Methods of comparable data obtaining. Currency conversion. Average annual exchange rate. The purchasing power parity презентация
Содержание
- 2. Methods of comparable data obtaining Currency conversion Average annual exchange rate The purchasing power parity Market
- 3. PPP (purchasing power parity) A Prototype Is The "Big Mac" Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
- 4. 3200 main consumer of goods and services 236 main investment products 16 typical construction projects Тимофеева
- 5. When PPP? Cross-country comparisons Rational allocation of limited funds (quotas of the IMF) The identification of
- 6. Сomparable price level Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
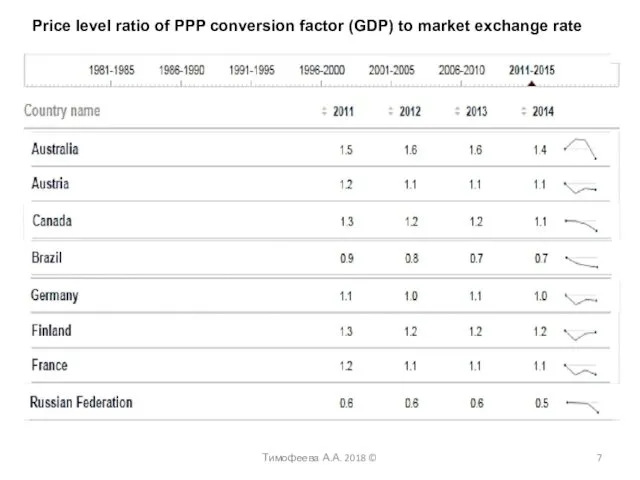
- 7. Price level ratio of PPP conversion factor (GDP) to market exchange rate Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
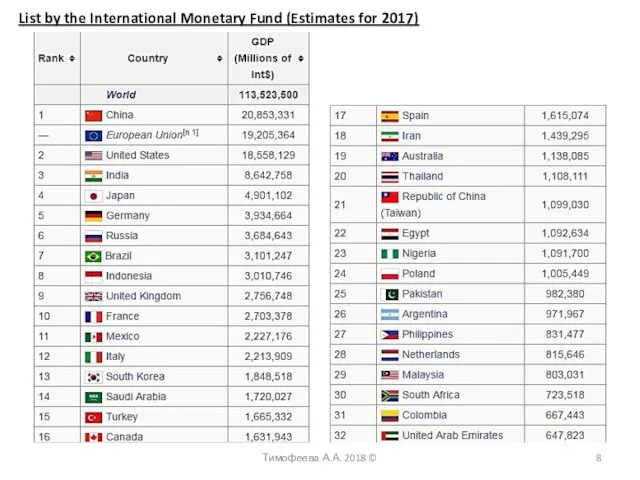
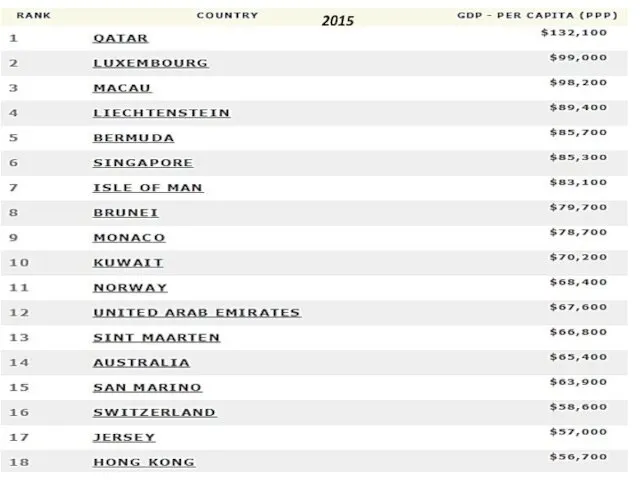
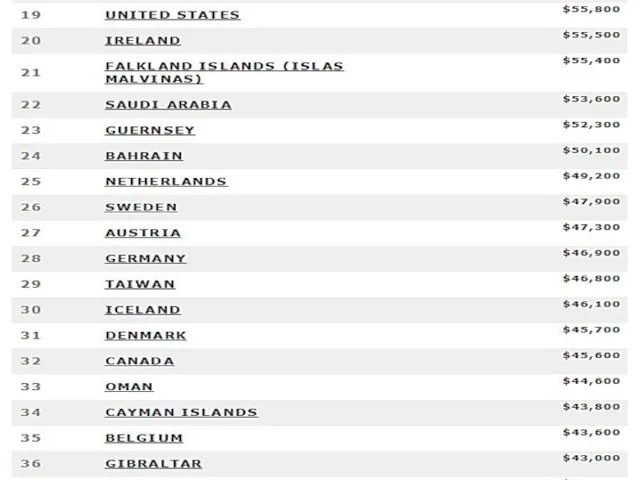
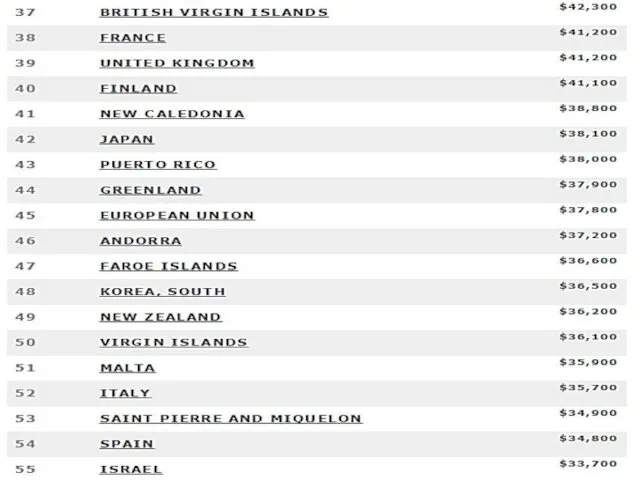
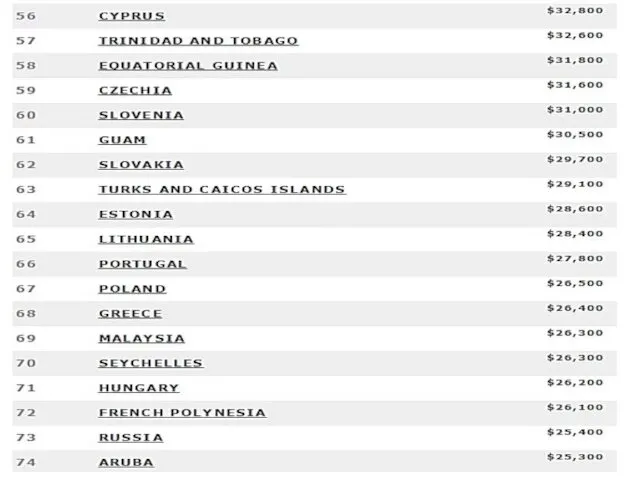
