Содержание
- 2. 4 Accounting Review Questions
- 3. Reviews What is the Accounting? Accounting is an information process, which is related with collecting and
- 4. How to govern accounting? I. Governing Organizations: SEC in USA, FASB in USA, IASB in UK,
- 5. Comparison of FA and MA
- 6. Learning Objective Describe five Elements of Accounts Use the accounting equation to analyze transactions Basic Accounting
- 7. Account An account is a separate record of financial transactions ,which shows the increases and decreases
- 8. Account Format Ledger account- formal format Cash Account No. 101 ‘T’ account- informal Debit: what comes
- 9. Five Elements (Groups) of Accounts Assets(A) Liabilities(L) Owner's Equity(O/E) Revenue( R ) Expenses ( E )
- 10. 1. Assets (A) Assets (A) economic resources controlled by the entity as a result of past
- 11. 1.Typical Asset Accounts (A)
- 12. 1. Assets (A) Intangibles Copyrights Trademarks Patents Databases PPE Equipments Furniture Cash at bank Office Supplies
- 13. Taxes Payable Creditors loan Accounts Payable (AP) 2. Liabilities (L) Liabilities (L) present obligations that legally
- 14. 2.Typical Liability Accounts (L)
- 15. - - Oxford Education ? Non-current Liabilities Current L - - Loan - - 2. Liabilities
- 16. Owner’s Claims on Assets 3. Owner's Equity (O/E) Owner’s Equity (O/E) the amount of ownership an
- 17. 3.Typical Equity Accounts (O/E)
- 18. Discount received Bank interest received Rent received Sales ( of inventories) 4. Revenue (R) Things increase
- 19. salaries telephone expense Advertising Purchases Rent bank interest paid Commission paid cleaning wages Cost of doing
- 20. III. Basic Accounting Assumption and Principle 1. Economic Entity Assumption 2. Goning Concern Assumption 3. Monetary
- 21. 5. Profit Determination The Profit Formula: Revenues – Expenses = Profit(or Loss) Revenues: amounts earned from
- 22. Multiple Choices 2mins Svelte Living Inc. sold goods on account for $75,000, incurred and paid expenses
- 23. 6. The Accounting Equation The basic,vital tool of accounting, measuring the resources of a business(what the
- 24. 6. The Accounting Equation 1- Liabilities Assets = + Rule: The Balance Sheet Equation must ALWAYS
- 25. 1- Liabilities Assets = + Equity Owner’s Capital – Owner’s Withdrawals + Revenues - Expenses 6.
- 26. >TRY IT!
- 27. >TRY IT!
- 28. Business Transaction Think of a transaction as a very special kind of historical event. It involves
- 29. How do we analyze a transaction? Three steps: Step 1: identify the accounts and account type
- 30. How Do You Analyze A Transaction? Sheena Bright starts a new business named Smart Touch. She
- 31. Multiple Choices 2mins Viva Inc. produces and sells coffee beans. This month it earned $500 by
- 32. How Do You Analyze A Transaction? Next, Smart Touch purchases land for $20,000 cash. 1- In
- 33. How Do You Analyze A Transaction? In Transaction #3, Smart Touch buys $500 of office supplies,
- 34. How Do You Analyze A Transaction? In Transaction #4, Smart Touch provides training services to customers
- 35. How Do You Analyze A Transaction? In Transaction #5, Smart Touch performs $3,000 of services for
- 36. How Do You Analyze A Transaction? In Transaction #6, Smart Touch pays $3,200 in cash expenses;
- 37. How Do You Analyze A Transaction? In Transaction #7, Smart Touch pays $300 to the store
- 38. How Do You Analyze A Transaction? In Transaction #8, Smart Touch collects $2,000 from the client
- 39. Homework Wega Inc. sold watches to a retailer on account for $50,000. Ignore cost of goods
- 40. Homework Fashion Fusion is famous for fashion wristwatches and leather goods. At the end of the
- 41. True or False Questions 3 mins The total of amount of assets that a business possesses,
- 43. Скачать презентацию








































 Синтаксический разбор простого предложения
Синтаксический разбор простого предложения Славные люди нашего поселка.
