Theories of acids and bases. Ionic equilibria in electrolyte solutions. Buffer solutions (topic 3.4) презентация
Содержание
- 2. Outline Introduction Main part 1. Theories of acids and bases. 2. Ionic equilibria in electrolyte solutions.
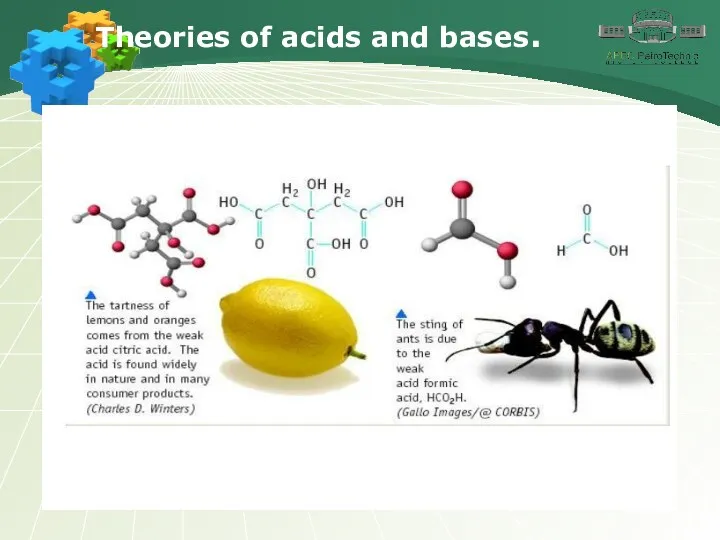
