Слайд 2

AGENDA
Homogenous Transformation Matrix
Link Connections
Denavit-Hartneberg Parameters
DH-Parameters
Слайд 3

WHAT DO WE KNOW FOR NOW?
We can make a complete rotation
matrix all the way from base to the end-effector frame by multiplying together each of the individual rotation matrices from one frame to the next frame:
Слайд 4

CAN WE DO IT WITH DISPLACEMENT VECTORS?
Слайд 5

HOMOGENOUS TRANSFORMATION MATRIX
Слайд 6
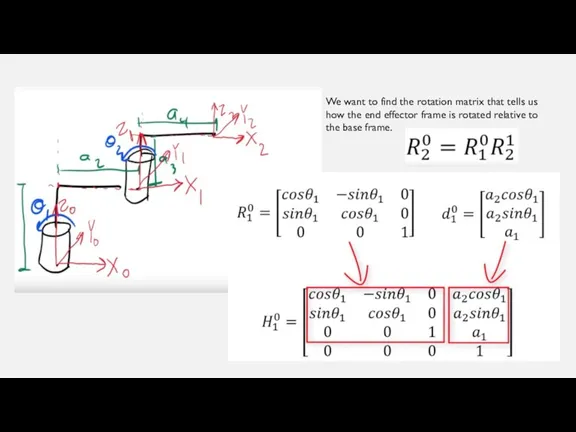
We want to find the rotation matrix that tells us how
the end effector frame is rotated relative to the base frame.
Слайд 7
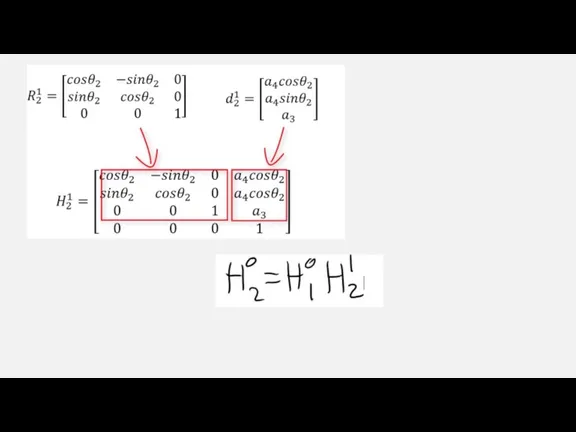
Слайд 8

DENAVIT-HARTENBERG METHOD
Industry standard
Faster
Obscures the meaning behind the rotation matrix and displacement
vector
Слайд 9

STEP 1: ASSIGN FRAMES ACCORDING TO THE 4 DH RULES
STEP 2:
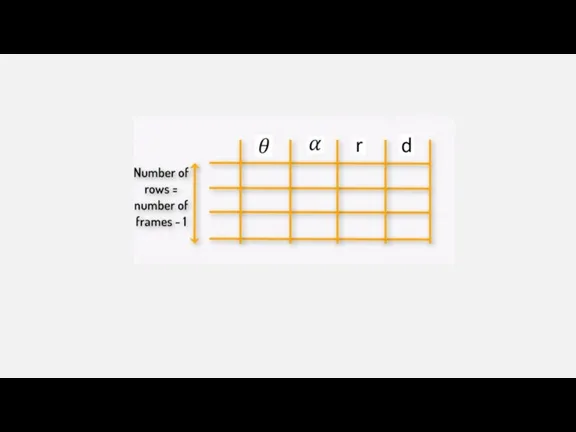
FILL OUT THE DH PARAMETER TABLE
Слайд 10

NOTES:
Assigning coordinate systems:Assign Zi along the axis of joint i.
For a revolute
joint, the joint axis is along the axis of rotation.
For a prismatic joint, the joint axis is along the axis of translation.
Choose Xi to point along the common perpendicular of Zi and Zi+1 pointing towards the next joint.
if Zi and Zi+1 intersect, then choose Xi to be normal to the plane of intersection.
Choose Yi to round out a right hand coordinate system.
The Y-axis is not used for Denavit Hartenberg so it is usually not drawn in the interest of less clutter.
Слайд 11
Слайд 12
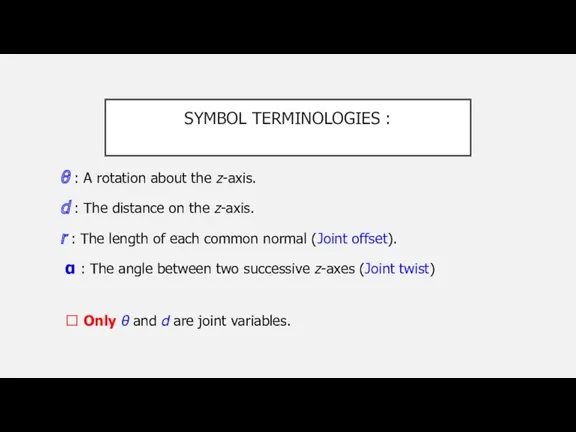
SYMBOL TERMINOLOGIES :
θ : A rotation about the z-axis.
d
: The distance on the z-axis.
r : The length of each common normal (Joint offset).
α : The angle between two successive z-axes (Joint twist)
? Only θ and d are joint variables.
Слайд 13

