Содержание
- 2. OVERVIEW OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM FUNCTION OF FINANCIAL MARKETS STRUCTURE OF FINANCIAL MARKETS FUNCTIONS OF FINANCIAL
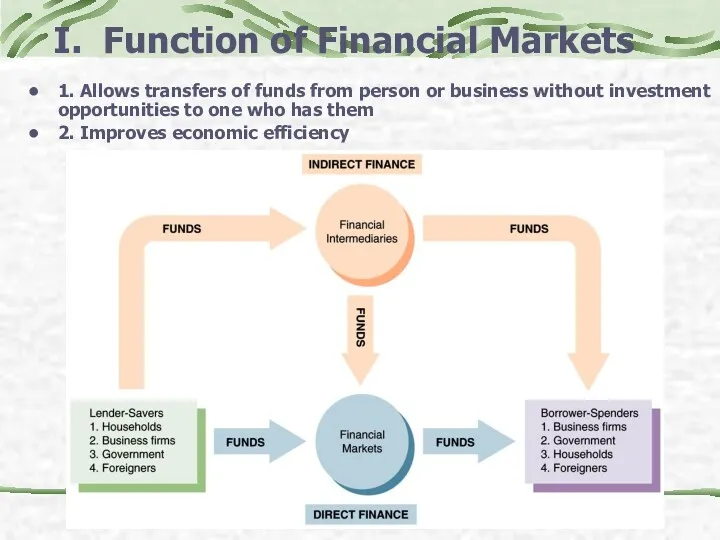
- 3. I. Function of Financial Markets 1. Allows transfers of funds from person or business without investment
- 4. II. Classification of Financial Markets 1. Debt Market Short-Term (maturity Medium-Term (1 Long-Term (maturity > 10
- 5. II. Classification of Financial Markets Money Market the short-term debt instruments with the maturity of less
- 6. Classification of Financial Markets 1. Primary Market New security issues sold to initial buyers Investment Banks
- 7. Classifications of Financial Markets 1. Exchanges Trades conducted in central locations (e.g., New York Stock Exchange,
