- Главная
- Математика
- Winston p. 313

Содержание
- 2. Winston p. 313, # 2 Dual: min 3y1 + 2y2 + y3 subject to y1 +
- 3. Winston p. 815, #11 Find the floor and ceiling of the value of this game. Does
- 4. Winston p. 815, #11 min -1 -10 -10 -1 -10 max 20 20 -1 7 2
- 5. Schrage #4 The next 5 slides show the crop recourse homework problem I assigned, plus the
- 6. Schrage #4 (Formulate Only)
- 7. Schrage Handout, #4 Indices s = season {wet,dry} c = crops {corn, sorg, bean} Data YIELDcs
- 8. Schrage Handout, #4 (cont’d)
- 9. Schrage #4 (Sample MPL Code) TITLE RecourseCrops; INDEX s := (wet,dry); { seasons } c :=
- 10. Schrage #4 (Sample MPL code) DECISION VARIABLES live; { units of livestock to raise } pcrop[c];
- 12. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
Winston p. 313, # 2
Dual:
min 3y1 + 2y2 + y3
subject to
y1
Winston p. 313, # 2
Dual:
min 3y1 + 2y2 + y3
subject to
y1
+ y3 ≥ -2
y1+y2 ≥ -1
y1 + y2 + y3 ≥ 1
y1 ≥ 0 , y2 ≤ 0, y3 unrestricted
y1+y2 ≥ -1
y1 + y2 + y3 ≥ 1
y1 ≥ 0 , y2 ≤ 0, y3 unrestricted
Слайд 3
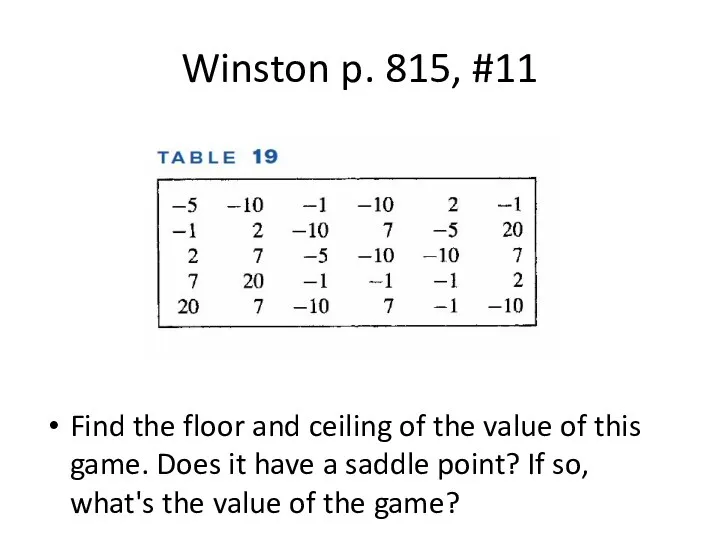
Winston p. 815, #11
Find the floor and ceiling of the value
Winston p. 815, #11
Find the floor and ceiling of the value
of this game. Does it have a saddle point? If so, what's the value of the game?