Слайд 14
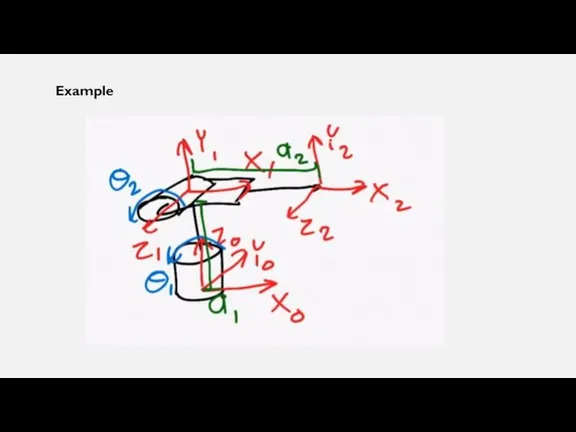
Слайд 15
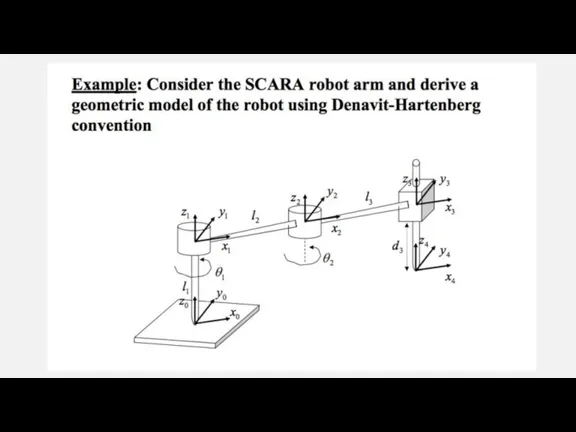
Слайд 16
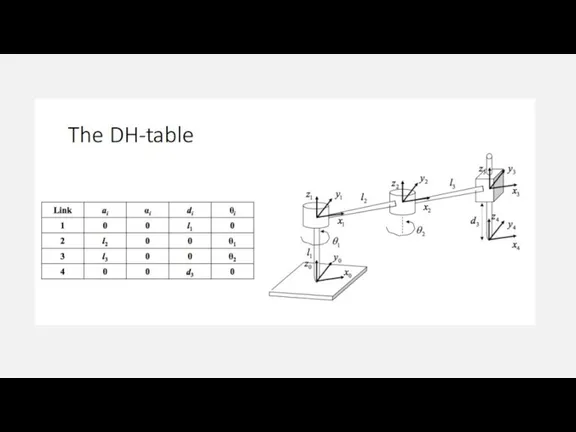
Слайд 17
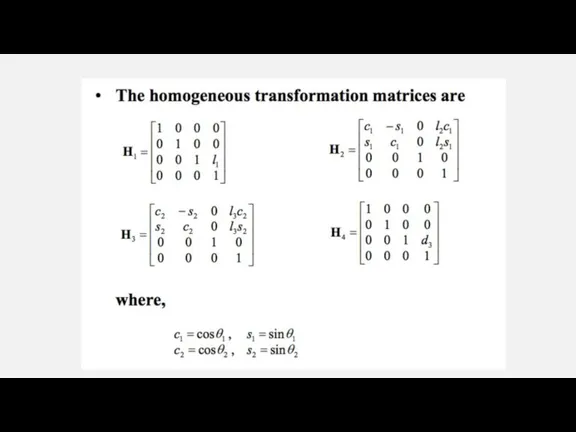
















 Параллельность прямых и плоскостей
Параллельность прямых и плоскостей Метод координат в пространстве
Метод координат в пространстве Келісім белгісі.Келісім белгісін қолданудың тәжірибелік үлгісі (Мендель заңы)
Келісім белгісі.Келісім белгісін қолданудың тәжірибелік үлгісі (Мендель заңы) Свойства параллельных прямых
Свойства параллельных прямых Зачетная система подготовки учащихся к выпускному экзамену по математике в форме ГИА
Зачетная система подготовки учащихся к выпускному экзамену по математике в форме ГИА Признаки возрастания и убывания функции
Признаки возрастания и убывания функции Математическая викторина (7-8 класс)
Математическая викторина (7-8 класс) Основы фрактальной теории, знакомство с математическим обоснованием графической интерпретации фрактальных образов
Основы фрактальной теории, знакомство с математическим обоснованием графической интерпретации фрактальных образов Деление на 2
Деление на 2 Преобразование графиков функций
Преобразование графиков функций Отношение величин математика. 6 класс
Отношение величин математика. 6 класс Дифференциал функции
Дифференциал функции Теорема Пифагора
Теорема Пифагора Нормированные пространства и Л.Н.О. Функциональный анализ
Нормированные пространства и Л.Н.О. Функциональный анализ Сложение и вычитание многозначных чисел. Алгоритм письменного вычисления
Сложение и вычитание многозначных чисел. Алгоритм письменного вычисления Применение интеграла для нахождения площадей объектов ландшафтного дизайна
Применение интеграла для нахождения площадей объектов ландшафтного дизайна Математический КВН с учащимися 8-9 классов
Математический КВН с учащимися 8-9 классов Теорема о равенстве односторонних углов. Теорема о свойстве односторонних углов
Теорема о равенстве односторонних углов. Теорема о свойстве односторонних углов Координатная плоскость. 6 класс
Координатная плоскость. 6 класс Изучение взаимосвязи между явлениями методами корреляционно-регрессионного анализа
Изучение взаимосвязи между явлениями методами корреляционно-регрессионного анализа Производные высших порядков
Производные высших порядков Сокращение дробей
Сокращение дробей Геометрический материал к уроку
Геометрический материал к уроку Тест по математике по теме Величины.
Тест по математике по теме Величины. Дискретная математика. Основные понятия теории множеств
Дискретная математика. Основные понятия теории множеств Отношение двух чисел. Работа с математической моделью
Отношение двух чисел. Работа с математической моделью Табличное сложение. Приём сложения чисел с переходом через десяток
Табличное сложение. Приём сложения чисел с переходом через десяток Состав числа
Состав числа