Содержание
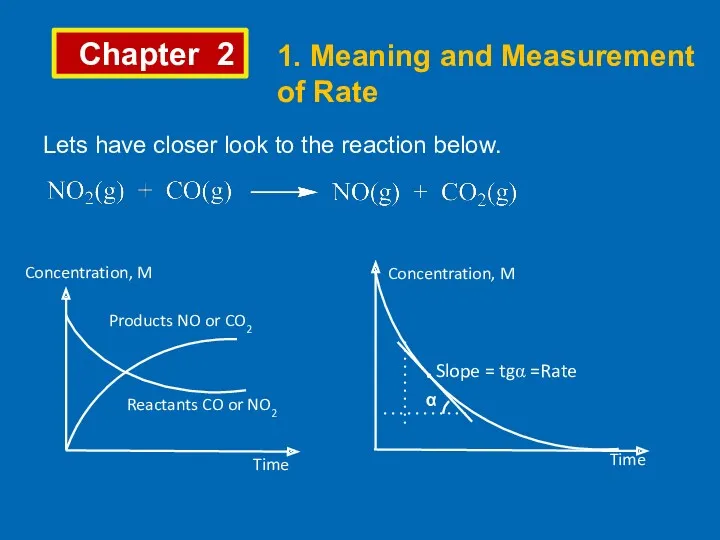
- 2. Chapter 2 1. Meaning and Measurement of Rate Lets have closer look to the reaction below.
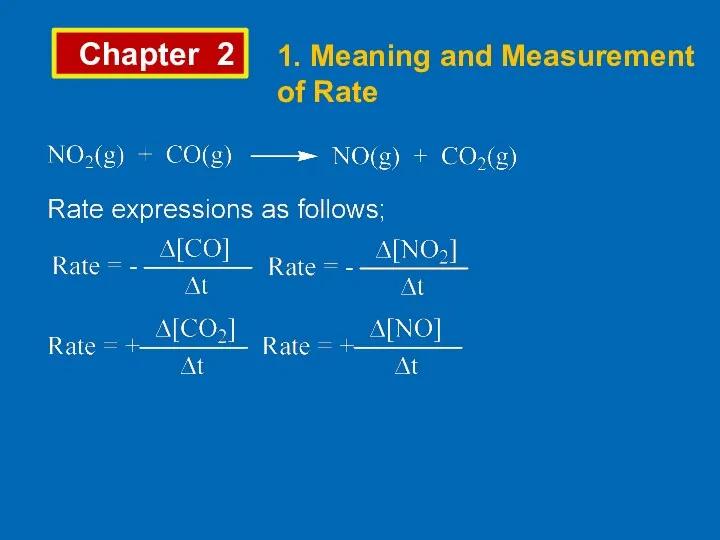
- 3. Chapter 2 1. Meaning and Measurement of Rate
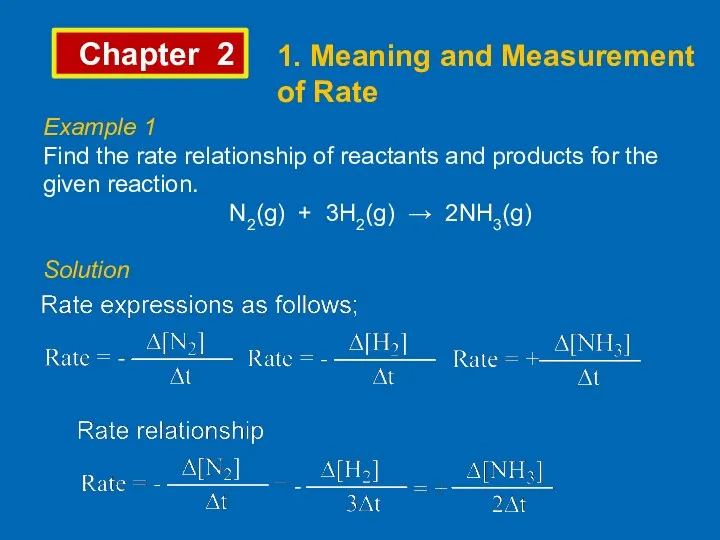
- 4. Chapter 2 1. Meaning and Measurement of Rate Example 1 Find the rate relationship of reactants
- 5. The decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide can be represented by the equation; 2N2O5 → 4NO2 + O2
- 6. RateN2O5 = (0.008 – 0.004)/20 = 0.0002 = 2.10−4 mol/L. s
- 7. Chapter 2 1. Meaning and Measurement of Rate Example 2 In the following decomposition reaction, 2N2O5
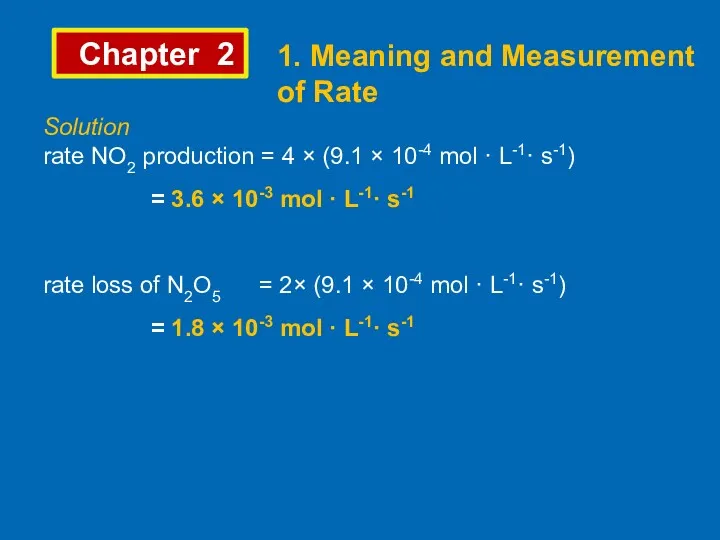
- 8. Chapter 2 1. Meaning and Measurement of Rate Solution rate NO2 production = 4 × (9.1
- 9. Chapter 2 3. Rate Expression and Rate Constant Consider the one step following reaction; mA +
- 10. Chapter 2 3. Rate Expression and Rate Constant Example 10 Write the possible rate expression of
- 11. Chapter 2 3. Rate Expression and Rate Constant Example 11 Write the rate expression of the
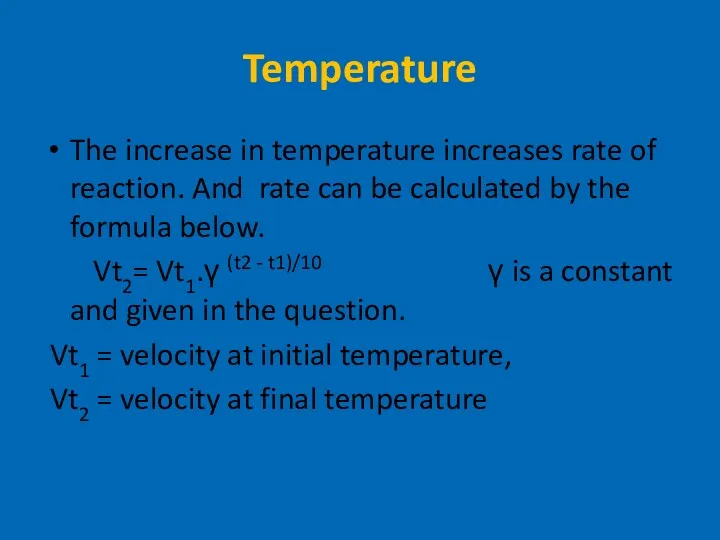
- 12. Temperature The increase in temperature increases rate of reaction. And rate can be calculated by the
- 14. Скачать презентацию