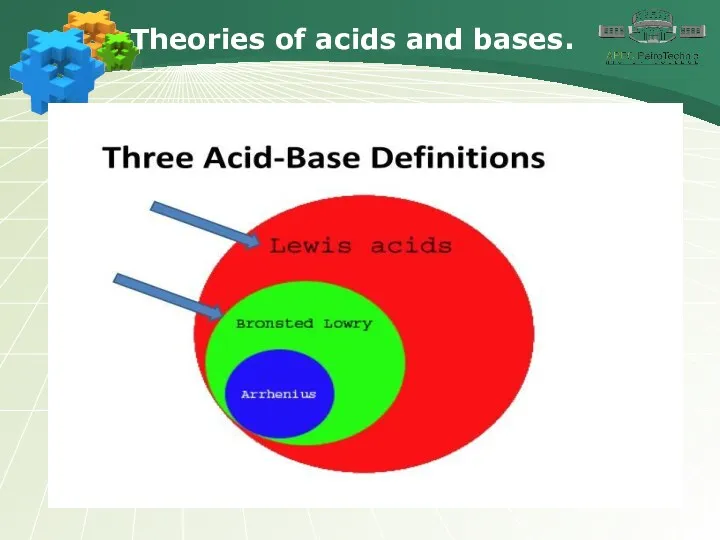
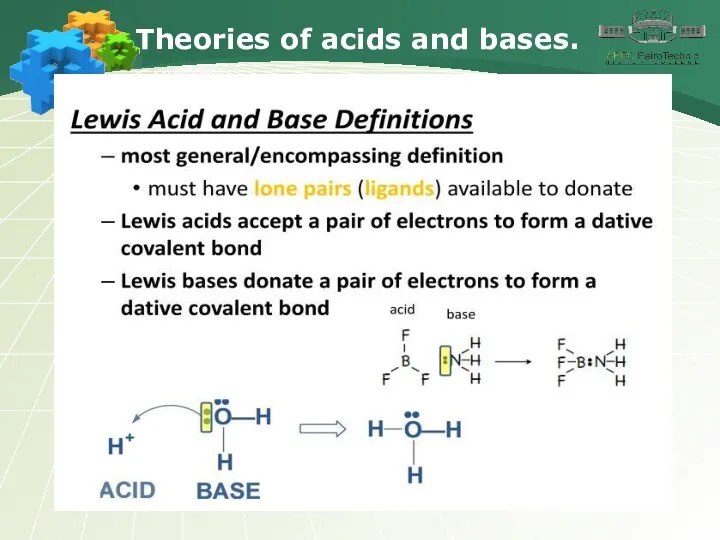
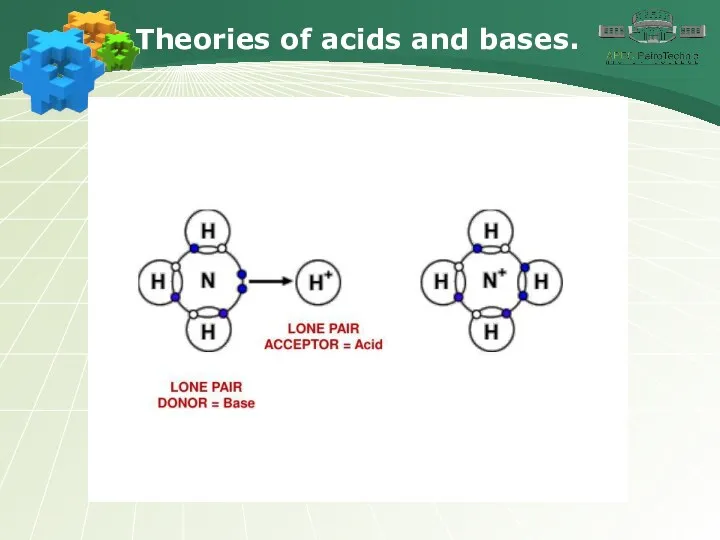
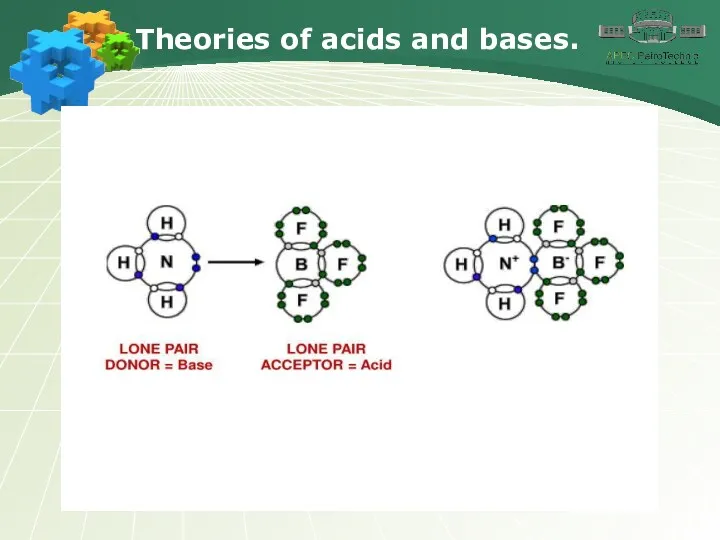
- 3. Theories of acids and bases.
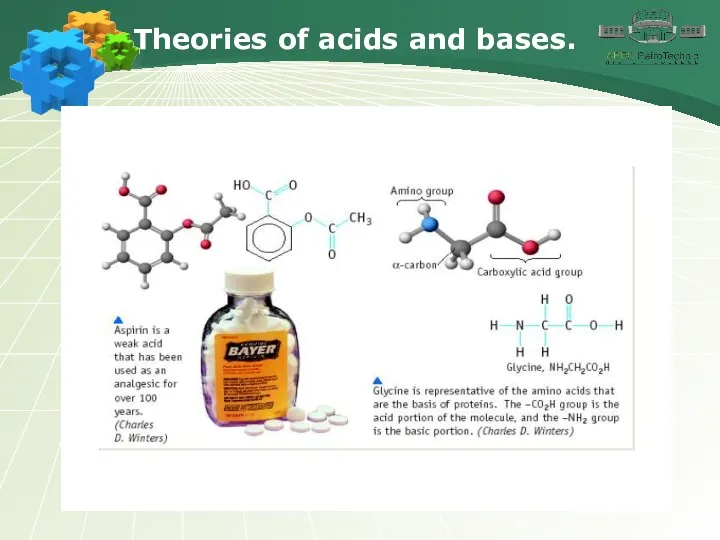
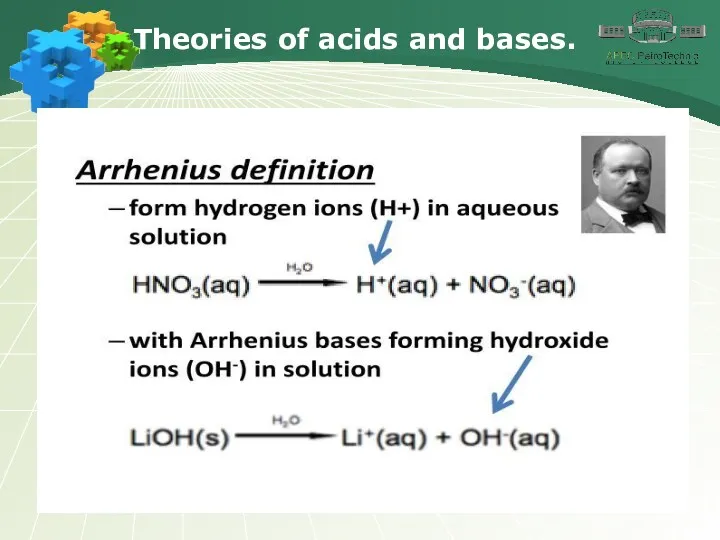
- 4. Theories of acids and bases.
