Содержание
- 2. What is a mobile cloud computing?
- 3. Motivation Mobile devices (e.g., smartphone, tablet pcs, etc) are increasingly becoming an essential part of human
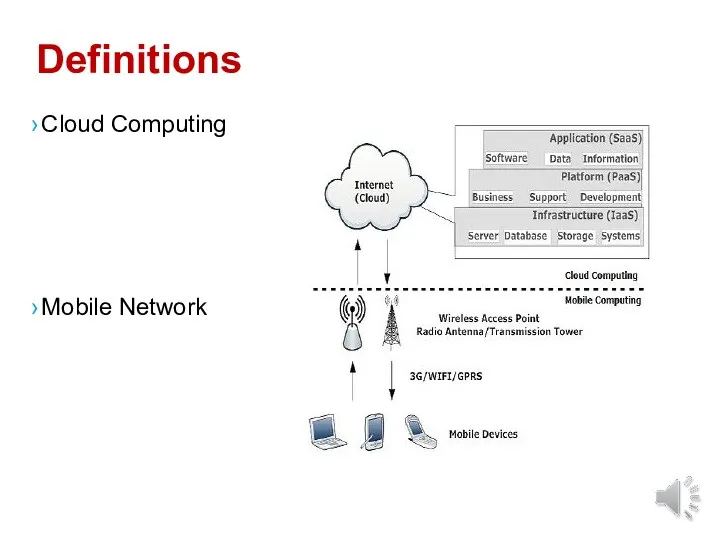
- 4. Definitions Mobile Network Cloud Computing
- 5. Definitions utility
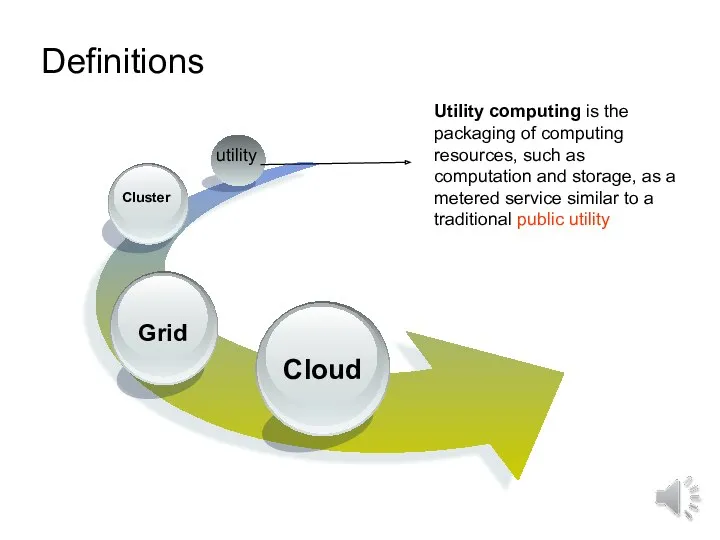
- 6. Definitions utility Utility computing is the packaging of computing resources, such as computation and storage, as
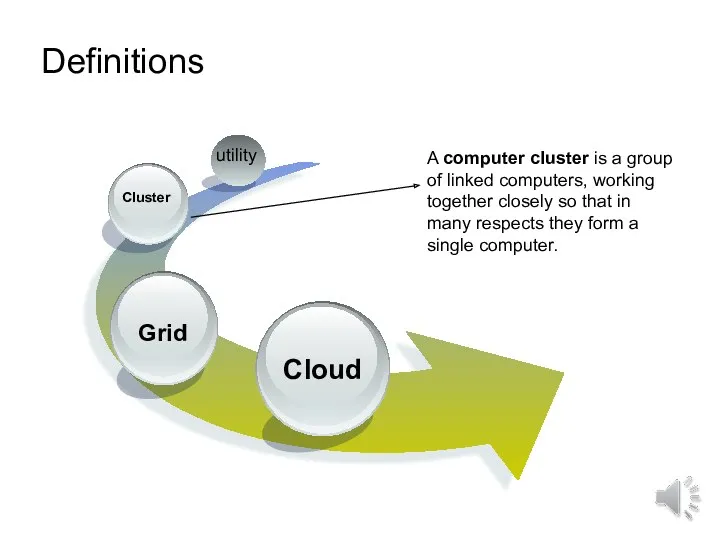
- 7. Definitions utility A computer cluster is a group of linked computers, working together closely so that
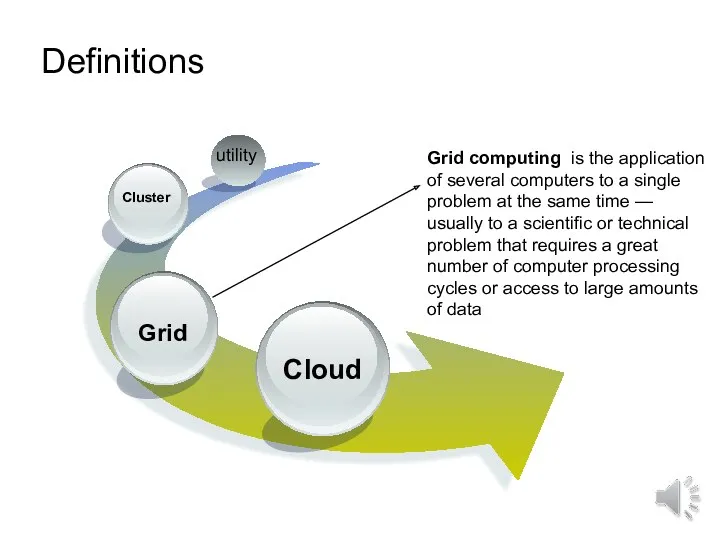
