Содержание
- 2. Kingdom Eubacteria (True Bacteria) Bacteria are located everywhere – air, water, land, and living organisms including
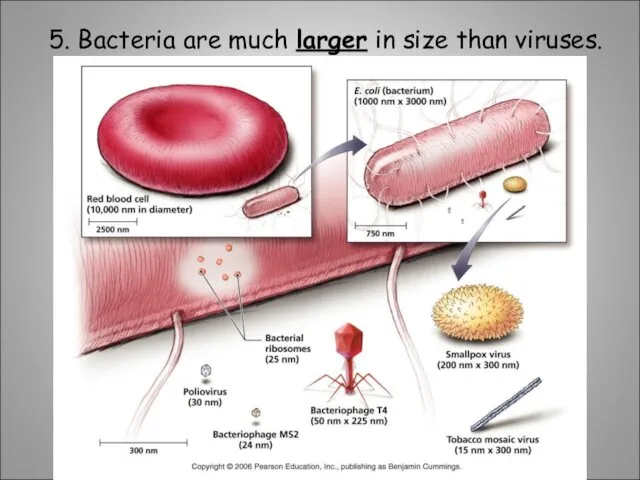
- 3. 5. Bacteria are much larger in size than viruses.
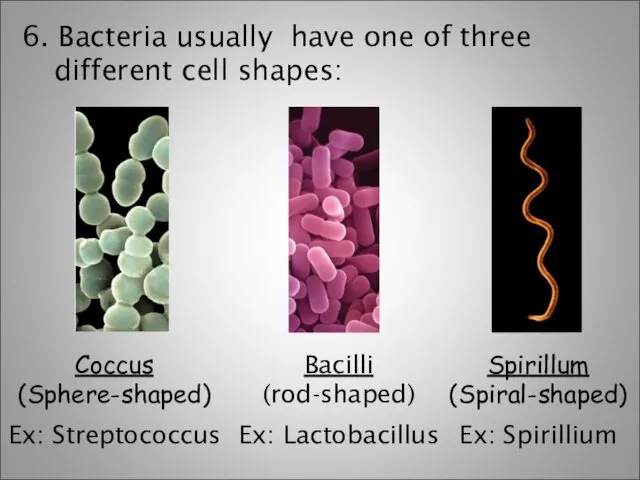
- 4. 6. Bacteria usually have one of three different cell shapes: Coccus (Sphere-shaped) Ex: Streptococcus Bacilli (rod-shaped)
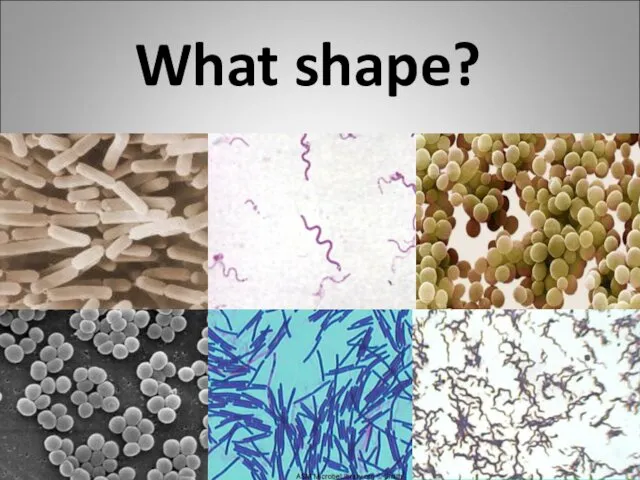
- 5. coccus bacillus spirillum coccus spirillum bacillus What shape?
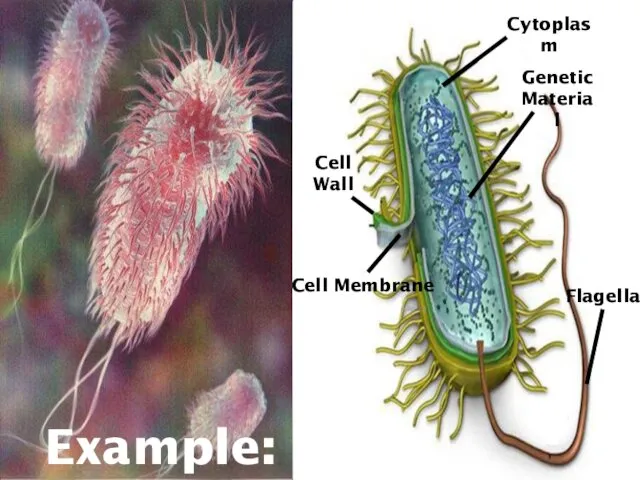
- 6. Example: E. coli
- 7. Causes Disease by: 1. Destroying cells of infected organisms by breaking the cells down for food.
