Содержание
- 2. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Course target What is the structure of a financial system? How does
- 3. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Literature and materials Buckle, M. and E. Beccalli Principles of banking and
- 4. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Grade determination Class-work during lectures and classes – 15% Home assignments –
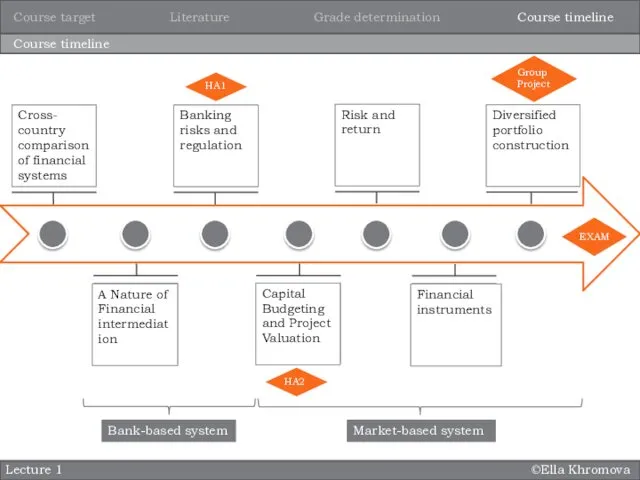
- 5. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Course timeline Essential reading for the course: A Nature of Financial intermediation
- 6. Lecture 1. Cross-country comparison of financial systems ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 International finance and globalization Bank-based
- 7. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Functions of financial systems Set of institutions, which allow the exchange of
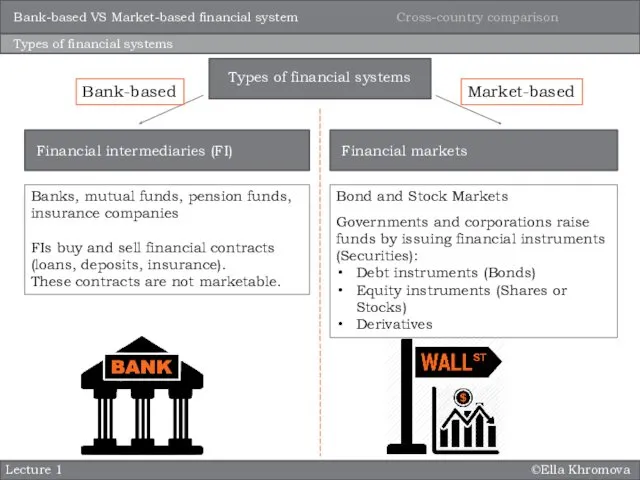
- 8. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Types of financial systems Banks, mutual funds, pension funds, insurance companies FIs
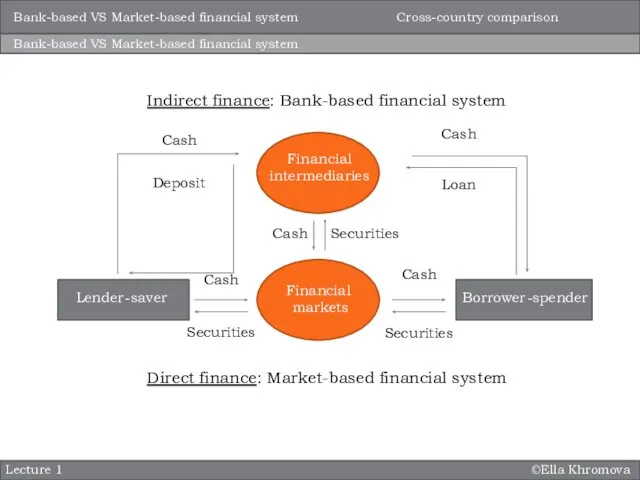
- 9. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Bank-based VS Market-based financial system Indirect finance: Bank-based financial system Direct finance:
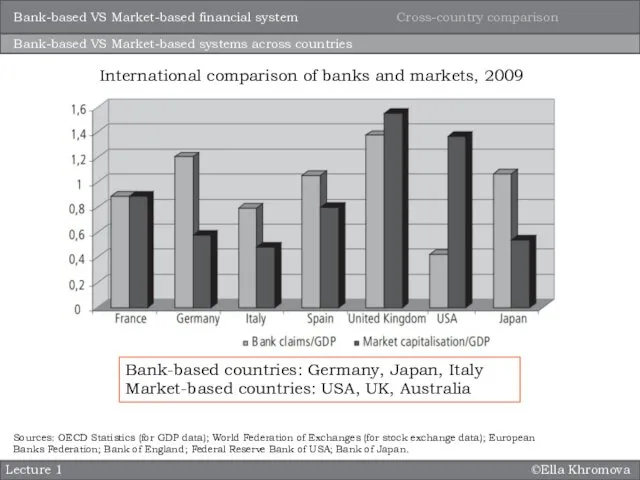
- 10. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Bank-based VS Market-based systems across countries Sources: OECD Statistics (for GDP data);
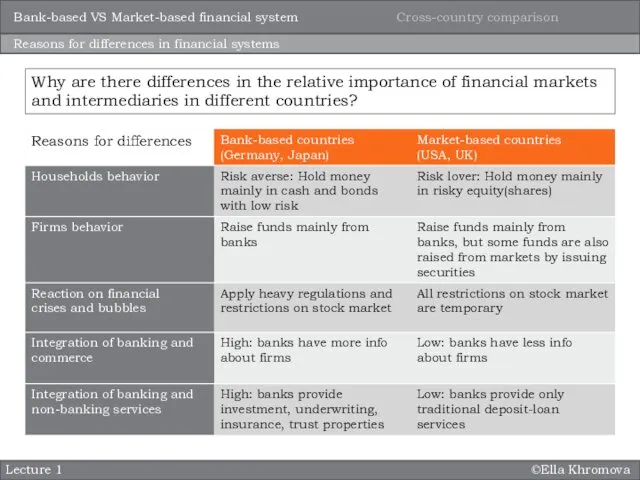
- 11. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Reasons for differences in financial systems Why are there differences in the
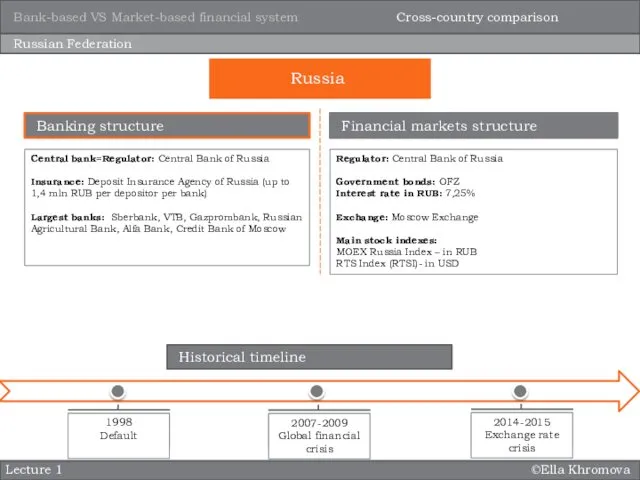
- 12. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Russian Federation Central bank=Regulator: Central Bank of Russia Insurance: Deposit Insurance Agency