 Цеолиты. Свойства и область применения
Цеолиты. Свойства и область применения Массообменные процессы
Массообменные процессы Степень загрязнения почвы по химическому составу снежного покрова на разном удалении от источника загрязнения
Степень загрязнения почвы по химическому составу снежного покрова на разном удалении от источника загрязнения Щелочные металлы
Щелочные металлы Химическое равновесие
Химическое равновесие Дисперсные системы
Дисперсные системы Азотсодержащие соединения
Азотсодержащие соединения Кислородсодержащие органические соединения. Лабораторная работа
Кислородсодержащие органические соединения. Лабораторная работа Неорганические полимеры
Неорганические полимеры Анализ лекарственных средств паминофенола, ароматических кислот: бензойная кислота, натрия бензоат, салициловая кислота
Анализ лекарственных средств паминофенола, ароматических кислот: бензойная кислота, натрия бензоат, салициловая кислота Азот қышқылын өндіру
Азот қышқылын өндіру Алкадиены (диены, диеновые углеводороды)
Алкадиены (диены, диеновые углеводороды) Шестичленные гетероциклические соединения с одним и двумя гетероатомами. Конденсированные системы гетероциклов
Шестичленные гетероциклические соединения с одним и двумя гетероатомами. Конденсированные системы гетероциклов Cromatografia ionică