- 8. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © List by the International Monetary Fund (Estimates for 2017)
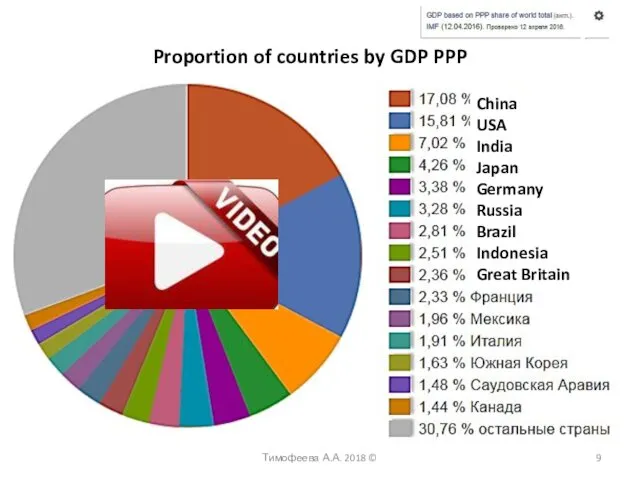
- 9. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © Proportion of countries by GDP PPP China USA India Japan Germany Russia
- 10. Сlassification of the countries
- 11. 195 countries, 72 dependent areas Country = economy ≠ state The number of States and dependent
- 12. Signs of dependent areas Advantages for mother-country Advantages for dependent area
- 13. Group of countries Developed countries Developing countries Transition economy(?) 5
- 14. Criteria: The nature of the economy The level of socio-economic development 6
- 15. Sectoral structure of GDP as an indicator of the level of socio-economic development The level and
- 16. Sectoral structure of GDP as an indicator of the level of socio-economic development of the country
- 17. The level and quality of life Lifespan The incidence Personal safety Natural environment Unemployment Consumption Human
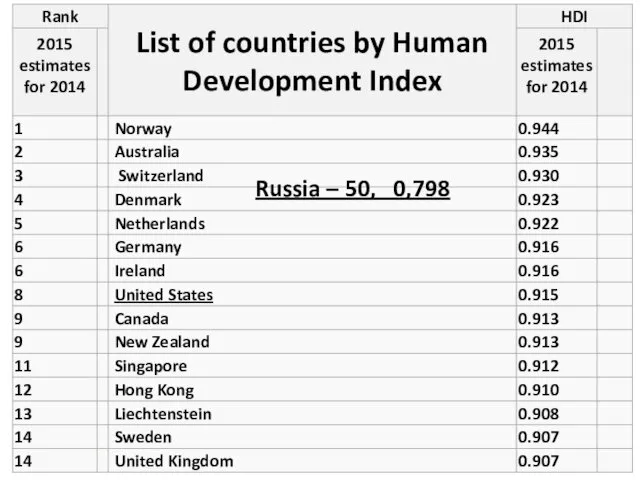
- 18. ИРЧП 2013 Russia – 50, 0,798
