Слайд 2

SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITIES
TERMS
Solution: a homogeneous mixture containing particles the size of
a typical ion or covalent molecule. (0.1–2.0 nm in diameter)
Colloid: a homogeneous mixture containing particles with diameters in the range 2–500 nm
Suspensions are mixtures with even larger particles, but they are not considered true solutions because they separate upon standing.
Solute: the dissolved substance in a solution
Solvent: the major component in a solution
Слайд 3

SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITIES
A solution is saturated when no additional solute can
be dissolved at a particular temperature
A Supersaturated solution can form when more than the equilibrium amount of solute is dissolved at an elevated temperature, and then the supersaturated solution is slowly cooled.
An Unsaturated solution is formed when more of the solute can dissolve in it at a particular temperature.
Слайд 4
SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITIES
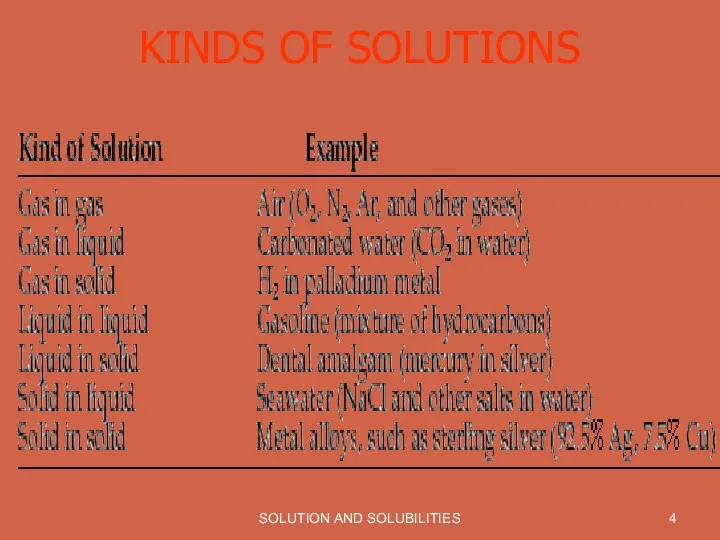
KINDS OF SOLUTIONS
Слайд 5

SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITIES
Слайд 6

SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITIES
SOLUBILITY
The amount of solute per unit solvent required to
form a saturated solution is called the solute's Solubility.
When two liquids are completely soluble in each other they are said to be Miscible.
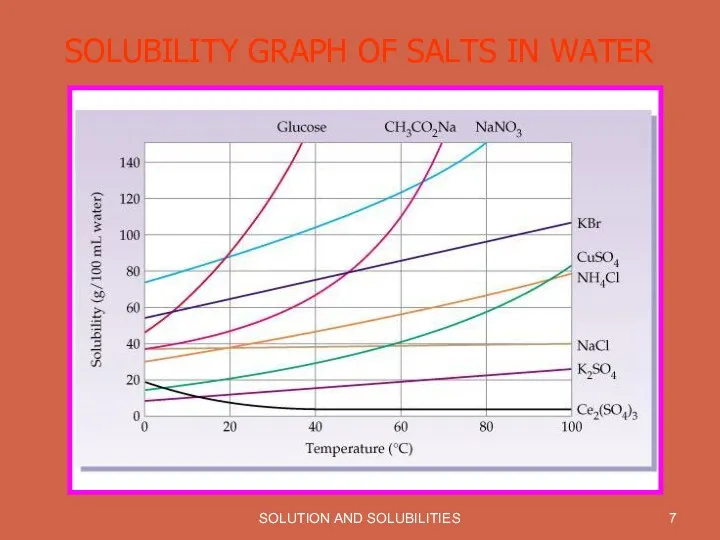
Solubility is effected by Temperature. With increase in temperature solubility of most of the substances increases.
Most gases become less soluble in water as the temperature increases.
Слайд 7
SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITIES
SOLUBILITY GRAPH OF SALTS IN WATER
Слайд 8
SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITIES
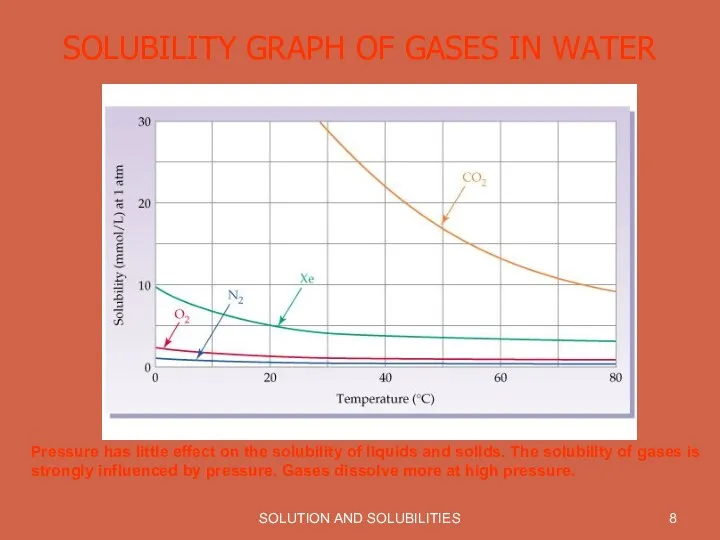
SOLUBILITY GRAPH OF GASES IN WATER
Pressure has little effect
on the solubility of liquids and solids. The solubility of gases is strongly influenced by pressure. Gases dissolve more at high pressure.
Слайд 9
SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITIES
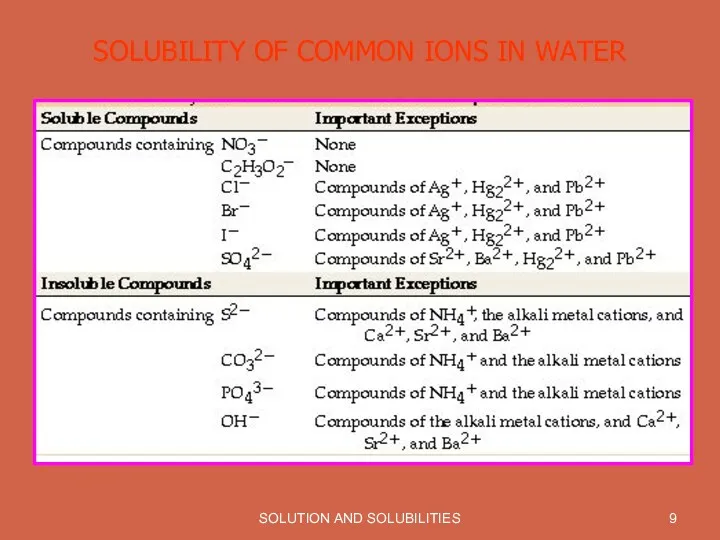
SOLUBILITY OF COMMON IONS IN WATER
Слайд 10

