Содержание
- 2. Technologies and Protocols Explain how security technologies affect security monitoring. Explain the behavior of common network
- 3. 11.1 Technologies and Protocols
- 4. Syslog and Network Time Protocol (NTP) essential to work of cybersecurity analyst Syslog is used for
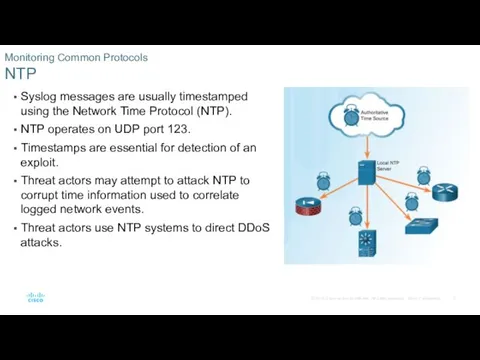
- 5. Syslog messages are usually timestamped using the Network Time Protocol (NTP). NTP operates on UDP port
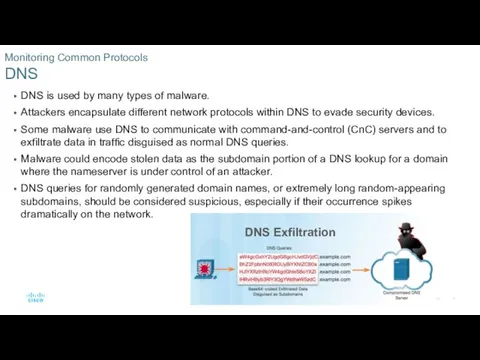
- 6. DNS is used by many types of malware. Attackers encapsulate different network protocols within DNS to
- 7. All information carried in HTTP is transmitted in plaintext from the source computer to the destination
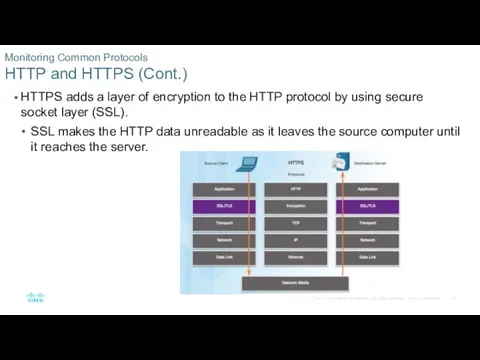
- 8. HTTPS adds a layer of encryption to the HTTP protocol by using secure socket layer (SSL).
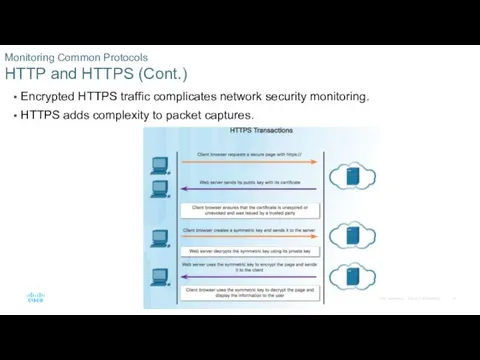
- 9. Encrypted HTTPS traffic complicates network security monitoring. HTTPS adds complexity to packet captures. Monitoring Common Protocols
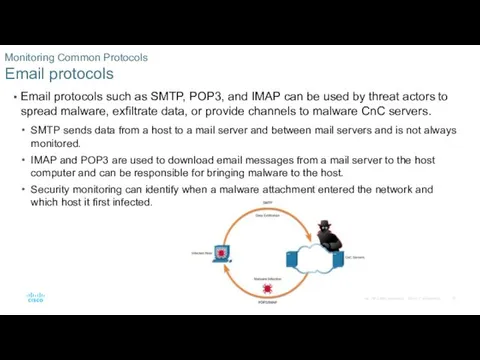
- 10. Email protocols such as SMTP, POP3, and IMAP can be used by threat actors to spread
- 11. ICMP can be used to craft a number of types of exploits. Can be used to
- 12. ACLs may provide a false sense of security. Attackers can determine which IP addresses, protocols, and
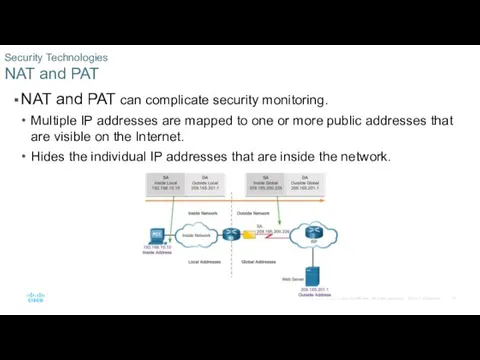
- 13. NAT and PAT can complicate security monitoring. Multiple IP addresses are mapped to one or more
- 14. Encryption Makes traffic contents unreadable by cybersecurity analysts. Part of Virtual Private Network (VPN) and HTTPS.
