Содержание
- 2. The art of war teaches us to rely not on the likelihood of the enemy's not
- 3. The combination of space, time, and strength that must be considered as the basic elements of
- 4. Computer Security The protection afforded to an automated information system in order to attain the applicable
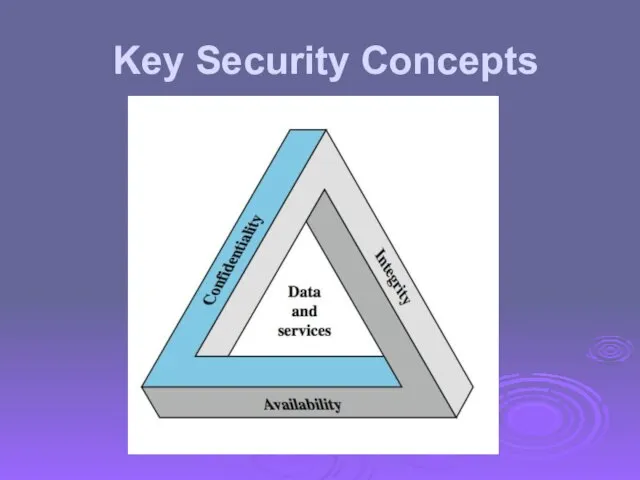
- 5. Key Security Concepts
- 6. Three Key Objectives Confidentiality Data confidentiality Privacy Integrity Data integrity System integrity Availability Additional concepts Authenticity
- 7. Examples of Security Requirements confidentiality – student grades integrity – patient information availability – authentication service
- 8. Computer Security Challenges not simple must consider potential attacks procedures used counter-intuitive involve algorithms and secret
- 9. OSI Security Architecture ITU-T X.800 “Security Architecture for OSI” defines a systematic way of defining and
- 10. Aspects of Security 3 aspects of information security: security attack security mechanism: detect, prevent, recover security
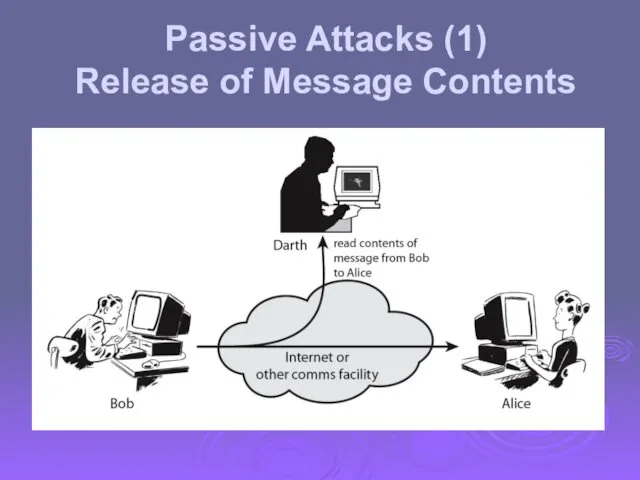
- 11. Passive Attacks (1) Release of Message Contents
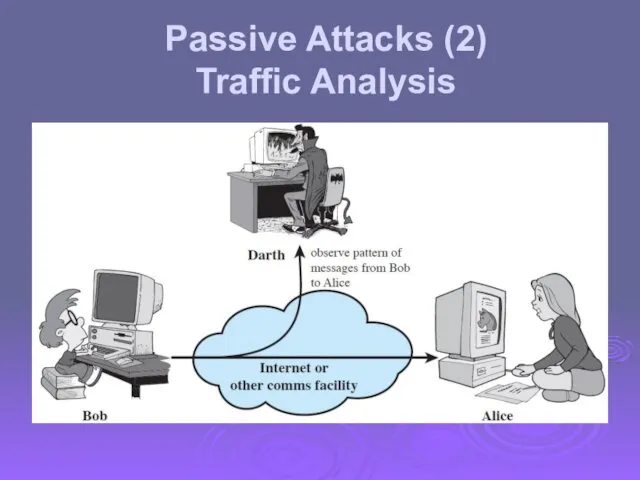
- 12. Passive Attacks (2) Traffic Analysis
- 13. Passive attacks do not affect system resources Eavesdropping, monitoring Two types of passive attacks Release of
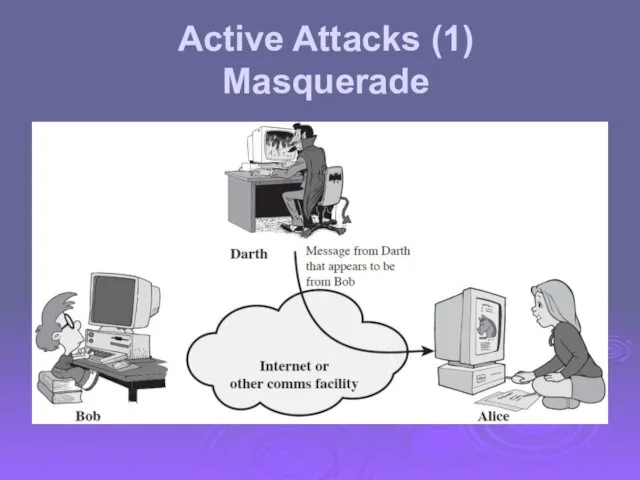