Слайд 4
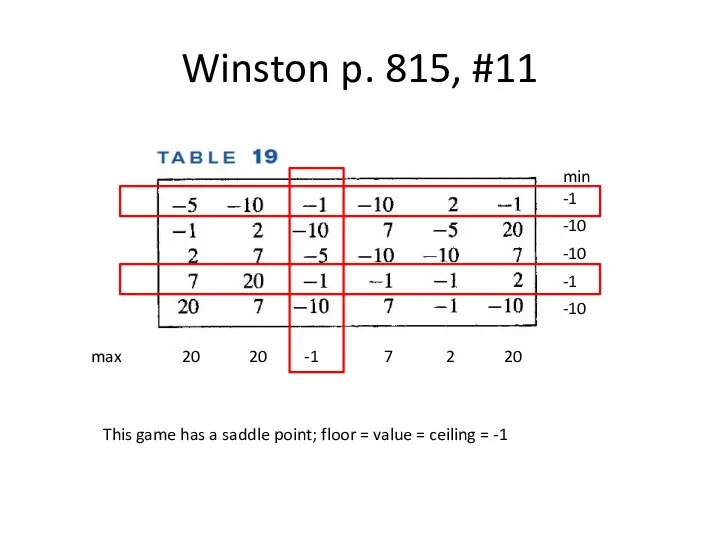
Winston p. 815, #11
min
-1
-10
-10
-1
-10
max 20 20 -1 7 2 20
This game
Winston p. 815, #11
min
-1
-10
-10
-1
-10
max 20 20 -1 7 2 20
This game
has a saddle point; floor = value = ceiling = -1
Слайд 5
Schrage #4
The next 5 slides show the crop recourse homework problem
Schrage #4
The next 5 slides show the crop recourse homework problem
I assigned, plus the MPL code
Modify the code to compute the worst-case probabilities of a wet or dry season
Hint: you only have to add one variable, modify the objective function, and add one set of constraints; the other constraints in the model stay the same
What are the worst-case probabilities? How does the overall expected cost change?
Modify the code to compute the worst-case probabilities of a wet or dry season
Hint: you only have to add one variable, modify the objective function, and add one set of constraints; the other constraints in the model stay the same
What are the worst-case probabilities? How does the overall expected cost change?
Слайд 6
Schrage #4 (Formulate Only)
Schrage #4 (Formulate Only)
Слайд 7
Schrage Handout, #4
Indices
s = season {wet,dry}
c = crops {corn, sorg, bean}
Data
YIELDcs
Schrage Handout, #4
Indices
s = season {wet,dry}
c = crops {corn, sorg, bean}
Data
YIELDcs
= yield/acre (bushels) of crop c in season s
PROBs = probablility of season s
SPRICEs = sale price ($) per bushel of crop c
PCOST = production cost/acre ($) for crops
LCROPc = bushels of crop c required per “unit” of livestock
LPROFIT = profit/unit ($) of livestock
MCOSTc = cost/bushel ($) of crop c on open market
ACRES = total acreage available for planting
MAXCROPc = maximum bushels of crop c that can be bought on the open market
Variables
live = units of livestock to raise
pcropc = acres of crop c to plant
bcropcs = bushels of crop c bought under scenario s
csoldcs = bushels of crop c sold in scenario s
PROBs = probablility of season s
SPRICEs = sale price ($) per bushel of crop c
PCOST = production cost/acre ($) for crops
LCROPc = bushels of crop c required per “unit” of livestock
LPROFIT = profit/unit ($) of livestock
MCOSTc = cost/bushel ($) of crop c on open market
ACRES = total acreage available for planting
MAXCROPc = maximum bushels of crop c that can be bought on the open market
Variables
live = units of livestock to raise
pcropc = acres of crop c to plant
bcropcs = bushels of crop c bought under scenario s
csoldcs = bushels of crop c sold in scenario s
Слайд 8
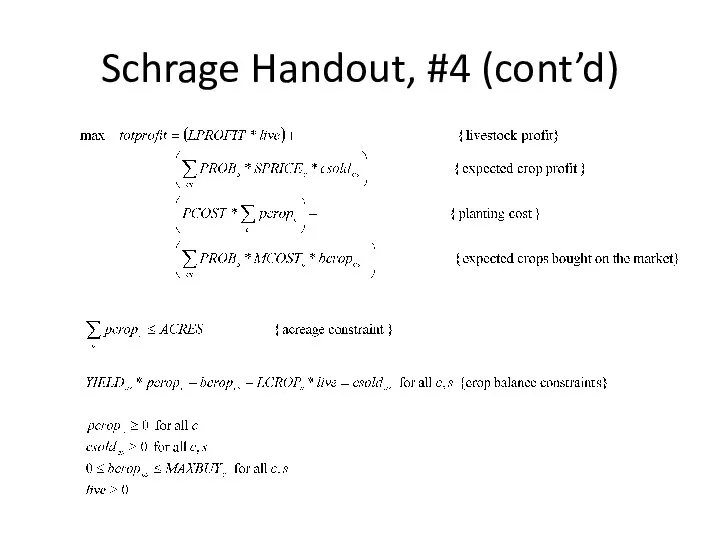
Schrage Handout, #4 (cont’d)
