Содержание
- 2. The translation and transcription
- 3. Learning objectives Specifies the translation and transcription
- 4. Success criteria Knows the definition of transcription and translation terms Defines the terms of transcription and
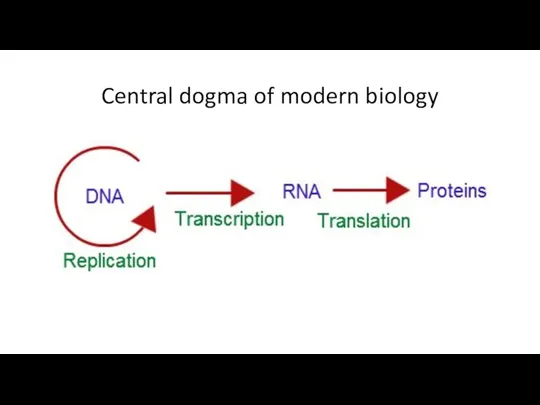
- 5. Central dogma of modern biology
- 6. Central dogma of modern biology The Central Dogma. This states that once ‘information’ has passed into
- 7. The central dogma suggests that DNA contains the information needed to make all of our proteins,
- 8. The central dogma states that the pattern of information that occurs most frequently in our cells
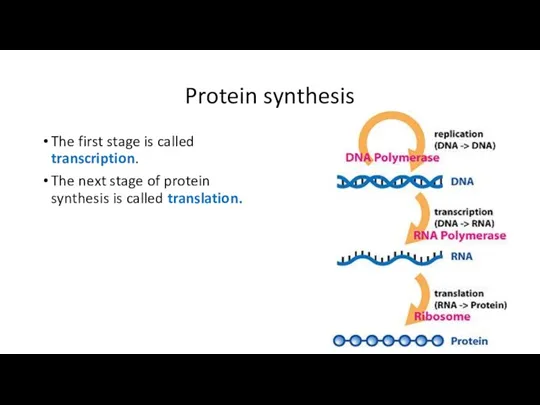
- 9. Protein synthesis The first stage is called transcription. The next stage of protein synthesis is called
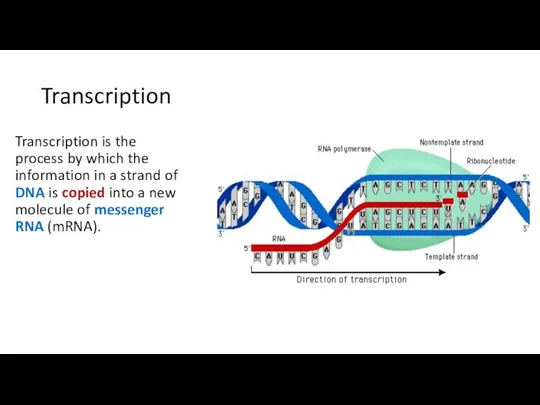
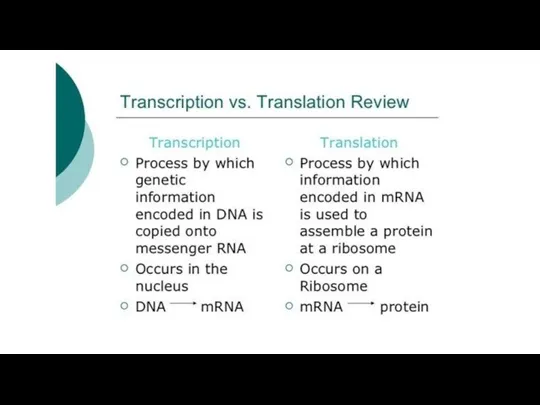
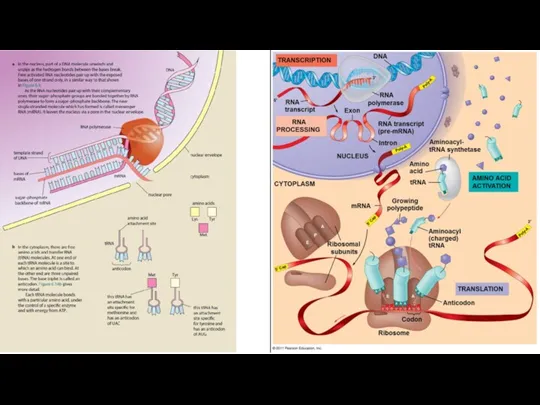
- 10. Transcription Transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied
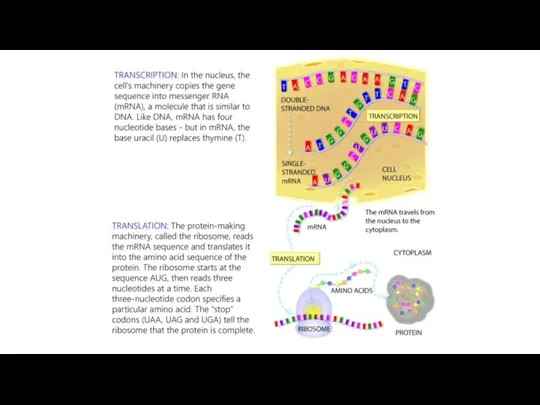
- 11. Transcription In the nucleus, a complementary copy of the code from a gene is made by
- 12. Transcription DNA safely and stably stores genetic material in the nuclei of cells as a reference,
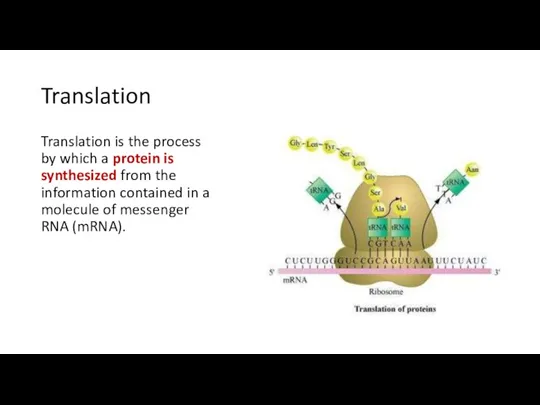
- 14. Translation Translation is the process by which a protein is synthesized from the information contained in
- 15. Translation Protein synthesis is called translation because this is when the DNA code is translated into
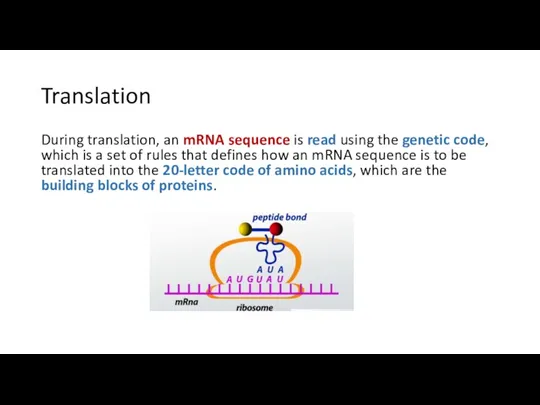
- 16. Translation During translation, an mRNA sequence is read using the genetic code, which is a set
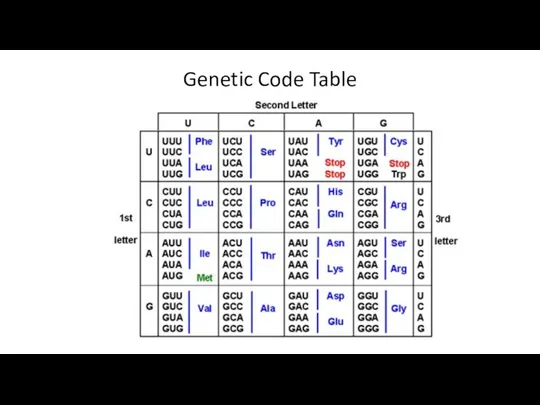
- 17. Translation The genetic code is a set of three-letter combinations of nucleotides called codons, each of
- 20. The triplet code The code is a three-letter, or triplet, code. Each sequence of three bases
- 21. Genetic Code Table
- 24. Скачать презентацию







 Огнетушащие вещества химического торможения реакции горения
Огнетушащие вещества химического торможения реакции горения Центрифугирование в почвоведении
Центрифугирование в почвоведении Принципы наноармирования волокнистых композитов
Принципы наноармирования волокнистых композитов Алкины. 10 класс