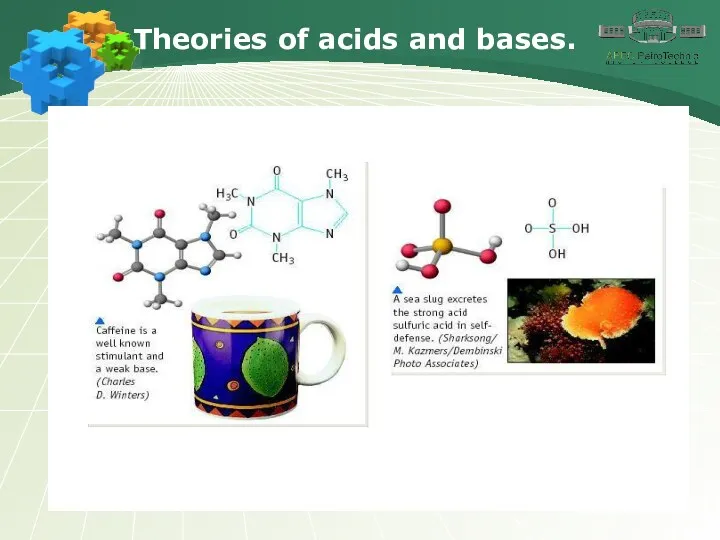
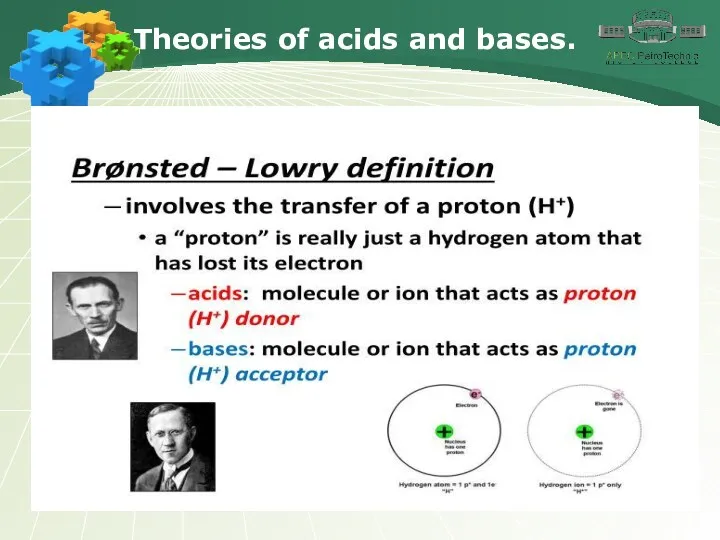
- 5. Theories of acids and bases.
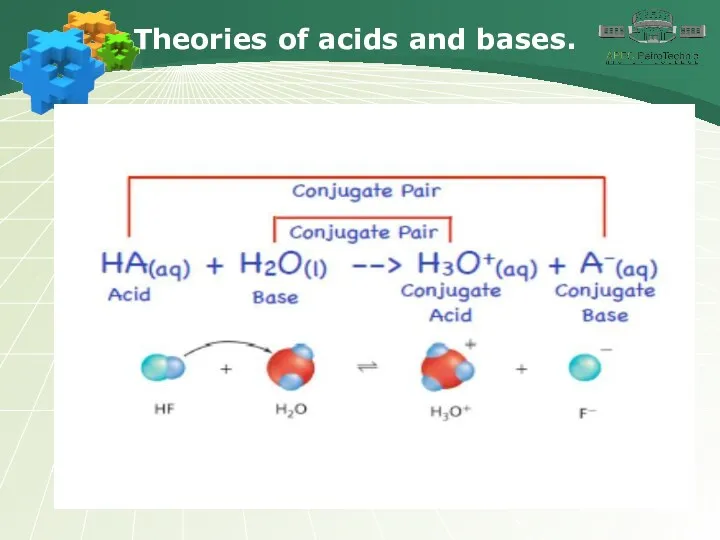
- 6. Theories of acids and bases.