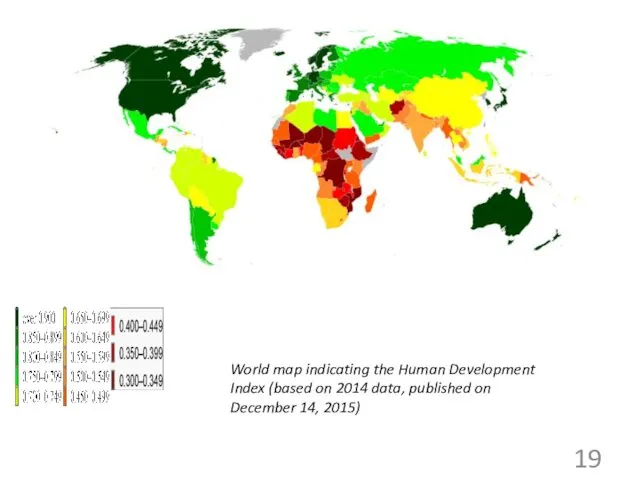
- 19. World map indicating the Human Development Index (based on 2014 data, published on December 14, 2015)
- 20. Approximate characteristics of developed countries 1) GDP per capita is on average about 30 thousand dollars
- 21. 4) Evolution towards domination of the industry and the trend of transformation of the industrial economy
- 22. 7) Business structure is non-uniform. The leading role in the economy belongs to powerful corporations –
- 23. 9) The state of developed countries is an active participant in economic activity Approximate characteristics of
- 24. 10) The openness to the world economy and the liberal organization of the foreign trade regime
- 25. Countries with economies in transition: The former socialist countries of Central and Eastern Europe: Albania, Bulgaria,
- 26. The term "transition economy" is used to describe the transformation of the socialist economy to the
- 27. Exemplary characteristics of developing countries The low level of socio-economic development 1) Suppliers of raw materials