- 8. Definitions utility Grid computing is the application of several computers to a single problem at the
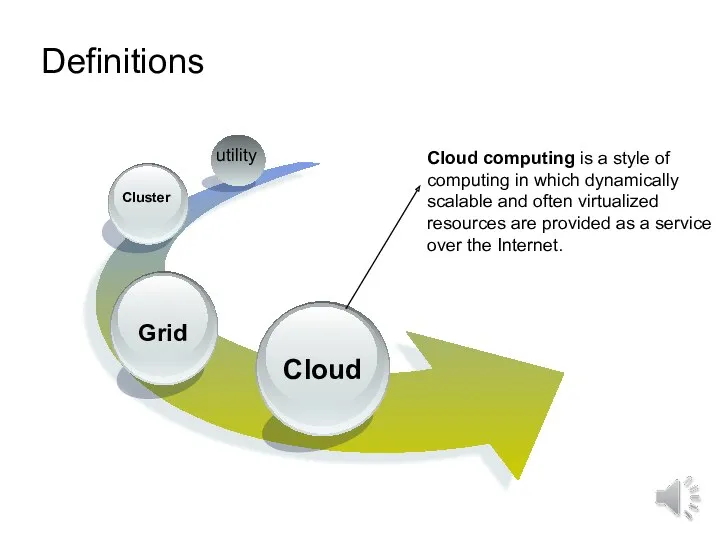
- 9. Definitions utility Cloud computing is a style of computing in which dynamically scalable and often virtualized
- 10. WHAT IS CLOUD COMPUTING? NIST Definition “A model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a
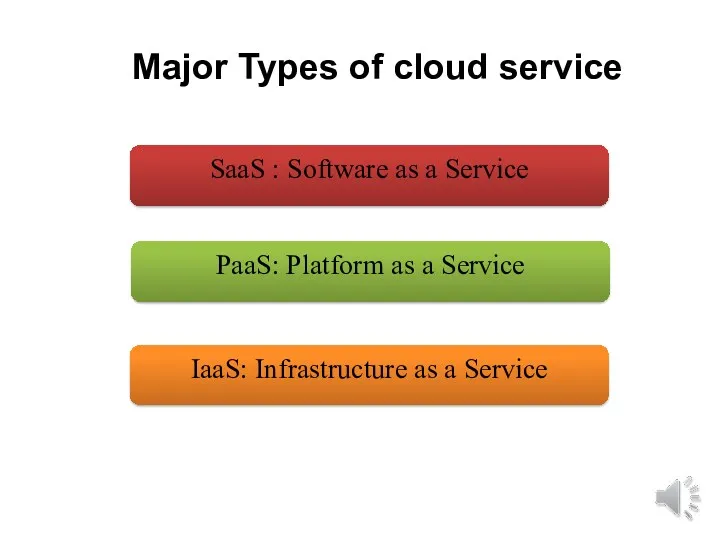
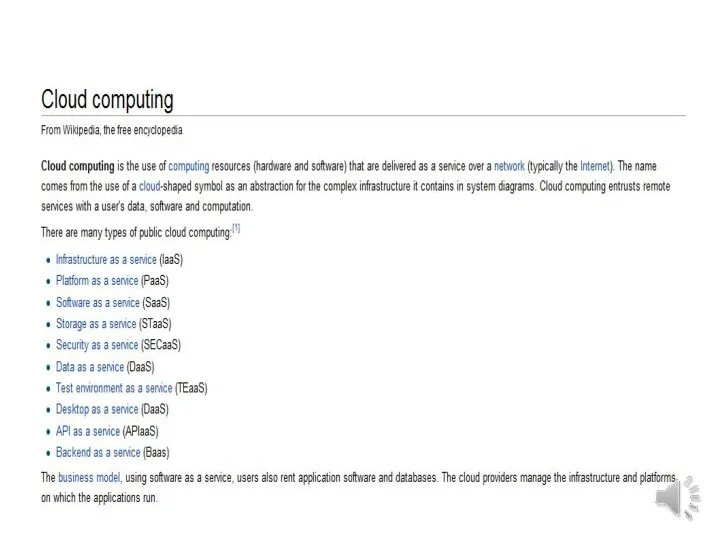
- 11. IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service PaaS: Platform as a Service SaaS : Software as a Service
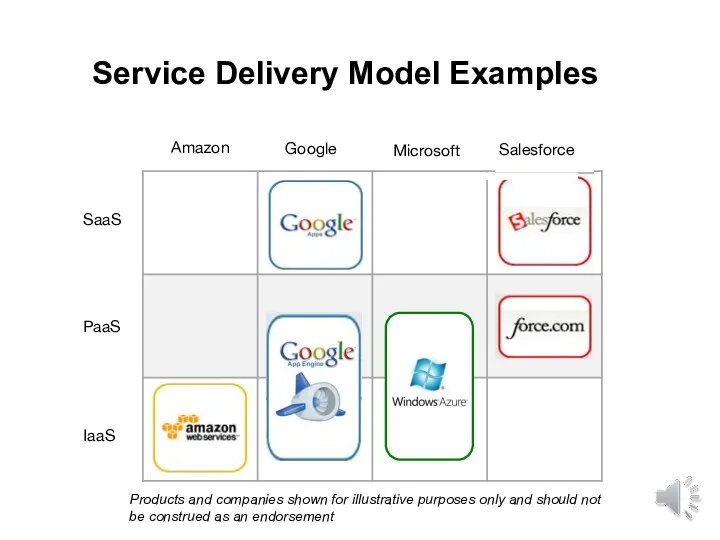
- 13. SaaS PaaS IaaS Amazon Google Microsoft Salesforce Service Delivery Model Examples Products and companies shown for
