Содержание
- 2. Telecommunications Tele (Far) + Communications Early telecommunications smoke signals and drums visual telegraphy (or semaphore in
- 3. Communications and Networks Data Communications Transmission of signals Encoding, interfacing, signal integrity, multiplexing etc. Networking Topology
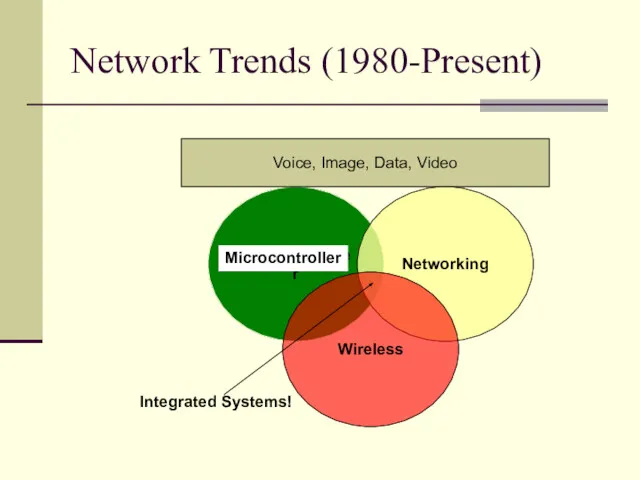
- 4. Network Trends (1980-Present) Microcontroller Networking Wireless Voice, Image, Data, Video Integrated Systems! Microcontroller
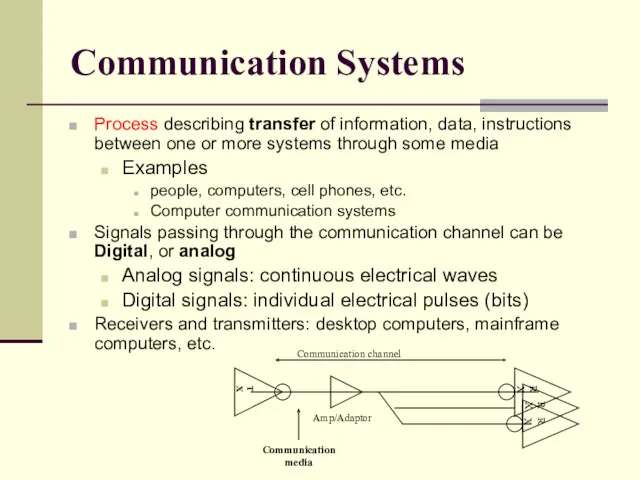
- 5. Communication Systems Process describing transfer of information, data, instructions between one or more systems through some
- 6. Communication Systems
- 7. Communications Components Basic components of a communication system Communication technologies Communication devices Communication channels Communication software
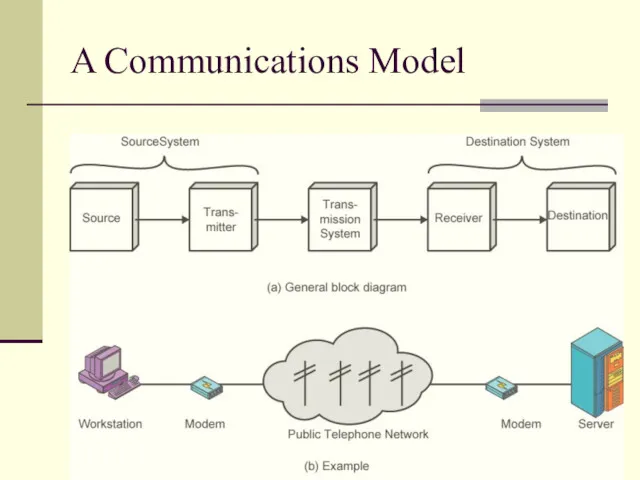
- 8. A Communications Model
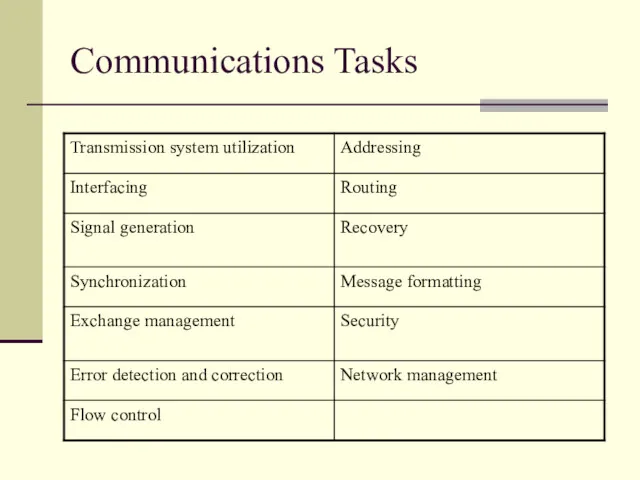
- 9. Communications Tasks
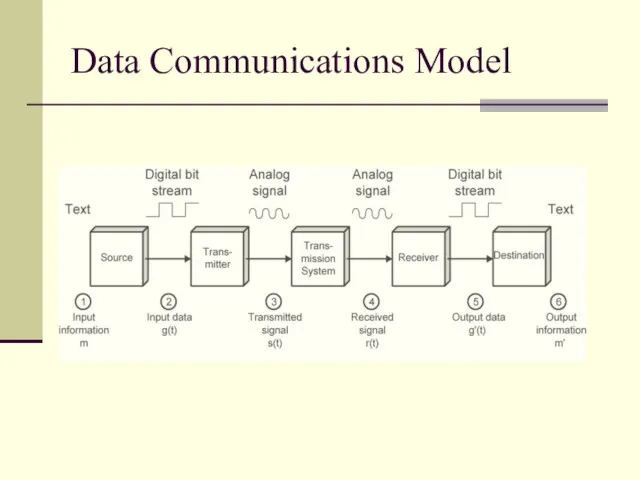
- 10. Data Communications Model
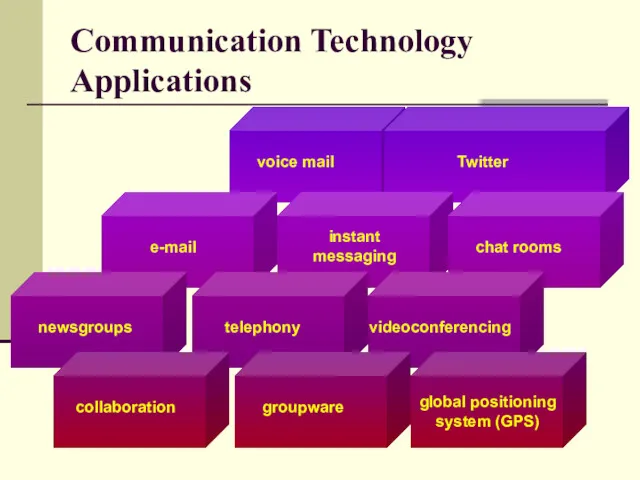
- 11. Communication Technology Applications
