Содержание
- 2. Management & Planning Tools Why Why?? Forced Field Analysis Nominal Group Technique
- 3. Why Why Tool Very simple and effective tool. Focuses on the process rather than on people.
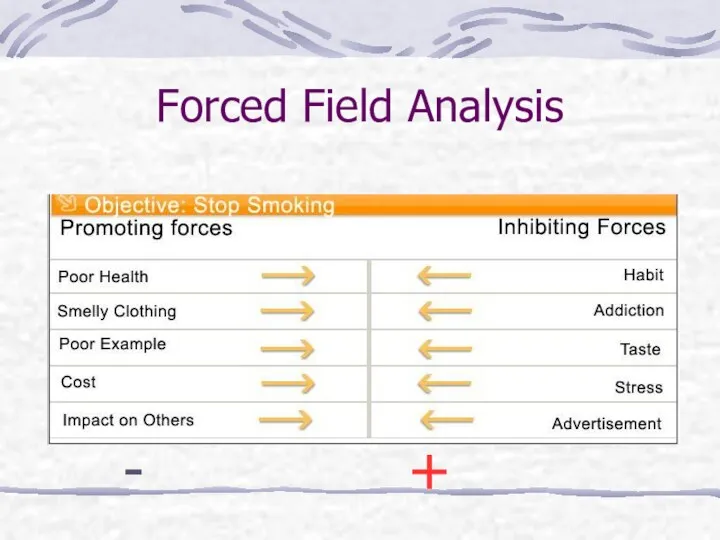
- 4. Forced Field Analysis What it does? How to use it: Define the objective Determine criteria/problem Brainstorm
- 5. Forced Field Analysis - +
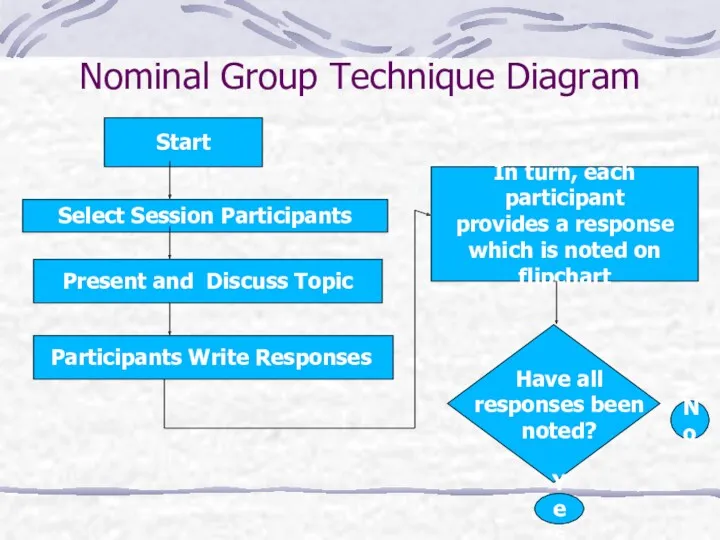
- 6. Nominal Group Technique Developed in 1971 Consensus planning tool Used for: Identifying major strengths Equal opportunity/voice
- 7. Nominal Group Technique Diagram Start Select Session Participants Present and Discuss Topic Participants Write Responses In
- 8. Management & Planning Tools Affinity Diagram Interrelationship Digraph Tree Diagram Matrix Diagram Prioritization Matrices Process Decision
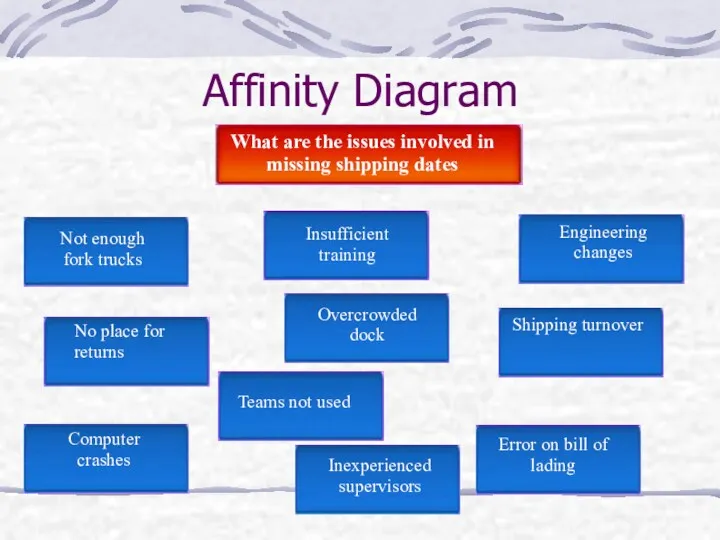
- 9. Affinity Diagram What it does? When to use? Benefits of using The Process State the issue
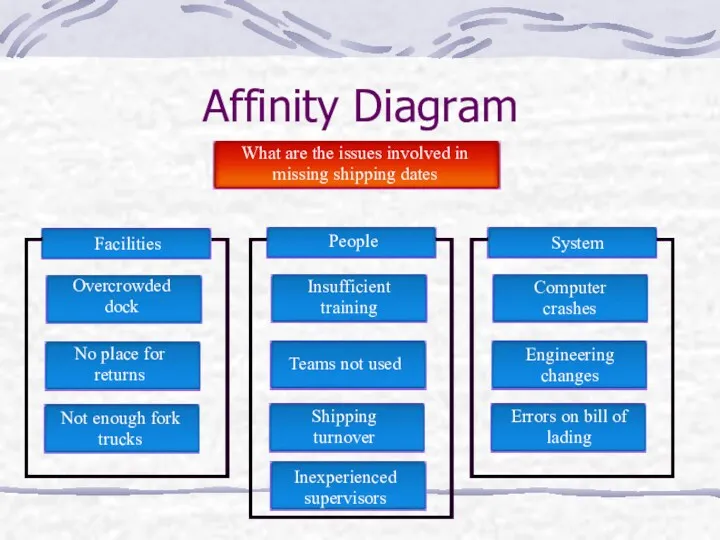