- 8. Globalization of Financial Markets International Bond Market Foreign bonds sold in a foreign country and denominated
- 9. III. Functions of Financial Intermediaries Financial Intermediaries 1. Engage in process of indirect finance 2. More
- 10. Transactions Costs 1. Financial intermediaries make profits by reducing transactions costs 2. Reduce transactions costs by
- 11. Function of Financial Intermediaries A financial intermediary’s low transaction costs mean that it can provide its
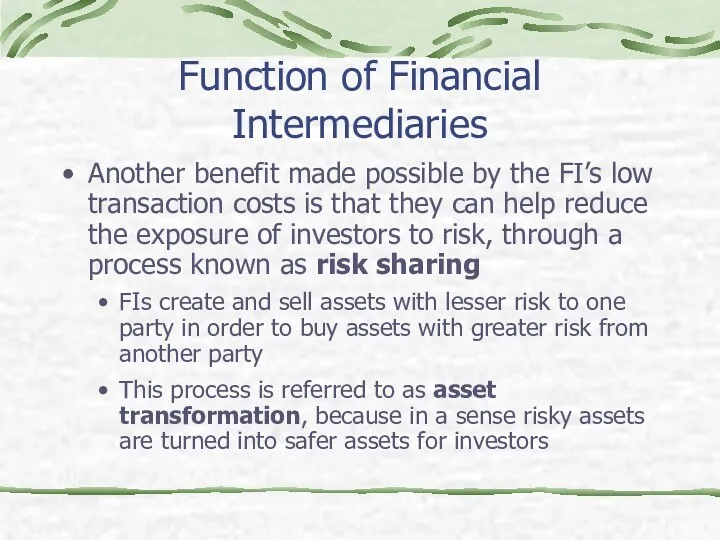
- 12. Function of Financial Intermediaries Another benefit made possible by the FI’s low transaction costs is that
- 13. Asymmetric Information: Adverse Selection and Moral Hazard Adverse Selection 1. Before the transaction occurs 2. Potential
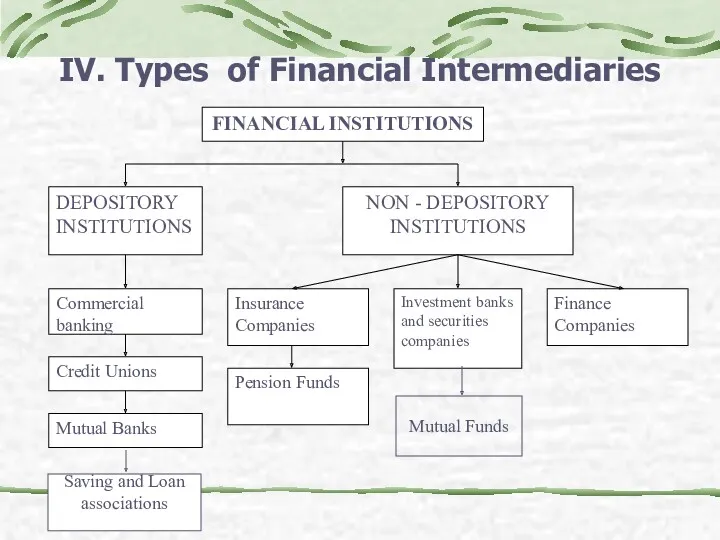
- 14. IV. Types of Financial Intermediaries Saving and Loan associations Mutual Funds