- 12. Communication Technologies - Applications Different technologies allowing us to communicate Examples: Voice mail, fax, email, instant
- 13. Communication Devices Any type of hardware capable of transmitting data, instructions, and information between devices Functioning
- 14. Communication Software Examples of applications (Layer 7) take advantage of the transport (Layer 4) services of
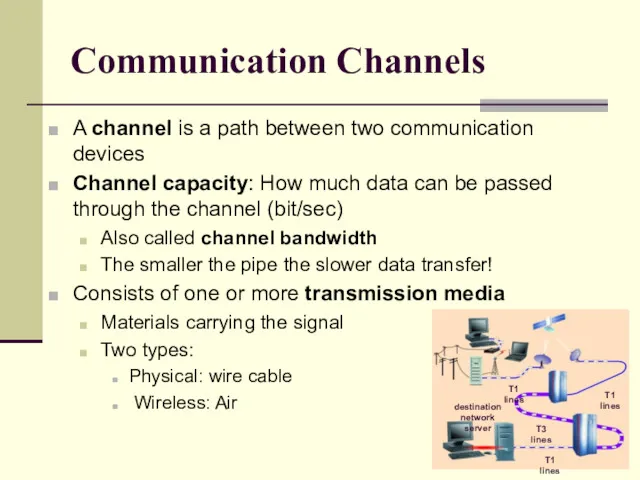
- 15. Communication Channels A channel is a path between two communication devices Channel capacity: How much data
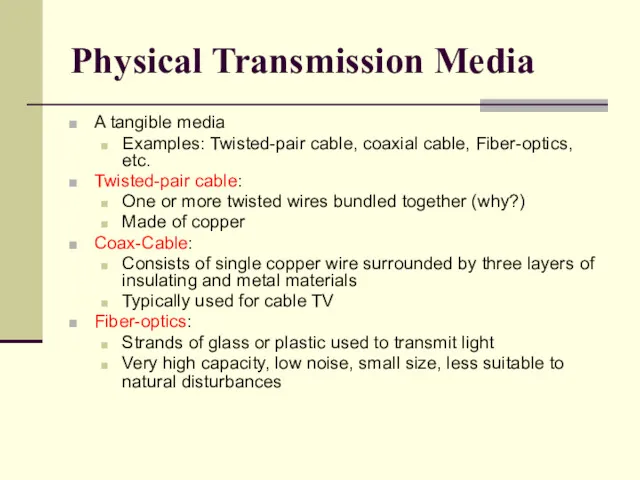
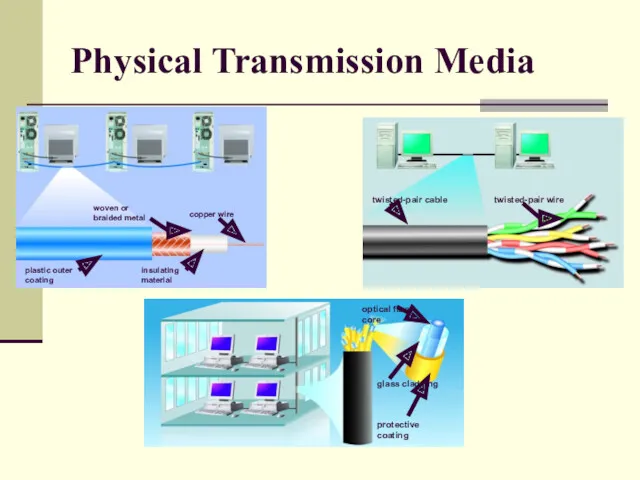
- 16. Physical Transmission Media A tangible media Examples: Twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, Fiber-optics, etc. Twisted-pair cable: One
- 17. Physical Transmission Media
- 18. Wireless Transmission Media Broadcast Radio Distribute signals through the air over long distance Uses an antenna
- 19. Wireless Transmission Media Microwaves Radio waves providing high speed transmission They are point-to-point (can’t be obstructed)
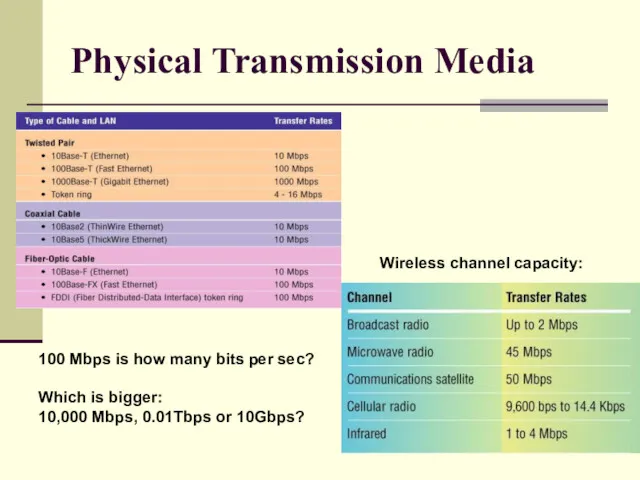