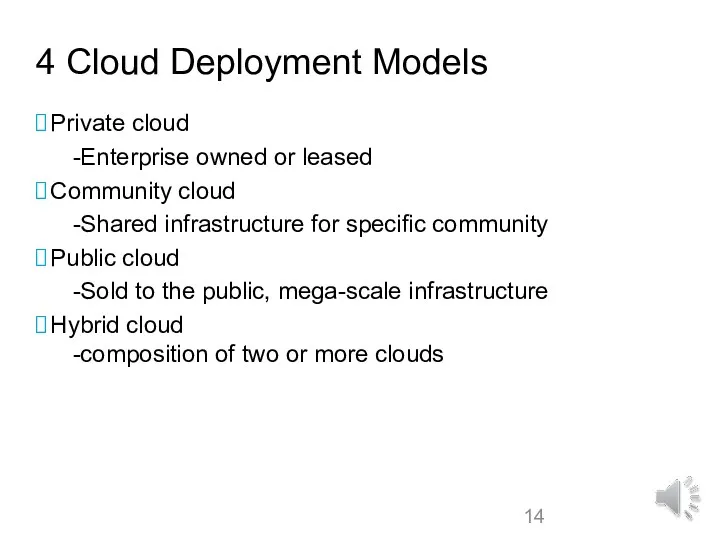
- 14. 4 Cloud Deployment Models Private cloud -Enterprise owned or leased Community cloud -Shared infrastructure for specific
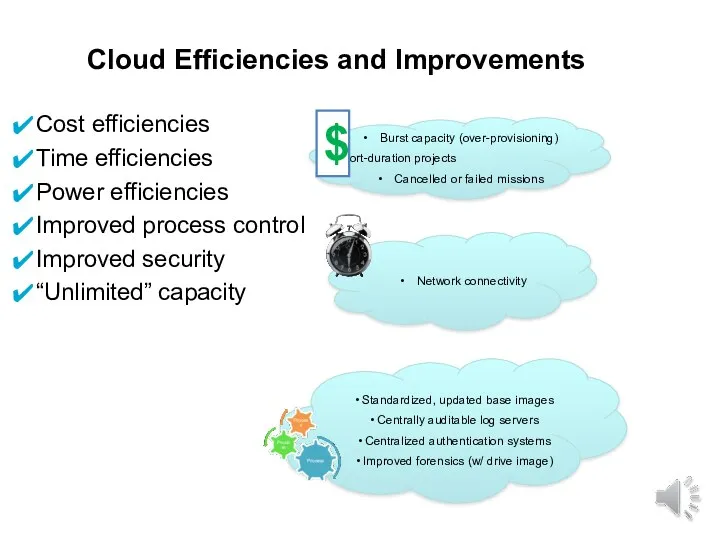
- 15. Cost efficiencies Time efficiencies Power efficiencies Improved process control Improved security “Unlimited” capacity Cloud Efficiencies and
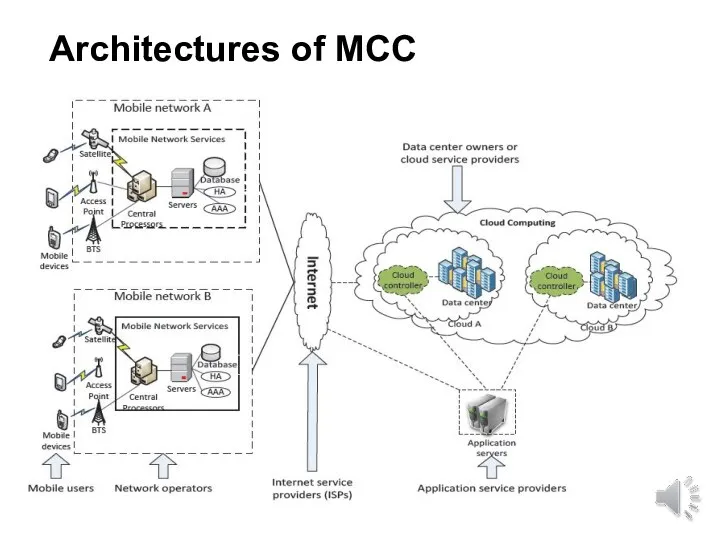
- 16. Where is the MCC? Mobile Cloud Computing (MCC) at its simplest, refers to an infrastructure where
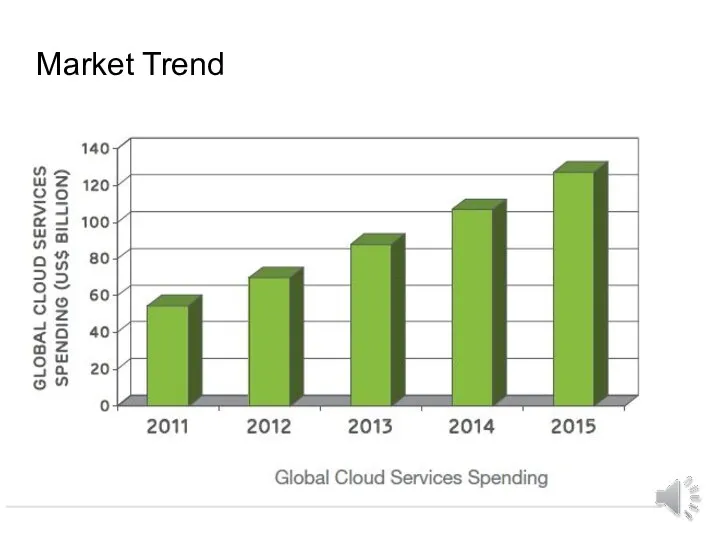
- 17. Market Trend
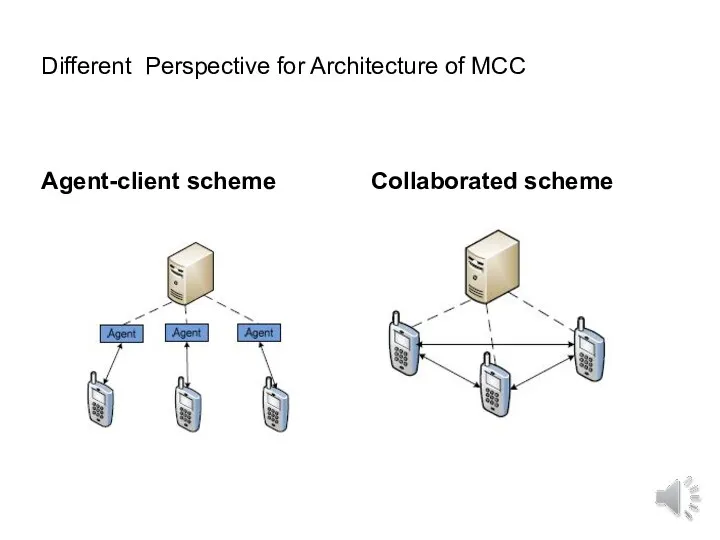
- 18. Different Perspective for Architecture of MCC Agent-client scheme Collaborated scheme