Славные люди нашего поселка. Новые педагогические технологии
Новые педагогические технологии Экскурсия как средство духовно-нравственного развития и гражданско-патриотического воспитания подростков гимназии.
Экскурсия как средство духовно-нравственного развития и гражданско-патриотического воспитания подростков гимназии. Координаты вектора
Координаты вектора Кросскультурный маркетинг: Понятие международного маркетинга. Тема 1
Кросскультурный маркетинг: Понятие международного маркетинга. Тема 1 Праздник посвящённый Дню матери МАМА - ПЕРВОЕ СЛОВО
Праздник посвящённый Дню матери МАМА - ПЕРВОЕ СЛОВО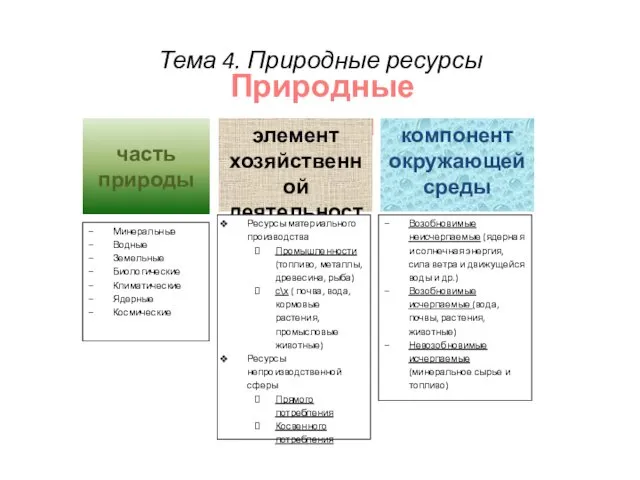 Природные ресурсы
Природные ресурсы Алгебраический метод решения задач В-9 – элемент решения задач С4
Алгебраический метод решения задач В-9 – элемент решения задач С4 Создание теста через программу MyTest
Создание теста через программу MyTest Правописание гласных -о- и -а- в корнях с чередованием
Правописание гласных -о- и -а- в корнях с чередованием Практическое занятие по русскому языку для педагогов, родителей, обучающихся.
Практическое занятие по русскому языку для педагогов, родителей, обучающихся. Презентация к методическому объединению Развитие социальной уверенности у дошкольников2011г.
Презентация к методическому объединению Развитие социальной уверенности у дошкольников2011г. ТНУ в схемах ПГУ. Опыт использования ТНУ для теплоснабжения
ТНУ в схемах ПГУ. Опыт использования ТНУ для теплоснабжения Робот вычислитель
Робот вычислитель SMM-погружение-2018
SMM-погружение-2018 Презентация творческого проекта По следам воинской славы
Презентация творческого проекта По следам воинской славы ОВЕН ПЧВ3 IP54. Представление линейки
ОВЕН ПЧВ3 IP54. Представление линейки Картотека подвижных игр для детей дошкольного возраста по программе От рождения до школы под редакцией Н.Е.Вераксы,Т.С.Комаровой,М.А.Васильевой.
Картотека подвижных игр для детей дошкольного возраста по программе От рождения до школы под редакцией Н.Е.Вераксы,Т.С.Комаровой,М.А.Васильевой. Презентация к уроку Резьба по дереву (вводное занятие)
Презентация к уроку Резьба по дереву (вводное занятие) Центр изучения восточной культуры Амрита. Выступления ансамбля
Центр изучения восточной культуры Амрита. Выступления ансамбля Шаблон презентации УМНИК 2016
Шаблон презентации УМНИК 2016 Интеллектуальная игра. Знатоки Завьяловского района
Интеллектуальная игра. Знатоки Завьяловского района История возникновения городов Западной Европы в их названиях
История возникновения городов Западной Европы в их названиях Скорость химической реакции и химическое равновесие
Скорость химической реакции и химическое равновесие Второе начало термодинамики. Энтропия
Второе начало термодинамики. Энтропия Гонки шагающих роботов. Соревнование
Гонки шагающих роботов. Соревнование Игра для детей раннего возраста Назови цвет
Игра для детей раннего возраста Назови цвет