Содержание
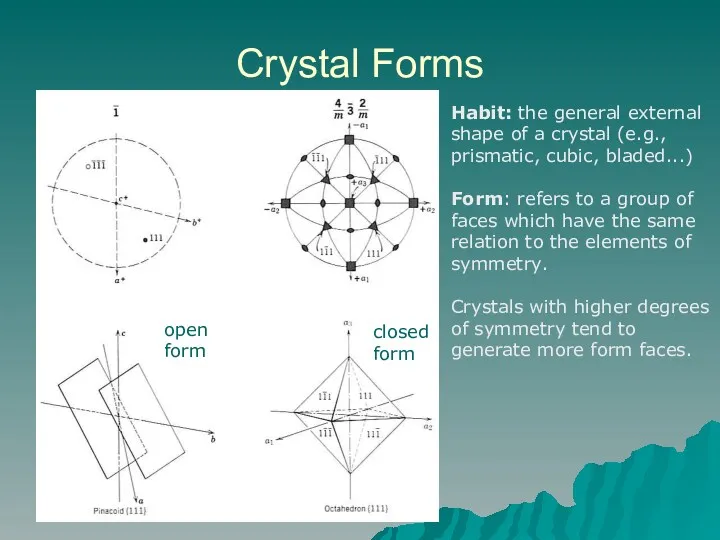
- 2. Crystal Forms Habit: the general external shape of a crystal (e.g., prismatic, cubic, bladed...) Form: refers
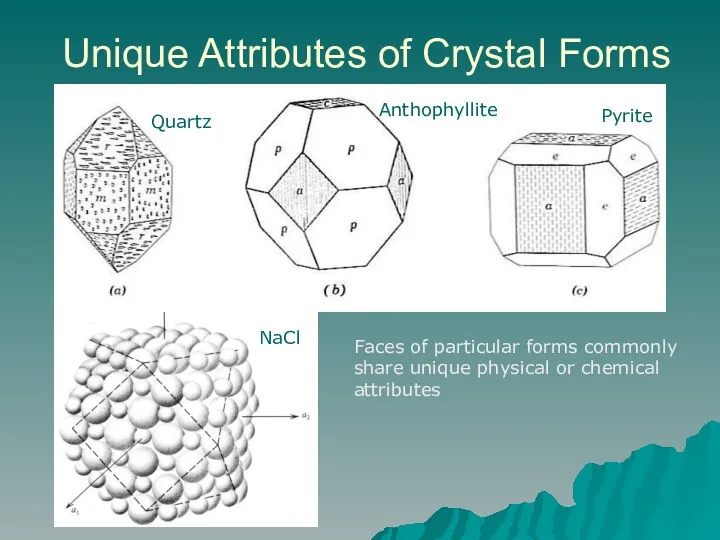
- 3. Unique Attributes of Crystal Forms NaCl Faces of particular forms commonly share unique physical or chemical
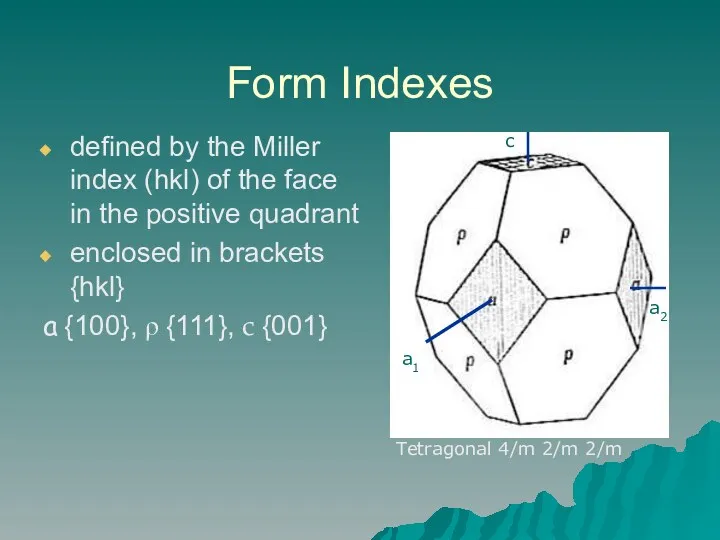
- 4. Form Indexes defined by the Miller index (hkl) of the face in the positive quadrant enclosed