Алкины. 10 класс Вирощування кристалів солей
Вирощування кристалів солей Решение задач по теме Растворы
Решение задач по теме Растворы Введение в токсикологическую химию. Объекты химико-токсикологического исследования
Введение в токсикологическую химию. Объекты химико-токсикологического исследования Некоторые d-элементы
Некоторые d-элементы Валентность химических элементов. 8 класс
Валентность химических элементов. 8 класс Тотығу-тотықсыздану реакциялары
Тотығу-тотықсыздану реакциялары Разбор сложных заданий ЕГЭ по химии
Разбор сложных заданий ЕГЭ по химии Общая теория протолитических равновесий и процессов. Буферные системы
Общая теория протолитических равновесий и процессов. Буферные системы Электрохимические процессы
Электрохимические процессы Непредельные углеводороды. Алкены
Непредельные углеводороды. Алкены Сероводород. Сернистый водород, сульфид водорода, дигидросульфид
Сероводород. Сернистый водород, сульфид водорода, дигидросульфид Теории химической кинетики Лекция 5
Теории химической кинетики Лекция 5 Запалювання нагрітим тілом та електричним розрядом
Запалювання нагрітим тілом та електричним розрядом Состояние электронов в атоме
Состояние электронов в атоме Crystal defects and imperfections
Crystal defects and imperfections Своя игра Знаешь ли ты химические элементы?
Своя игра Знаешь ли ты химические элементы? Класифікація неорганічних сполук, їхній склад і номенклатура
Класифікація неорганічних сполук, їхній склад і номенклатура Неметаллы. Элементы неметаллы в ПСХЭ
Неметаллы. Элементы неметаллы в ПСХЭ Изучение физико-химических свойств мицеллярных растворов индивидуальных ПАВ, композиций различных ПАВ
Изучение физико-химических свойств мицеллярных растворов индивидуальных ПАВ, композиций различных ПАВ Относительная молекулярная масса вещества. Задачи
Относительная молекулярная масса вещества. Задачи Алкодиены или диеновые углеводороды
Алкодиены или диеновые углеводороды Бинарные соединения и их номенклатура
Бинарные соединения и их номенклатура Неметаллы. Обобщающий урок. 9 класс
Неметаллы. Обобщающий урок. 9 класс Определение нефтепродуктов в воде с использованием Флюората-02-5М
Определение нефтепродуктов в воде с использованием Флюората-02-5М