- 19. Architectures of MCC
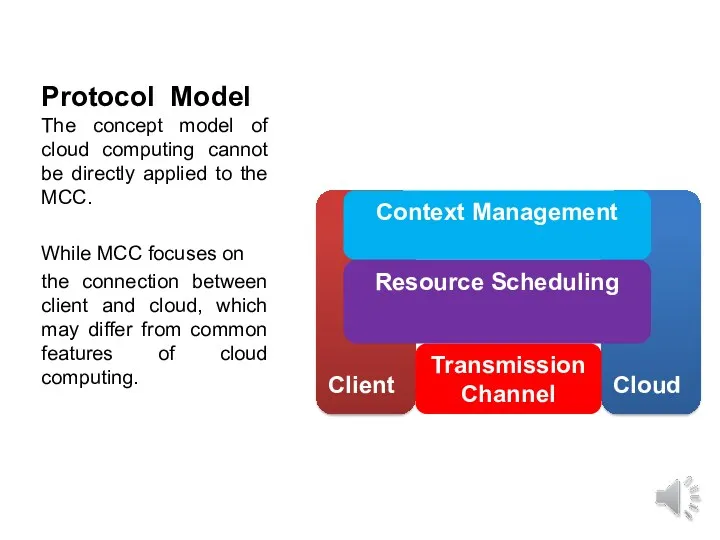
- 20. Protocol Model The concept model of cloud computing cannot be directly applied to the MCC. While
- 21. Resource Scheduling Resource scheduling components address the schedule of resource, such as computing resource and storage
- 22. Context Management Context Enabled features of mobile device allow us to ascertain additional information from the
- 23. Two major approaches Application partition and offloading technology play an important role for the implementation of
- 24. Advantageous of MCC Improving reliability
- 25. How MCC Can Extend Battery Lifetime? Challenges: Battery is one of the main concerns for mobile