Cromatografia ionică Алкены. Номенклатура. Строение молекулы
Алкены. Номенклатура. Строение молекулы Метанол. Фізичні властивості
Метанол. Фізичні властивості Энергетика химических реакций
Энергетика химических реакций Классификация химических реакций
Классификация химических реакций Основні класи неорганічних сполук
Основні класи неорганічних сполук Уральские самоцветы
Уральские самоцветы Склад та властивості основних класів неорганічних сполук
Склад та властивості основних класів неорганічних сполук Конструкционные материалы
Конструкционные материалы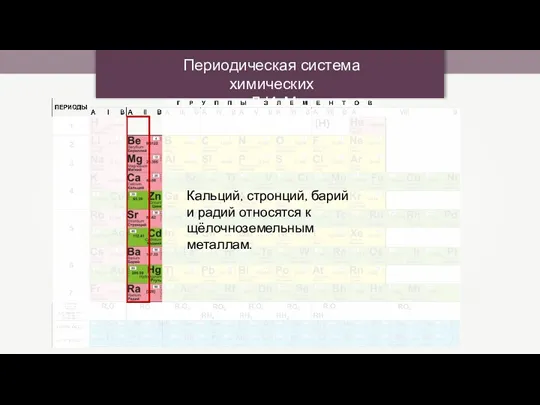 Периодическая система химических элементов Д.И. Менделеева
Периодическая система химических элементов Д.И. Менделеева Оксид меди
Оксид меди Электроповерхностные явления. Строение двойного электрического слоя
Электроповерхностные явления. Строение двойного электрического слоя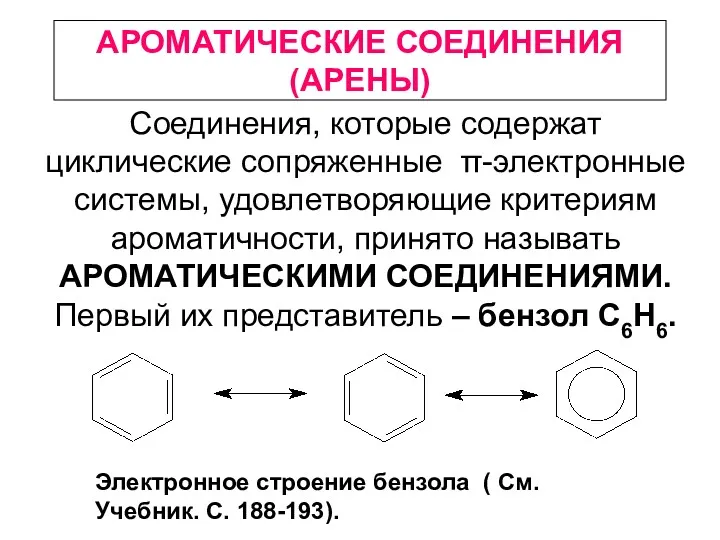 Ароматические соединения (арены)
Ароматические соединения (арены) λ-MnO2 as material with pseudocapacitive properties
λ-MnO2 as material with pseudocapacitive properties Svante Arrhenius and the theory of electrolytic and non-electrolytic dissociation
Svante Arrhenius and the theory of electrolytic and non-electrolytic dissociation