The structure and properties of the nitrogen and ammonia molecules. Industrial production of nitrogen fertilizers (topic 4.4) презентация
Содержание
- 2. Outline Introduction Main part 1. Nitrogen 2. Ammonia 3. Nitrogen oxides 4. Nitric acid 5. Ammonium
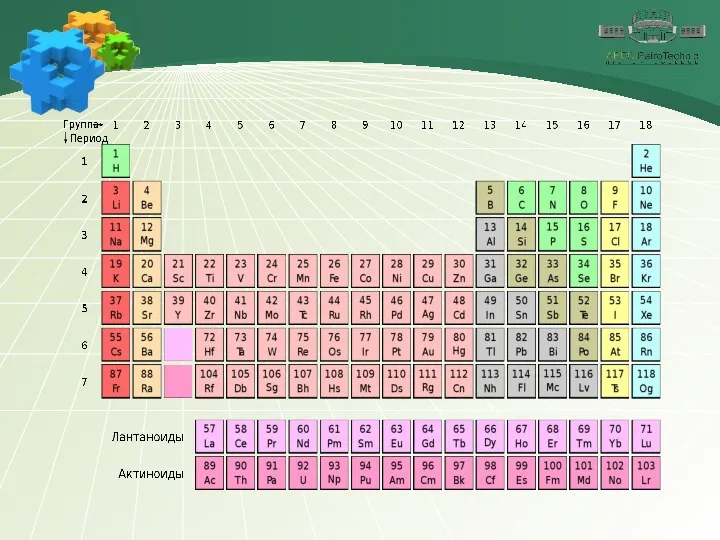
- 3. 1. Nitrogen Chemical element Nitrogen is a chemical element number 7. It is located in the
- 5. 1. Nitrogen Chemical element Nitrogen is found in the air as a simple substance. Its volume
- 6. 1. Nitrogen Simple substance Molecules of a simple substance consist of two atoms linked by a
- 7. 1. Nitrogen Simple substance When heated, it forms nitrides with some other metals: t 3Ca +
- 8. 1. Nitrogen Simple substance The reducing properties of nitrogen are manifested in reaction with oxygen: t
- 9. 1. Nitrogen Application and obtaining A large amount of nitrogen is used to obtain ammonia and
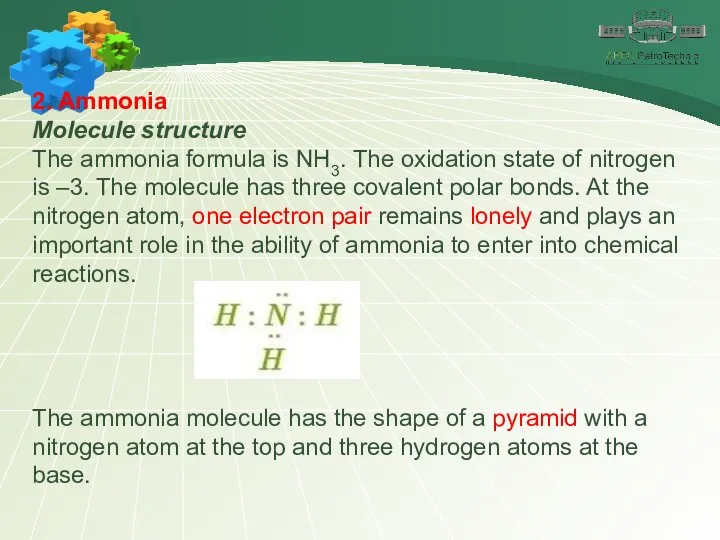
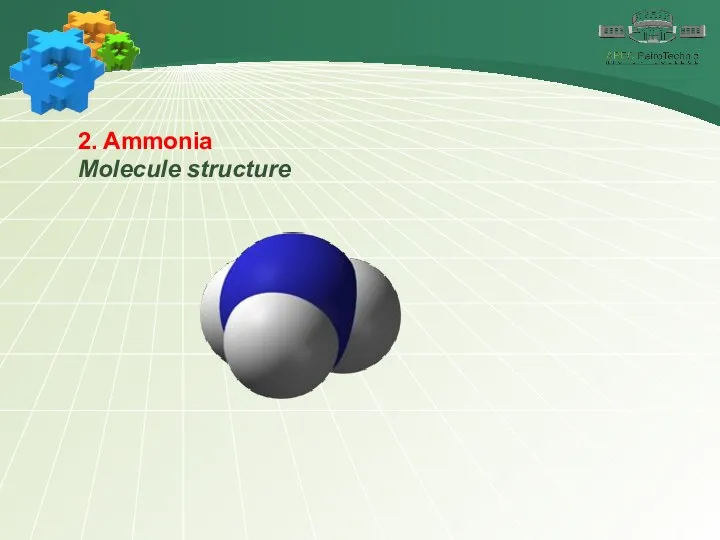
- 10. 2. Ammonia Molecule structure The ammonia formula is NH3. The oxidation state of nitrogen is –3.
