Содержание
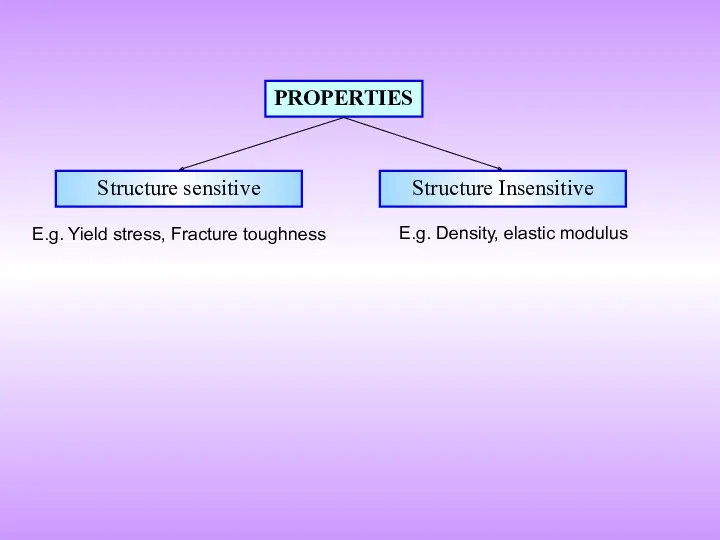
- 2. PROPERTIES Structure sensitive Structure Insensitive E.g. Yield stress, Fracture toughness E.g. Density, elastic modulus
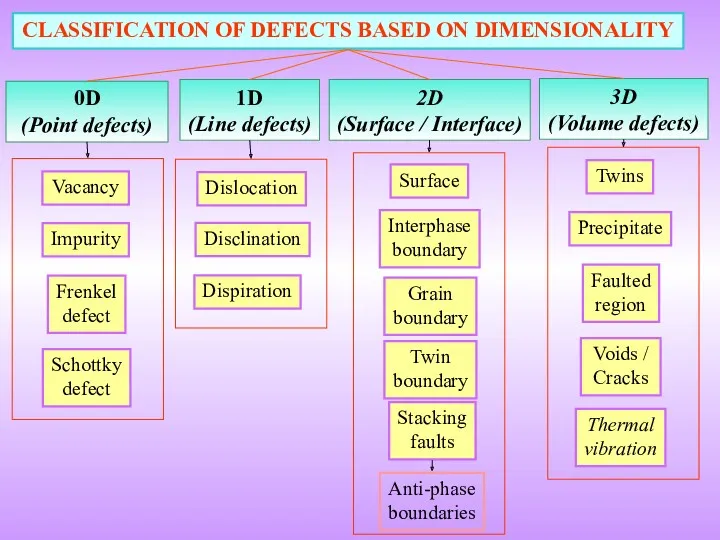
- 3. 0D (Point defects) CLASSIFICATION OF DEFECTS BASED ON DIMENSIONALITY 1D (Line defects) 2D (Surface / Interface)
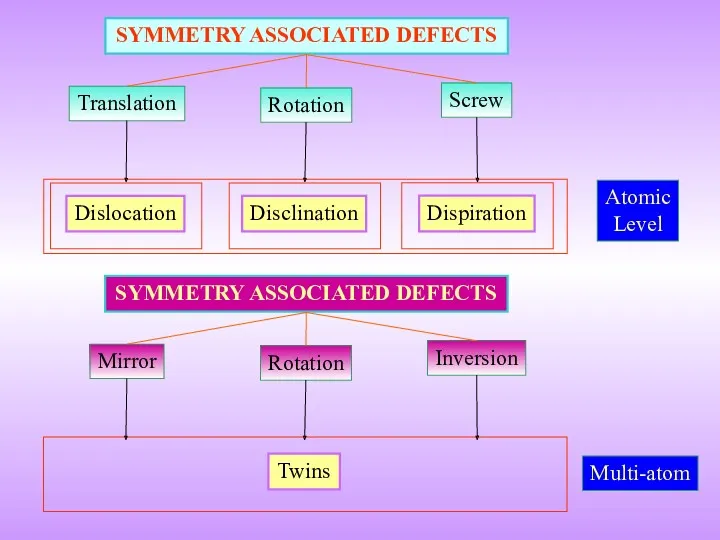
- 4. Translation SYMMETRY ASSOCIATED DEFECTS Rotation Screw Atomic Level Dislocation Disclination Dispiration Mirror SYMMETRY ASSOCIATED DEFECTS Rotation
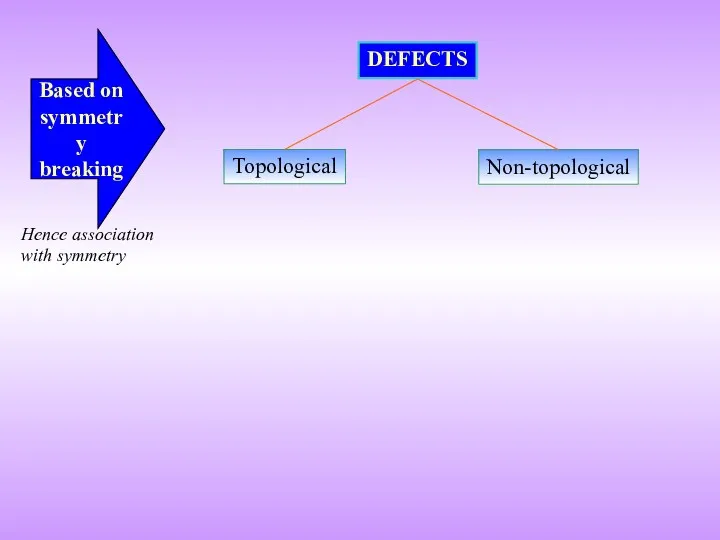
- 5. Topological DEFECTS Non-topological Based on symmetry breaking Hence association with symmetry
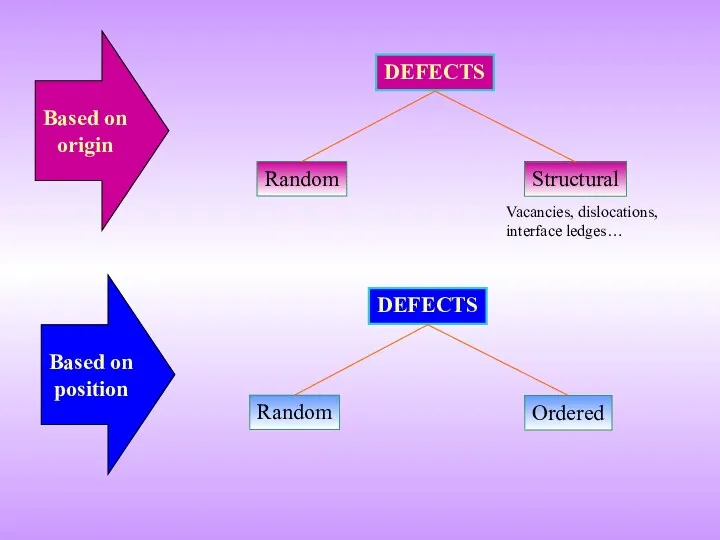