- 10. Affinity Diagram What are the issues involved in missing shipping dates Not enough fork trucks No
- 11. Affinity Diagram Facilities Overcrowded dock No place for returns Not enough fork trucks People Insufficient training
- 12. Affinity Diagram Example
- 13. Interrelationship Digraph Clarifies interrelationship of many factors Classifies cause-and-effect relationships
- 14. The Process: Agree on the issue or question Add a symbol to the diagram Put ideas
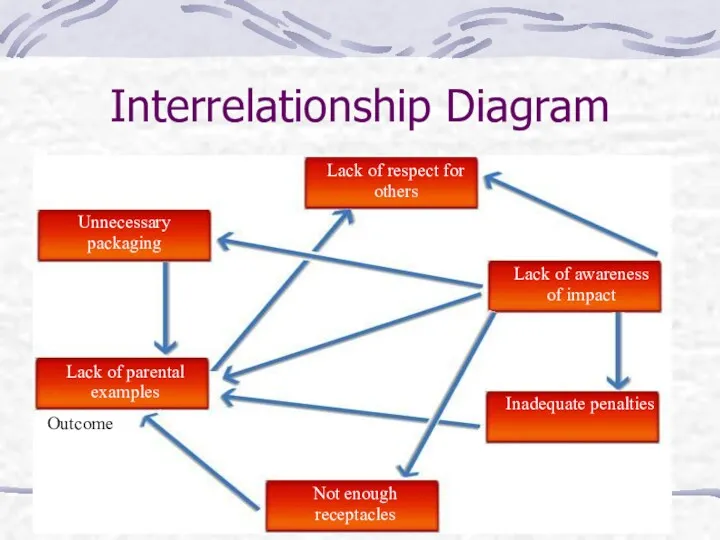
- 15. Interrelationship Diagram Unnecessary packaging Lack of parental examples Not enough receptacles Inadequate penalties Lack of awareness
- 16. Questions Comments
- 17. Tree Diagram Used to reduce encourage team members to think creatively, make large projects manageable and
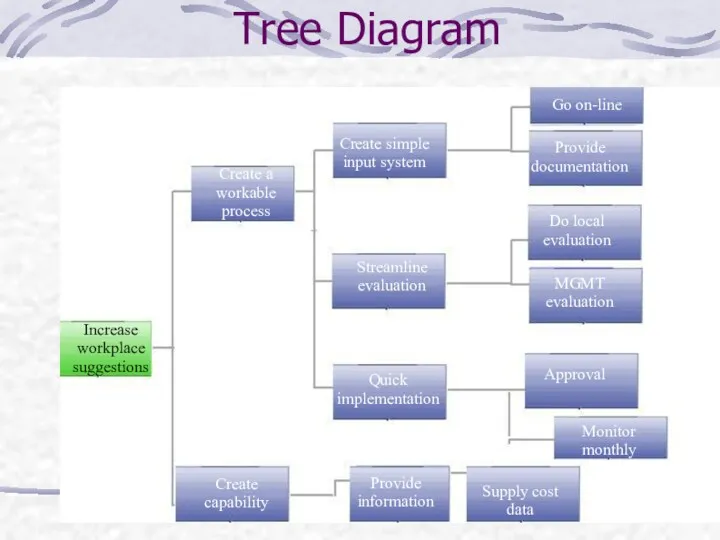
- 18. Tree Diagram Increase workplace suggestions Create a workable process Create simple input system Provide documentation Do
- 19. Matrix Diagram Used to identify, analyze and rate the relationship among two or more variables. Select
