Содержание
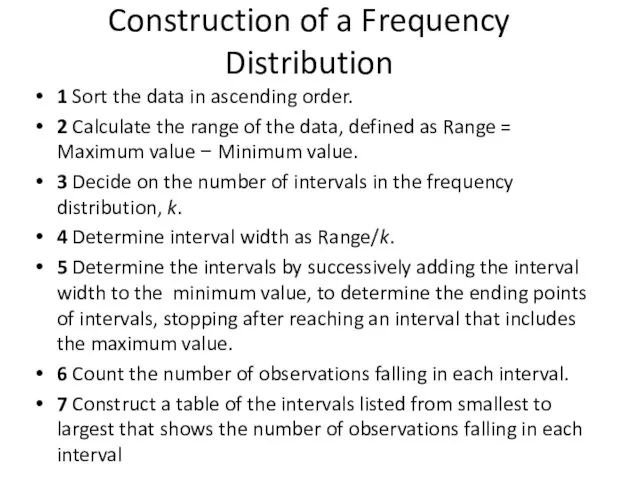
- 2. Construction of a Frequency Distribution 1 Sort the data in ascending order. 2 Calculate the range
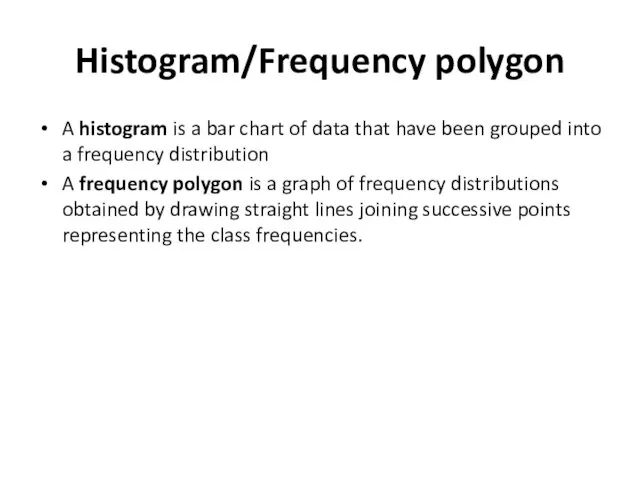
- 3. Histogram/Frequency polygon A histogram is a bar chart of data that have been grouped into a
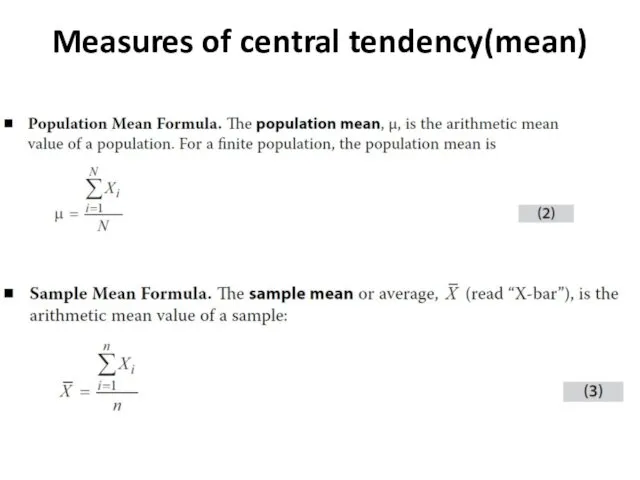
- 4. Measures of central tendency(mean)
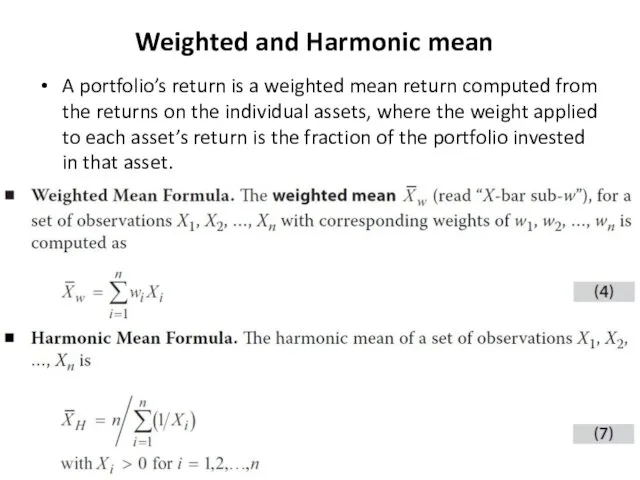
- 5. Weighted and Harmonic mean A portfolio’s return is a weighted mean return computed from the returns
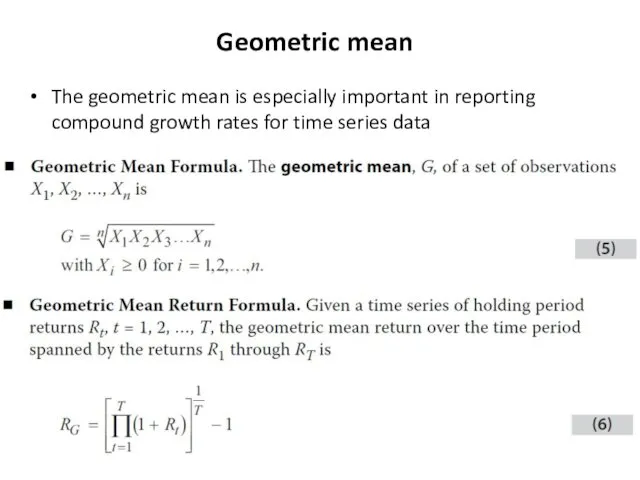
- 6. Geometric mean The geometric mean is especially important in reporting compound growth rates for time series
- 7. Median, quartiles, quintiles, deciles, and percentiles Quartiles divide the distribution into quarters. Quintiles into fifths. Deciles
- 8. Population variance/standard deviation
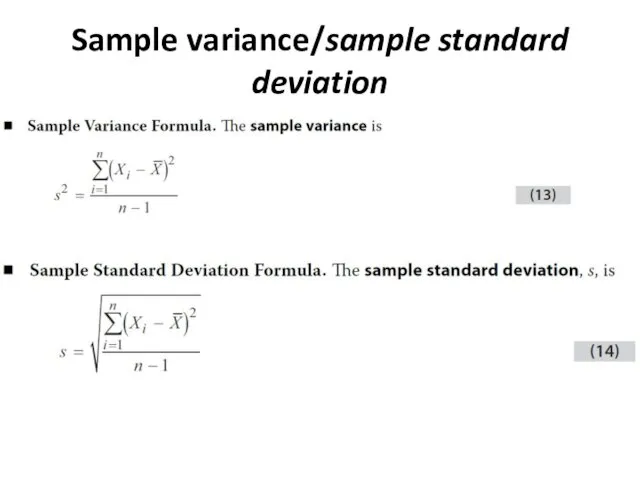
- 9. Sample variance/sample standard deviation
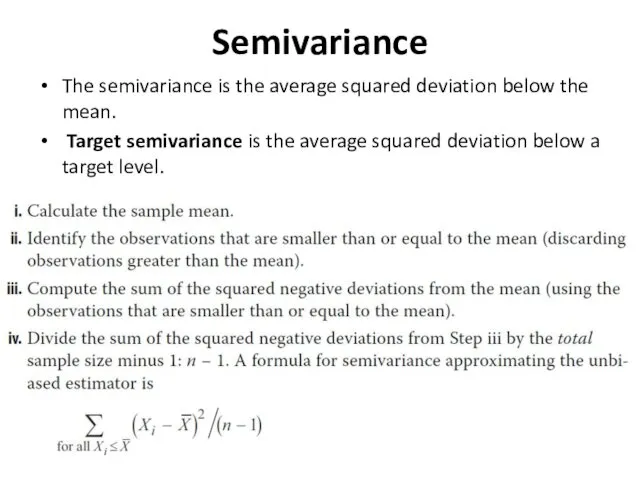
- 10. Semivariance The semivariance is the average squared deviation below the mean. Target semivariance is the average
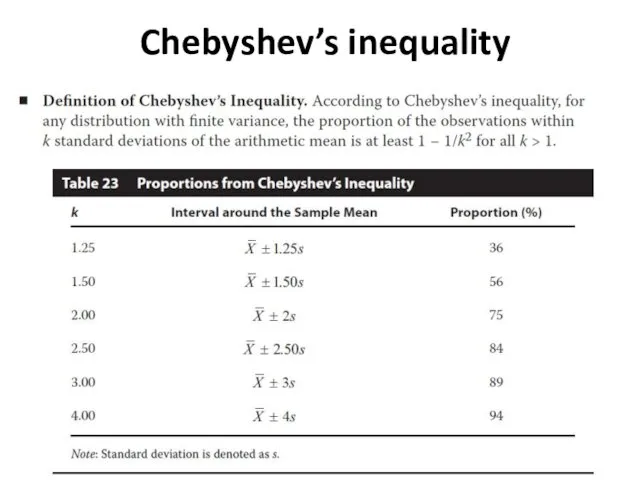
- 11. Chebyshev’s inequality
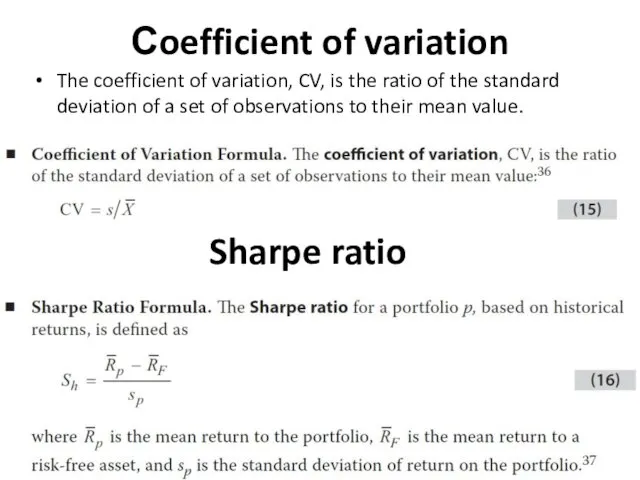
- 12. Сoefficient of variation The coefficient of variation, CV, is the ratio of the standard deviation of
- 13. Skewness Skew describes the degree to which a distribution is not symmetric about its mean. A