- 7. Theories of acids and bases.
- 8. Theories of acids and bases.
- 9. Theories of acids and bases.
- 10. Theories of acids and bases.
- 11. Theories of acids and bases.
- 12. Theories of acids and bases.
- 13. Theories of acids and bases.
- 14. Theories of acids and bases.
- 15. Theories of acids and bases.
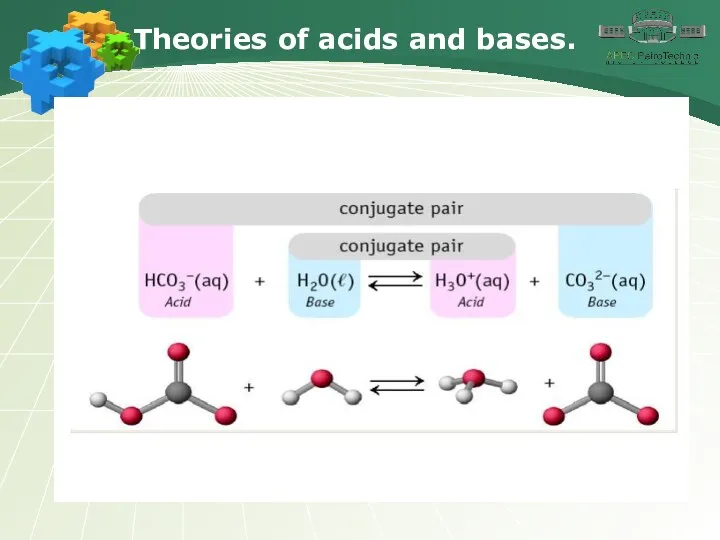
- 16. Theories of acids and bases.
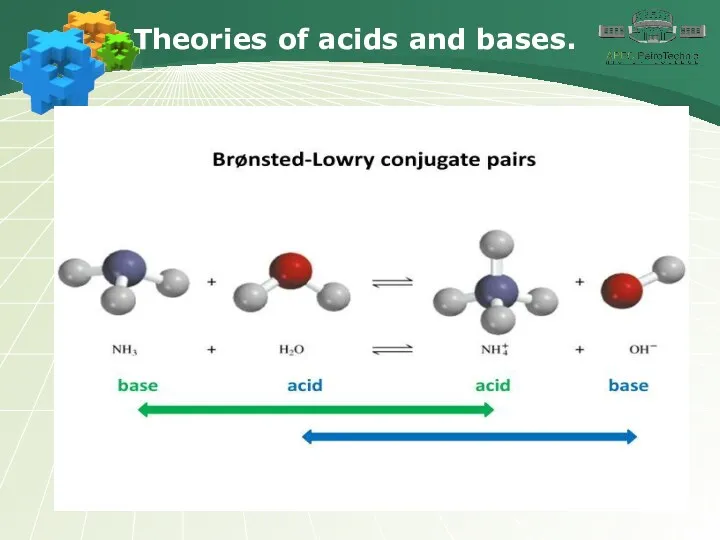
- 17. Theories of acids and bases.
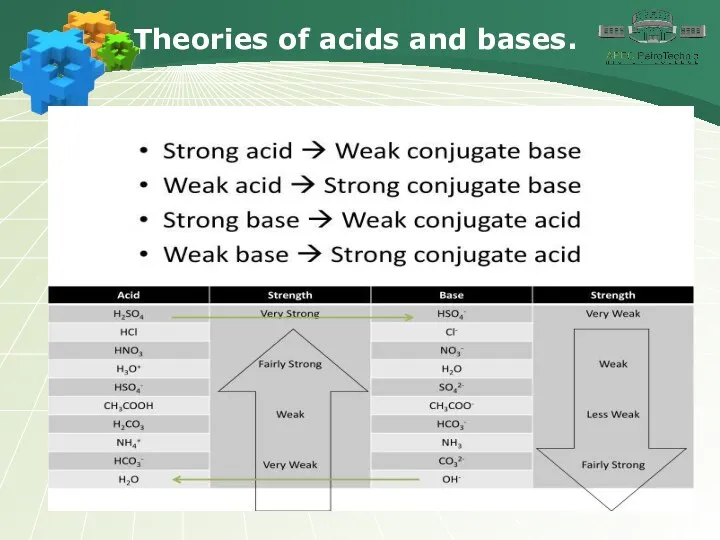
- 18. Theories of acids and bases.