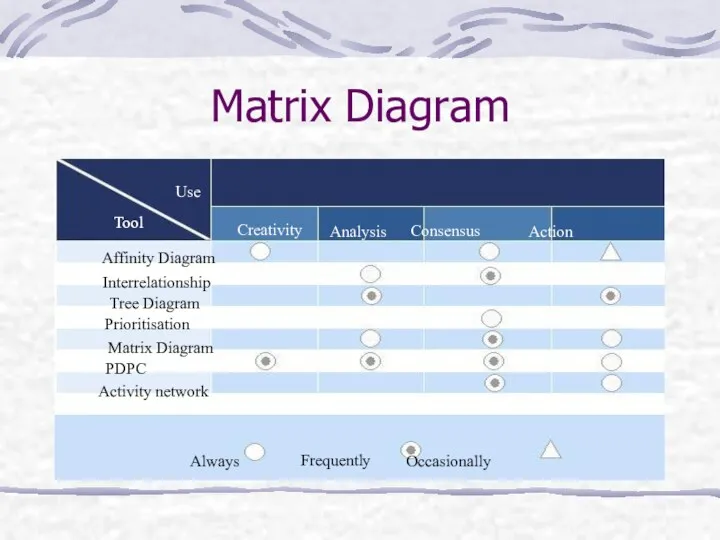
- 20. Matrix Diagram Affinity Diagram Interrelationship Tree Diagram Prioritisation Matrix Diagram PDPC Activity network Tool Use Creativity
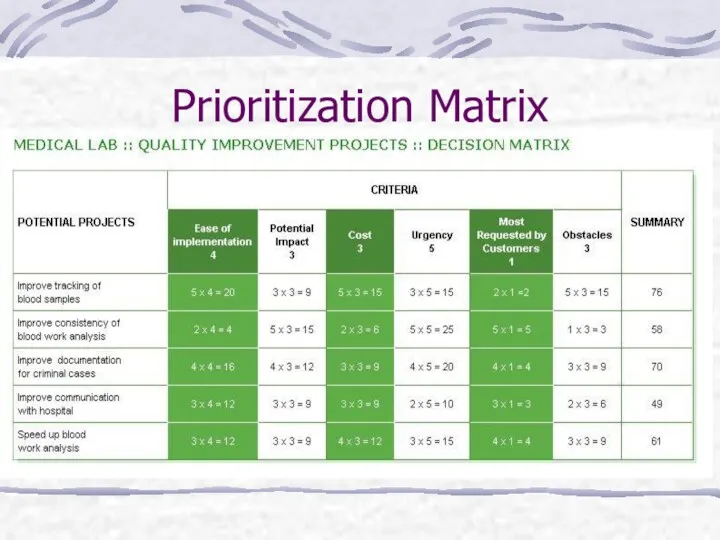
- 21. Prioritization Matrix What it does? When to use it: Broad objectives must be broken down All
- 22. Prioritization Matrix
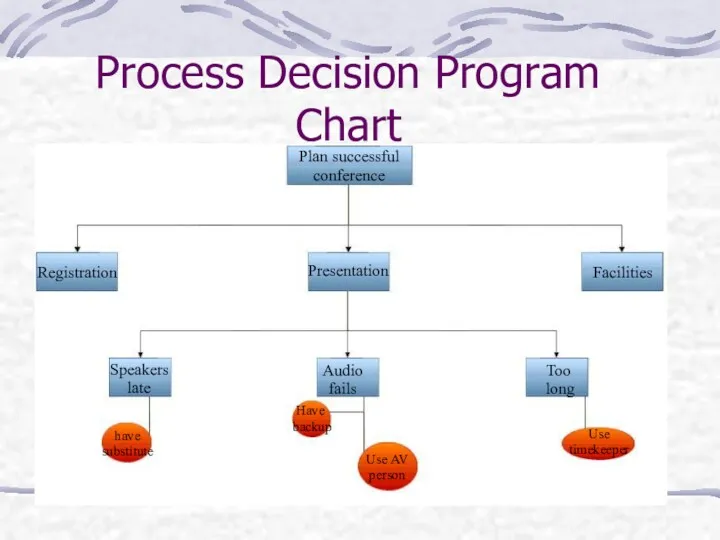
- 23. Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC) What it does? When to use it: The task is new,
- 24. PDPC The process decision program chart is a tool for contingency planning. Helps the user to
- 25. Process Decision Program Chart Plan successful conference Registration Presentation Facilities Speakers late Audio fails Too long
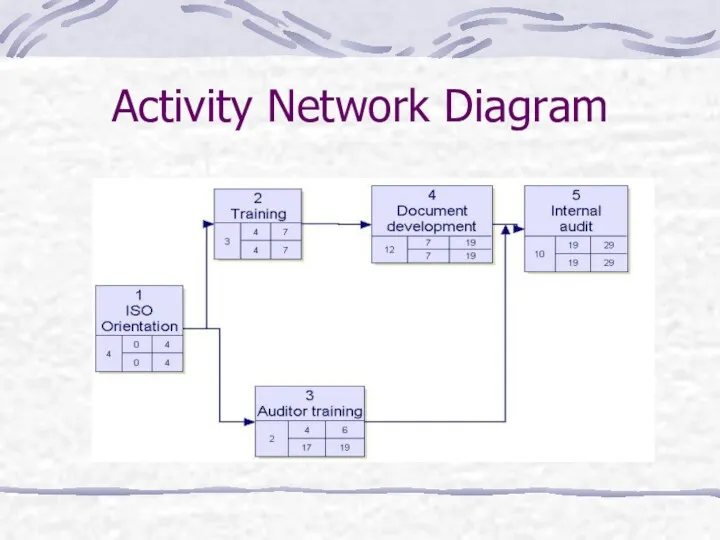
- 26. Activity Network Diagram
- 27. Activity Network Diagram What it does? When to use it: The task is a complex one
- 28. Activity Network Design Some other versions of this method PERT chart Programme evaluation review technique Arrow