SOLUTION AND SOLUBILITIES
DISSOLUTION OF SODIUM CHLORIDE IN WATER









 Превращение веществ. Роль химии в жизни человека
Превращение веществ. Роль химии в жизни человека Природные каменные материалы. (Лекция 3)
Природные каменные материалы. (Лекция 3) Химия өнеркәсібі
Химия өнеркәсібі Алкандар. (қаныққан көмірсутектер. Парафиндер.)
Алкандар. (қаныққан көмірсутектер. Парафиндер.) Электролитическая диссоциация
Электролитическая диссоциация Химическая посуда и лабораторное оборудование
Химическая посуда и лабораторное оборудование Сутектік көрсеткіш ph. Тұздар гидролизі
Сутектік көрсеткіш ph. Тұздар гидролизі Основания. Формула сильной кислоты
Основания. Формула сильной кислоты Минералы
Минералы Природные источники углеводородов
Природные источники углеводородов Молярный объем газов
Молярный объем газов Визитка химического элемента. Водород
Визитка химического элемента. Водород Аминокислоты. Белки
Аминокислоты. Белки Неметаллы. Особенности строения атомов неметаллов
Неметаллы. Особенности строения атомов неметаллов Многоатомные спирты
Многоатомные спирты Типы химических реакций в органической химии
Типы химических реакций в органической химии Коррозия и методы борьбы с ней
Коррозия и методы борьбы с ней Физические, химические свойства предельных и непредельных карбоновых кислот, получение
Физические, химические свойства предельных и непредельных карбоновых кислот, получение Неметаллические и композиционные материалы
Неметаллические и композиционные материалы Кислород. Распространение кислорода в природе (8 класс)
Кислород. Распространение кислорода в природе (8 класс) Вклад ученых-химиков в победу в Великой Отечественной войне
Вклад ученых-химиков в победу в Великой Отечественной войне Нанотехнологии и Наноматериалы
Нанотехнологии и Наноматериалы Коррозия металлов и способы защиты от неё. (11 класс)
Коррозия металлов и способы защиты от неё. (11 класс) Химический процесс. Практические занятия
Химический процесс. Практические занятия Стехиометрия и классификация твердых веществ
Стехиометрия и классификация твердых веществ Общая характеристика твердого, жидкого и газообразного видов топлива
Общая характеристика твердого, жидкого и газообразного видов топлива Тайна мыльного пузыря
Тайна мыльного пузыря Алюминий и его соединения
Алюминий и его соединения