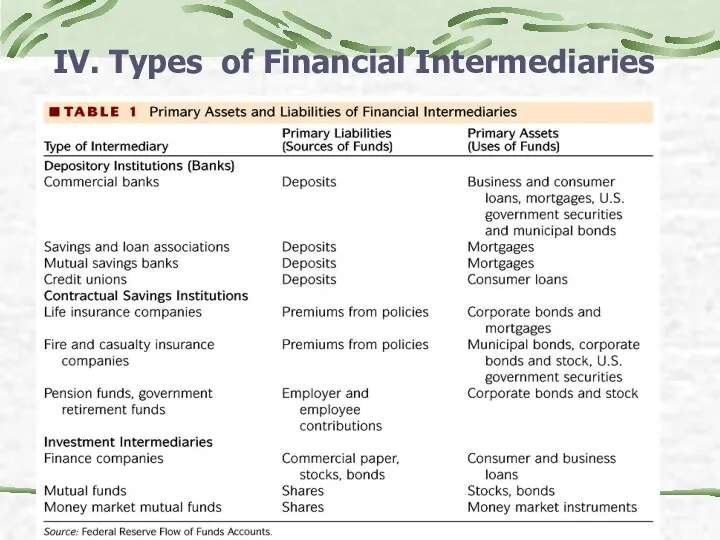
- 15. IV. Types of Financial Intermediaries
- 16. Depository institutions: Significant proportion of their funds comes from deposits. Commercial banks Money centre banks Wholesale
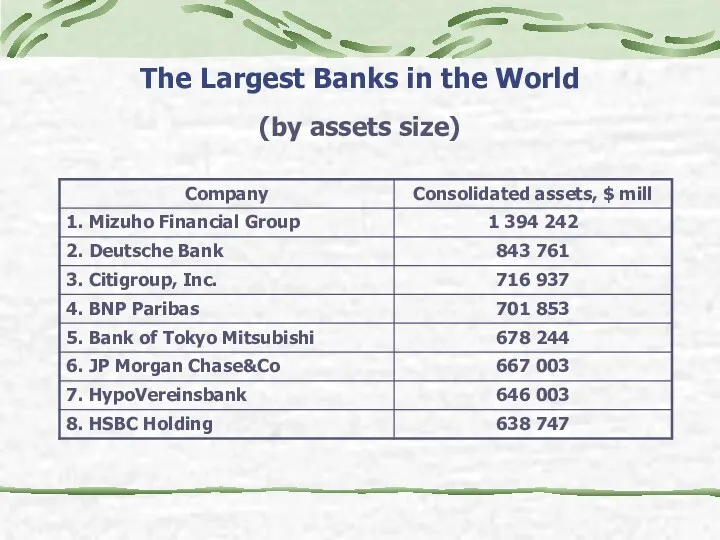
- 17. The Largest Banks in the World (by assets size)
- 18. CONTRACTUAL SAVING INSTITUTIONS Insurance Companies : protection of policyholders from adverse events Life/health insurance companies; Property/Casualty
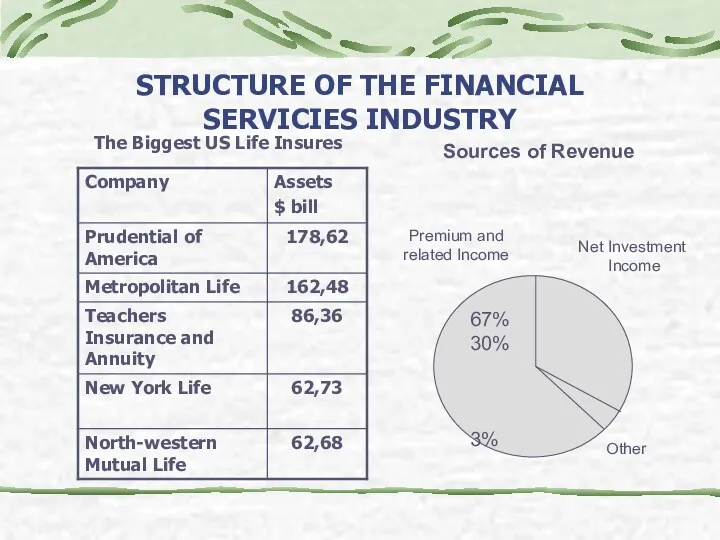
- 19. STRUCTURE OF THE FINANCIAL SERVICIES INDUSTRY The Biggest US Life Insures Sources of Revenue 67% 30%
- 20. CONTRACTUAL SAVING INSTITUTIONS Pension Funds: Private and Government organizations that provide financial services for retirement or