- 29. Quality Control Tools Cause & Effect (Fish bone) Flow Chart Run Chart Control Chart Histogram Pareto
- 30. Cause & Effect Diagram
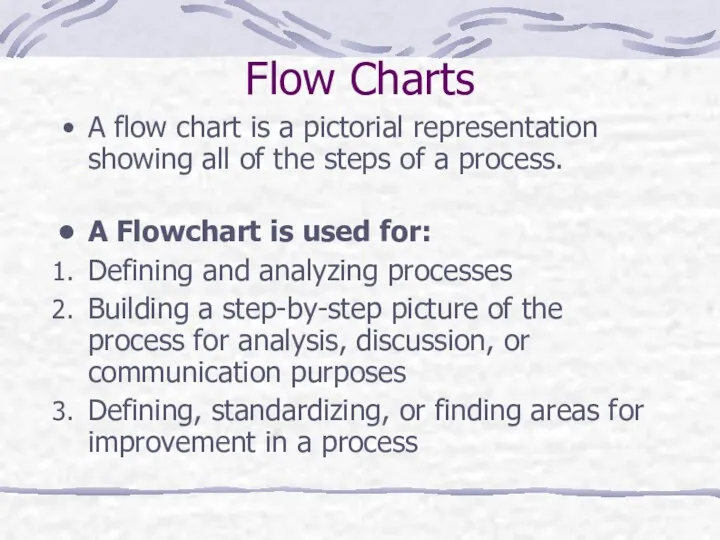
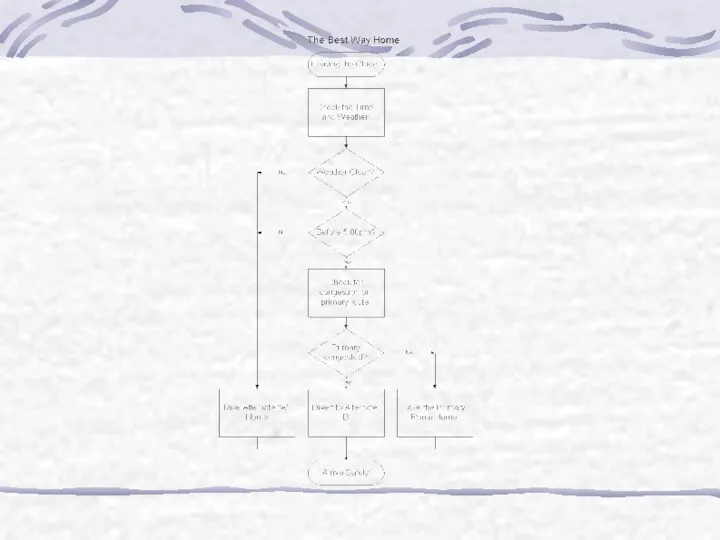
- 31. Flow Charts A flow chart is a pictorial representation showing all of the steps of a
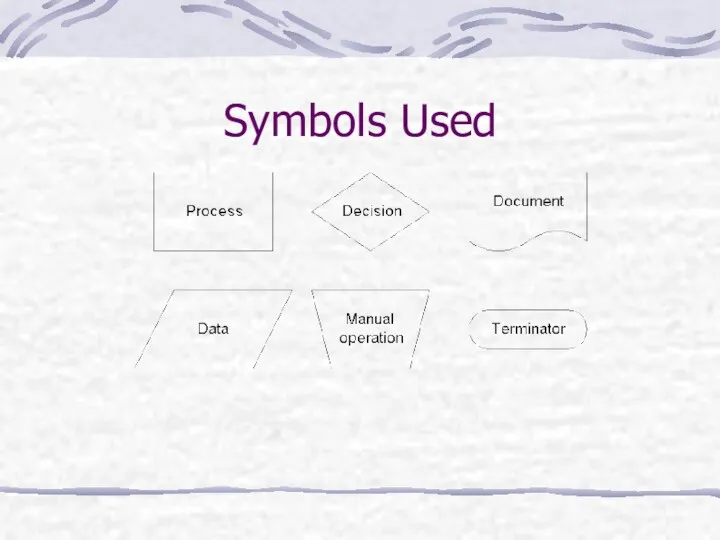
- 32. Symbols Used
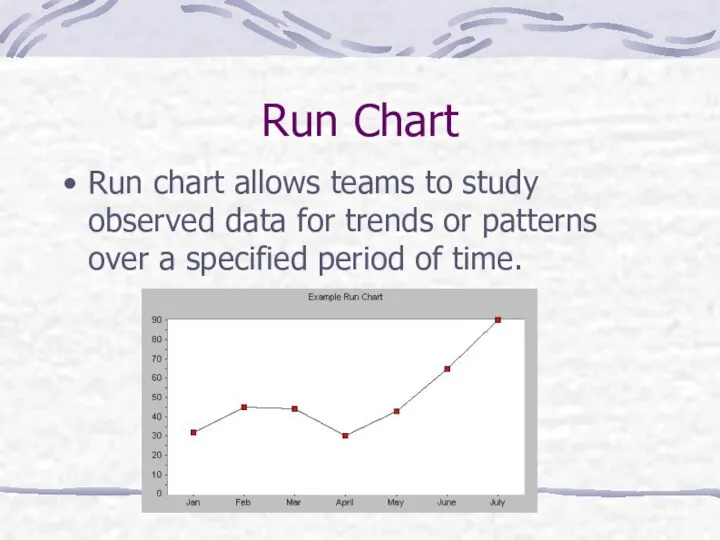
- 34. Run Chart Run chart allows teams to study observed data for trends or patterns over a
- 35. Control Chart A statistical control chart is a graphic comparison of process performance data to computed
- 36. Control Chart Benefits Monitor process variation over time Differentiate between special cause and common cause variation
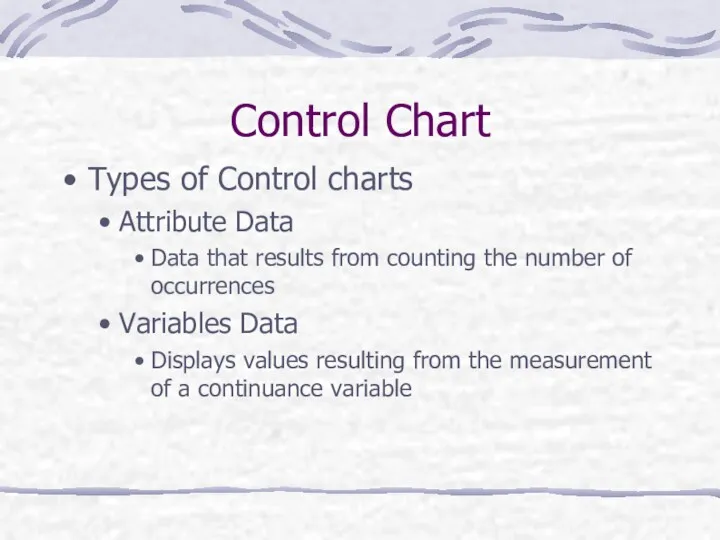
- 37. Control Chart Types of Control charts Attribute Data Data that results from counting the number of
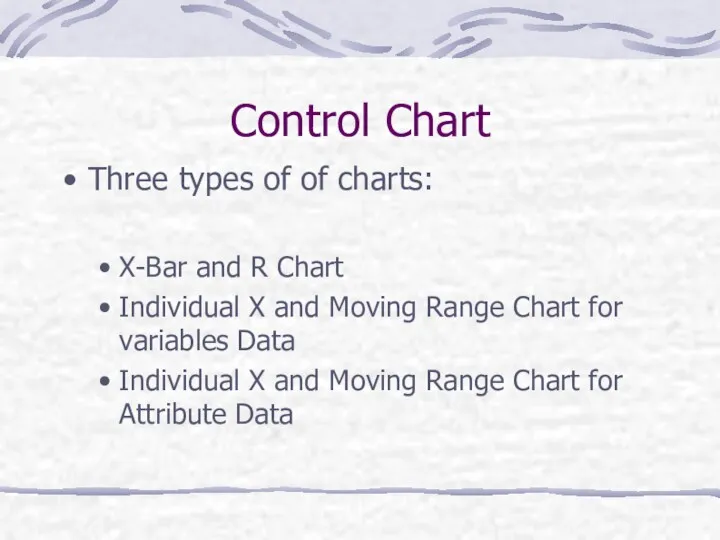
- 38. Control Chart Three types of of charts: X-Bar and R Chart Individual X and Moving Range
