So we can say: the geometrical meaning of the derivative of
the
at the point is the tangent of the angle
between the OX axis and the tangent of the curve at the point
The physical meaning of the derivative of the function
It is the instantaneous velocity at the moment when we have
the nonuniform motion , that is
The equation of the tangent of the curve at the point
Let is the equation of the tangent of the curve at the
point As the point
belongs to the curve and the tangent
then we have the following system of equations
where is the distance covered.





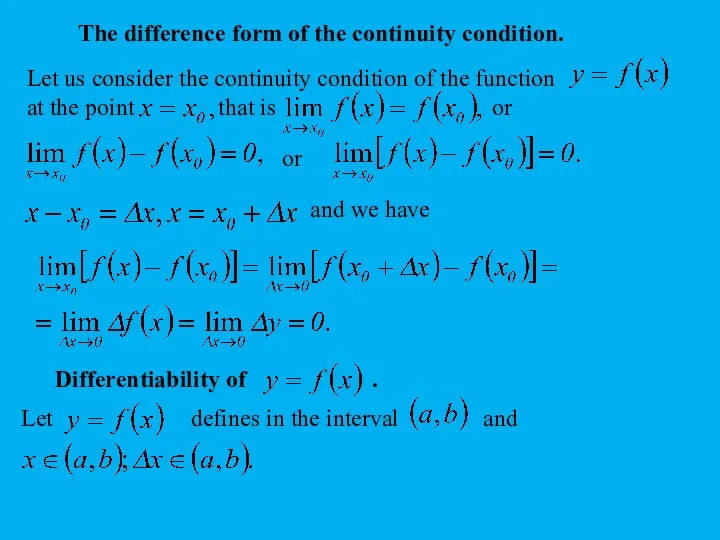

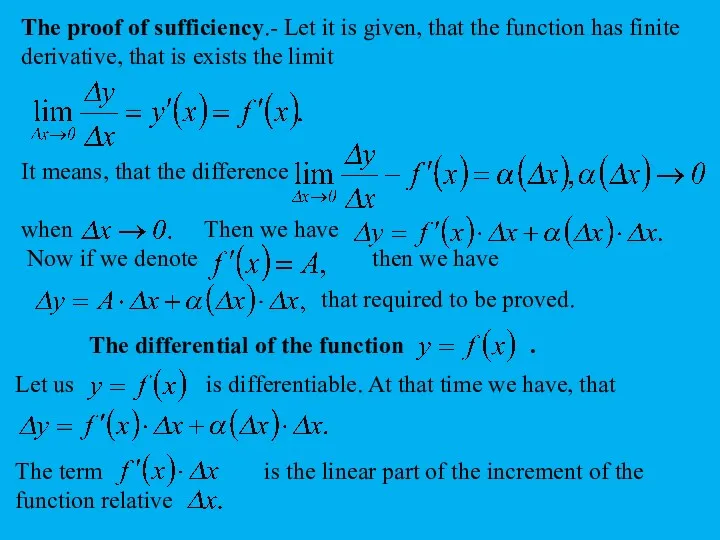

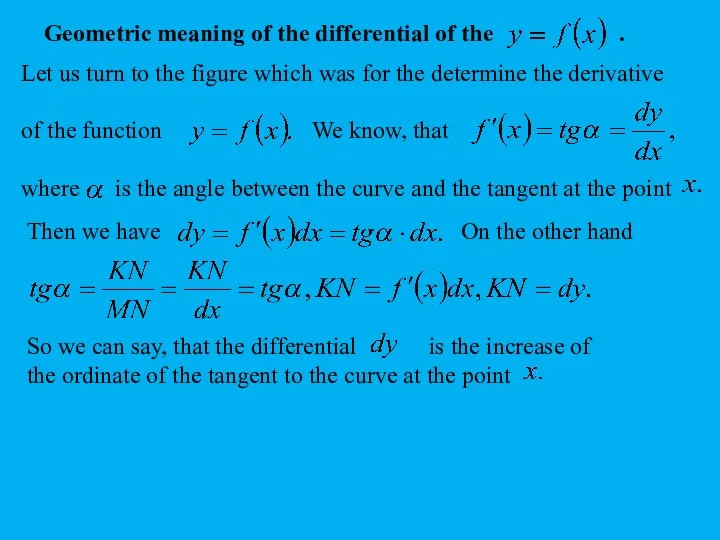

 Radix sort
Radix sort Объемы тел
Объемы тел Разминка. Быстрее. Выше. Сильнее
Разминка. Быстрее. Выше. Сильнее Математика в 3 классе
Математика в 3 классе Теория вероятностей
Теория вероятностей Геометрия куполов
Геометрия куполов Тренажёр к уроку геометрии в 7 классе. УМК Геометрия 7-9. Атанасян Л.С
Тренажёр к уроку геометрии в 7 классе. УМК Геометрия 7-9. Атанасян Л.С Векторы и прямые произведения множеств. Проекция вектора на ось
Векторы и прямые произведения множеств. Проекция вектора на ось Математические тесты
Математические тесты Устный журнал по математике
Устный журнал по математике Аполлоній Перзький
Аполлоній Перзький Перпендикулярность прямых и плоскостей
Перпендикулярность прямых и плоскостей Изменение величин
Изменение величин Первообразная. Неопределенный интеграл
Первообразная. Неопределенный интеграл Решение геометрических задач при подготовке к ГИА
Решение геометрических задач при подготовке к ГИА Trigonometry 4. Lecture Outline
Trigonometry 4. Lecture Outline Презентация Площадь геометрической фигуры
Презентация Площадь геометрической фигуры Устный счёт 1 класс
Устный счёт 1 класс Внеклассное мероприятие по математике Своя игра (для учащихся 5-х классов)
Внеклассное мероприятие по математике Своя игра (для учащихся 5-х классов) Степень с натуральным показателем. Умножение степеней с одинаковыми а основаниями
Степень с натуральным показателем. Умножение степеней с одинаковыми а основаниями Задачи на движение
Задачи на движение Обобщающий урок по теме Четырёхугольники.
Обобщающий урок по теме Четырёхугольники. Понятие квадратного корня из неотрицательного числа
Понятие квадратного корня из неотрицательного числа Что есть угол? Математика. Лекция №6
Что есть угол? Математика. Лекция №6 Урок математики
Урок математики Теория комплексных чисел. (Тема 2)
Теория комплексных чисел. (Тема 2) Элементы теории матричных игр
Элементы теории матричных игр Методическое пособие по развитию сенсорных представлений, развитие внимания, памяти, мышления
Методическое пособие по развитию сенсорных представлений, развитие внимания, памяти, мышления