- 20. Physical Transmission Media 100 Mbps is how many bits per sec? Which is bigger: 10,000 Mbps,
- 21. Networks Collection of computers and devices connected together Used to transfer information or files, share resources,
- 22. Network coverage Local Area Networks: Used for small networks (school, home, office) Examples and configurations: Wireless
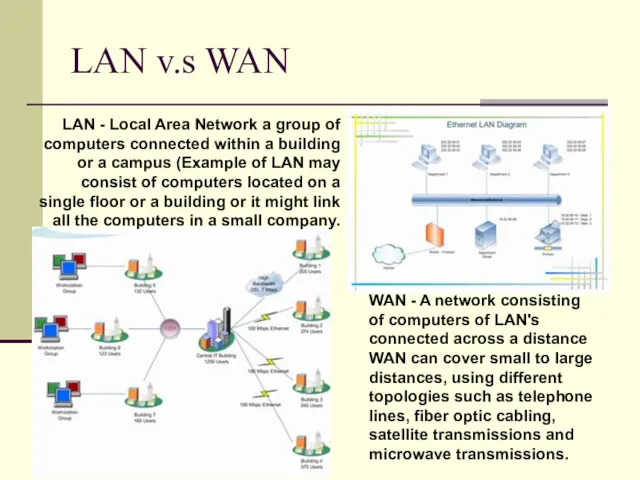
- 23. LAN v.s WAN LAN - Local Area Network a group of computers connected within a building
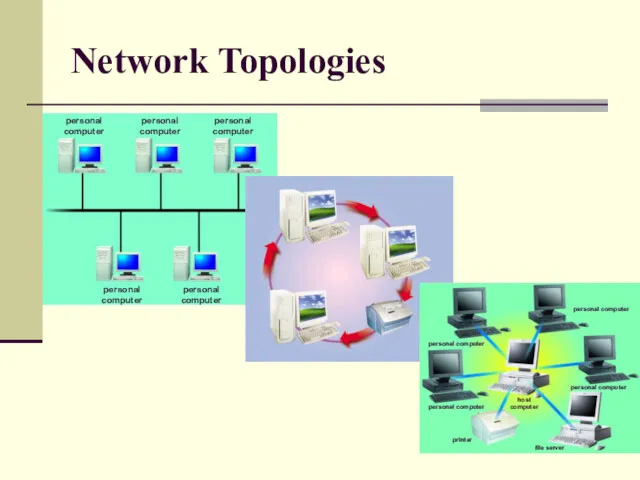
- 24. Network Topologies Configuration or physical arrangement in which devices are connected together BUS networks: Single central
- 25. Network Topologies
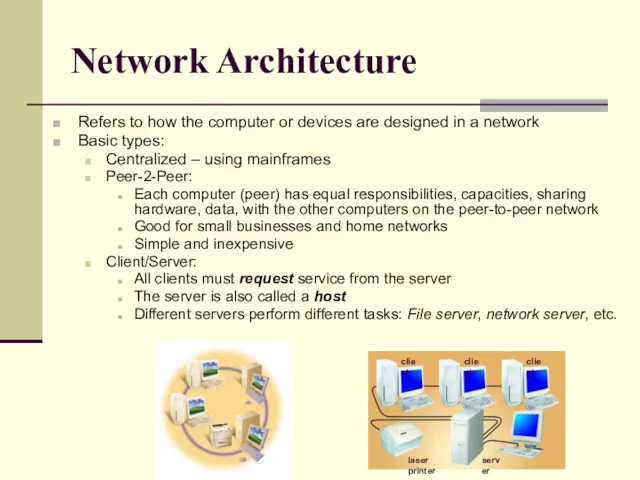
- 26. Network Architecture Refers to how the computer or devices are designed in a network Basic types:
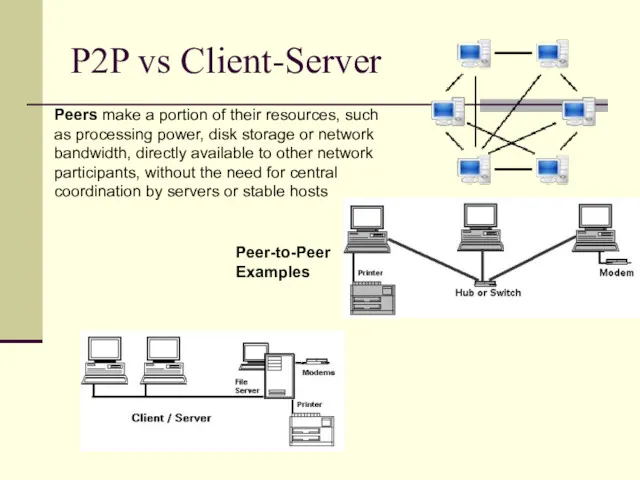
- 27. P2P vs Client-Server Peer-to-Peer Examples Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power,
- 28. (Data) Network Technologies Vary depending on the type of devices we use for interconnecting computers and
