Содержание
- 2. Agenda Definition and Basic Characteristics of Insurance Characteristics of An Ideally Insurable Risk Adverse Selection and
- 3. Definition of Insurance Insurance is the pooling of fortuitous losses by transfer of such risks to
- 4. Basic Characteristics of Insurance Pooling of losses Pooling involves spreading losses incurred by the few over
- 5. Basic Characteristics of Insurance (Continued) Example of Pooling: Two business owners own identical buildings valued at
- 6. Basic Characteristics of Insurance (Continued) Example, continued: If the owners instead pool (combine) their loss exposures,
- 7. Basic Characteristics of Insurance (Continued) Payment of fortuitous losses A fortuitous loss is one that is
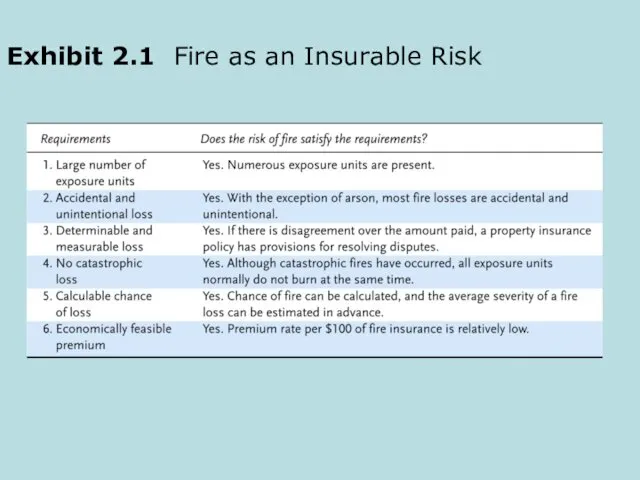
- 8. Characteristics of an Ideally Insurable Risk Large number of exposure units to predict average loss based
- 9. Characteristics of an Ideally Insurable Risk (Continued) No catastrophic loss to allow the pooling technique to
- 10. Economically feasible premium so people can afford to purchase the policy For insurance to be an
- 11. Exhibit 2.1 Fire as an Insurable Risk
- 12. Exhibit 2.2 Unemployment as an Insurable Risk
- 13. Adverse Selection and Insurance Adverse selection is the tendency of persons with a higher-than-average chance of
- 14. Insurance vs. Gambling Insurance Handles an already existing pure risk Is always socially productive: both parties
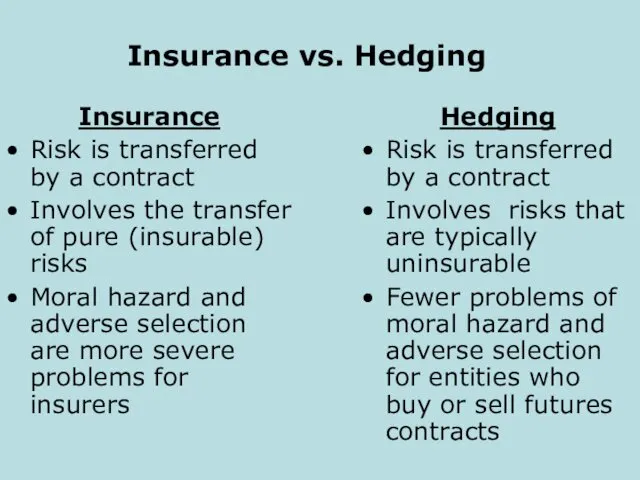
- 15. Insurance vs. Hedging Insurance Risk is transferred by a contract Involves the transfer of pure (insurable)
- 16. Types of Private Insurance Life and Health Life insurance pays death benefits to beneficiaries when the
- 17. Types of Private Insurance (Continued) Property and Liability Property insurance indemnifies property owners against the loss
- 18. Types of Private Insurance (Continued) Private insurance coverages can be grouped into two major categories Personal
- 19. Types of Government Insurance Social Insurance Programs Financed entirely or in large part by contributions from
- 20. Social Benefits of Insurance Indemnification for Loss Reduction of Worry and Fear Source of Investment Funds
- 22. Скачать презентацию

















 Основы инвестиционного анализа
Основы инвестиционного анализа Поняття та класифікація фінансового посередництва
Поняття та класифікація фінансового посередництва Оценка расходов на построение сети
Оценка расходов на построение сети Управление рисками
Управление рисками Бюджет для граждан (2021-2023)
Бюджет для граждан (2021-2023) Ақша-несие саясаты
Ақша-несие саясаты Банк ВТБ24
Банк ВТБ24 World Way Capital
World Way Capital Оценка стоимости бизнеса. Массажный салон ООО Лакшми
Оценка стоимости бизнеса. Массажный салон ООО Лакшми МСФО 1. Представление финансовой отчетности
МСФО 1. Представление финансовой отчетности Основы криптовалют и технологии блокчейн
Основы криптовалют и технологии блокчейн ТОВ Експертфінанс. Послуги на аутсорсинг
ТОВ Експертфінанс. Послуги на аутсорсинг Организация бухгалтерского и налогового учета готовой продукции в АО Тайфун
Организация бухгалтерского и налогового учета готовой продукции в АО Тайфун Новый формат проведения профессионального конкурса по 1С:Бухгалтерии 8: мастер-класс
Новый формат проведения профессионального конкурса по 1С:Бухгалтерии 8: мастер-класс Банковская система России: современные проблемы и перспективы развития
Банковская система России: современные проблемы и перспективы развития Добровольное медицинское страхование. Налоговые льготы
Добровольное медицинское страхование. Налоговые льготы Основные задачи и функции Федеральной налоговой службы
Основные задачи и функции Федеральной налоговой службы Акцизний податок
Акцизний податок Прошлое и будущее международной валютной системы
Прошлое и будущее международной валютной системы Автоматизированные банковские системы
Автоматизированные банковские системы Облік і звітність в оподаткуванні діяльності підприємств
Облік і звітність в оподаткуванні діяльності підприємств Материально-техническая база заготовок. Модуль 7
Материально-техническая база заготовок. Модуль 7 Принципы оценочной деятельности
Принципы оценочной деятельности Облік власного капіталу
Облік власного капіталу Экономическое содержание проектного финансирования
Экономическое содержание проектного финансирования Банкноти України
Банкноти України Обеспечительные меры
Обеспечительные меры Создание скоринговой модели в Ms Excel
Создание скоринговой модели в Ms Excel