- 14. Active Attacks (1) Masquerade
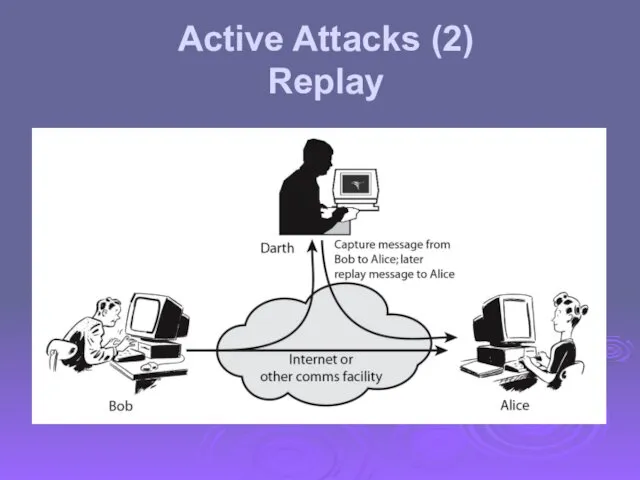
- 15. Active Attacks (2) Replay
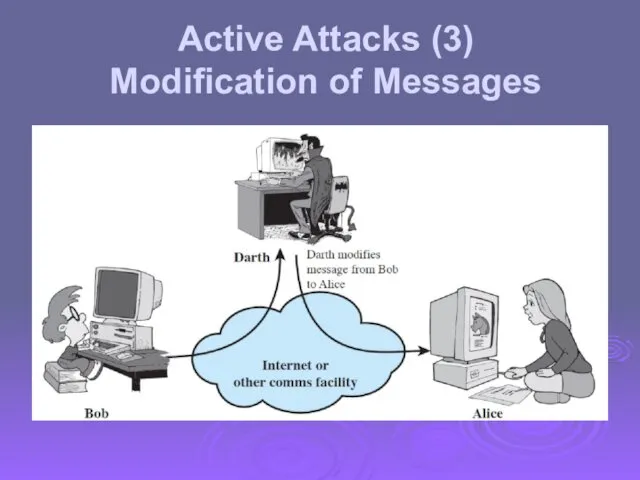
- 16. Active Attacks (3) Modification of Messages
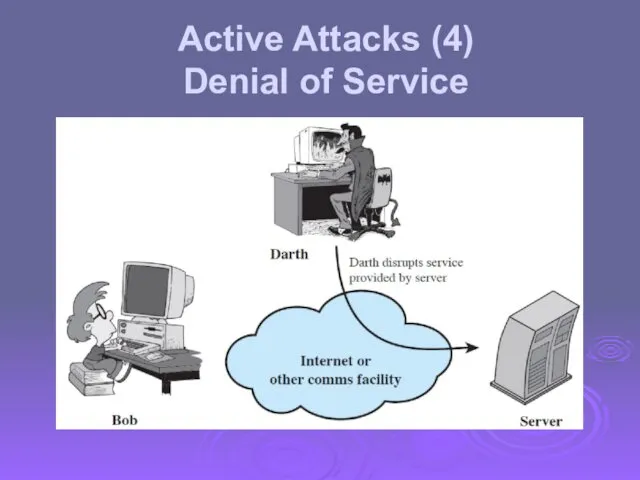
- 17. Active Attacks (4) Denial of Service
- 18. Active attacks try to alter system resources or affect their operation Modification of data, or creation
- 19. Security Service enhance security of data processing systems and information transfers of an organization intended to
- 20. Security Services X.800: “a service provided by a protocol layer of communicating open systems, which ensures
- 21. Security Services (X.800) Authentication - assurance that communicating entity is the one claimed have both peer-entity
- 22. Security Mechanism feature designed to detect, prevent, or recover from a security attack no single mechanism
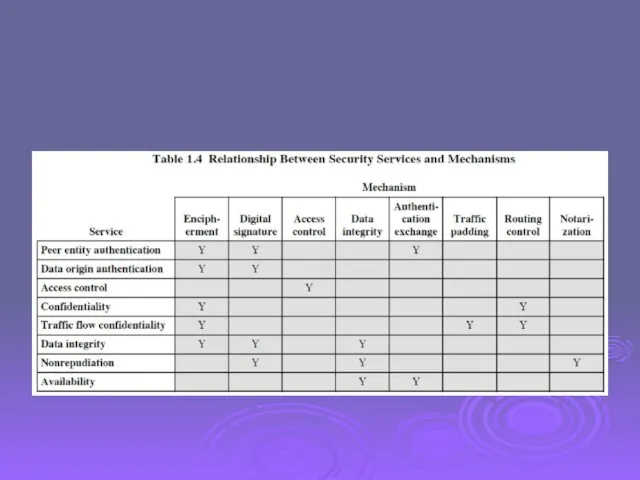
- 23. Security Mechanisms (X.800) specific security mechanisms: encipherment, digital signatures, access controls, data integrity, authentication exchange, traffic
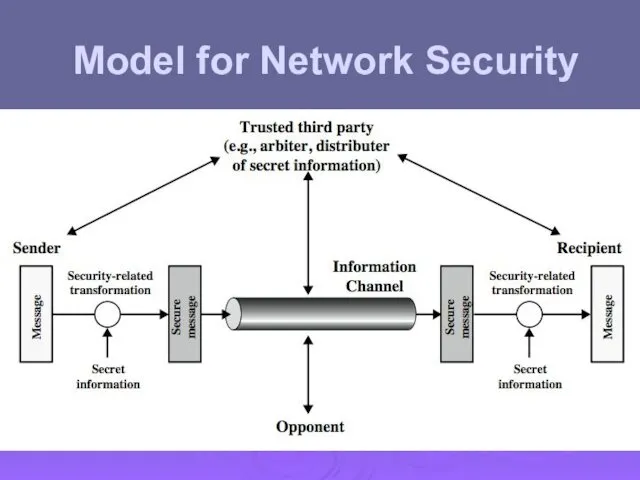
- 25. Model for Network Security
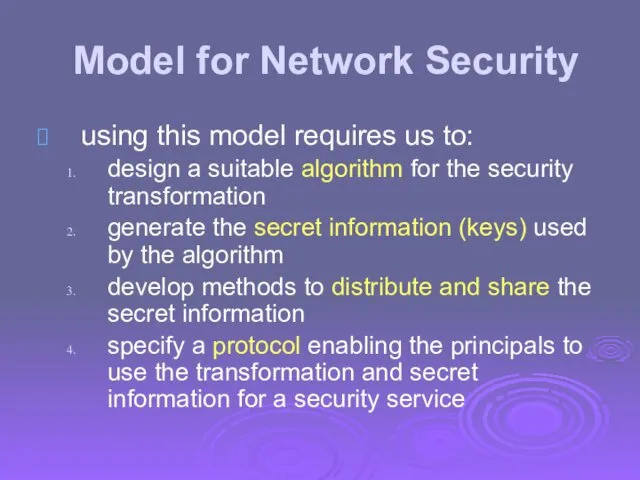
- 26. Model for Network Security using this model requires us to: design a suitable algorithm for the
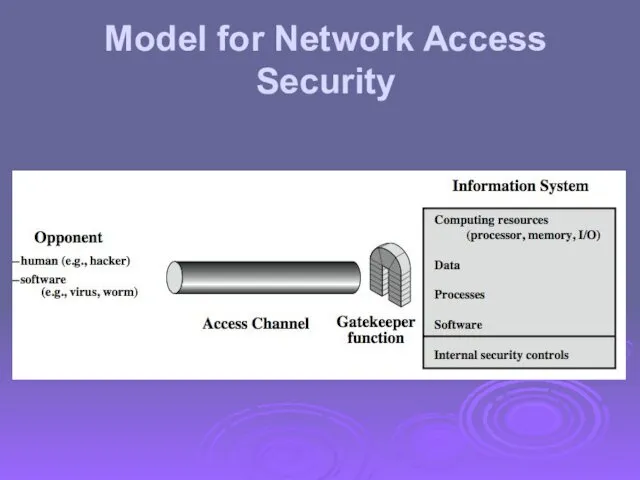
- 27. Model for Network Access Security