- 26. How MCC Can Improve Storage Capacity? Challenges Users need more and more capacity for saving the
- 27. How MCC Can Improve Reliability? Challenges Users need reliable backup for their information, Lack of data
- 28. Other advantageous of MCC Dynamic provisioning, Scalability, Multi-tenancy, Ease of integration.
- 29. Applications of MCC Mobile commerce, Mobile healthcare, Mobile learning, Mobile Gaming.
- 30. Mobile Commerce Mobile commerce (m-commerce) is a business model for commerce using mobile devices.
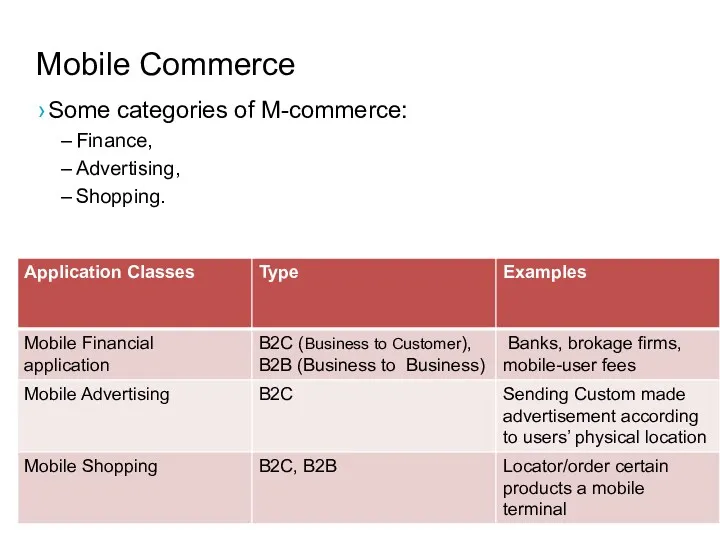
- 31. Mobile Commerce Some categories of M-commerce: Finance, Advertising, Shopping.
