Содержание
- 2. Learning objectives Explore rewards, reward strategies and their use in organisations Outline how business and reward
- 3. What is reward? Reward refers to all of the monetary, non-monetary & psychological payments that an
- 4. Why are rewards important? Motivation and performance levels Commitment to the organisation Job satisfaction and engagement
- 5. Terminology related to Reward Management Compensation – sometimes used to refer to pay, but more commonly
- 6. Types of rewards Extrinsic reward – Tangible or transactional reward for undertaking work e.g. salary, incentive
- 7. The Reward Strategy This is a business focused statement of the intentions of the organisation concerning
- 8. Management Approach to Reward Generally, the approach to reward strategies adopted by employers takes one of
- 9. Examples of Business Strategy linked to the Reward Strategy thereby achieving integration
- 10. Consider… Which reward goals (when designing the company reward strategy) would be most critical for a
- 11. Research evidence from the CIPD (2008) Drivers of reward strategy Recruit & retain key talent Reward
- 12. Features of an Effective Reward Strategy They have clearly defined goals & well defined link to
- 13. Consider… What the main objectives of employee reward can be from an employer’s point of view
- 14. Objectives of reward systems Employer Perspective Prestige Competition Control Motivation Performance Cost Employee Perspective Purchasing power
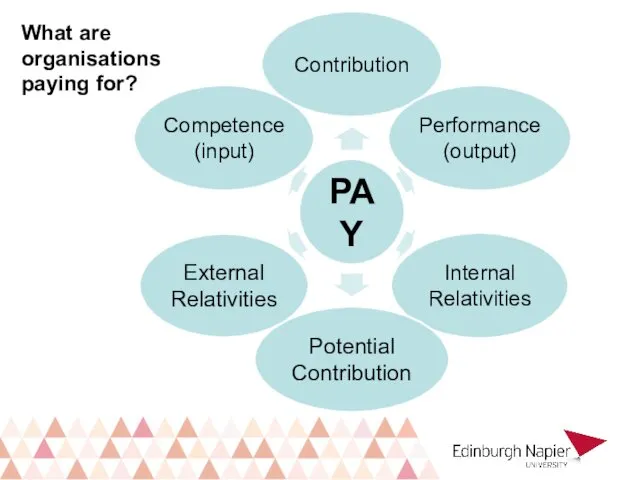
- 15. What are organisations paying for?
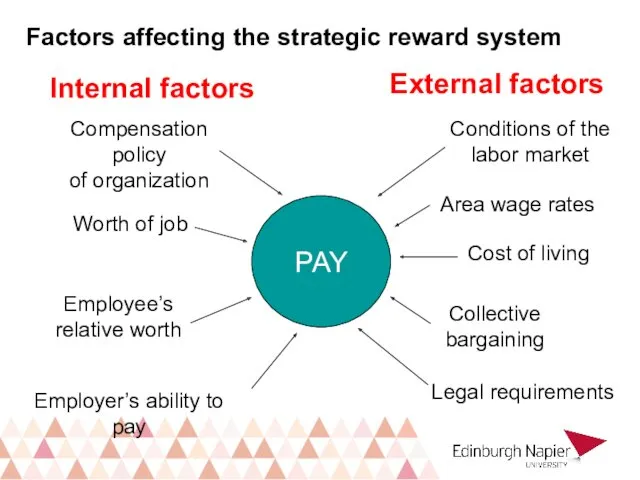
- 16. Factors affecting the strategic reward system PAY Internal factors External factors
- 17. In your opinion… Are these statements correct? Why? Diverse organisational strategies and cultures require different reward
- 18. Common pitfalls of developing reward strategies The organisation focuses on financial incentives and little else Perks
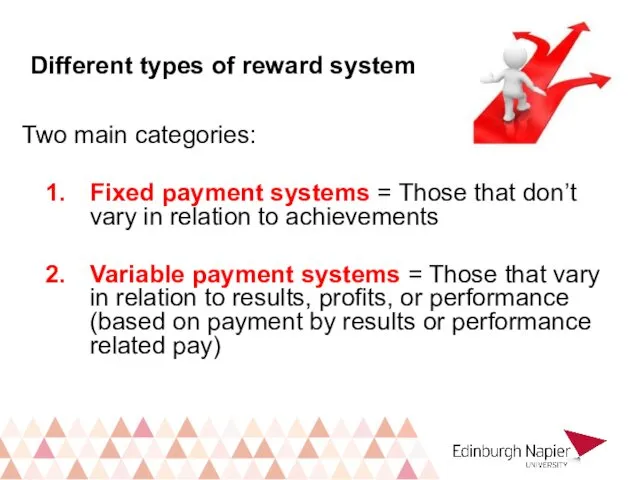
- 19. Different types of reward system Two main categories: Fixed payment systems = Those that don’t vary
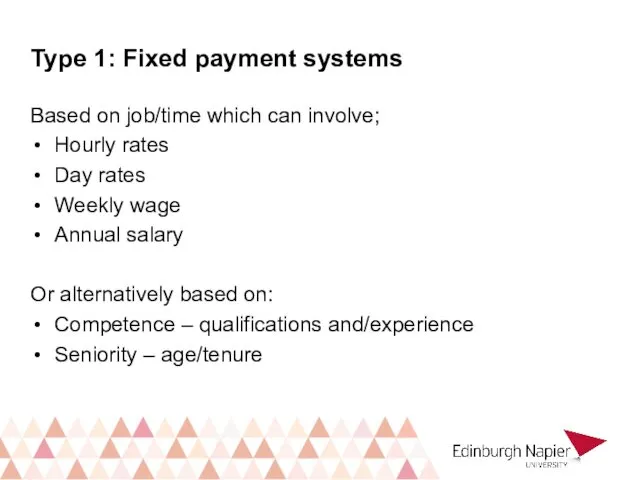
- 20. Type 1: Fixed payment systems Based on job/time which can involve; Hourly rates Day rates Weekly
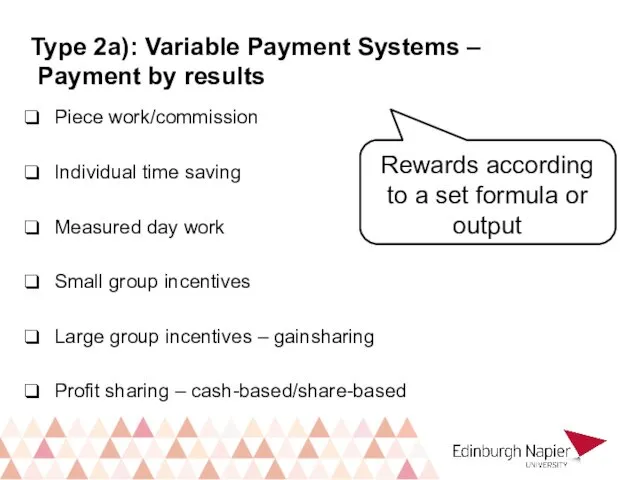
- 21. Type 2a): Variable Payment Systems – Payment by results Piece work/commission Individual time saving Measured day
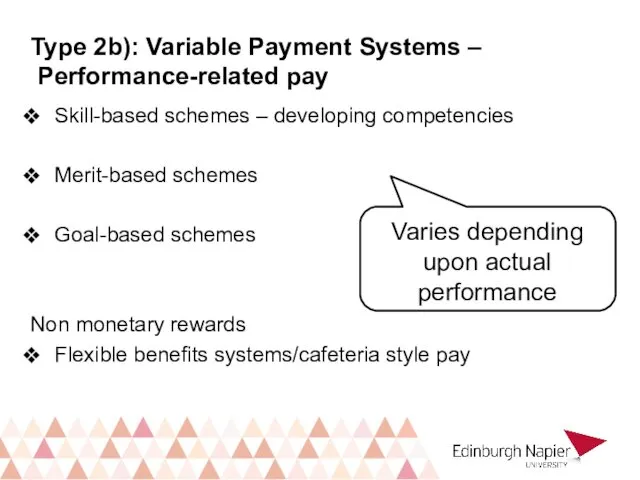
- 22. Skill-based schemes – developing competencies Merit-based schemes Goal-based schemes Non monetary rewards Flexible benefits systems/cafeteria style
- 23. Group Discussion… What are the advantages and disadvantages of performance related payment (PRP) systems?
- 24. Advantages of PRP Employees are able to influence performance by changing their behaviour The reward is
- 25. Total Reward Takes a holistic approach to reward management - ‘extrinsic’ and ‘intrinsic’ rewards Combines a