- 6. Random DEFECTS Structural Random DEFECTS Ordered Based on origin Based on position Vacancies, dislocations, interface ledges…
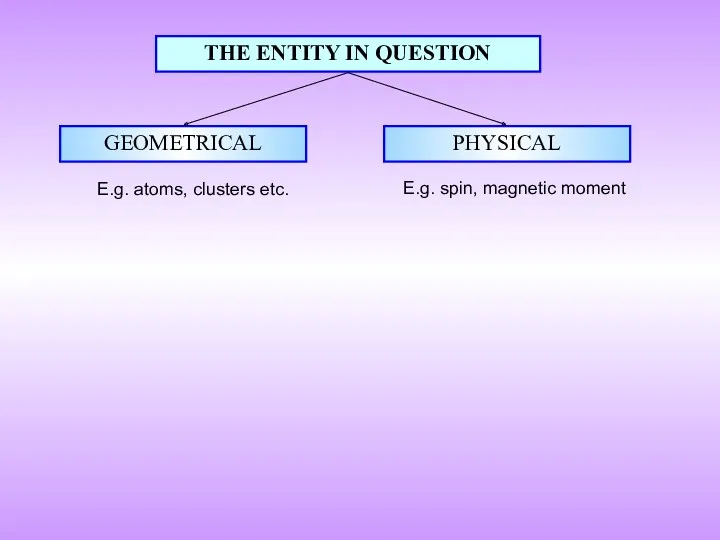
- 7. THE ENTITY IN QUESTION GEOMETRICAL PHYSICAL E.g. atoms, clusters etc. E.g. spin, magnetic moment
- 8. THE OPERATION DEFINING A DEFECT CANNOT BE A SYMMETRY OPERATION OF THE CRYSTAL A DEFECT “ASSOCIATED”
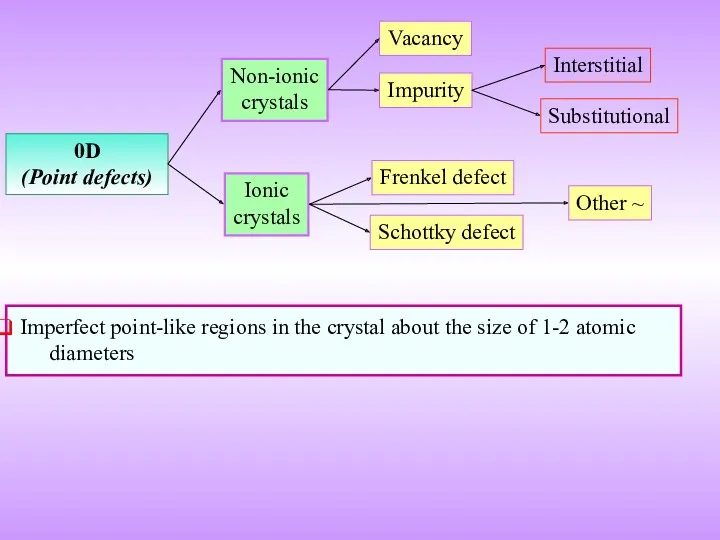
- 9. 0D (Point defects) Vacancy Impurity Frenkel defect Schottky defect Non-ionic crystals Ionic crystals Imperfect point-like regions
- 10. Vacancy Missing atom from an atomic site Atoms around the vacancy displaced Tensile stress field produced
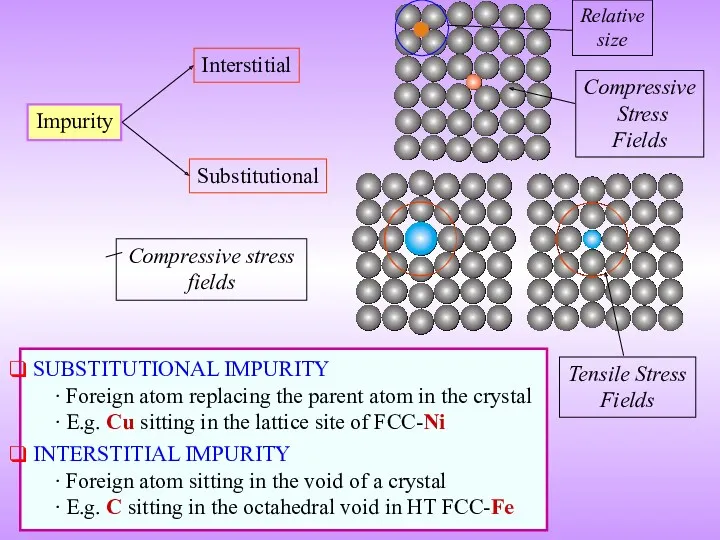
- 11. Impurity Interstitial Substitutional SUBSTITUTIONAL IMPURITY ∙ Foreign atom replacing the parent atom in the crystal ∙