Schrage Handout, #4 (cont’d)
Слайд 9
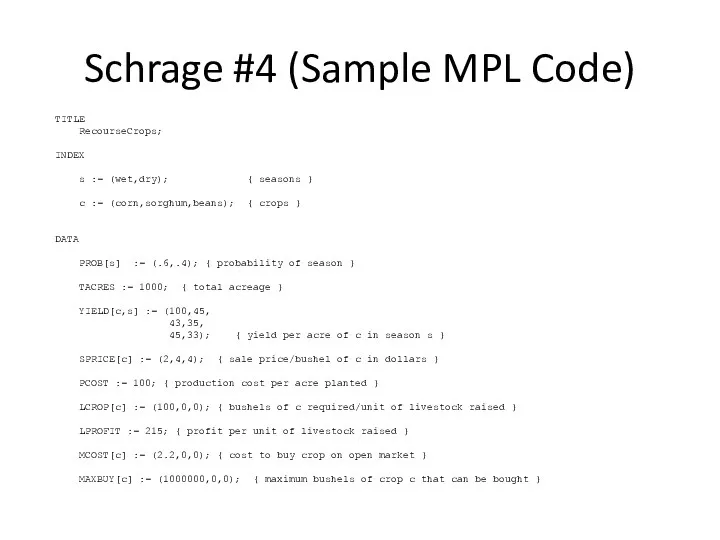
Schrage #4 (Sample MPL Code)
TITLE
RecourseCrops;
INDEX
s := (wet,dry); { seasons
Schrage #4 (Sample MPL Code)
TITLE
RecourseCrops;
INDEX
s := (wet,dry); { seasons
}
c := (corn,sorghum,beans); { crops }
DATA
PROB[s] := (.6,.4); { probability of season }
TACRES := 1000; { total acreage }
YIELD[c,s] := (100,45,
43,35,
45,33); { yield per acre of c in season s }
SPRICE[c] := (2,4,4); { sale price/bushel of c in dollars }
PCOST := 100; { production cost per acre planted }
LCROP[c] := (100,0,0); { bushels of c required/unit of livestock raised }
LPROFIT := 215; { profit per unit of livestock raised }
MCOST[c] := (2.2,0,0); { cost to buy crop on open market }
MAXBUY[c] := (1000000,0,0); { maximum bushels of crop c that can be bought }
c := (corn,sorghum,beans); { crops }
DATA
PROB[s] := (.6,.4); { probability of season }
TACRES := 1000; { total acreage }
YIELD[c,s] := (100,45,
43,35,
45,33); { yield per acre of c in season s }
SPRICE[c] := (2,4,4); { sale price/bushel of c in dollars }
PCOST := 100; { production cost per acre planted }
LCROP[c] := (100,0,0); { bushels of c required/unit of livestock raised }
LPROFIT := 215; { profit per unit of livestock raised }
MCOST[c] := (2.2,0,0); { cost to buy crop on open market }
MAXBUY[c] := (1000000,0,0); { maximum bushels of crop c that can be bought }
Слайд 10
Schrage #4 (Sample MPL code)
DECISION VARIABLES
live; { units of livestock
Schrage #4 (Sample MPL code)
DECISION VARIABLES
live; { units of livestock
to raise }
pcrop[c]; { number of acres of c to plant }
bcrop[c,s]; { bushels of c to buy on market under scenario s }
csold[c,s]; { bushels of c grown and sold (excess of livestock requirements ) }
MODEL
MAX totexpcost = LPROFIT*live + { livestock profit }
SUM(c,s: PROB[s]*SPRICE[c]*csold[c,s]) - { expected crop sales profit }
PCOST*SUM(c: pcrop[c]) - { planting cost }
SUM(c,s: PROB[s]*MCOST[c]*bcrop[c,s]); { expected corn bought }
SUBJECT TO
acres: { acreage constraints}
SUM(c: pcrop[c]) < TACRES;
balance[c,s]:
YIELD[c,s]*pcrop[c] + bcrop[c] - LCROP[c]*live = csold[c,s];
BOUNDS
bcrop[c] < MAXBUY[c]; WE HAVE TO DO THIS TO DISALLOW BEAN AND SORGHUM BUYS
END
pcrop[c]; { number of acres of c to plant }
bcrop[c,s]; { bushels of c to buy on market under scenario s }
csold[c,s]; { bushels of c grown and sold (excess of livestock requirements ) }
MODEL
MAX totexpcost = LPROFIT*live + { livestock profit }
SUM(c,s: PROB[s]*SPRICE[c]*csold[c,s]) - { expected crop sales profit }
PCOST*SUM(c: pcrop[c]) - { planting cost }