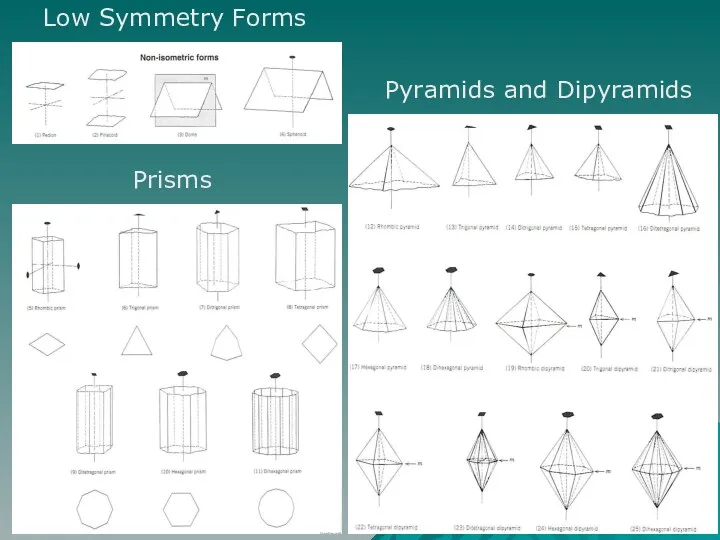
- 5. Pyramids and Dipyramids Prisms Low Symmetry Forms
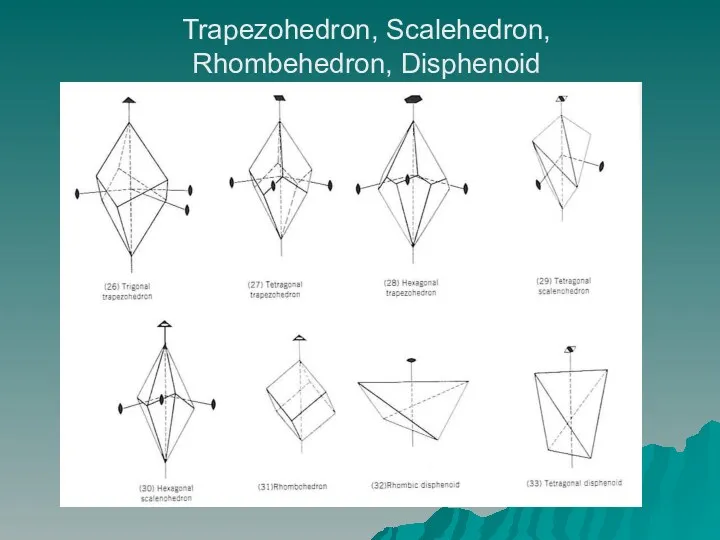
- 6. Trapezohedron, Scalehedron, Rhombehedron, Disphenoid
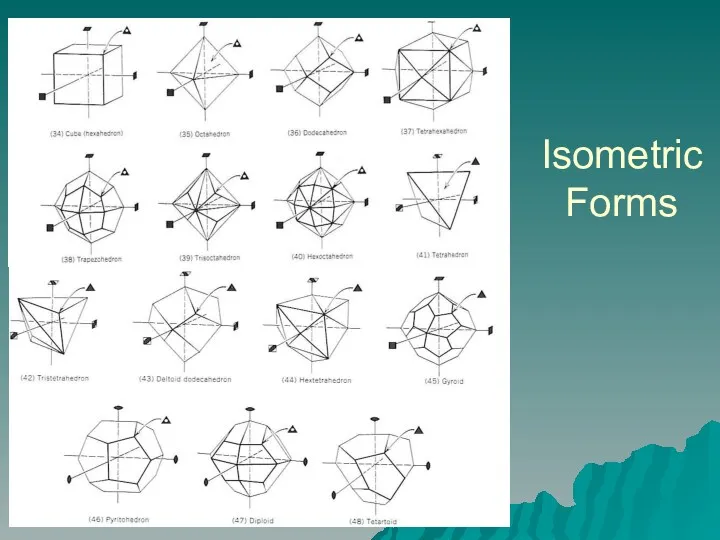
- 7. Isometric Forms
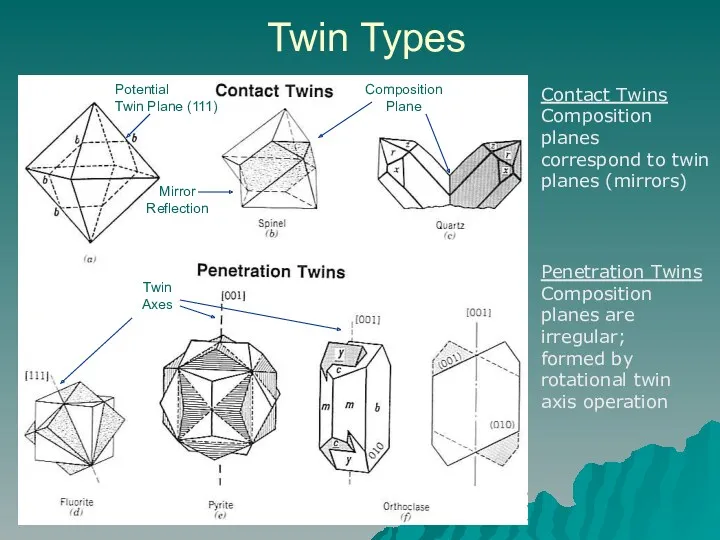
- 8. Twinning Symmetrical intergrowth of two or more crystals related to a symmetry operation (twin element) that