- 15. Скачать презентацию



 Учёт затрат и калькулирование себестоимости готовой продукции
Учёт затрат и калькулирование себестоимости готовой продукции Учет расчетов с персоналом по оплате труда
Учет расчетов с персоналом по оплате труда О применении Федерального закона от 28 декабря 2013 года № 400-ФЗ О страховых пенсиях
О применении Федерального закона от 28 декабря 2013 года № 400-ФЗ О страховых пенсиях Про виконання доходної частини місцевих бюджетів області за 2017 рік та основні резерви по наповненню бюджетів на 2018 рік
Про виконання доходної частини місцевих бюджетів області за 2017 рік та основні резерви по наповненню бюджетів на 2018 рік Анализ роли криптовалют в современной экономике
Анализ роли криптовалют в современной экономике Сутність та значення фондової біржі
Сутність та значення фондової біржі Право социального обеспечения. Тема 3 и тема 4
Право социального обеспечения. Тема 3 и тема 4 Бүгінгі БАӘ – араб әлеміндегі ең бай мемлекеттердің бірі
Бүгінгі БАӘ – араб әлеміндегі ең бай мемлекеттердің бірі Банки и небанковские кредитные учреждения: услуги для населения
Банки и небанковские кредитные учреждения: услуги для населения Финансы, как экономическая категория
Финансы, как экономическая категория Итоги исполнения бюджета по доходам за 2021 год
Итоги исполнения бюджета по доходам за 2021 год Бюджетная классификация РФ
Бюджетная классификация РФ Бюджет и бюджетная система РФ