- 26. Benefits of the Total Reward Approach Increased flexibility – tailored to particular challenges and circumstances Recruitment
- 27. Activity… Review case study – Designing reward systems (Redman and Wilkinson, 2009:170) Are the above companies
- 28. Current trends in UK reward management Organisations are looking at pay structures that promote: Acquisition of
- 29. Source: HayGroup (2011)
- 30. Source: HayGroup (2011)
- 31. Source: HayGroup (2011)
- 33. Скачать презентацию
























 Формы разработки и реализации УР
Формы разработки и реализации УР Планирование, организация, мотивация и контроль как основные функции менеджмента
Планирование, организация, мотивация и контроль как основные функции менеджмента Мотивація для продавців
Мотивація для продавців Баскет-метод
Баскет-метод Постановка целей и методы разработки УР
Постановка целей и методы разработки УР Руководитель в системе управления
Руководитель в системе управления Кадровый резерв
Кадровый резерв Управление стоимостью проекта
Управление стоимостью проекта IT House. Предложение по централизации персонала ИТ в едином офисном пространстве. Ростелеком
IT House. Предложение по централизации персонала ИТ в едином офисном пространстве. Ростелеком Развитие карьеры проектного менеджера. Стратегия и тактика
Развитие карьеры проектного менеджера. Стратегия и тактика Управление персоналом
Управление персоналом Метод Дельфи: история появления, основные правила и приемы, области и примеры применения
Метод Дельфи: история появления, основные правила и приемы, области и примеры применения Инструкция по работе в ПО ВИВА-ЗАЙМЫ для специалистов выездного взыскания
Инструкция по работе в ПО ВИВА-ЗАЙМЫ для специалистов выездного взыскания Определение целей ЗАО Автосервис
Определение целей ЗАО Автосервис Компетентностный подход. Тема 15
Компетентностный подход. Тема 15 Самоменеджмент
Самоменеджмент Исследование причин кризисных явлений в индустрии гостеприимства
Исследование причин кризисных явлений в индустрии гостеприимства Административная и деловая этика. Игра
Административная и деловая этика. Игра Задание для самостоятельной работы
Задание для самостоятельной работы Официально-деловой стиль речи
Официально-деловой стиль речи Повышение качества типографического процесса
Повышение качества типографического процесса Памятка вахтовика
Памятка вахтовика Проявления и классификация инноваций. Лекция 3
Проявления и классификация инноваций. Лекция 3 Модуль Управление персоналом (Нuman Resources). Управление организационными структурами
Модуль Управление персоналом (Нuman Resources). Управление организационными структурами Теоретические основы финансового менеджмента
Теоретические основы финансового менеджмента Экономика туристского рынка
Экономика туристского рынка Enquiry - Quotation - Comparison and Contracting of storage services
Enquiry - Quotation - Comparison and Contracting of storage services Критерии постановки целей производственной стратегии
Критерии постановки целей производственной стратегии