- 32. Mobile Learning (M-LEARNING) = (E-LEARNING) + Mobility Traditional m-learning applications have limitations in terms of 1-
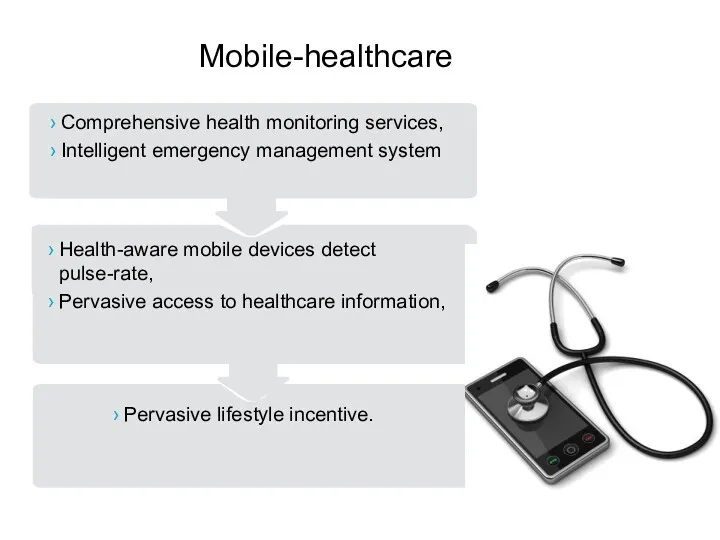
- 33. Mobile-healthcare Comprehensive health monitoring services, Intelligent emergency management system Health-aware mobile devices detect pulse-rate, Pervasive access
- 34. Mobile Gaming Mobile game (m-game) is a potential market generating revenues for service providers. M-game can
- 35. Other applications on MCC Keyword based searching Voice based searching Tag- Based searching
- 36. ISSUES AND APPROACHES OF MCC Due to the integration of two different fields, i.e., cloud computing
- 37. Issues in Mobile Communication Side Availability Heterogeneity Network latency and limited bandwidth
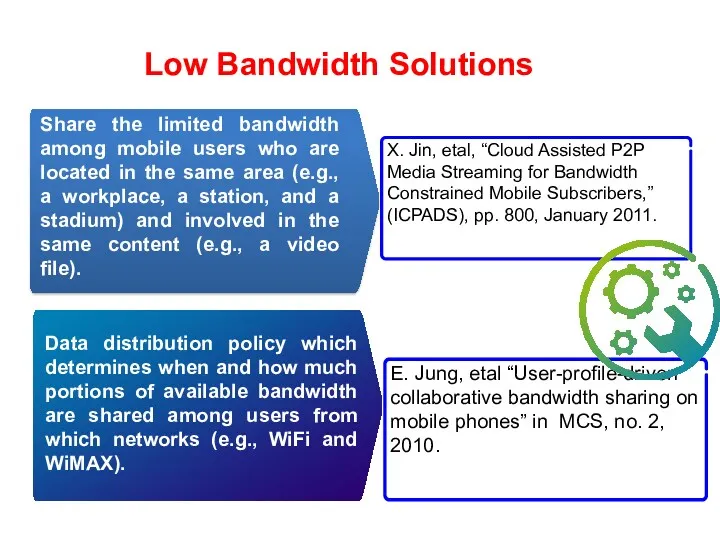
- 38. Low Bandwidth Solutions Availability Data distribution policy which determines when and how much portions of available
- 39. Availability Solutions Finding stable neighbour WiFi multi-hop networking system G. Huerta “A virtual cloud computing provider
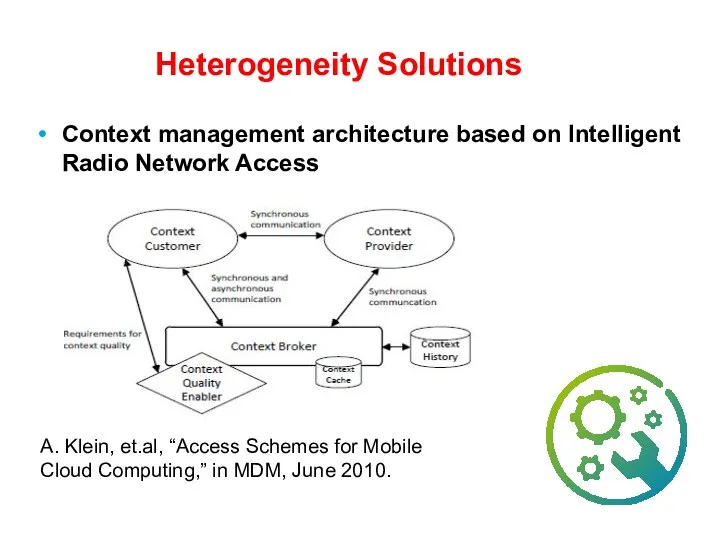
- 40. Heterogeneity Solutions Context management architecture based on Intelligent Radio Network Access A. Klein, et.al, “Access Schemes
- 41. Issues in Computing Side Availability Context aware mobile cloud services Computing offload Security Enhancing the efficiency
- 42. Issue and Solutions in Computing Offload Offloading in the statistic environment is not always the efficient
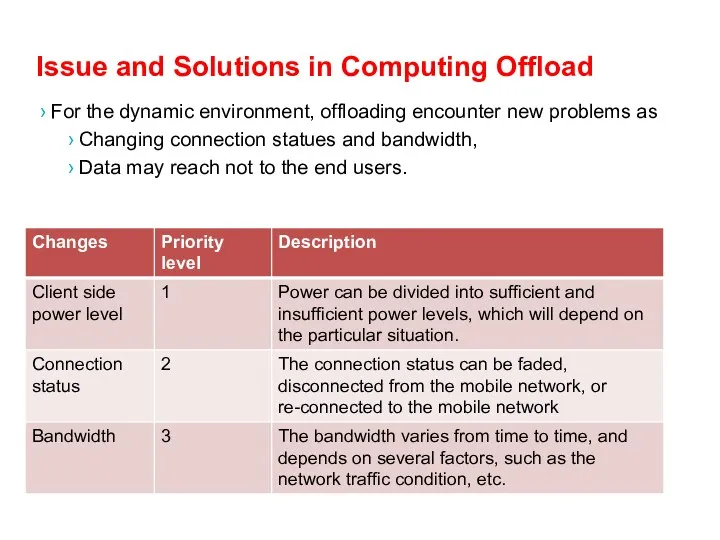
- 43. Issue and Solutions in Computing Offload For the dynamic environment, offloading encounter new problems as Changing
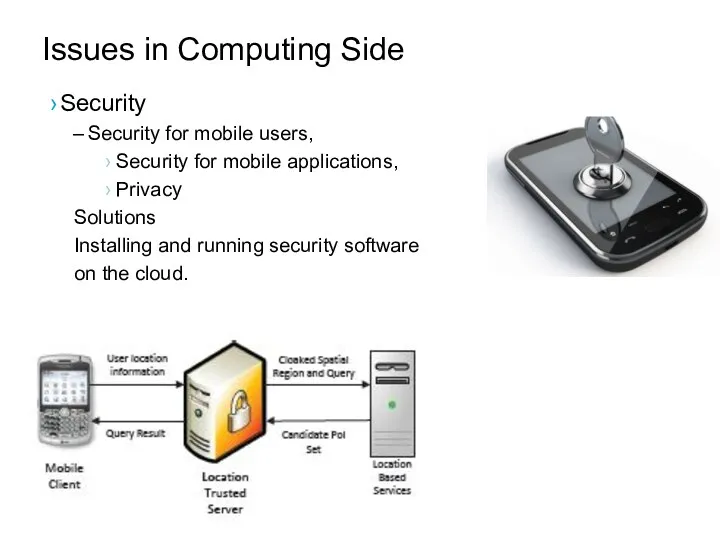
- 44. Issues in Computing Side Security Security for mobile users, Security for mobile applications, Privacy Security of
- 45. Issues in Computing Side Security Security for mobile users, Security for mobile applications, Privacy Solutions Installing