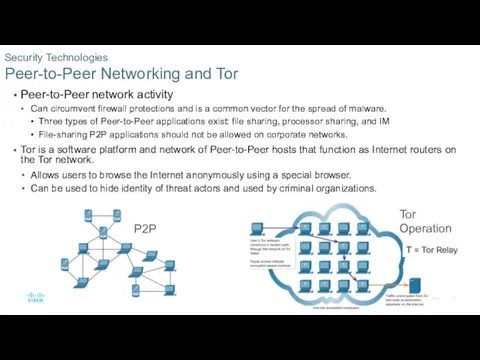
- 15. Peer-to-Peer network activity Can circumvent firewall protections and is a common vector for the spread of
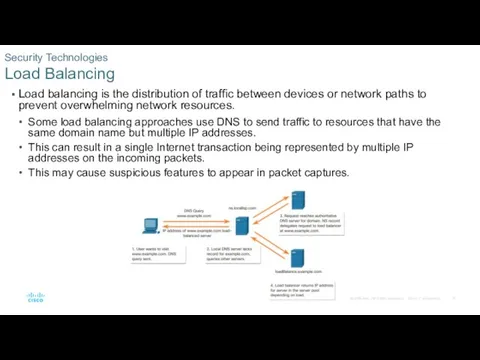
- 16. Load balancing is the distribution of traffic between devices or network paths to prevent overwhelming network
- 17. Log Files
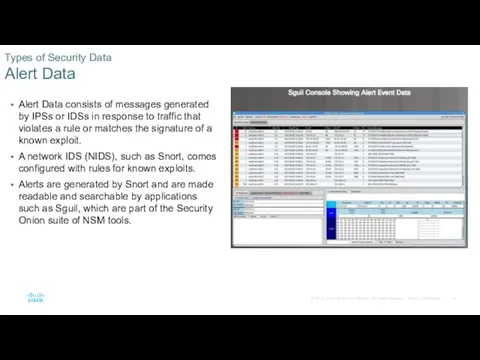
- 18. Alert Data consists of messages generated by IPSs or IDSs in response to traffic that violates
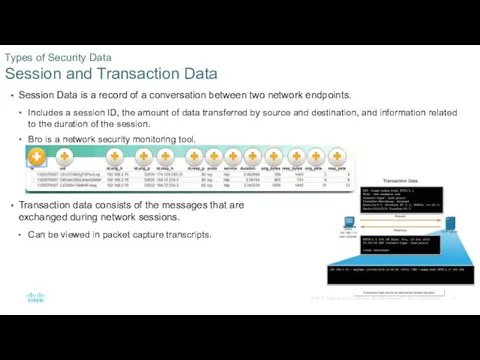
- 19. Session Data is a record of a conversation between two network endpoints. Includes a session ID,
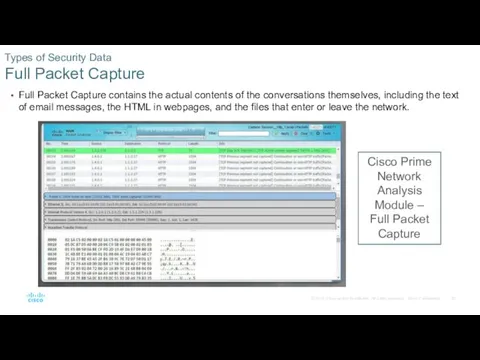
- 20. Full Packet Capture contains the actual contents of the conversations themselves, including the text of email
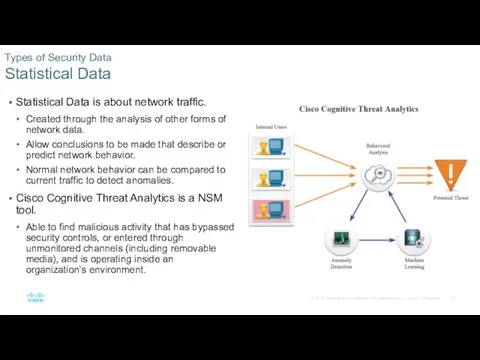
- 21. Statistical Data is about network traffic. Created through the analysis of other forms of network data.