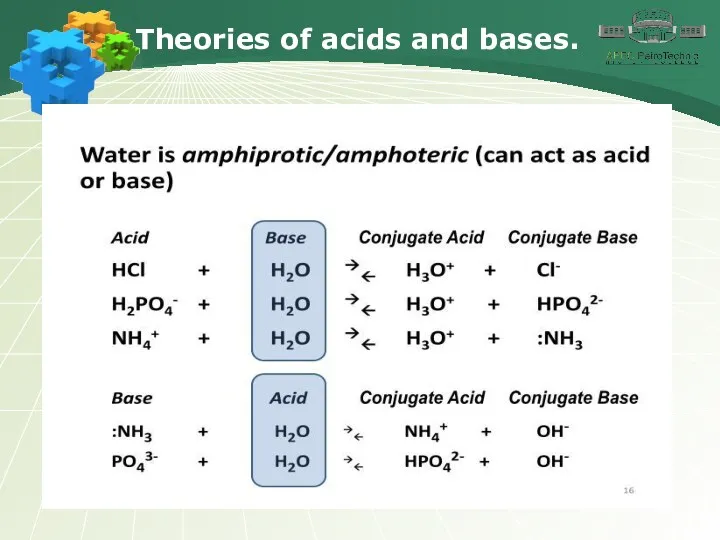
- 19. Theories of acids and bases.
- 20. Theories of acids and bases.
- 21. Theories of acids and bases.
- 22. 2. Ionic equilibria in electrolyte solutions. Ionic Equilibrium in Solutions The equilibrium established between the unionized
- 23. 2. Ionic equilibria in electrolyte solutions. The idea of the ionic product of water can be
- 24. 2. Ionic equilibria in electrolyte solutions. pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration. It's a
- 25. 2. Ionic equilibria in electrolyte solutions. Let's discuss how to calculate pH with an example. What
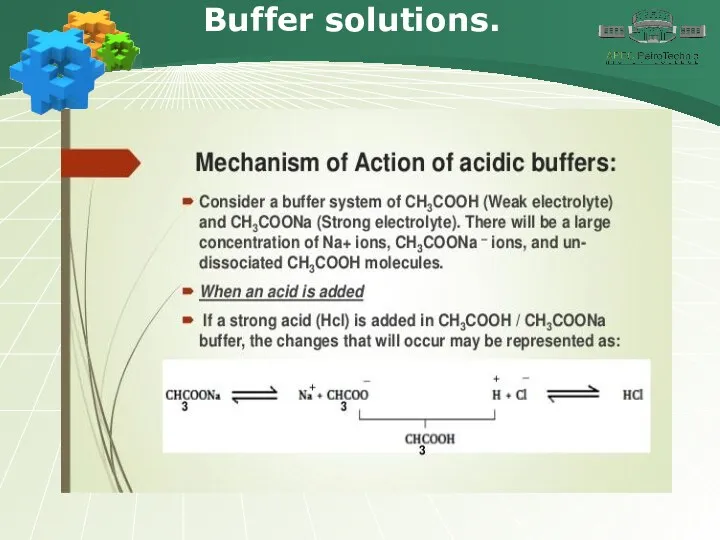
- 26. Buffer solutions.
- 27. Buffer solutions.
- 28. Buffer solutions.
- 29. Buffer solutions.
- 30. Buffer solutions. .
- 31. Buffer solutions.
- 32. Buffer solutions.
- 33. Buffer solutions.
- 34. Buffer solutions.
- 35. Buffer solutions.
- 36. Buffer solutions.