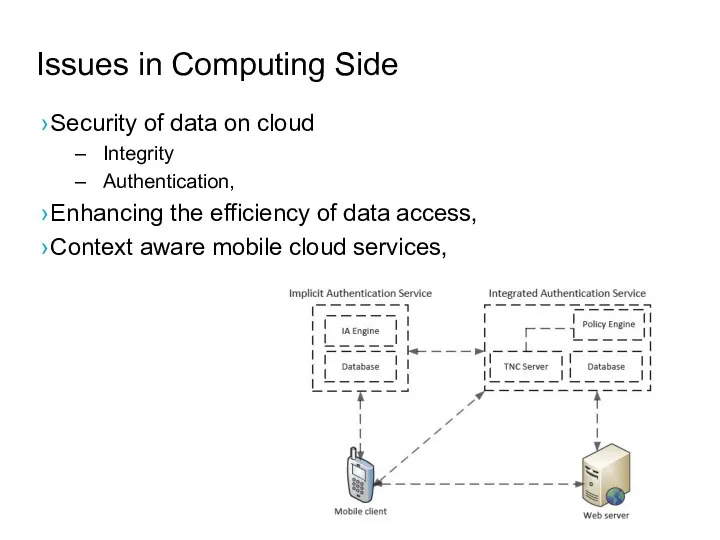
- 46. Issues in Computing Side Security of data on cloud Integrity Authentication, Enhancing the efficiency of data
- 47. Open Issues
- 48. How to combine the two technology seamlessly? The main aim of MCC is to provide PC_like
- 49. Low bandwidth Mobility of users Increasing the demand of mobile users, More Bandwidth is required to
- 50. Low bandwidth: 4G Solutions Increases bandwidth for subscribers up to 100 Mbit/s (for “LTE Advanced” standard)
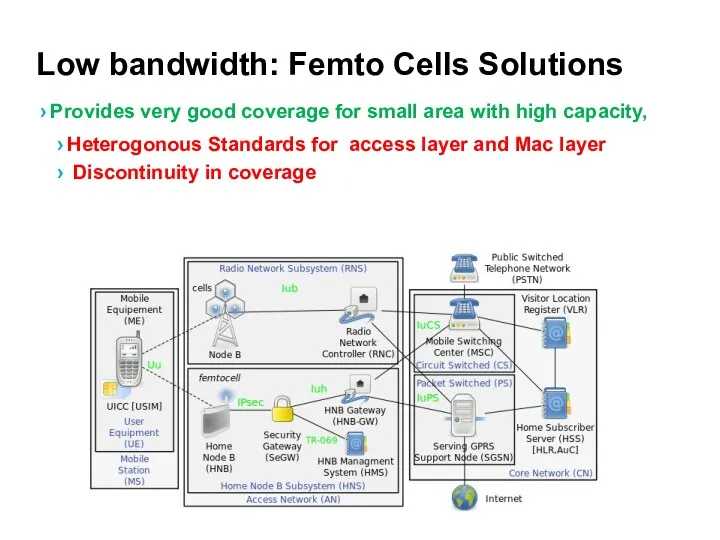
- 51. Low bandwidth: Femto Cells Solutions Provides very good coverage for small area with high capacity, Heterogonous
- 52. Low Bandwidth: Cognitive Radios Solutions Cognitive radio can be expected as a solution to achieve more
- 53. Handover (HO) in MCC Due to mobility of users, MCC encounters HO of users during the
- 54. Pricing Mechanism Using services in MCC involves with Mobile service provider (MSP) Cloud service provider (CSP).
- 55. Service Convergence The development and competition of cloud service providers can lead to the fact that
- 56. References [1] Hoang T. Dinh, etal, “A survey of Mobile Cloud Computing: architecture, applications, and approaches”,
- 58. Скачать презентацию


















![References [1] Hoang T. Dinh, etal, “A survey of Mobile](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/367016/slide-55.jpg)
 Программирование (Python). §19. Ветвления
Программирование (Python). §19. Ветвления Ветвления. Циклы (профориентация)
Ветвления. Циклы (профориентация) Арифметические основы ЭВМ
Арифметические основы ЭВМ Антивирусные программы
Антивирусные программы Інформаційні ресурси мережі
Інформаційні ресурси мережі Нормализация Алгоритм. Методические указания к выполнению курсовой работы по дисциплине РИЭАИС
Нормализация Алгоритм. Методические указания к выполнению курсовой работы по дисциплине РИЭАИС Web-конструирование на HTML. Форматирование текста. Компьютер текст заголовка