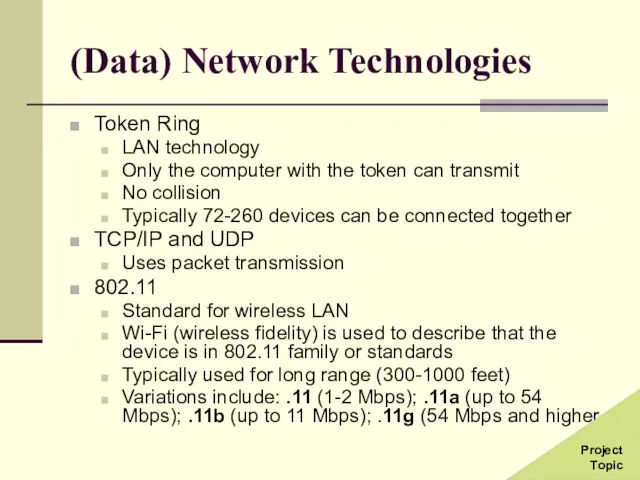
- 29. (Data) Network Technologies Token Ring LAN technology Only the computer with the token can transmit No
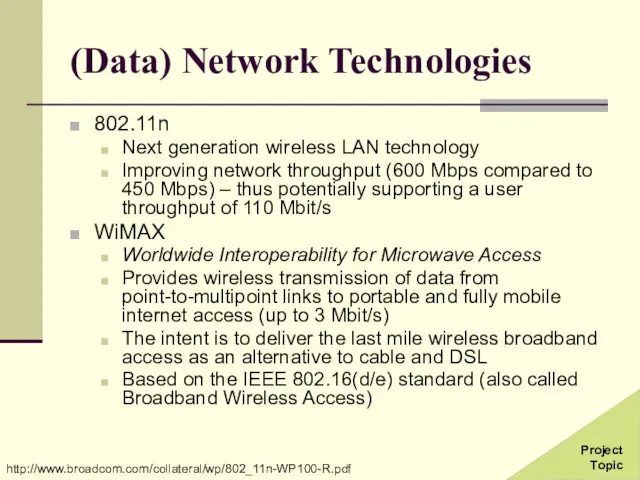
- 30. (Data) Network Technologies 802.11n Next generation wireless LAN technology Improving network throughput (600 Mbps compared to
- 31. Network Technologies Personal area network (PAN) A low range computer network PANs can be used for
- 32. Network Technologies Zigbee High level communication protocols using small, low-power digital radios based on the IEEE
- 33. Network Examples IEEE 802.15.4 Low-rate wireless personal area networks (LR-WPANs) Bases for e ZigBee, WirelessHART, and
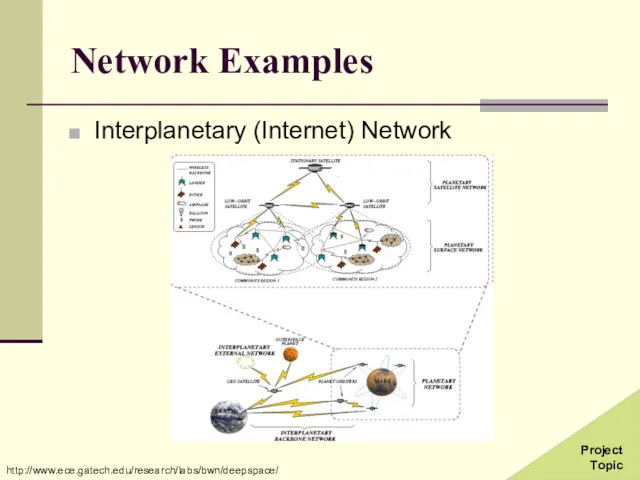
- 34. Network Examples Interplanetary (Internet) Network http://www.ece.gatech.edu/research/labs/bwn/deepspace/ Project Topic
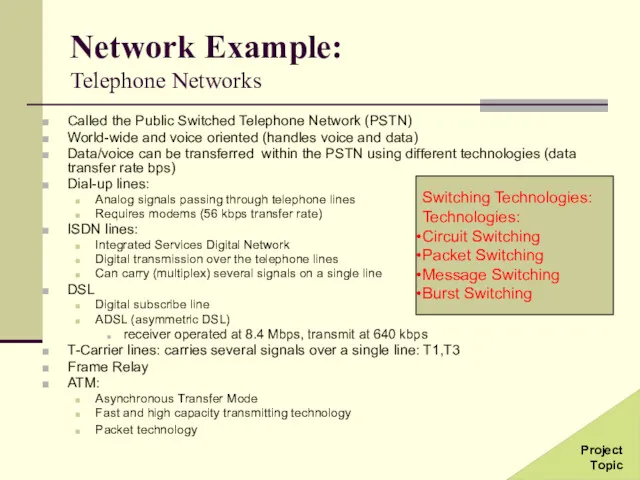
- 35. Network Example: Telephone Networks Called the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) World-wide and voice oriented (handles
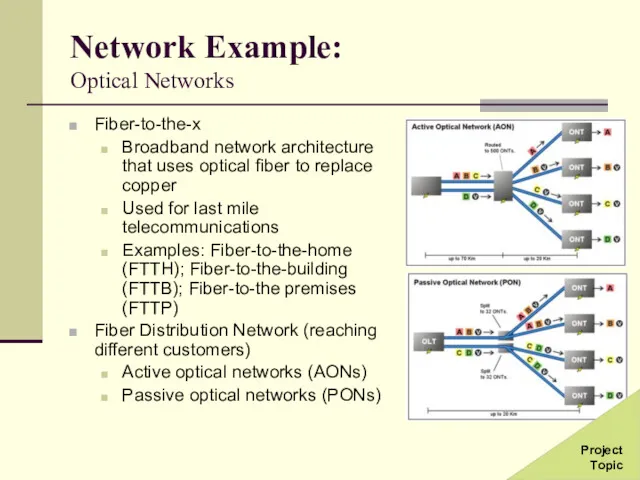