- 28. 5) The agricultural profile of the economy and the share of the population employed in agriculture
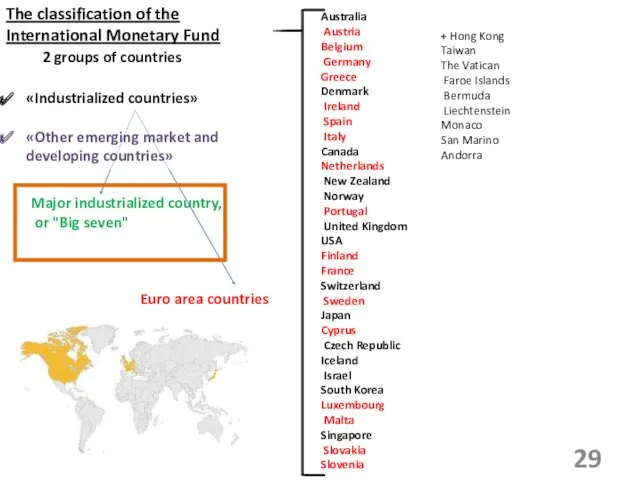
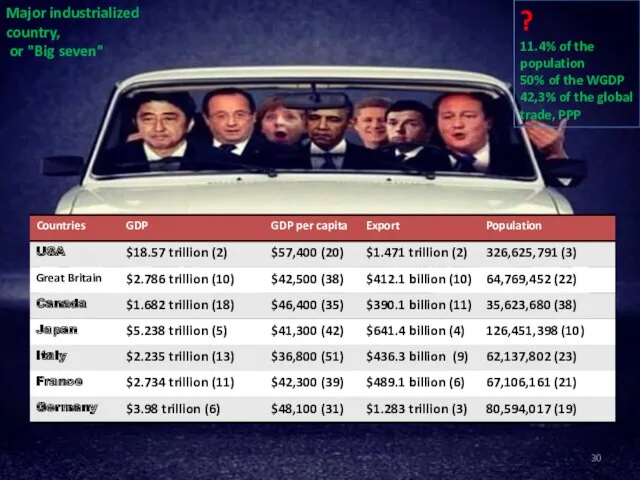
- 29. The classification of the International Monetary Fund 2 groups of countries Major industrialized country, or "Big
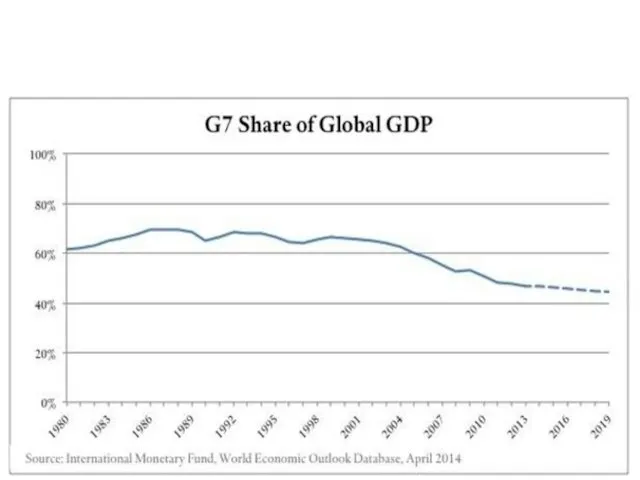
- 30. Major industrialized country, or "Big seven" ? 11.4% of the population 50% of the WGDP 42,3%
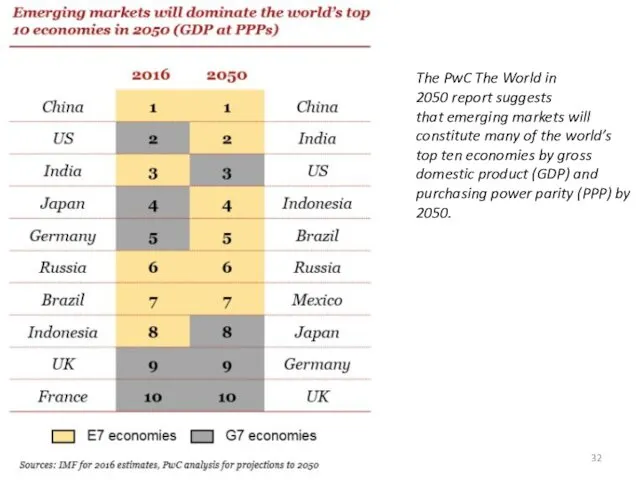
- 32. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © The PwC The World in 2050 report suggests that emerging markets will
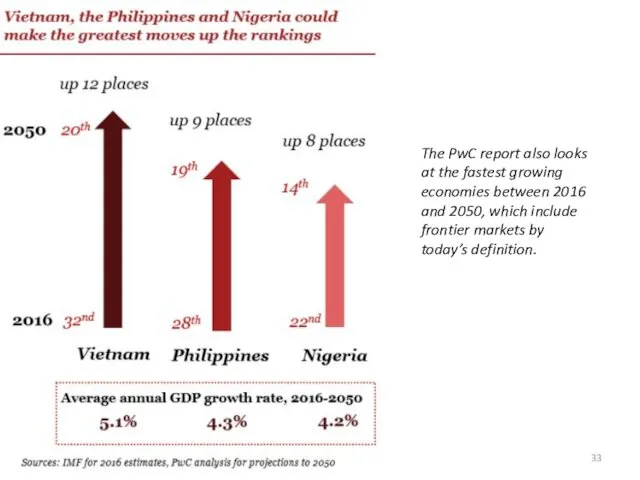
- 33. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © The PwC report also looks at the fastest growing economies between 2016
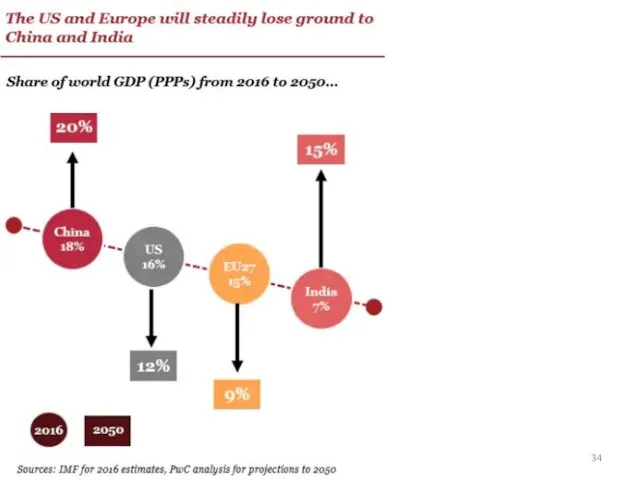
- 34. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
- 35. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 ©
- 36. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © Challenges for policymakers Protectionism Benefits of globalisation ⬄ equity Green technologies