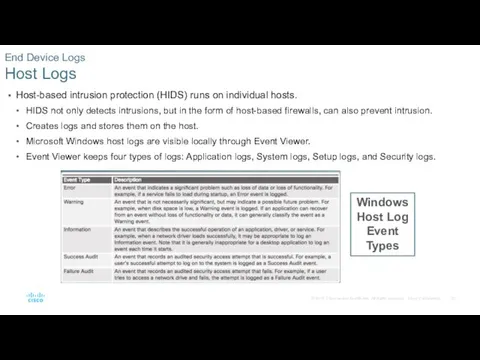
- 22. Host-based intrusion protection (HIDS) runs on individual hosts. HIDS not only detects intrusions, but in the
- 23. Many types of network devices can be configured to log events to syslog servers. Client/server protocol
- 24. End Device Logs Syslog (Cont.)
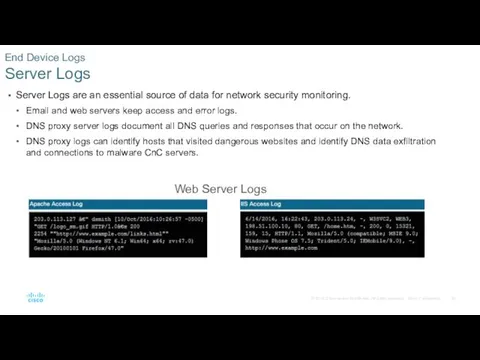
- 25. Server Logs are an essential source of data for network security monitoring. Email and web servers
- 26. Apache Webserver access logs record the requests for resources from clients to the server. Two log
- 27. Microsoft IIS creates access logs that can be viewed from the server with Event Viewer. End
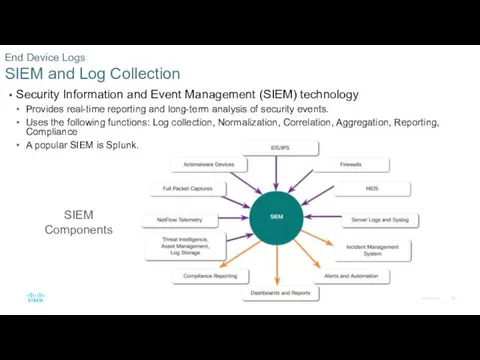
- 28. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) technology Provides real-time reporting and long-term analysis of security events.