- 11. 2. Ammonia Molecule structure The common electron pairs in the molecule are shifted towards the more
- 12. 2. Ammonia Molecule structure
- 13. 2. Ammonia Physical properties Under normal conditions, ammonia is a colorless gas with a pungent, unpleasant
- 14. 2. Ammonia Physical properties
- 15. 2. Ammonia Chemical properties 1. Reducing properties. The oxidation state of nitrogen in ammonia is –3,
- 16. 2. Ammonia Chemical properties 1. Reducing properties. 4N−3H3 + 3O20 = 2N20 + 6H2O−2. If the
- 17. 2. Ammonia 2. Basic properties. If you add a few drops of phenolphthalein to an aqueous
- 18. 2. Ammonia 2. Basic properties. Ammonia reacts with acids. In this case, ammonium salts are formed.
- 19. 2. Ammonia Receiving and using In industry, ammonia is synthesized from nitrogen and hydrogen: t, p,
- 20. Ammonia production
- 21. 3. Nitrogen oxides Nitrogen exhibits positive oxidation states from +1 to +5 and forms compounds with
- 22. 3. Nitrogen oxides Colorless nitric (II) oxide is formed in the reaction of nitrogen with oxygen
- 23. 3. Nitrogen oxides Pay attention! Nitric (I) oxide and nitrogen (II) oxide are non-salt-forming oxides. They
- 24. 3. Nitrogen oxides Other oxides are salt-forming (acidic). Nitric (III) oxide corresponds to a weak nitrous
- 25. 4. Nitric acid Physical properties Nitric acid HNO3 is a colorless liquid fuming in air with
- 26. 4. Nitric acid
- 27. 4. Nitric acid General properties of acids Nitric acid reacts with basic and amphoteric oxides and
- 28. 4. Nitric acid Special properties Unlike other acids, nitric acid reacts with most metals except noble
- 29. 4. Nitric acid The oxidizing agent in these reactions is the nitrogen atom of the acid
- 30. 4. Nitric acid Copper with concentrated nitric acid
- 31. 4. Nitric acid Pay attention! Concentrated nitric acid passivates iron and aluminum. A strong film forms
- 32. 4. Nitric acid Application Nitric acid is used in industry to obtain: -mineral fertilizers, -medicines, -explosives,
- 33. 5. Ammonium salts. Nitrates Ammonium salts Ammonium salts are complex substances formed by the ammonium cation
- 34. 5. Ammonium salts. Nitrates Ammonium nitrate
- 35. 5. Ammonium salts. Nitrates Ammonium salts Ammonium salts are formed when ammonia interacts with acids: NH3
- 36. 5. Ammonium salts. Nitrates Ammonium salts The general properties of salts include the ability to enter
- 37. The special properties of salts are due to the instability of the ammonium ion and its
- 38. Nitrates Nitrates are salts of nitric acid. NaNO3 - sodium nitrate, Cu (NO3)2 - copper (II)
- 39. Questions for self control 1.Indicate the formula for saltpeter: A)NH4HCO3 B)Na3PO4 C)NaNO3 2.Choose the name of
- 40. 4.Specify the characteristic of nitrogen: A)easily liquefies when cooled B)reacts with oxygen at high temperature C)oxidizes
- 41. 7.Choose the properties of ammonium salts: A)resistant to heat B)formed in the reaction of ammonia with