- 28. Model for Network Access Security using this model requires us to: select appropriate gatekeeper functions to
- 29. Standards NIST: National Institute of Standards and Technology FIPS: Federal Information Processing Standards SP: Special Publications
- 31. Скачать презентацию

















 Корректировки по сайту NLS Kazakhtan
Корректировки по сайту NLS Kazakhtan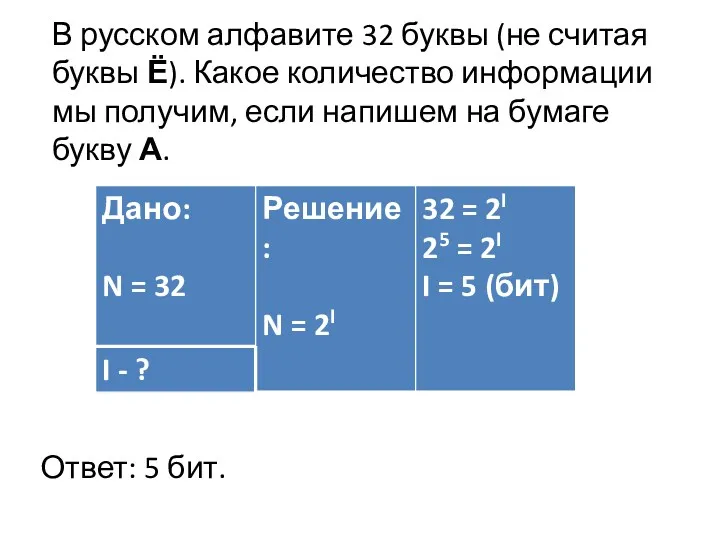 Алфавитный подход к определению количества информации
Алфавитный подход к определению количества информации Основные компоненты компьютера и их функции
Основные компоненты компьютера и их функции Библиографическое описание источников информации
Библиографическое описание источников информации Правила составления списка литературы
Правила составления списка литературы Database management systems. Relational algebra
Database management systems. Relational algebra Эксплуатация подсистем безопасности АС. Криптографическое преобразование информации в АС. (Тема 7)
Эксплуатация подсистем безопасности АС. Криптографическое преобразование информации в АС. (Тема 7) Информатика, медицинская информатика и статистика
Информатика, медицинская информатика и статистика Разработка консольного приложения с элементами ООП. Интернет магазин продуктов
Разработка консольного приложения с элементами ООП. Интернет магазин продуктов Компьютерная графика