- 36. Network Example: Optical Networks Fiber-to-the-x Broadband network architecture that uses optical fiber to replace copper Used
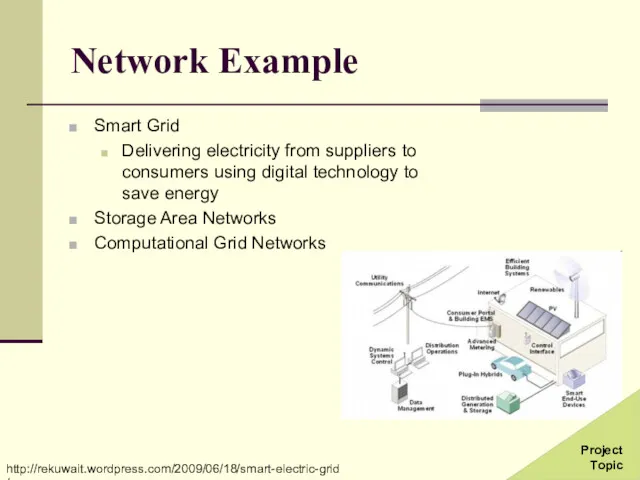
- 37. Network Example Smart Grid Delivering electricity from suppliers to consumers using digital technology to save energy
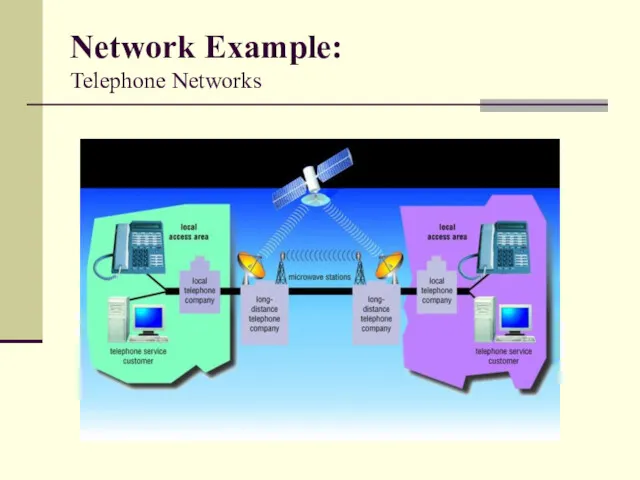
- 38. Network Example: Telephone Networks
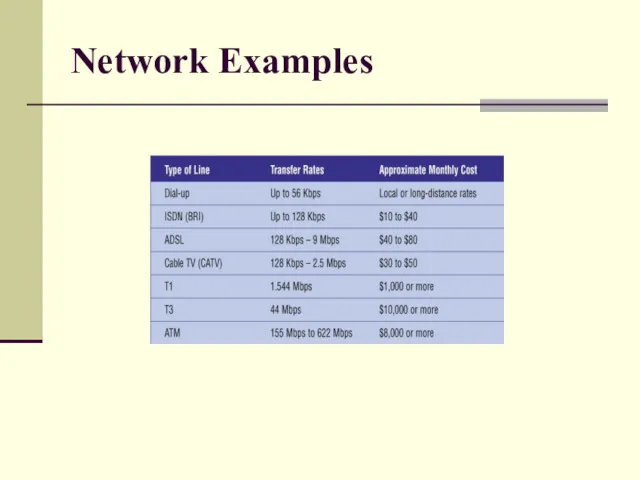
- 39. Network Examples
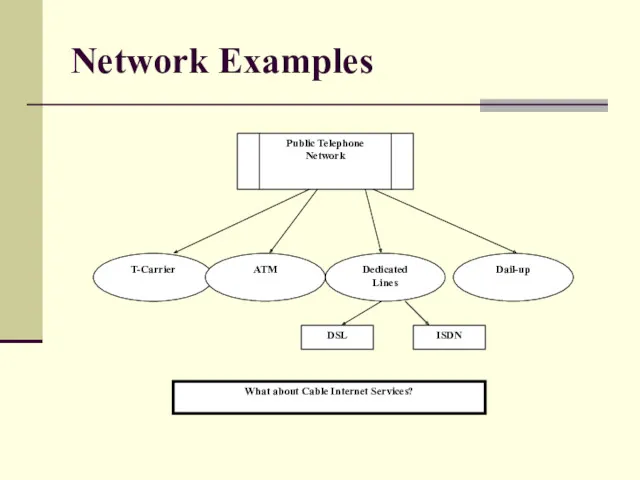
- 40. Network Examples
- 41. Cellular Network Examples 0G Single, powerful base station covering a wide area, and each telephone would
- 42. Cellular Network Examples 3G: Faster than PCS; Used for multimedia and graphics Compared to 2G and
- 43. Merging Technologies m-Cash Pay using your cell phone Scan-free shopping using Radio frequency identification VeriChip Implanted
- 45. Скачать презентацию















 презентация Основы классификации (объектов)
презентация Основы классификации (объектов) Программирование на языке Python. Символьные строки
Программирование на языке Python. Символьные строки Отчет по продвижению в социальных сетях Oson
Отчет по продвижению в социальных сетях Oson Графический редактор Paint