- 42. 10.Establish an accordance between the formula of a substance and its characteristics. 1 - N2, 2
- 43. Literature 1.Basic literature : 1. Jenkins, Chemistry, ISBN 978-0-17-628930-0 2. Alberta Learning, Chemistry data booklet 2010,
- 44. 2.Additional literature : 1.Б.А.Мансуров «Химия» 10-11 кл., Атамура 2015 г 2.Б.Мансуров., Н.Торшина «Методика преподавания органической химии»
- 46. Скачать презентацию







































 Инструментальные методы исследования органических веществ
Инструментальные методы исследования органических веществ III А – топтың элементтері
III А – топтың элементтері Удивительные свойства воды
Удивительные свойства воды Гидролиз солей (11 класс)
Гидролиз солей (11 класс) Кристаллизация. Структура жидких металлов
Кристаллизация. Структура жидких металлов Глюкоза. Хімічні властивості глюкози. Сахароза, гідроліз
Глюкоза. Хімічні властивості глюкози. Сахароза, гідроліз Алкены. Строение алкенов, характерные типы химических реакций
Алкены. Строение алкенов, характерные типы химических реакций Кремнийдің құрамы, құрылысы және қасиеттері
Кремнийдің құрамы, құрылысы және қасиеттері Защита от коррозии каменных и бетонных строительных материалов и конструкций
Защита от коррозии каменных и бетонных строительных материалов и конструкций Химиялық элемент оттегі
Химиялық элемент оттегі Теплота горения
Теплота горения Закон сохранения массы веществ. Химические уравнения
Закон сохранения массы веществ. Химические уравнения Окислительно-восстановительные реакции
Окислительно-восстановительные реакции Фенолдар, аминдер, альдегидтер
Фенолдар, аминдер, альдегидтер СФ- И ЯМР-ИССЛЕДОВАНИЕ РЕДОКС-ПРОЦЕССОВ В СИСТЕМЕ Со(II)-ЭДТА-H2O2
СФ- И ЯМР-ИССЛЕДОВАНИЕ РЕДОКС-ПРОЦЕССОВ В СИСТЕМЕ Со(II)-ЭДТА-H2O2 Кислород. Общая характеристика, получение и свойства
Кислород. Общая характеристика, получение и свойства Некоторые d-элементы
Некоторые d-элементы Пенообразование в растворах поверхностно-активных веществ. Лекция 13
Пенообразование в растворах поверхностно-активных веществ. Лекция 13 Ендотермічні реакції на службі людини
Ендотермічні реакції на службі людини Неоднородные системы, их классификация, методы разделения. Лекция 4
Неоднородные системы, их классификация, методы разделения. Лекция 4 Химические свойства солей
Химические свойства солей Хімічні явища, їх ознаки
Хімічні явища, їх ознаки Особенности органических веществ. Классификация органических соединений. 9 класс
Особенности органических веществ. Классификация органических соединений. 9 класс Разработка проектных решений по переводу паровых котлов электростанций в конденсационный режим с целью увеличения кпд котла
Разработка проектных решений по переводу паровых котлов электростанций в конденсационный режим с целью увеличения кпд котла Алюминий. Определите элемент
Алюминий. Определите элемент 20230219_prezentatsiya_k_uroku_neft
20230219_prezentatsiya_k_uroku_neft 20231028_kislorod
20231028_kislorod Материаловедение и технологии конструкционных материалов
Материаловедение и технологии конструкционных материалов