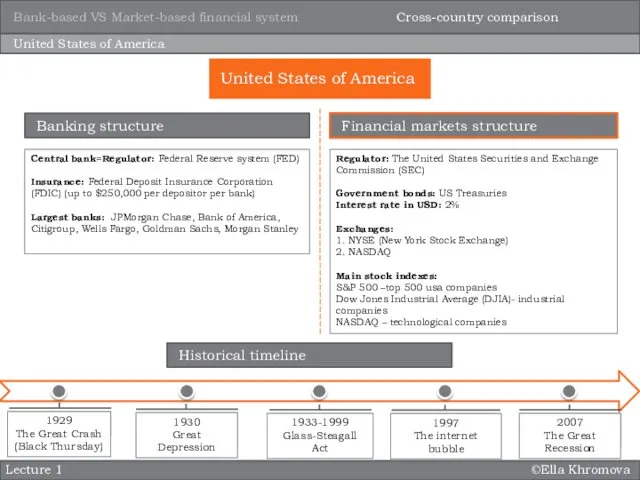
- 13. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 United States of America Central bank=Regulator: Federal Reserve system (FED) Insurance: Federal
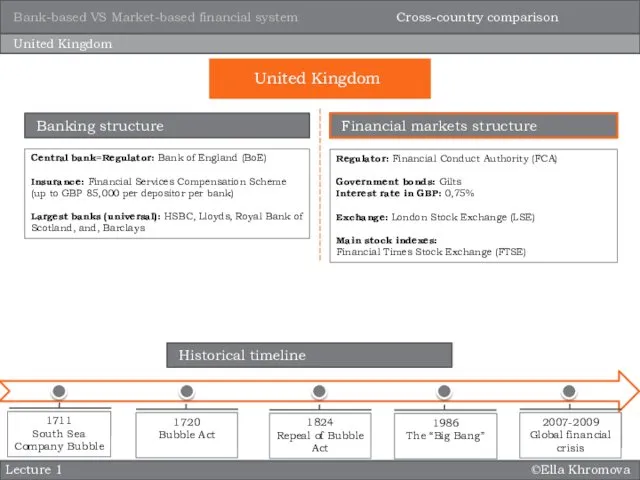
- 14. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 United Kingdom Central bank=Regulator: Bank of England (BoE) Insurance: Financial Services Compensation
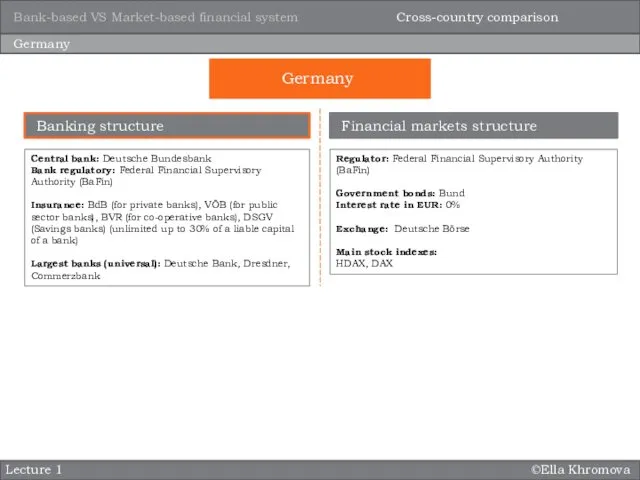
- 15. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Germany Central bank: Deutsche Bundesbank Bank regulatory: Federal Financial Supervisory Authority (BaFin)
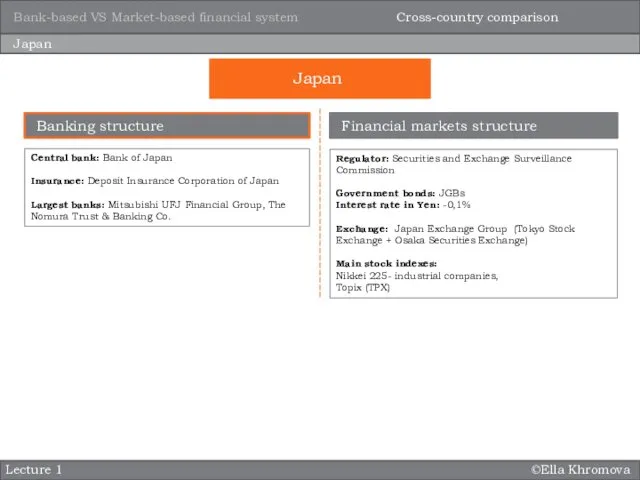
- 16. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Japan Central bank: Bank of Japan Insurance: Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan
- 17. ©Ella Khromova Lecture 1 Current trends The current trend is towards market-based systems (disintermediation) government intervention
- 19. Скачать презентацию


 Учет операций по привлечению денежных средств по договорам займа и кредитным договорам. Глава 6
Учет операций по привлечению денежных средств по договорам займа и кредитным договорам. Глава 6 Бухгалтерский учет в сельскохозяйственных кооперативах (для начинающих)
Бухгалтерский учет в сельскохозяйственных кооперативах (для начинающих) Проект поддержки местных инициатив 2020
Проект поддержки местных инициатив 2020 Муниципальное автономное учреждение города Новосибирска Городской центр развития предпринимательства
Муниципальное автономное учреждение города Новосибирска Городской центр развития предпринимательства Продажа объекта коммерческой недвижимости в городе Орёл
Продажа объекта коммерческой недвижимости в городе Орёл Метод функционально-стоимостного анализа
Метод функционально-стоимостного анализа Цена и ценообразование. Понятие цена
Цена и ценообразование. Понятие цена Совершенствование организации денежных расчетов на предприятии