Компьютерная графика Расчетные методики ПП ЭкоСфера-предприятие. Расчет выбросов при растаривании химреагентов
Расчетные методики ПП ЭкоСфера-предприятие. Расчет выбросов при растаривании химреагентов Файловые системы
Файловые системы Сайт andreevats.ru
Сайт andreevats.ru Менеджер блогера
Менеджер блогера Как попасть на обучение
Как попасть на обучение Урок Модели и моделирование
Урок Модели и моделирование Рекомендации по оформлению мультимедийной презентации
Рекомендации по оформлению мультимедийной презентации Электронная библиотека БГУ
Электронная библиотека БГУ Режимы и способы обработки данных
Режимы и способы обработки данных Поиск информации в Интернет отличная презентация
Поиск информации в Интернет отличная презентация Системный анализ и моделирование процессов в промышленной безопасности
Системный анализ и моделирование процессов в промышленной безопасности Комп’ютерна графіка
Комп’ютерна графіка Firewall
Firewall Информатизация общества. Основы классификации и структурирования информации
Информатизация общества. Основы классификации и структурирования информации Выполнение интеграционного тестирования программы
Выполнение интеграционного тестирования программы Разработка приложения для файлового обмена (WEB)
Разработка приложения для файлового обмена (WEB) Основные понятия баз данных. Лекция 1
Основные понятия баз данных. Лекция 1 Символьные строки
Символьные строки