Web-конструирование на HTML. Форматирование текста. Компьютер текст заголовка Совершенствование форм дистанционного банковского обслуживания в ПАО Сбербанк России
Совершенствование форм дистанционного банковского обслуживания в ПАО Сбербанк России Подготовка и проведение пресс-конференции
Подготовка и проведение пресс-конференции Уязвимости традиционных средств защиты
Уязвимости традиционных средств защиты Разнообразие объектов и их классификация
Разнообразие объектов и их классификация Введение в ASP.Net Core MVC
Введение в ASP.Net Core MVC Устройство компьютера
Устройство компьютера Компьютерная мышь
Компьютерная мышь GSIS Инструкция пользователя (Для сервисного центра)
GSIS Инструкция пользователя (Для сервисного центра) Система контроля версий Git
Система контроля версий Git КАК РЕБЕНКУ ВЕСТИ СЕБЯ В СЕТИ ИНТЕРНЕТ.
КАК РЕБЕНКУ ВЕСТИ СЕБЯ В СЕТИ ИНТЕРНЕТ. Работа в компьютерной сети Internet
Работа в компьютерной сети Internet Нейронные сети
Нейронные сети Программирование на языке ассемблер
Программирование на языке ассемблер Обработка информации и алгоритмы
Обработка информации и алгоритмы Современные системы автоматизации и цифровые устройства автоматизации на службах ГСМ и ТЗК
Современные системы автоматизации и цифровые устройства автоматизации на службах ГСМ и ТЗК Основные понятия. Программное обеспечение
Основные понятия. Программное обеспечение ЕАС ОПС. Задачи системы и роль ключевых пользователей
ЕАС ОПС. Задачи системы и роль ключевых пользователей Основы безопасной учебы в НИУ ВШЭ
Основы безопасной учебы в НИУ ВШЭ Построение сетей сигнализации ОКС №7 на местных и внутризоновых сетях на базе коммутационного оборудования семейства SI2000
Построение сетей сигнализации ОКС №7 на местных и внутризоновых сетях на базе коммутационного оборудования семейства SI2000 Excel: вычисления в таблицах
Excel: вычисления в таблицах Uses of the internet in our daily life
Uses of the internet in our daily life