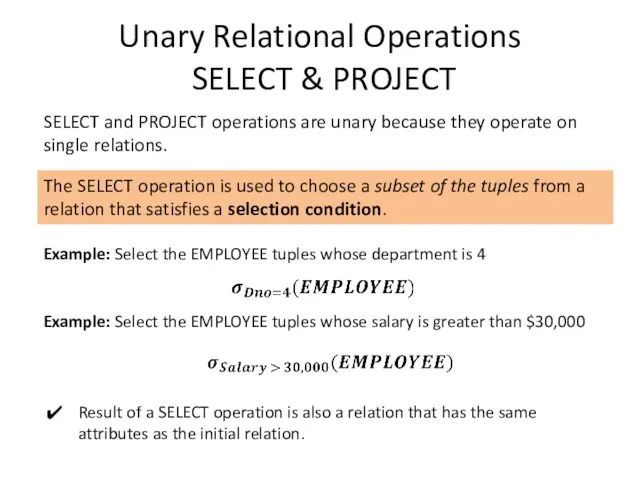
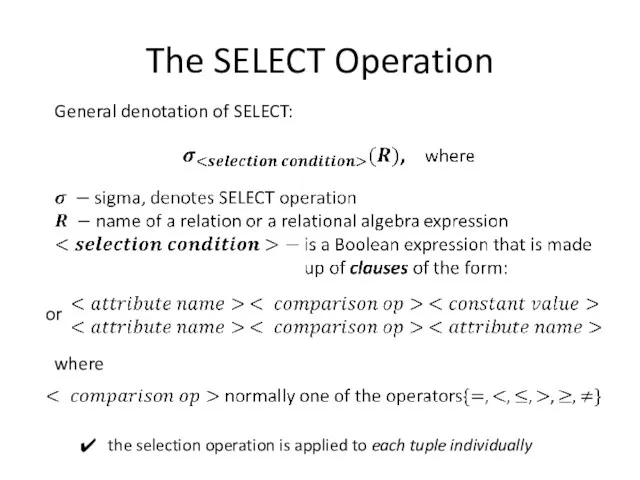
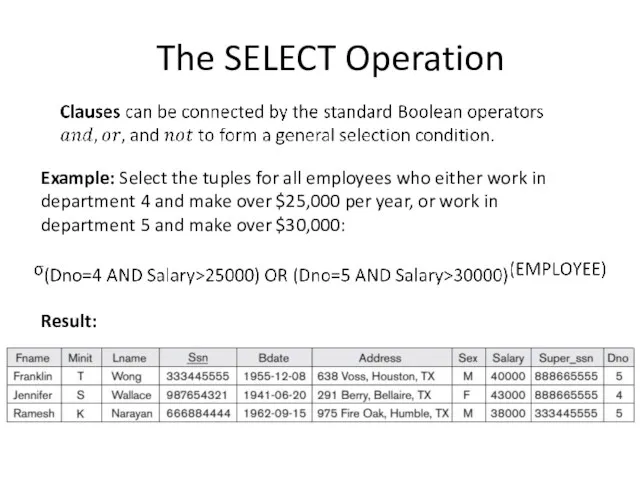
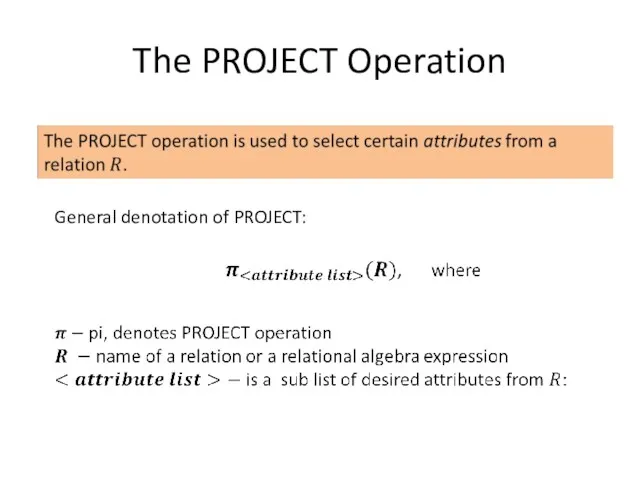
Introduction
Relational Algebra is a family of algebra used for modelling the
data stored in relational database, and defining queries on it.