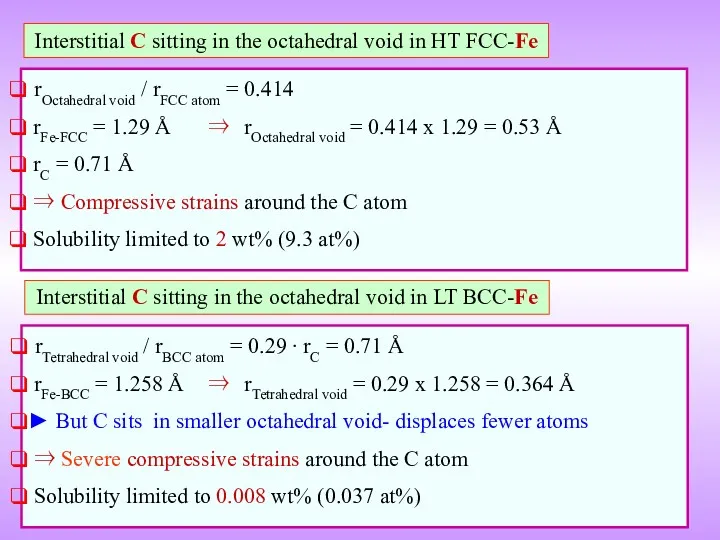
- 12. Interstitial C sitting in the octahedral void in HT FCC-Fe rOctahedral void / rFCC atom =
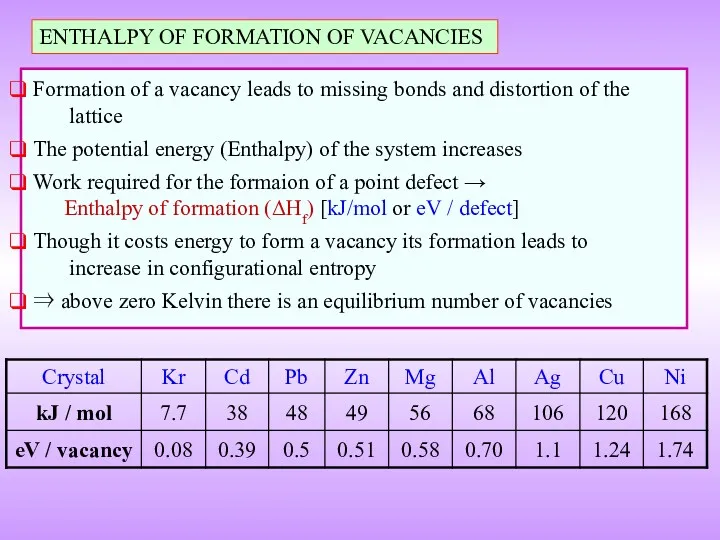
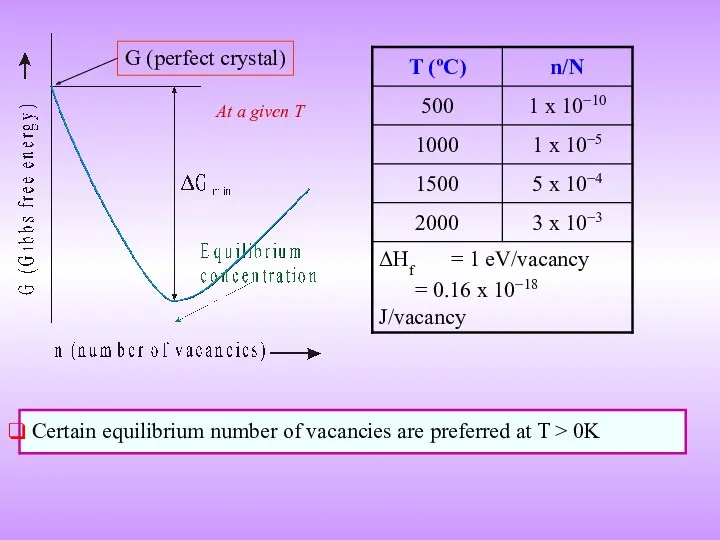
- 13. ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF VACANCIES Formation of a vacancy leads to missing bonds and distortion of
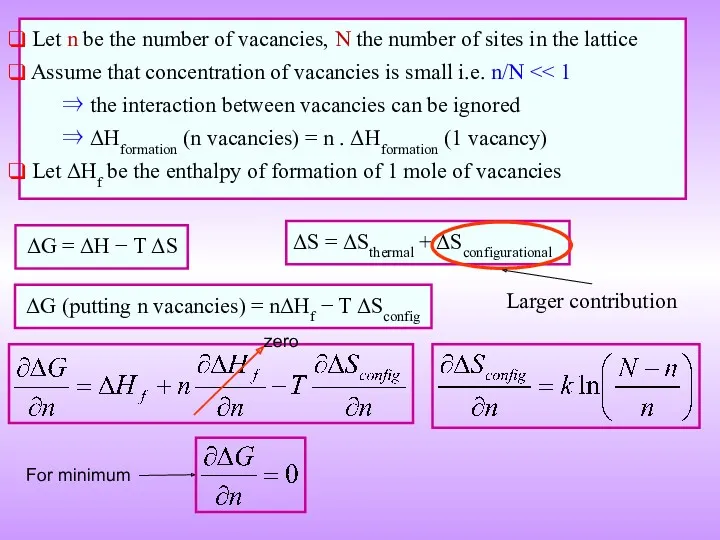
- 14. ΔG = ΔH − T ΔS ΔG (putting n vacancies) = nΔHf − T ΔSconfig Let
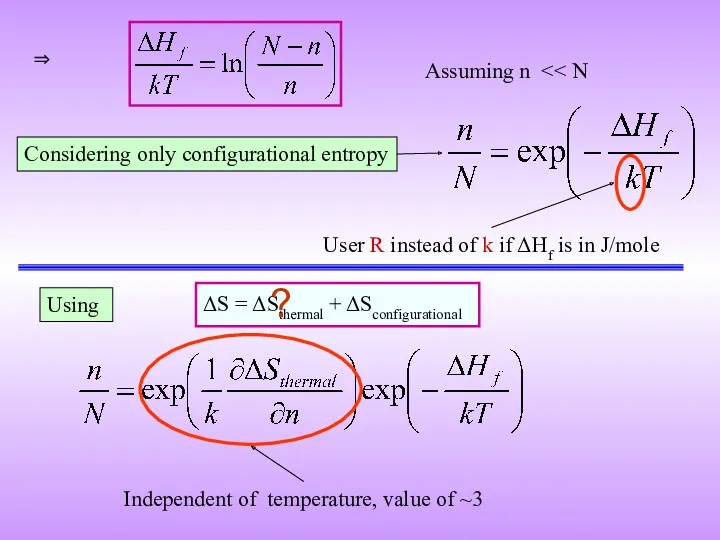
- 15. Considering only configurational entropy ⇒ User R instead of k if ΔHf is in J/mole Assuming
- 16. Certain equilibrium number of vacancies are preferred at T > 0K At a given T