- 37. Тимофеева А.А. 2018 © Opportunities for business : Mature emerging markets (costs, consumers, B2B)
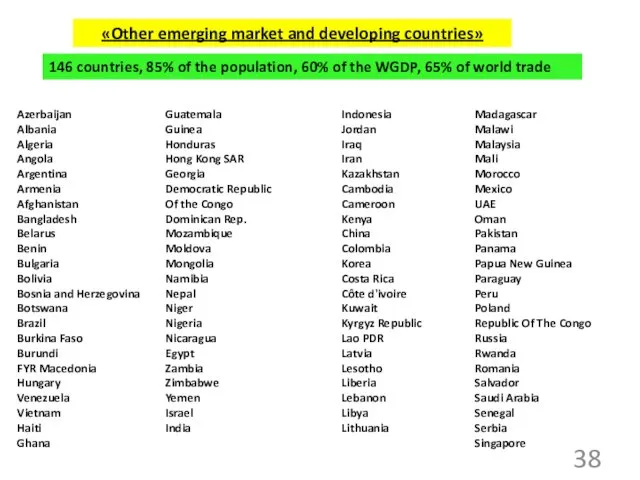
- 38. «Other emerging market and developing countries» 146 countries, 85% of the population, 60% of the WGDP,
- 39. Sub-group "Other emerging market and developing countries" exporters of liquid fuel; b) exporters of other raw
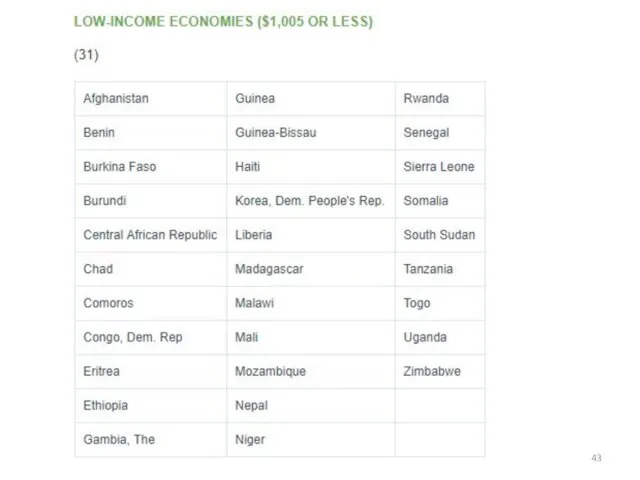
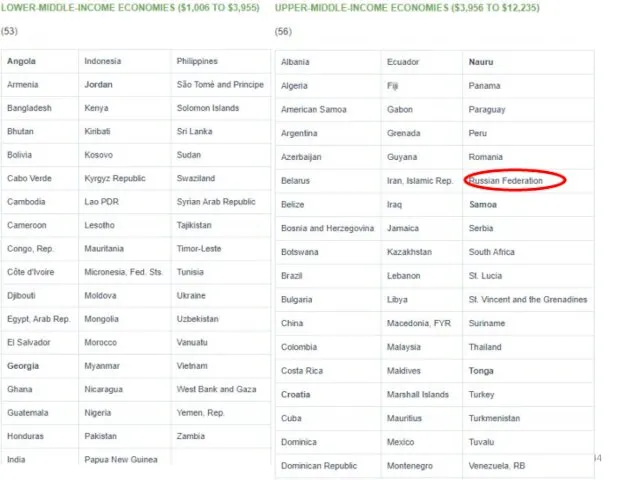
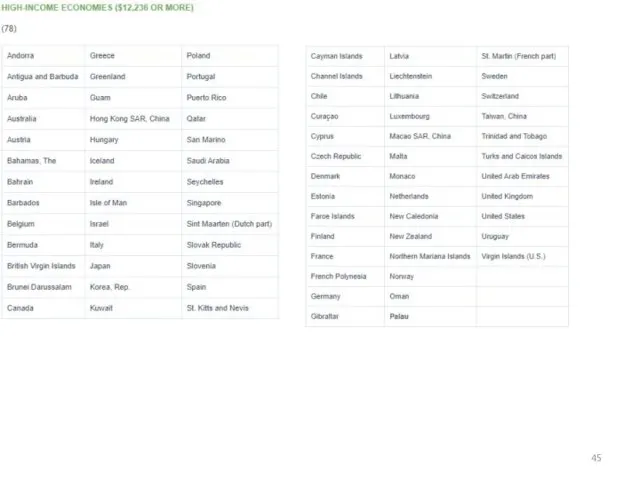
- 40. The classification of the world Bank GNI per capita 3 groups: Countries with low income Crane
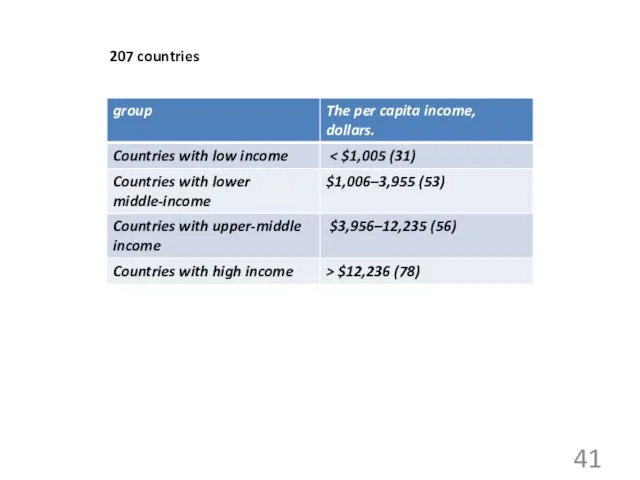
- 41. 207 countries
- 42. The state of external debt Poor countries with largest external debt Countries with moderate debt Countries
- 47. 2015
- 52. Скачать презентацию

























 Электронный бюджет
Электронный бюджет Бухгалтерский учет материальных запасов
Бухгалтерский учет материальных запасов Бағалы қағаздар нарығы
Бағалы қағаздар нарығы О механизме предоставления государственной поддержки сельскохозяйственным товаропроизводителям