- 37. Questions for self control 1.Whose definition of acids and bases emphasizes the role of protons? Brønsted
- 38. Questions for self control 4.A buffer solution comprises which of the following? a) A weak acid
- 39. Question for self control 6.If NaOH is added in CH3COOH/CH3COONa buffer than hydroxyl ions yielded by
- 40. Literature 1.Basic literature : 1. Jenkins, Chemistry, ISBN 978-0-17-628930-0 2. Alberta Learning, Chemistry data booklet 2010,
- 41. 2.Additional literature : 1.Б.А.Мансуров «Химия» 10-11 кл., Атамура 2015 г 2.Б.Мансуров., Н.Торшина «Методика преподавания органической химии»
- 43. Скачать презентацию
























 Карбоновые кислоты. Тест
Карбоновые кислоты. Тест Кремний и его соединения
Кремний и его соединения Водородная связь
Водородная связь Природные источники углеводородов, их переработка, применение и экологические проблемы
Природные источники углеводородов, их переработка, применение и экологические проблемы Металлы и их свойства. Способы получения
Металлы и их свойства. Способы получения Органическая химия. Вещества
Органическая химия. Вещества Магматизм. (Лекция 6)
Магматизм. (Лекция 6) Кислород
Кислород Спроби класифікації хімічних елементів
Спроби класифікації хімічних елементів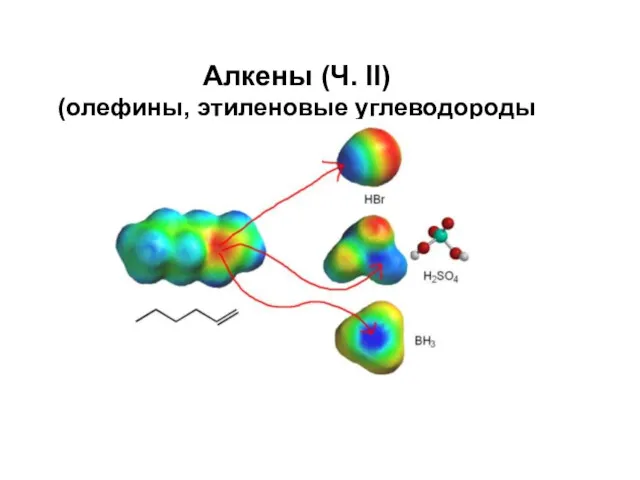 Алкены (олефины, этиленовые углеводороды)
Алкены (олефины, этиленовые углеводороды) Прочность полимеров
Прочность полимеров Амфотерные органические и неорганические соединения
Амфотерные органические и неорганические соединения Буферные растворы
Буферные растворы Місце хімії серед наук про природу
Місце хімії серед наук про природу Химические волокна
Химические волокна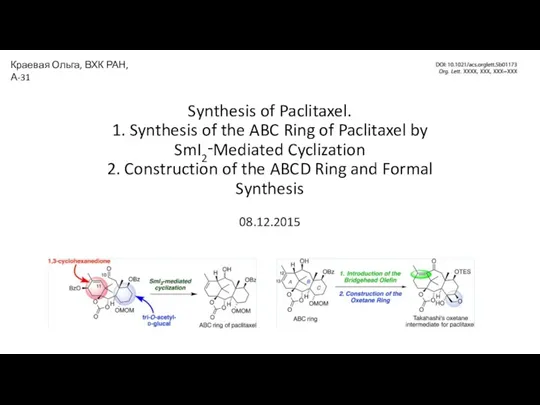 Synthesis of Paclitaxel
Synthesis of Paclitaxel Строение атома. 8 класс
Строение атома. 8 класс Лекция 3. Разновидности химических связей
Лекция 3. Разновидности химических связей Витамины. Ашылу тарихы
Витамины. Ашылу тарихы ГИА-9 Химия. А4
ГИА-9 Химия. А4 Массовая и объемная доли компонентов смеси (раствора)
Массовая и объемная доли компонентов смеси (раствора) Классификация органических соединений, углеводородов
Классификация органических соединений, углеводородов Рідкі кристали
Рідкі кристали Спирты
Спирты Химические уравнения
Химические уравнения Вещества молекулярного и немолекулярного строения
Вещества молекулярного и немолекулярного строения Применение алюминия и его сплава в машиностроении
Применение алюминия и его сплава в машиностроении Химическая связь. 8 класс
Химическая связь. 8 класс