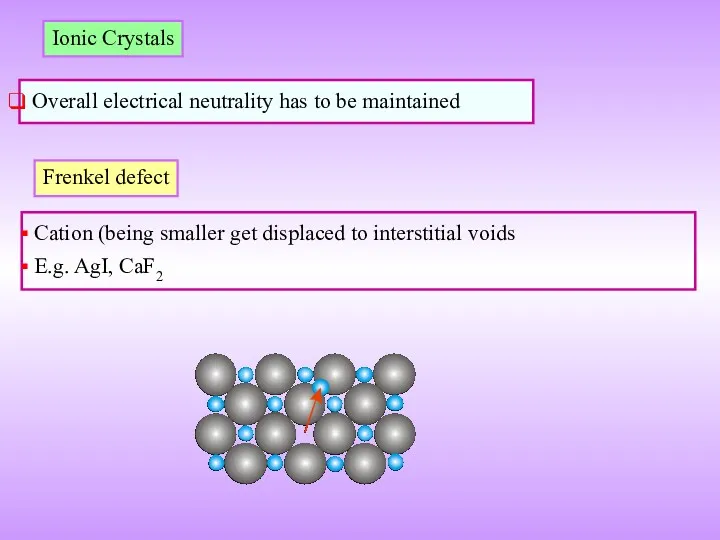
- 17. Ionic Crystals Overall electrical neutrality has to be maintained Frenkel defect Cation (being smaller get displaced
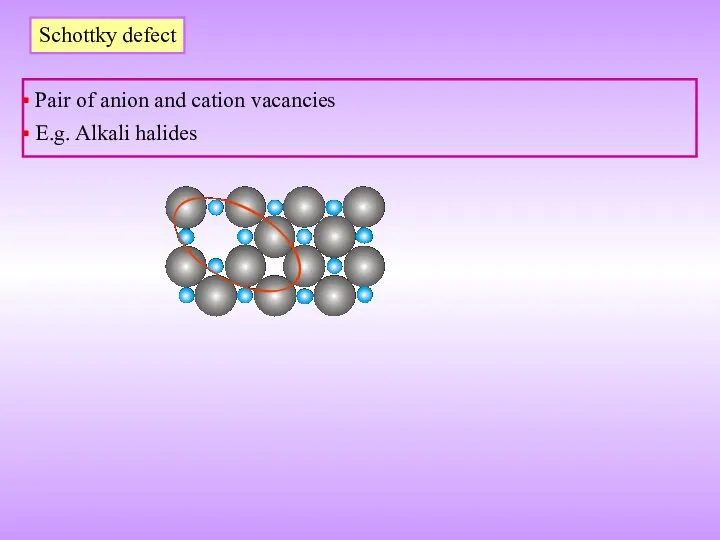
- 18. Schottky defect Pair of anion and cation vacancies E.g. Alkali halides
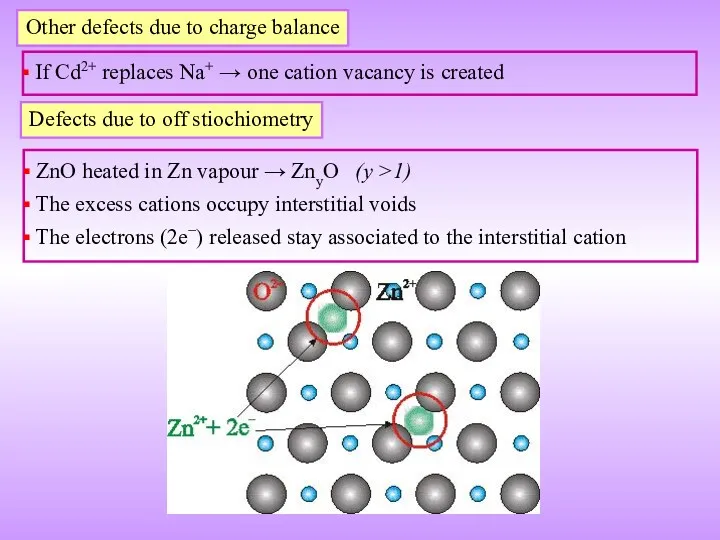
- 19. Other defects due to charge balance If Cd2+ replaces Na+ → one cation vacancy is created
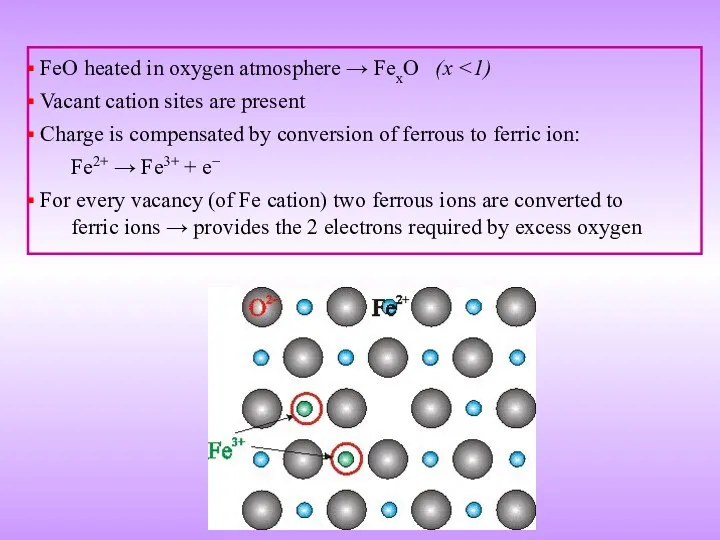
- 20. FeO heated in oxygen atmosphere → FexO (x Vacant cation sites are present Charge is compensated
- 22. Скачать презентацию


 Теория электролитической диссоциации
Теория электролитической диссоциации Алюминий и его соединения
Алюминий и его соединения Химические свойства металлов