Графический редактор Paint Макрорекордер (MacroRecorder)
Макрорекордер (MacroRecorder) Голосовое управление в облачных веб-проектах с помощью Яндекс.Станции и Google Assistant
Голосовое управление в облачных веб-проектах с помощью Яндекс.Станции и Google Assistant Компоненты в React. Урок №1
Компоненты в React. Урок №1 Правовые и этические аспекты использования интернета
Правовые и этические аспекты использования интернета Аудитория интернета в России
Аудитория интернета в России Internet etikasi va odob-axloq qoidalari
Internet etikasi va odob-axloq qoidalari Информационная безопасность
Информационная безопасность Технологія та організація створення електронного підручника за допомогою програми Dr. Explain
Технологія та організація створення електронного підручника за допомогою програми Dr. Explain Анимация в WinForms
Анимация в WinForms Основы системного администрирования и сетевых технологий. Домашняя работа №1
Основы системного администрирования и сетевых технологий. Домашняя работа №1 Моменты, на которые нужно обратить внимание. Защитное программирование. Модульное тестирование
Моменты, на которые нужно обратить внимание. Защитное программирование. Модульное тестирование IP-телефония мен стримингтік технологиялар негіздері
IP-телефония мен стримингтік технологиялар негіздері Моделирование в системе компас
Моделирование в системе компас History of Cologne Digital Lexicons
History of Cologne Digital Lexicons Опасности в интернете
Опасности в интернете Введение. Компиляция и запуск. (Тема 1.2)
Введение. Компиляция и запуск. (Тема 1.2) Статичні члени класів
Статичні члени класів Компьютерная анимация
Компьютерная анимация Язык GPSS. Изменение маршрутов транзактов. Вычислительные объекты языка
Язык GPSS. Изменение маршрутов транзактов. Вычислительные объекты языка Формат. История развития термина
Формат. История развития термина Виды изображений. Растровая и векторная графика
Виды изображений. Растровая и векторная графика Создание HTML. Примеры тегов с атрибутами
Создание HTML. Примеры тегов с атрибутами 2. Java Basics. Data Types
2. Java Basics. Data Types Разработка программы для управления устройством умного дома
Разработка программы для управления устройством умного дома