- 21. INVESTMENT INTERMEDIARIES Investment Banks engage in originating, underwriting and distribution of securities’ issue, investing and speculation,
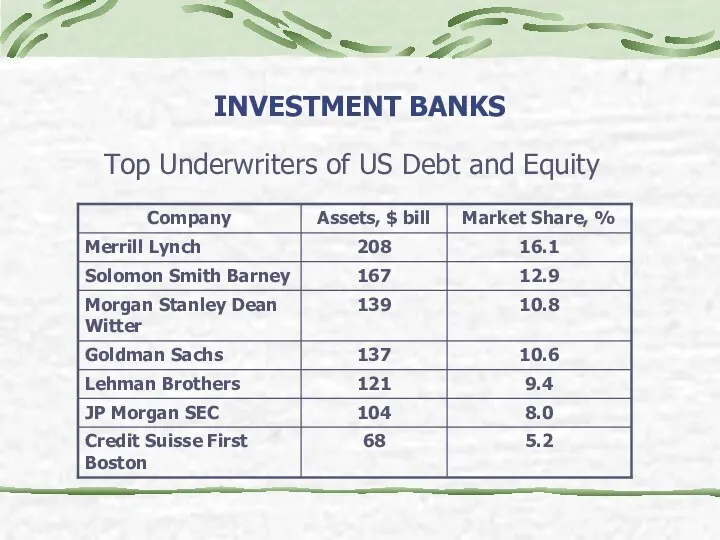
- 22. INVESTMENT BANKS Top Underwriters of US Debt and Equity
- 23. INVESTMENT INTERMEDIARIES Mutual Funds Pool the financial resources of individuals and companies and invest in diversified
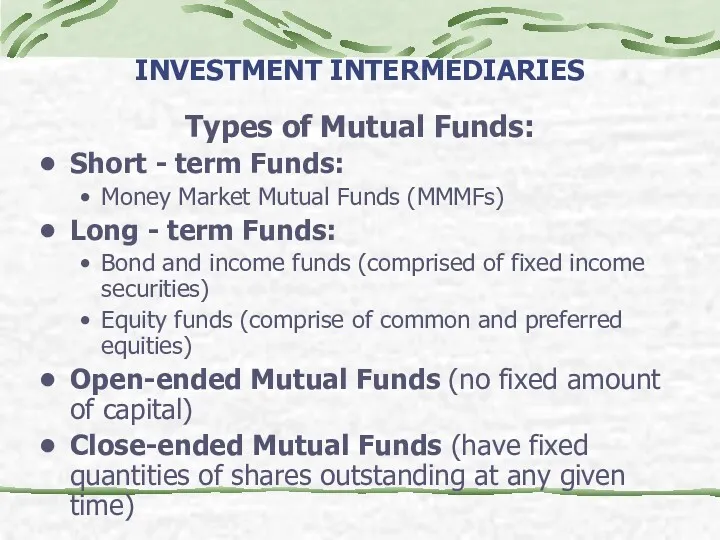
- 24. INVESTMENT INTERMEDIARIES Types of Mutual Funds: Short - term Funds: Money Market Mutual Funds (MMMFs) Long
- 25. INVESTMENT INTERMEDIARIES Finance Companies Do not accept deposits but rely on short and long-term debt; Make
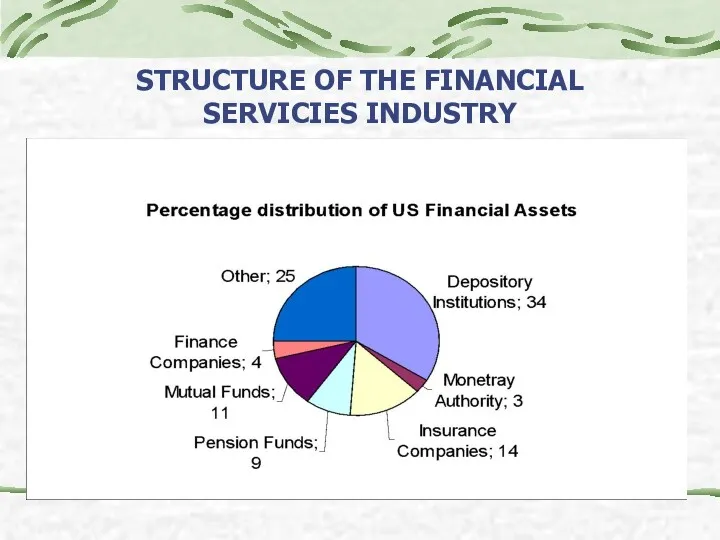
- 26. STRUCTURE OF THE FINANCIAL SERVICIES INDUSTRY
- 27. V. Regulation of Financial Markets Three Main Reasons for Regulation: 1. Increase Information to Investors A.