Химические свойства металлов Хромопротеиды: биологическая роль. Синтез и распад гема. Метаболизм билирубина
Хромопротеиды: биологическая роль. Синтез и распад гема. Метаболизм билирубина Азот. Соединения азота
Азот. Соединения азота Атомы и молекулы
Атомы и молекулы Нахождение металлов в природе. Общие способы получения металлов. 9 класс
Нахождение металлов в природе. Общие способы получения металлов. 9 класс Строение и свойства металлов. Физические и механические свойства металлов
Строение и свойства металлов. Физические и механические свойства металлов Вода: фізичні та хімічні властивості. Поширеність в природі
Вода: фізичні та хімічні властивості. Поширеність в природі Реакции при участии катализатора
Реакции при участии катализатора Органикалық қосылыстардың химиялық құрылыс теориясы, органикалық қосылыстардың структурасы және қосылыстары
Органикалық қосылыстардың химиялық құрылыс теориясы, органикалық қосылыстардың структурасы және қосылыстары Оксиды в минералогии
Оксиды в минералогии Гниение. Брожение
Гниение. Брожение Термо-и радиационностойкие полимерные матрицы для композиционных материалов
Термо-и радиационностойкие полимерные матрицы для композиционных материалов Окислительно-восстановительные реакции
Окислительно-восстановительные реакции Классификация химических реакций
Классификация химических реакций Ионная хроматография
Ионная хроматография Экспериментальным исследованием установить тип данной химической реакции
Экспериментальным исследованием установить тип данной химической реакции Химическая связь
Химическая связь Цветные металлы и сплавы
Цветные металлы и сплавы Твердые вещества
Твердые вещества Периодический закон и строение атома
Периодический закон и строение атома Роль побутової хімії у житті
Роль побутової хімії у житті Генетическая связь органических и неорганических соединений
Генетическая связь органических и неорганических соединений Нанокаталіз. Активність каталізатора
Нанокаталіз. Активність каталізатора Синтетические моющие средства. Использование их в повседневной жизни
Синтетические моющие средства. Использование их в повседневной жизни Мило та миловаріння
Мило та миловаріння Методы количественного определения. Химические методы анализа
Методы количественного определения. Химические методы анализа