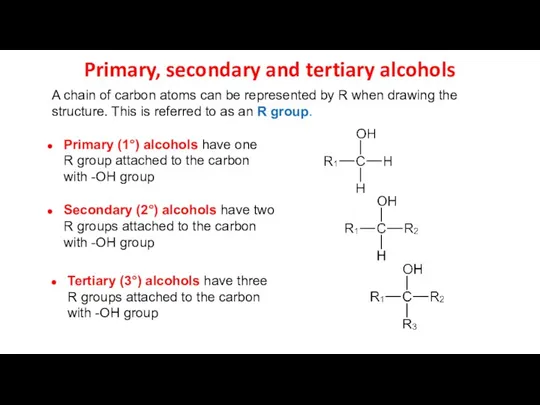
- 12. A chain of carbon atoms can be represented by R when drawing the structure. This is
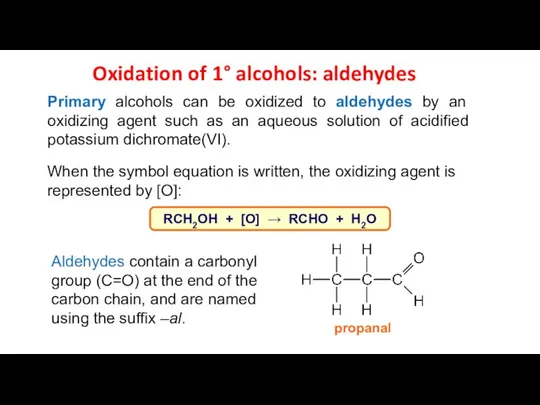
- 13. Oxidation of 1° alcohols: aldehydes Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes by an oxidizing agent
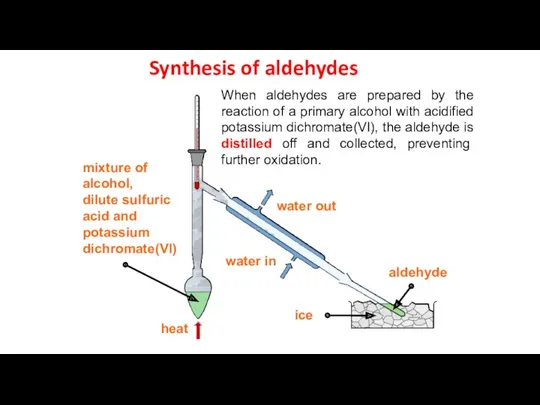
- 14. Synthesis of aldehydes When aldehydes are prepared by the reaction of a primary alcohol with acidified
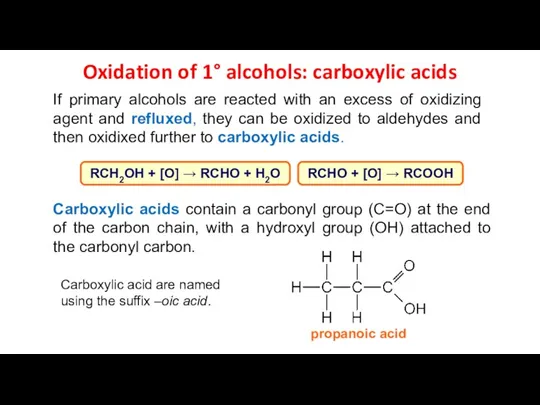
- 15. Oxidation of 1° alcohols: carboxylic acids If primary alcohols are reacted with an excess of oxidizing
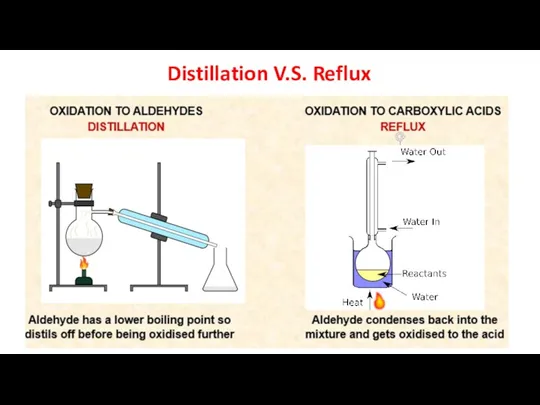
- 16. Distillation V.S. Reflux
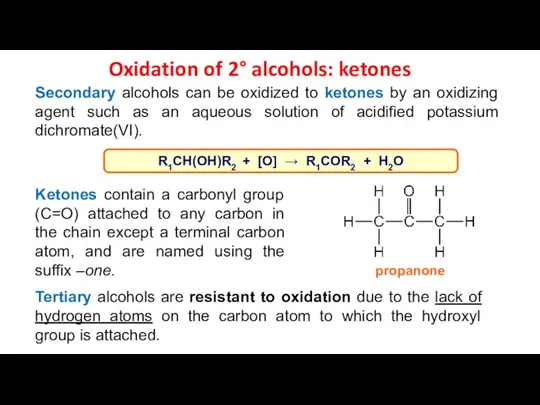
- 17. Oxidation of 2° alcohols: ketones Secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones by an oxidizing agent
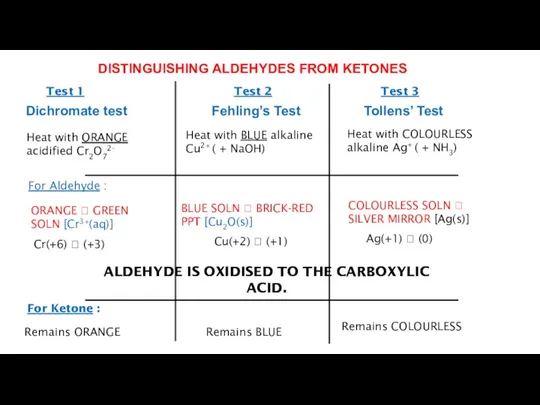
- 19. Heat with ORANGE acidified Cr2O72- Heat with BLUE alkaline Cu2+ ( + NaOH) Heat with COLOURLESS
- 20. Task 2: MCQ on Oxidation of alcohols
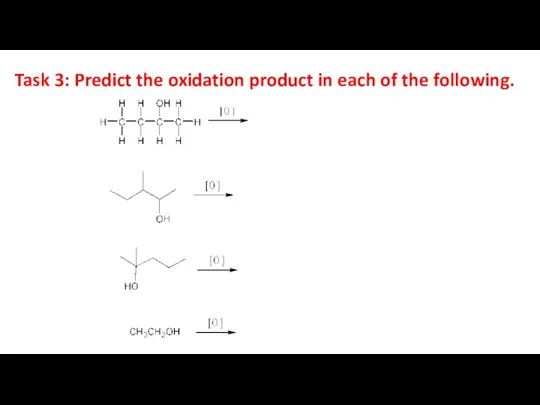
- 25. Task 3: Predict the oxidation product in each of the following.
