Содержание
- 2. About Transforming Technologies Transforming Technologies is a leading solution provider for static control in the electronics
- 3. ESD definition Common causes of ESD Sources of ESD Types of ESD damage What is ESD?
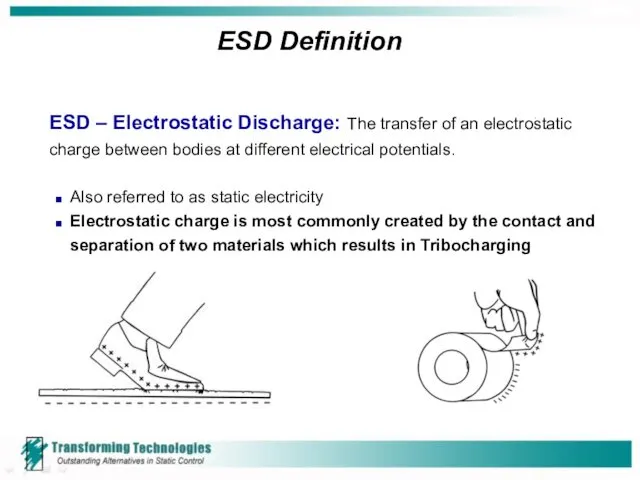
- 4. ESD Definition ESD – Electrostatic Discharge: The transfer of an electrostatic charge between bodies at different
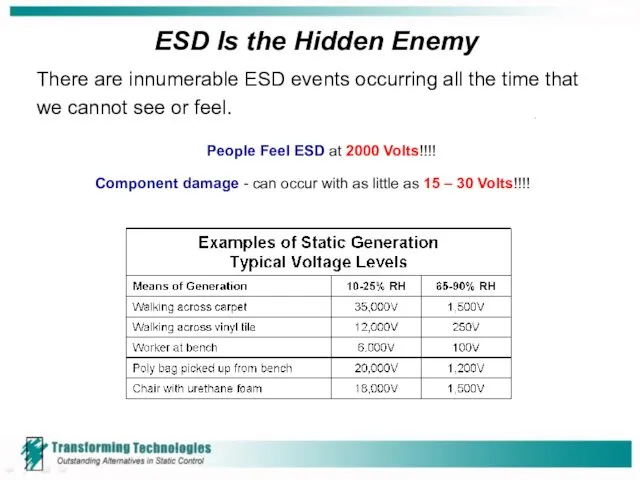
- 5. ESD Is the Hidden Enemy There are innumerable ESD events occurring all the time that we
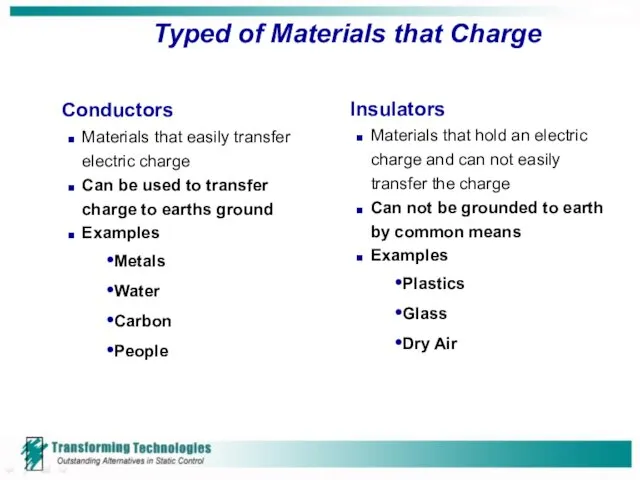
- 6. Typed of Materials that Charge Conductors Materials that easily transfer electric charge Can be used to
- 7. Sources of ESD Vinyl binders Equipment covers Plastic document holders/sheet protectors Post-ItTM notes Plastic pens Bubble
- 8. What type of Materials are ESD Sensitive? ESDS – Electrostatic Discharge Sensitive Integrated Circuits (DIPs, QFP,
- 9. Common Causes of ESD Opening a common plastic bag Removing adhesive tape from a roll or
- 10. Types of ESD Damage CATASTROPHIC FAILURE A device is exposed to ESD and it no longer
- 11. Example of ESD Damage Optical photo of a large Integrated Circuit which has experienced ESD damage
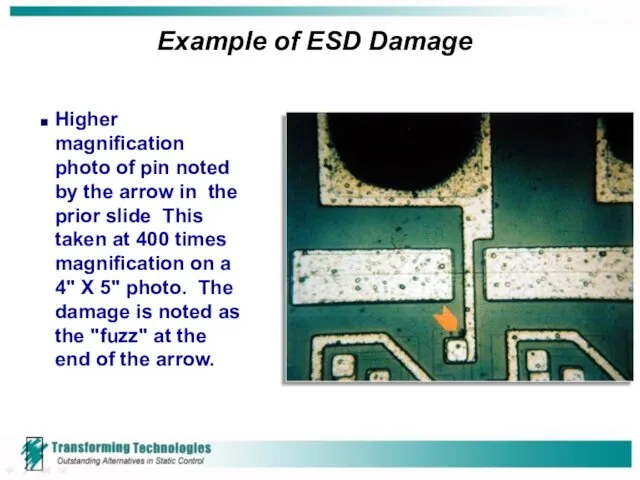
- 12. Example of ESD Damage Higher magnification photo of pin noted by the arrow in the prior
- 13. Example of ESD Damage Overlying glassivation has been removed and the surface decorated to show the
- 14. Why is ESD Important? Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) can damage sensitive electronic devices, resulting in: Higher manufacturing
- 15. How to control ESD? ESD Training ESD Control Areas Ground Conductors Ionization ESDS Component Handling and
- 16. ESD Control Program Proper use of personal grounding equipment such as heel grounders or wrist straps
- 17. ESD Control Program Any area where unprotected ESD sensitive parts and assemblies may be handled shall
- 18. Create an ESD Control Area Any area where unprotected ESDS parts and assemblies may be handled
- 19. ESD Control Program Cont. All Conductors within the EPA must be grounded Personal Grounding: All personnel,
- 20. Personal Grounding Wrist Straps and Coil Cords Wrist Straps ground personnel at workstations Heel Grounders Ground
- 21. Personal Grounding All Personal Grounding Equipment Should be Tested or Monitored Daily Wrist Strap and Footwear
- 22. Equipment Grounding Work Stations and Tables Must have static dissipative surfaces connected to the building ground
- 23. Equipment Grounding Shelving and Cabinets Must provide a grounded surface unless the parts remain fully enclosed