- 39. Histogram A histogram is a graphic summary of variation in a set of data Basic data
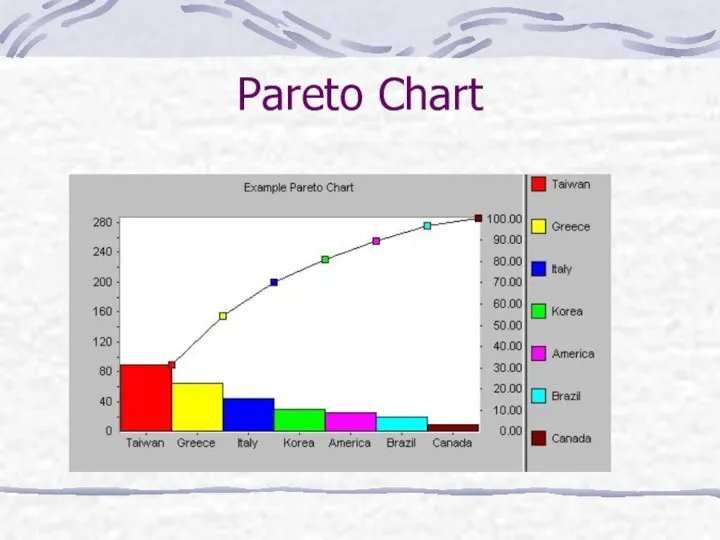
- 40. Pareto Chart Pareto analysis is a ranked comparison of factors related to a quality problem Prioritized
- 41. Pareto Chart
- 42. Creativity Tools Brainwriting 6-3-5 Classic Brainstorming Imaginary Brainstorming Knowledge mapping Morphological Box Picture Associations and Biotechniques
- 44. Скачать презентацию
























 Возникновение и исторические этапы развития научного менеджмента
Возникновение и исторические этапы развития научного менеджмента Система менеджмента качества (СМК)
Система менеджмента качества (СМК) Приглашение - это искусство назначения встреч. Основные правила
Приглашение - это искусство назначения встреч. Основные правила Грейдовые системы оплаты труда и возможность их применения в казахстанских фирмах
Грейдовые системы оплаты труда и возможность их применения в казахстанских фирмах Научные школы на которых базируется стратегическое государственное управление
