Содержание
- 2. Content I. Not all the money is the same II. Credits III. Formal and informal vc
- 3. I « Not all the money is the same »
- 4. Equity
- 5. Valley of death
- 6. Definitions Private equity = equity capital to enterprises not quoted on a stock market Venture capital
- 7. Definitions Expansion = financing provided for the growth and expansion of a company which is breaking
- 8. CAPITAL NEEDS TIME High Risk Low Risk Growth Idea Development Business Creation Family Seed Capital Business
- 9. Marktstandaarden
- 10. Financing of a company: concepts bank Venture capitalist Business angel entrepreneur concept prototype Product introduction marketing
- 11. Composition of investments Source: EIBIS (2019)
- 12. II. Venture capital Credits versus venture capital
- 13. III. Formal versus informal
- 14. General Partners $ 20% “Carry” $ 1.5-3% Fee Portfolio Company Portfolio Company Portfolio Company Portfolio Company
- 15. VC: AGENCY PROBLEM AND THE CARRIED INTREST Enterprise « Costs » Own funds Intangibles - x
- 16. Flows of Risk Capital Investors -Provide Capital Money Limited partners: -Pension Funds -Sovereign Wealth Funds -Individuals
- 17. INVESTORS
- 18. Investors by stage
- 19. Fundraising – Investment - Divestment
- 20. Where does the money comes from?
- 21. Success is easier in US raernoudt@gmail.com
- 22. EXITROUTES
- 23. What does a vc want? Management capacity and track record Market and growth potential Market niche
- 24. Due diligence (analysis of business plan/market/technology/competition/...) Analysis of gaps Optimal financial structure Valuation Stock option plan
- 25. choice of distribution channels product/marketing strategy fixing priorities networks: financial advice (next rounds) What does VC
- 26. What does VC offers after the investment?? R&D, fiscal advice M&A Exit Organisation (IPO, trade sale,
- 27. VC Market Supply Venture capitalist avoid risk (MBO preference) Pervert risk – return relation Demand Lack
- 28. Pervert risk – return relation
- 29. MBO has higher return than VC
- 30. Venture capital
- 31. Unicorns
- 32. Average employment growth (VC-backed companies)
- 33. Average sales growth (VC-backed companies)
- 34. Offer rarely meets demand (p.208)
- 35. Natural tendency for « big deals » Need high fees High volume Prove good return Larger
- 36. Corona-impact: The Outlook for European VC-Backed Startups Source: European Startups.co (2020) Europe’s Startup Ecosystem Navigating The
- 38. Скачать презентацию
 1СПАРК Риски и 1С:Контрагент. Сравнение, позиционирование, целевая аудитория и немного статистики
1СПАРК Риски и 1С:Контрагент. Сравнение, позиционирование, целевая аудитория и немного статистики Ценообразование, рентабельность и прибыль. Тема 4
Ценообразование, рентабельность и прибыль. Тема 4 Валютное регулирование и валютный контроль
Валютное регулирование и валютный контроль Аналіз поведінки споживача. Тема 6
Аналіз поведінки споживача. Тема 6 Технический и фундаментальный анализ фондовых рынков
Технический и фундаментальный анализ фондовых рынков Заем Проектный в рамках программы социально-экономического развития РМ
Заем Проектный в рамках программы социально-экономического развития РМ Аудиторські докази. (Тема 2.1)
Аудиторські докази. (Тема 2.1) Понятие субъектов страхового дела
Понятие субъектов страхового дела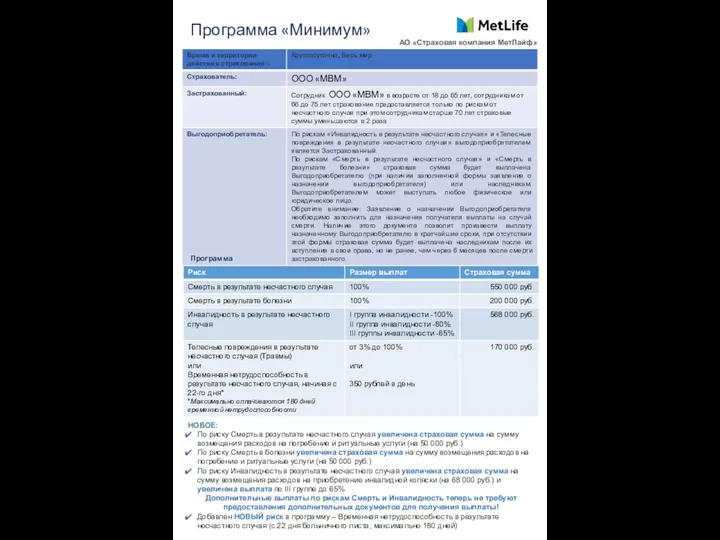 Программа Минимум АО Страховая компания МетЛайф
Программа Минимум АО Страховая компания МетЛайф Построение сети GPON в посёлке Новое Доскино
Построение сети GPON в посёлке Новое Доскино Города России на банкнотах разного достоинства
Города России на банкнотах разного достоинства Бухгалтерский учет, контроль и анализ движения денежных средств организации
Бухгалтерский учет, контроль и анализ движения денежных средств организации Анализ показателей деловой активности организации
Анализ показателей деловой активности организации Повышение фиксированной выплаты к страховой пенсии за работу в сельском хозяйстве
Повышение фиксированной выплаты к страховой пенсии за работу в сельском хозяйстве Сведения для ведения индивидуального учета и сведения о начисленных страховых взносах на обязательное социальное страхование
Сведения для ведения индивидуального учета и сведения о начисленных страховых взносах на обязательное социальное страхование Равновесие на валютном рынке
Равновесие на валютном рынке Бухгалтерский баланс. (тема 3)
Бухгалтерский баланс. (тема 3) Виды инвентаризации. Порядок проведения инвентаризации и оформления результатов инвентаризации
Виды инвентаризации. Порядок проведения инвентаризации и оформления результатов инвентаризации Фонды коллективного инвестирования
Фонды коллективного инвестирования Международное налоговое планирование: от выбора юрисдикции до оспаривания в суде
Международное налоговое планирование: от выбора юрисдикции до оспаривания в суде Кредитование инвестиционных проектов
Кредитование инвестиционных проектов Урок финансовой грамотности. Слитки
Урок финансовой грамотности. Слитки Иследовательскиие решения
Иследовательскиие решения Особенности развития аудита в Южной Корее
Особенности развития аудита в Южной Корее Основы организации финансов организаций и домашних хозяйств
Основы организации финансов организаций и домашних хозяйств Система управления рисками и принципы методологии риск-менеджмента
Система управления рисками и принципы методологии риск-менеджмента Тренінг з дисципліни “Управлінський облік в банках”
Тренінг з дисципліни “Управлінський облік в банках” Инфраструктура поддержки предпринимательства в Лысьвенском городском округе
Инфраструктура поддержки предпринимательства в Лысьвенском городском округе