- 8. Releases toxins (poisons) which destroy cells of infected organism. Must have access to new hosts to
- 9. Different Hosts
- 10. D. Importance: 1. Beneficial a. breakdown dead matter to recycle nutrients into ecosystem - decomposers
- 11. Example: Compost piles need microorganisms (ex. bacteria) to decompose (breakdown) matter.
- 12. b. dairy industry - bacteria in 2:08 minute video yogurt, sour cream and cheese
- 13. c. Oil spills - bacteria can digest small oil spills
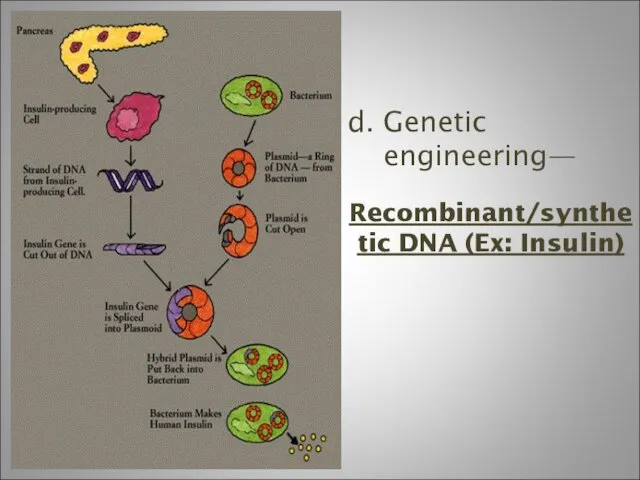
- 14. d. Genetic engineering— Recombinant/synthetic DNA (Ex: Insulin)
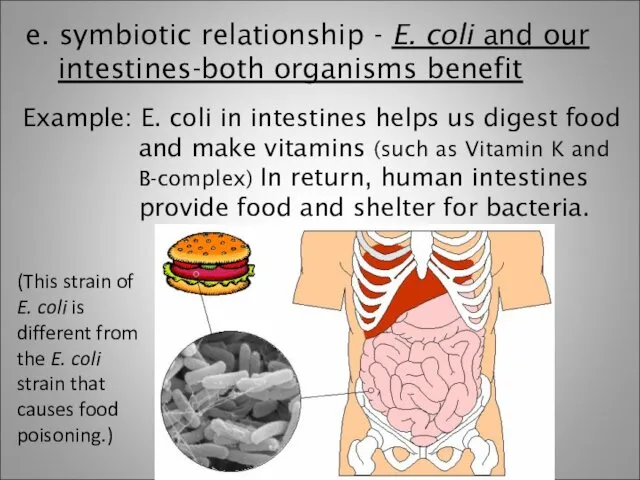
- 15. e. symbiotic relationship - E. coli and our intestines-both organisms benefit Example: E. coli in intestines
- 16. 3:07 minute video
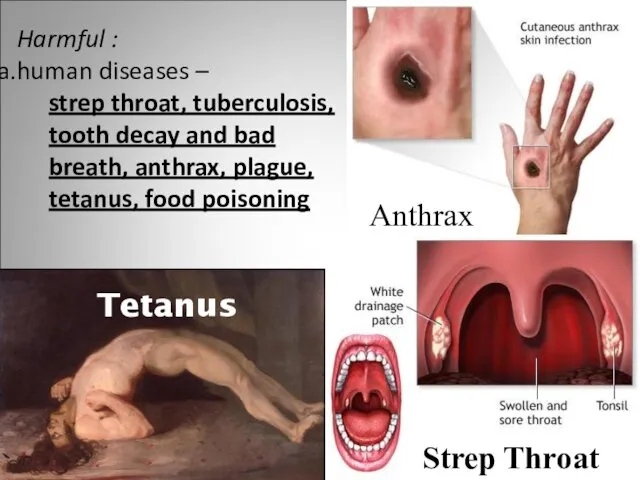
- 17. Harmful : human diseases – strep throat, tuberculosis, tooth decay and bad breath, anthrax, plague, tetanus,
- 18. 3:15 minute video
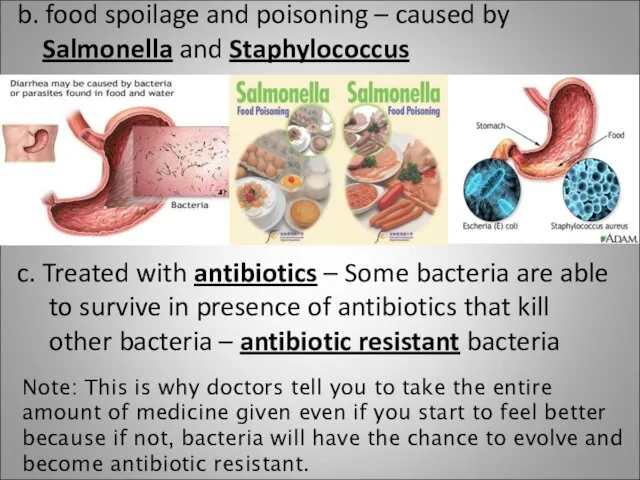
- 19. b. food spoilage and poisoning – caused by Salmonella and Staphylococcus c. Treated with antibiotics –
- 20. Kingdom Archaebacteria First known prokaryotes- Archaebacteria (archae=ancient) b. Live in very harsh environments (known as extremophiles)–
- 21. 3:12 minute video
- 23. Скачать презентацию










 Практ.работа № 7
Практ.работа № 7 Диспансеризация населения: методология и современные подходы
Диспансеризация населения: методология и современные подходы портфолио
портфолио Конструктивные дефекты швейных изделий
Конструктивные дефекты швейных изделий Взаимные положения прямой и плоскости, двух плоскостей. (Лекция 5)
Взаимные положения прямой и плоскости, двух плоскостей. (Лекция 5) Урок ИКН в 7 классе Тема: Марийский край и губернские реформы XVIII века. Гербы городов
Урок ИКН в 7 классе Тема: Марийский край и губернские реформы XVIII века. Гербы городов Лайфхаки семейной жизни от современных психологов