- 29. Tcpdump command line tool is a popular packet analyzer. Displays packet captures in real time, or
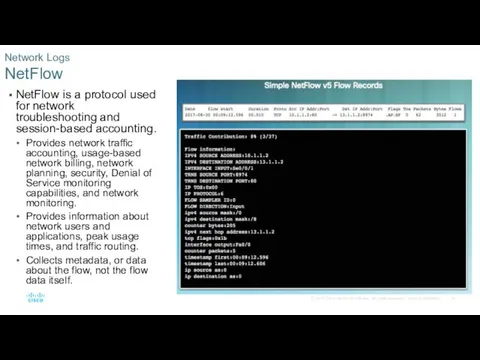
- 30. NetFlow is a protocol used for network troubleshooting and session-based accounting. Provides network traffic accounting, usage-based
- 31. Cisco Application Visibility and Control (AVC) system Combines multiple technologies to recognize, analyze, and control over
- 32. Devices that provide content filtering Cisco Email Security Appliance (ESA) Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA) Provide
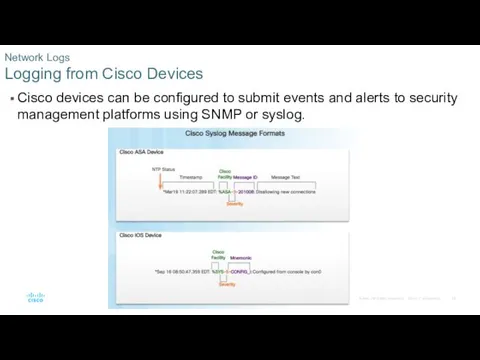
- 33. Cisco devices can be configured to submit events and alerts to security management platforms using SNMP
- 34. Proxy servers contain valuable logs that are a primary source of data for network security monitoring.
- 35. Cisco NexGen IPS devices extend network security to the application layer and beyond. Provide more functionality
- 36. Network Logs NextGen IPS (Cont.) Common NGIPS events include: Connection Event Intrusion Event Host or Endpoint
- 37. Summary
- 38. Summary In this lecture, you learned about the security technologies and log files used in security
- 39. Summary (Cont.) Syslog includes specifications for message formats, a client-server application structure, and network protocol. Network
- 40. Summary (Cont.) NetFlow provides network traffic accounting, usage-based network billing, network planning, security, Denial of Service
- 42. Скачать презентацию






















 Настройка анимации при создании презентаций в программе Power Point
Настройка анимации при создании презентаций в программе Power Point Інформаційні ресурси мережі
Інформаційні ресурси мережі Единый портал государственных услуг
Единый портал государственных услуг Экономическая информатика. Microsoft Excel
Экономическая информатика. Microsoft Excel Нелинейные структуры данных. (Тема 4)
Нелинейные структуры данных. (Тема 4) Введение в безопасность веб-приложений
Введение в безопасность веб-приложений Системы счисления
Системы счисления Формирование изображения на экране монитора. Обработка графической информации
Формирование изображения на экране монитора. Обработка графической информации Искусственный интеллект как ключевой драйвер цифровизации. Возможности и вызовы
Искусственный интеллект как ключевой драйвер цифровизации. Возможности и вызовы Искусственный интеллект и его применение в дизайне
Искусственный интеллект и его применение в дизайне VPN. Виртуальные частные сети
VPN. Виртуальные частные сети Анимированные ребусы (презентация)
Анимированные ребусы (презентация) Lecture 6 Routing
Lecture 6 Routing Компьютер
Компьютер Маршрутизація в мережах зв’язку. (Лекція 1)
Маршрутизація в мережах зв’язку. (Лекція 1) Презентация. Инструктаж по правилам дорожного движения
Презентация. Инструктаж по правилам дорожного движения C++ Programming
C++ Programming Нормализация данных
Нормализация данных Фотоаппараты и программы обработки фото
Фотоаппараты и программы обработки фото Автоматизация деятельности архивной службы организации. Система “Архивное дело” (версия 4.2)
Автоматизация деятельности архивной службы организации. Система “Архивное дело” (версия 4.2) Модель вариантов использования в Rose. (Тема 4)
Модель вариантов использования в Rose. (Тема 4) Язык программирования Pascal. Типы данных, определяемые программистом
Язык программирования Pascal. Типы данных, определяемые программистом Деректер базасының архитектурасы
Деректер базасының архитектурасы Информационные технологии управления
Информационные технологии управления Лекция 2 – Основы языка C#
Лекция 2 – Основы языка C# Routing concepts
Routing concepts Web-сайт – гиперструктура данных технология использования и разработки
Web-сайт – гиперструктура данных технология использования и разработки Анализ демографической ситуации в СФО
Анализ демографической ситуации в СФО