- 24. Ionization Many times, equipment or objects(insulators) are unable to be grounded in which case air ionizers
- 25. Types of Air Ionizers Bench Top Ionizing Nozzles Air Guns Overhead Ionizers
- 26. ESDS Component Handling and Storage To move ESDS parts or assemblies inside an ESD control area,
- 27. ESD Basics Review Things to remember about an ESD protection plan. Only allow trained or escorted
- 29. Скачать презентацию





















 Возникновение аниме
Возникновение аниме Технологія виробництва м'яса качок
Технологія виробництва м'яса качок Азбука дорожного движения
Азбука дорожного движения Прикидка результата действия.
Прикидка результата действия. Системы управления электроснабжением
Системы управления электроснабжением Формирование учетной политики организации
Формирование учетной политики организации State of connecticut department of education department of developmental services
State of connecticut department of education department of developmental services Анализ усилительного каскада
Анализ усилительного каскада презентация к уроку технологии плетение Диск
презентация к уроку технологии плетение Диск Индустриальная революция: достижения и проблемы
Индустриальная революция: достижения и проблемы Адвокат-профессия известная с древнейших времён
Адвокат-профессия известная с древнейших времён Грибы
Грибы Пояснительная записка. Южная специализированная производственная база БЕ 2901
Пояснительная записка. Южная специализированная производственная база БЕ 2901 Проектирование технологического процесса
Проектирование технологического процесса Щелочноземельные металлы
Щелочноземельные металлы Кроссворд Угадай-ка
Кроссворд Угадай-ка Непроизносимый согласный звук. Методика обучения правописанию. Непроизносимый согласный в корне слова
Непроизносимый согласный звук. Методика обучения правописанию. Непроизносимый согласный в корне слова История развития акушерства
История развития акушерства Презентация Значение имени (мальчики)
Презентация Значение имени (мальчики) Мышцы живота
Мышцы живота Прекращение обязательств
Прекращение обязательств Эффективность производства мороженных рыбных котлет
Эффективность производства мороженных рыбных котлет Компоненты СВЧ. Особенности волн СВЧ диапазона
Компоненты СВЧ. Особенности волн СВЧ диапазона Родительское собрание 4 класс Здоровое питание
Родительское собрание 4 класс Здоровое питание Функциональды диагностикалық тест
Функциональды диагностикалық тест Презентация Блокада.
Презентация Блокада. Ботаника. Тесты
Ботаника. Тесты Презентация рабочей программы Обучаем бережно в соответствии с ФГОС ДО
Презентация рабочей программы Обучаем бережно в соответствии с ФГОС ДО