Содержание
- 2. Outline Introduction Main part 1. Sulfur 2. Hydrogen sulfide and sulfides 3. Sulfur (IV) oxide, sulfurous
- 4. 1. Sulfur Chemical element Sulfur is a chemical element number 16. It is located in group
- 5. 1. Sulfur Chemical element In the earth's crust, sulfur is found in native form or in
- 6. 1. Sulfur Chemical element Sulfur belongs to the macronutrients of living organisms. It is found in
- 7. 1. Sulfur Simple substance Sulfur forms several allotropic modifications. Usually we are dealing with crystalline sulfur,
- 8. 1. Sulfur Simple substance When heated, sulfur melts, turns into a light liquid, and then begins
- 9. 1. Sulfur Simple substance Sulfur exhibits oxidizing properties in reactions with metals and hydrogen. Reacts with
- 10. 1. Sulfur Simple substance When heated, sulfur reacts with most metals - iron, aluminum, zinc and
- 11. 1. Sulfur Simple substance Sulfur application -Used in the chemical industry for the production of sulfuric
- 12. 2. Hydrogen sulfide and sulfides Hydrogen sulfide Hydrogen sulfide H2S is a colorless gas with an
- 13. 2. Hydrogen sulfide and sulfides Hydrogen sulfide In redox reactions, hydrogen sulfide exhibits strong reducing properties
- 14. 2. Hydrogen sulfide and sulfides Hydrosulfuric acid A solution of hydrogen sulfide in water is called
- 15. 2. Hydrogen sulfide and sulfides Hydrogen sulfide salts Medium salts of hydrogen sulfide are called sulfides.
- 16. 3. Sulfur (IV) oxide, sulfurous acid, sulfites Sulfur (IV) oxide Sulfur (IV) oxide, is formed during
- 17. 3. Sulfur (IV) oxide, sulfurous acid, sulfites Sulfur (IV) oxide Sulfur (IV) oxide also exhibits other
- 18. 3. Sulfur (IV) oxide, sulfurous acid, sulfites Sulfur (IV) oxide Sulfur dioxide exhibits oxidizing properties in
- 20. Sulfurous acid and its salts Sulfurous acid H2SO3 is an aqueous solution of sulfur (IV) oxide
- 21. Application Sulfur dioxide destroys microorganisms, therefore it is used for disinfection of premises and equipment. It
- 22. Sulfur (VI) oxide Sulfur oxide (VI) is formed during the catalytic oxidation of sulfur dioxide: t,
- 23. Sulfur (VI) oxide A feature of sulfur (VI) oxide is its ability to dissolve in concentrated
- 24. Sulfuric acid Sulfuric acid H2SO4 is the most important sulfur compound. Pure sulfuric acid is a
- 26. Sulfuric acid Sulfuric acid is very hygroscopic and is used to dry various substances.The chemical properties
- 27. Sulfuric acid Diluted acid reacts only with metals, located in the row of activity before hydrogen.
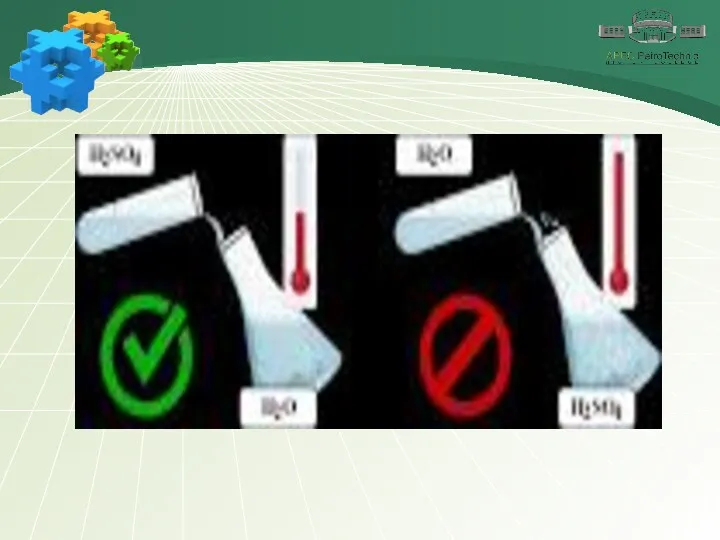
- 28. Sulfuric acid Pay attention! At low temperatures, iron and aluminum passivates and does not react with
- 29. Sulfuric acid Sugar Time : 0s Time: 15s Time: 60s
- 30. Sulfuric acid salts Sulfuric acid forms two series of salts. Medium salts are called sulfates (Na2SO4,
- 31. Application Sulfuric acid is one of the most important chemicals. It is used: to obtain other
- 32. The contact method of production of the sulfuric acid https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bu3ns9Ii80M
- 33. Questions for selfcontrol: 1.Note the name of the substance with the composition CaS: A)calcium hydrosulfite B)calcium
- 34. 5.Choose the characteristic of sulfur: A)in thick layers is purple B)not wetted with water C)obtained in
- 35. 8.Diluted sulfuric acid differs from concentrated sulfuric acid: A) By the ability to displace all other
- 36. 11.Only concentrated sulfuric acid reacts with all substances of the series: A)CO2, CO, NO B)Fe2O3, FeO,
- 37. Literature 1.Basic literature : 1. Jenkins, Chemistry, ISBN 978-0-17-628930-0 2. Alberta Learning, Chemistry data booklet 2010,
- 38. 2.Additional literature : 1.Б.А.Мансуров «Химия» 10-11 кл., Атамура 2015 г 2.Б.Мансуров., Н.Торшина «Методика преподавания органической химии»
- 40. Скачать презентацию


































 Сахар - вред или польза?