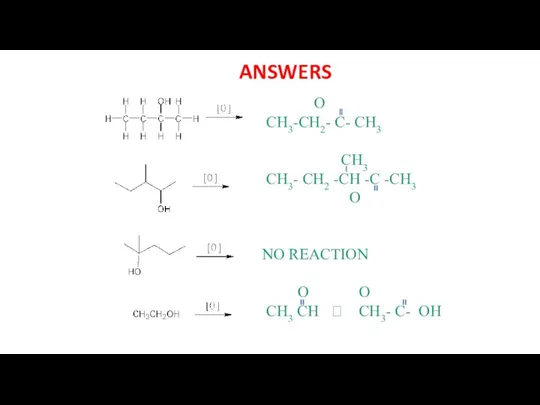
- 26. ANSWERS O CH3-CH2- C- CH3 CH3 CH3- CH2 -CH -C -CH3 O NO REACTION O O
- 28. Скачать презентацию










 Металлы в природе. Общие способы их получения
Металлы в природе. Общие способы их получения Карбон қышқылдары
Карбон қышқылдары Тепловой эффект химических реакций. Расчёты по термохимическим уравнениям (ТХУ)
Тепловой эффект химических реакций. Расчёты по термохимическим уравнениям (ТХУ) Побочная подгруппа. 8 группы
Побочная подгруппа. 8 группы Ароматические углеводороды (арены)
Ароматические углеводороды (арены) Соединения кремния
Соединения кремния Silicon. Silicate minerals. Weathering
Silicon. Silicate minerals. Weathering Ароматические углеводороды. Бензол
Ароматические углеводороды. Бензол Теория электролитической диссоциации
Теория электролитической диссоциации Chemical Formulas and Nomenclature of compounds
Chemical Formulas and Nomenclature of compounds Фосфор и его соединения
Фосфор и его соединения Биохимия нуклеиновых кислот
Биохимия нуклеиновых кислот Аммиак
Аммиак Гидрохимические определения. Методы определения растворенного кислорода в воде
Гидрохимические определения. Методы определения растворенного кислорода в воде Сульфидтер. Аз еруші сульфидтер
Сульфидтер. Аз еруші сульфидтер Интересные факты об углеводородах
Интересные факты об углеводородах Химическая посуда и лабораторное оборудование
Химическая посуда и лабораторное оборудование Prezentatsia
Prezentatsia Биохимия пәнінің мазмұны мен дамуы. Аминқышқылдар қасиеттері мен жіктелуі
Биохимия пәнінің мазмұны мен дамуы. Аминқышқылдар қасиеттері мен жіктелуі Метод нейтрализации. Расчёты в методе нейтрализации. Ионное произведение воды. Понятие Рн
Метод нейтрализации. Расчёты в методе нейтрализации. Ионное произведение воды. Понятие Рн Вредные вещества в продуктах питания
Вредные вещества в продуктах питания Строение и свойства циклоалканов
Строение и свойства циклоалканов Химическая связь
Химическая связь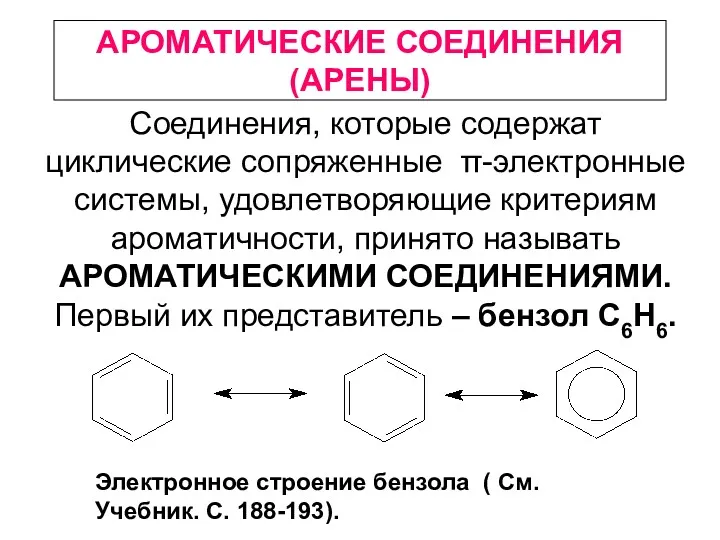 Ароматические соединения (арены)
Ароматические соединения (арены) Иондар және олардың түзілуі
Иондар және олардың түзілуі Нанопористые материалы
Нанопористые материалы Химическая кинетика
Химическая кинетика Химия в повседневной жизни человека
Химия в повседневной жизни человека