Analogy between Relational Algebra and Arithmetic:
SQL is based on concepts of Relational Algebra.
Arithmetic is the elementary branch of mathematics that deals with study of numbers and properties of operations on them, like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
In Relational Algebra the analogy of numbers are relations and its own set of operations to manipulate with relations, like select, project, join and other.




 Коммуникация без провокации, или этика общения в социальных сетях
Коммуникация без провокации, или этика общения в социальных сетях Основы тестирования
Основы тестирования Системный администратор, как профессия
Системный администратор, как профессия Измерение времени в ЭВМ
Измерение времени в ЭВМ Информация и её кодирование. Способы измерения информации
Информация и её кодирование. Способы измерения информации Текстовый процессор Microsoft Word 2010
Текстовый процессор Microsoft Word 2010 ТОВ “Балюліна та партнери”. Умовне віртуальне підприємство для практики у програмних продуктах 1С:Бухгалтерія та M.E.Doc
ТОВ “Балюліна та партнери”. Умовне віртуальне підприємство для практики у програмних продуктах 1С:Бухгалтерія та M.E.Doc Основы программирования
Основы программирования Основы ABAP часть 1
Основы ABAP часть 1 Модель системы защиты информации
Модель системы защиты информации Особенности восприятия цвета
Особенности восприятия цвета Задание. КИМы по ЕГЭ-2012
Задание. КИМы по ЕГЭ-2012 Графічний редактор Paint
Графічний редактор Paint Геоинформационная система ZuluGIS
Геоинформационная система ZuluGIS Spatial data catalogues
Spatial data catalogues Мова гіпертекстової розмітки HTML (теги)
Мова гіпертекстової розмітки HTML (теги) Представление о системах управления базами данных
Представление о системах управления базами данных Информационное общество
Информационное общество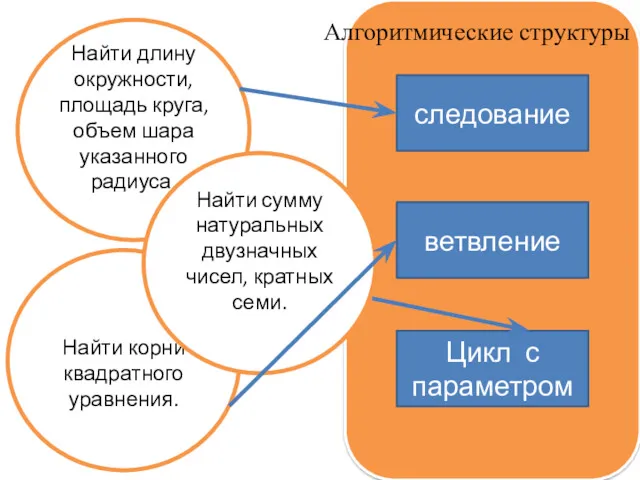 Решение задач с использованием алгоритмической структуры цикл с условием
Решение задач с использованием алгоритмической структуры цикл с условием Введение в разработку мобильных приложений Введение в разработку приложений для смартфонов на ОС Android
Введение в разработку мобильных приложений Введение в разработку приложений для смартфонов на ОС Android Алгоритмы работы с величинами
Алгоритмы работы с величинами Конспект и презентация к уроку информатики Граф. Построение графов
Конспект и презентация к уроку информатики Граф. Построение графов Аппаратное обеспечение компьютера
Аппаратное обеспечение компьютера Overview software development methodology Аgile.Вusiness approach
Overview software development methodology Аgile.Вusiness approach Тестировщик ПО. Блок 5. Нефункциональное тестирование
Тестировщик ПО. Блок 5. Нефункциональное тестирование Основы веб-программирования. Лекция 2
Основы веб-программирования. Лекция 2 План-конспект урока Информационные модели по информатике и ИКТ для 7 класса с презентацией и материалами для интерактивной доски. Учитель Лысенко Нина Александровна.
План-конспект урока Информационные модели по информатике и ИКТ для 7 класса с презентацией и материалами для интерактивной доски. Учитель Лысенко Нина Александровна. Дискретные и автономные транзакции Oracle
Дискретные и автономные транзакции Oracle