О механизме предоставления государственной поддержки сельскохозяйственным товаропроизводителям Социальные и медицинские услуги в праве социального обеспечения
Социальные и медицинские услуги в праве социального обеспечения Системы директ – костинг, стандарт – кост и нормативный метод
Системы директ – костинг, стандарт – кост и нормативный метод Робота банку з готівкою, розрахунково-касові операції
Робота банку з готівкою, розрахунково-касові операції Сферы применения BlockChain в бизнесе
Сферы применения BlockChain в бизнесе Стипендии
Стипендии Затраты на производство и реализацию продукции и их финансирование
Затраты на производство и реализацию продукции и их финансирование Организация ведения бухгалтерского учета и составления бухгалтерской отчетности в банках Республики Беларусь
Организация ведения бухгалтерского учета и составления бухгалтерской отчетности в банках Республики Беларусь Налоги. Прямые и косвенные налоги
Налоги. Прямые и косвенные налоги Понятия бюджетного устройства и бюджетной системы
Понятия бюджетного устройства и бюджетной системы Green Chemistry for Life
Green Chemistry for Life Возврат день в день розница. Карта
Возврат день в день розница. Карта Конференция. Бухотчетность за 2019 год
Конференция. Бухотчетность за 2019 год Содержание и организация государственных и муниципальных финансов
Содержание и организация государственных и муниципальных финансов Порядок исполнения бюджета Свердловской области
Порядок исполнения бюджета Свердловской области Тест по бухгалтерскому учету
Тест по бухгалтерскому учету Кәсіпорынның табыстылығын диверсификациялау мәселелері
Кәсіпорынның табыстылығын диверсификациялау мәселелері Финансовый рынок
Финансовый рынок Қаржы нарығы
Қаржы нарығы Налоги юридических лиц
Налоги юридических лиц Изменения в бухгалтерской (финансовой) отчетности за 2018 год
Изменения в бухгалтерской (финансовой) отчетности за 2018 год Отчетность. Форма 8-пр
Отчетность. Форма 8-пр Актуальные вопросы составления бюджетной (бухгалтерской) отчетности за 2021 год
Актуальные вопросы составления бюджетной (бухгалтерской) отчетности за 2021 год Soliq ma’murchiligi
Soliq ma’murchiligi Облікова політика підприємства
Облікова політика підприємства