Сахар - вред или польза? Evolution of Isoconversional Methods
Evolution of Isoconversional Methods Кислородсодержащие соединения серы. Оксиды серы
Кислородсодержащие соединения серы. Оксиды серы Простые вещества металлы
Простые вещества металлы Химическая стойкость тугоплавких металлов в различных реагентах
Химическая стойкость тугоплавких металлов в различных реагентах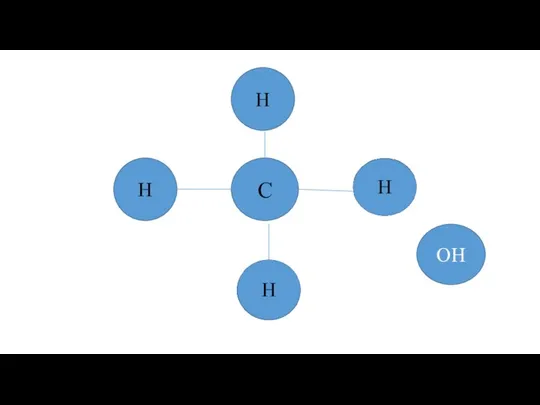 Предельные одноатомные спирты
Предельные одноатомные спирты Геохимическая классификация элементов
Геохимическая классификация элементов Химические реакции. Реакции разложения
Химические реакции. Реакции разложения Магній. Знаходження в періодичній системі і основні характеристики
Магній. Знаходження в періодичній системі і основні характеристики Количественный учет влияния заместителя на реакционную способность и его использование для интерпретации механизмов реакций
Количественный учет влияния заместителя на реакционную способность и его использование для интерпретации механизмов реакций Мұнай. Мұнайдың шығу тарихы
Мұнай. Мұнайдың шығу тарихы Пестициды. Лекция
Пестициды. Лекция Предмет и задачи химии. Вещества и их свойства (продолжение)
Предмет и задачи химии. Вещества и их свойства (продолжение) Анионы. Группы анионов
Анионы. Группы анионов Кислородсодержащие соединения серы
Кислородсодержащие соединения серы Лигандообменные равновесия и процессы. Строение комплексных соединений
Лигандообменные равновесия и процессы. Строение комплексных соединений Стронций
Стронций Классификация химических реакций
Классификация химических реакций 20231012_metally.fizicheskie_svoystva
20231012_metally.fizicheskie_svoystva Матеріальний баланс процесу горіння
Матеріальний баланс процесу горіння Химические аспекты метаболизма лекарственных препаратов
Химические аспекты метаболизма лекарственных препаратов Атомно-кристаллическое строение материалов
Атомно-кристаллическое строение материалов Щелочноземельные металлы
Щелочноземельные металлы Электролитическая диссоциация
Электролитическая диссоциация Алкани, насичені вуглеводні
Алкани, насичені вуглеводні Особенности строения, реакционной способности и методы синтеза гидроксилсодержащих соединений
Особенности строения, реакционной способности и методы синтеза гидроксилсодержащих соединений Количество вещества. 8 класс
Количество вещества. 8 класс Химические волокна (7 класс)
Химические волокна (7 класс)