SUM(c,s: PROB[s]*MCOST[c]*bcrop[c,s]); { expected corn bought }
SUBJECT TO
acres: { acreage constraints}
SUM(c: pcrop[c]) < TACRES;
balance[c,s]:
YIELD[c,s]*pcrop[c] + bcrop[c] - LCROP[c]*live = csold[c,s];
BOUNDS
bcrop[c] < MAXBUY[c]; WE HAVE TO DO THIS TO DISALLOW BEAN AND SORGHUM BUYS
END





 Предел числовой последовательности. Способы задания числовой последовательности
Предел числовой последовательности. Способы задания числовой последовательности Линейная функция и её график
Линейная функция и её график Задачи теории вероятностей. Повторение к ГИА и ЕГЭ
Задачи теории вероятностей. Повторение к ГИА и ЕГЭ Вынесение общего множителя
Вынесение общего множителя Урок Весёлый математик - 2 класс
Урок Весёлый математик - 2 класс Сравнение, сложение и вычитание дробей с разными знаменателями
Сравнение, сложение и вычитание дробей с разными знаменателями Умножение и деление на 9
Умножение и деление на 9 Свойства логарифмов. Джон Непер (1550-1617)
Свойства логарифмов. Джон Непер (1550-1617) Решение задач на движение
Решение задач на движение Векторное произведение векторов
Векторное произведение векторов презентация КВМ внеклассное мероприятие по математике 4 класс
презентация КВМ внеклассное мероприятие по математике 4 класс Презентация к уроку закрепление умножение и деление на 2
Презентация к уроку закрепление умножение и деление на 2 10 способов решения квадратных уравнений
10 способов решения квадратных уравнений Мәтінді есептерді шығару
Мәтінді есептерді шығару презентация Числа от 1 до 7
презентация Числа от 1 до 7 Определение степени с целым отрицательным показателем. 8 класс
Определение степени с целым отрицательным показателем. 8 класс Алгебра. Исторический очерк
Алгебра. Исторический очерк Деление суммы на число
Деление суммы на число Выражение. Составь выражение
Выражение. Составь выражение Сложение и вычитание алгебраических дробей с разными знаменателями
Сложение и вычитание алгебраических дробей с разными знаменателями презентация по математике Табличное умножение и деление 2 класс
презентация по математике Табличное умножение и деление 2 класс Линейная алгебра. Матрицы
Линейная алгебра. Матрицы Двусвязность. (Лекция 7)
Двусвязность. (Лекция 7) Физминутка в картинках
Физминутка в картинках Определённый интеграл
Определённый интеграл Слагаемое. Компоненты при умножении
Слагаемое. Компоненты при умножении Сложение однозначных чисел с переходом через десяток
Сложение однозначных чисел с переходом через десяток Пропорции» и «Прямая и обратная пропорциональность
Пропорции» и «Прямая и обратная пропорциональность