Бюджет и бюджетная система РФ Финансовое право. Понятие, предмет и метод
Финансовое право. Понятие, предмет и метод Автоматизация банковской деятельности. Лекция 5
Автоматизация банковской деятельности. Лекция 5 Астана халықаралық қаржы орталығы
Астана халықаралық қаржы орталығы Специальное предложение для вашей компании. Почта Банк
Специальное предложение для вашей компании. Почта Банк Планування заходів щодо залучення інвестицій
Планування заходів щодо залучення інвестицій КАСКО - добровольное страхование транспортного средства
КАСКО - добровольное страхование транспортного средства Технология блокчейн. Криптовалюты. Биткойн. Цифровая (виртуальная) валюта
Технология блокчейн. Криптовалюты. Биткойн. Цифровая (виртуальная) валюта Тарифы региональных операторов по обращению с ТКО в Московской области
Тарифы региональных операторов по обращению с ТКО в Московской области Риски реальных инвестиций. Тема 6
Риски реальных инвестиций. Тема 6 Водный налог
Водный налог Внебюджетные и целевые бюджетные фонды
Внебюджетные и целевые бюджетные фонды Денежно-кредитная политика
Денежно-кредитная политика Упрощенная система налогообложения. Тема 3
Упрощенная система налогообложения. Тема 3 Финансовая деятельность государства
Финансовая деятельность государства Информационные технологии в анализе инвестиционных проектов
Информационные технологии в анализе инвестиционных проектов