Лайфхаки семейной жизни от современных психологов освобождение Воронежа
освобождение Воронежа Podstawy finansów. Rachunek wyników
Podstawy finansów. Rachunek wyników Электронная система зажигания
Электронная система зажигания Презентация во 2 классе на тему Моя семья
Презентация во 2 классе на тему Моя семья Однородные члены предложения. Пунктуация
Однородные члены предложения. Пунктуация Общая характеристика металлов IА группы ПСХЭ Д.И. Менделеева
Общая характеристика металлов IА группы ПСХЭ Д.И. Менделеева Интеграция образовательных областей по приобщению детей к народной мордовской игровой культуре
Интеграция образовательных областей по приобщению детей к народной мордовской игровой культуре Подготовка к выполнению части 2 ЕГЭ по обществознанию
Подготовка к выполнению части 2 ЕГЭ по обществознанию Разработки уроков
Разработки уроков Приливные электростанции
Приливные электростанции Спортивный комплекс Крылатское
Спортивный комплекс Крылатское Проект День Светлой Пасхи
Проект День Светлой Пасхи Проведение расчетов с бюджетом и внебюджетными фондами. Федеральное агентство по рыболовству БГАРФ ФГБОУ ВО КГТУ
Проведение расчетов с бюджетом и внебюджетными фондами. Федеральное агентство по рыболовству БГАРФ ФГБОУ ВО КГТУ Презентация Пушкарева Татьяна Павловна. Портфолио учителя
Презентация Пушкарева Татьяна Павловна. Портфолио учителя Презентация День Победы
Презентация День Победы Система NTSC
Система NTSC Комплексная автоматизация технологического процесса компании ООО Дионис
Комплексная автоматизация технологического процесса компании ООО Дионис Религиоведение. Предмет, цель и задачи курса
Религиоведение. Предмет, цель и задачи курса Етті өңдейтің өнеркәсіптердің маңызы және сою цехы
Етті өңдейтің өнеркәсіптердің маңызы және сою цехы Заполнители из природных плотных каменных пород
Заполнители из природных плотных каменных пород Культура эпохи Мэйдзи
Культура эпохи Мэйдзи