Научные школы на которых базируется стратегическое государственное управление Басқару және ынтымақтастық
Басқару және ынтымақтастық Управление человеческими ресурсами
Управление человеческими ресурсами Реструктуризация как способ управления стоимостью бизнеса
Реструктуризация как способ управления стоимостью бизнеса Overcoming obstacles. Chapter 12
Overcoming obstacles. Chapter 12 Внутренние стандарты качества в гостиницах
Внутренние стандарты качества в гостиницах Технологические основы принятия управленческих решению
Технологические основы принятия управленческих решению Понятие транспортной организации и транспортного обслуживания
Понятие транспортной организации и транспортного обслуживания Pr-технологии в государственном и муниципальном управлении
Pr-технологии в государственном и муниципальном управлении Планирование задач проекта в Microsoft Office Project
Планирование задач проекта в Microsoft Office Project Инициирование проекта
Инициирование проекта Introduction to Human Resource management
Introduction to Human Resource management Японська модель менеджменту
Японська модель менеджменту Кошачье кафе
Кошачье кафе Складская логистика
Складская логистика Международные тарифы на рынке мультимодальных перевозок
Международные тарифы на рынке мультимодальных перевозок Управление рисками на предприятии (на примере ПАО Биосинтез)
Управление рисками на предприятии (на примере ПАО Биосинтез) Стандарты обслуживания покупателей в магазине
Стандарты обслуживания покупателей в магазине Основы государственного и муниципального управления
Основы государственного и муниципального управления Organizacja jako system otwarty i społeczno-techniczny. (Wyklad 2)
Organizacja jako system otwarty i społeczno-techniczny. (Wyklad 2) Антикризисное управление
Антикризисное управление Менеджмент эволюциясы
Менеджмент эволюциясы Риск-ориентированный подход в DIS ISO 9001:2015
Риск-ориентированный подход в DIS ISO 9001:2015 Методы и средства квалиметрии
Методы и средства квалиметрии