Совершенствование организации денежных расчетов на предприятии Финансовые результаты деятельности предприятия
Финансовые результаты деятельности предприятия Сравнительный подход к оценке недвижимости
Сравнительный подход к оценке недвижимости Деньги и их роль в экономической кредитно-денежной политике
Деньги и их роль в экономической кредитно-денежной политике Бюджетирование. Виды бюджетов
Бюджетирование. Виды бюджетов Депозитная политика коммерческого банка. На примере ПАО Сбербанк России
Депозитная политика коммерческого банка. На примере ПАО Сбербанк России Локальний кшторис
Локальний кшторис Акцизы. Подакцизные товары
Акцизы. Подакцизные товары ПриватБанк и Payoneer
ПриватБанк и Payoneer Accounting
Accounting Договор займа и кредита
Договор займа и кредита Credit Suisse or Credit Suisse Group AG is the second largest banking group in Switzerland
Credit Suisse or Credit Suisse Group AG is the second largest banking group in Switzerland Рентабельность финансово-хозяйственной деятельности коммерческих организаций
Рентабельность финансово-хозяйственной деятельности коммерческих организаций Причина высокой цены вывоза мусора для конечного потребителя
Причина высокой цены вывоза мусора для конечного потребителя Фінансова звітність підприємства
Фінансова звітність підприємства Функции финансов предприятия
Функции финансов предприятия Образовательные мероприятия. Система Госфинансы. Обучающая презентация для сотрудников
Образовательные мероприятия. Система Госфинансы. Обучающая презентация для сотрудников Понятие мошенничество
Понятие мошенничество Принципы финансового моделирования
Принципы финансового моделирования Программно-целевое управление бюджетными расходами в Иркутской области
Программно-целевое управление бюджетными расходами в Иркутской области Банковские услуги. 8 класс
Банковские услуги. 8 класс