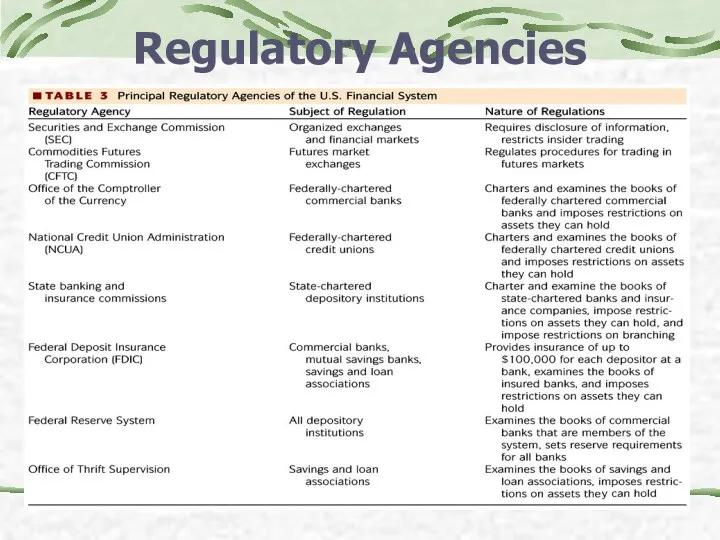
- 28. Regulatory Agencies
- 30. Скачать презентацию

















 Закон волн Эллиотта. Идентификация волн в режиме реального времени
Закон волн Эллиотта. Идентификация волн в режиме реального времени Отчет об исполнении бюджета Бардымского муниципального района за 2019 год
Отчет об исполнении бюджета Бардымского муниципального района за 2019 год Возможности программ Фонда содействия инновациям
Возможности программ Фонда содействия инновациям Индивидуальные инвестиционные cчета. Казначейство РНКБ Банк (ПАО) 2018
Индивидуальные инвестиционные cчета. Казначейство РНКБ Банк (ПАО) 2018 Банк Авангард. Программа Школьное питание
Банк Авангард. Программа Школьное питание Актуальные вопросы учета поступлений в бюджетную систему Российской Федерации в 2021 г. и администрирование
Актуальные вопросы учета поступлений в бюджетную систему Российской Федерации в 2021 г. и администрирование Деньги. История денег
Деньги. История денег Профессия бухгалтер
Профессия бухгалтер Налоги. Структура налога
Налоги. Структура налога ВТБ24. Лизинг оборудования
ВТБ24. Лизинг оборудования Депозитная программа. Депозитный модуль АБС
Депозитная программа. Депозитный модуль АБС Анализ финансовой устойчивости предприятия
Анализ финансовой устойчивости предприятия Проектирование бизнеса. Практика 5. Денежные потоки инвестиционного проекта
Проектирование бизнеса. Практика 5. Денежные потоки инвестиционного проекта Бухгалтерский учет и налогообложение в субъектах малого предпринимательства
Бухгалтерский учет и налогообложение в субъектах малого предпринимательства Учёт, анализ состояния и оценка динамики дебиторской задолженности
Учёт, анализ состояния и оценка динамики дебиторской задолженности Инициативное предложение члена бюджетной комиссии Андреевой Натальи Евгеньевны в рамках проекта Народный бюджет
Инициативное предложение члена бюджетной комиссии Андреевой Натальи Евгеньевны в рамках проекта Народный бюджет Бюджет для граждан
Бюджет для граждан Субсидии администрации Краснодарского края для реализации программ социально ориентированных некоммерческих организаций
Субсидии администрации Краснодарского края для реализации программ социально ориентированных некоммерческих организаций Оценка состояния бухгалтерского учета и внутреннего контроля основных средств в ООО Электротехническая компания
Оценка состояния бухгалтерского учета и внутреннего контроля основных средств в ООО Электротехническая компания Управление капиталом организации
Управление капиталом организации Мастер-класс Финансовые ресурсы предприятия и Эффективность и риски предпринимательской деятельности
Мастер-класс Финансовые ресурсы предприятия и Эффективность и риски предпринимательской деятельности Финансовая политика государства
Финансовая политика государства План-график закупок для обеспечения государственных и муниципальных нужд на финансовый год
План-график закупок для обеспечения государственных и муниципальных нужд на финансовый год Ипотечное кредитование. ПАО Банк ЗЕНИТ
Ипотечное кредитование. ПАО Банк ЗЕНИТ Виды ценных бумаг
Виды ценных бумаг Вопросы по продуктам РКО Tinkoff
Вопросы по продуктам РКО Tinkoff Цели и задачи управления государственным долгом
Цели и задачи управления государственным долгом Ночной аудитор отеля
Ночной аудитор отеля