- 9. Twin Types Potential Twin Plane (111) Mirror Reflection Composition Plane Contact Twins Composition planes correspond to
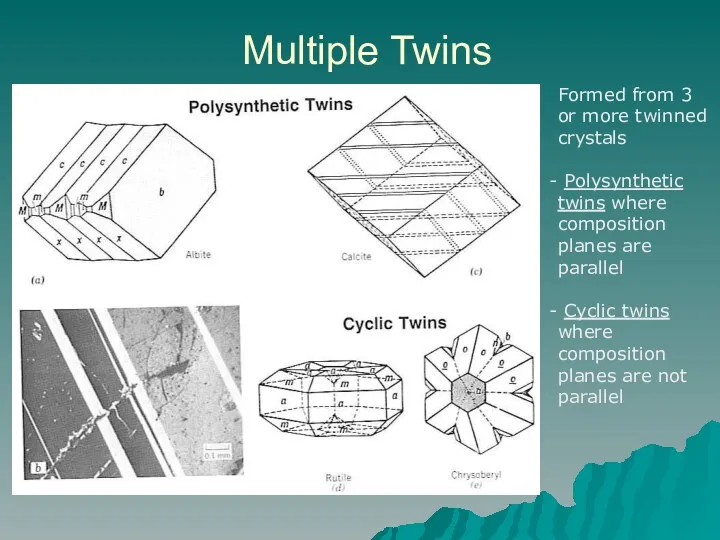
- 10. Multiple Twins Formed from 3 or more twinned crystals Polysynthetic twins where composition planes are parallel
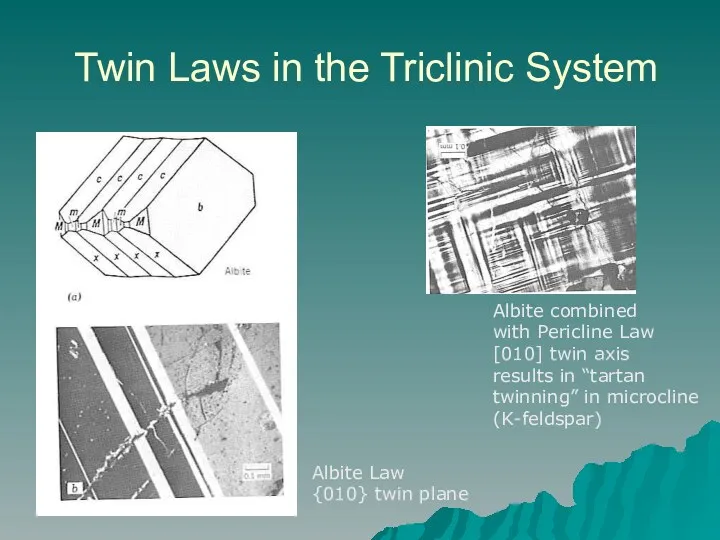
- 11. Twin Laws in the Triclinic System Albite Law {010} twin plane Albite combined with Pericline Law
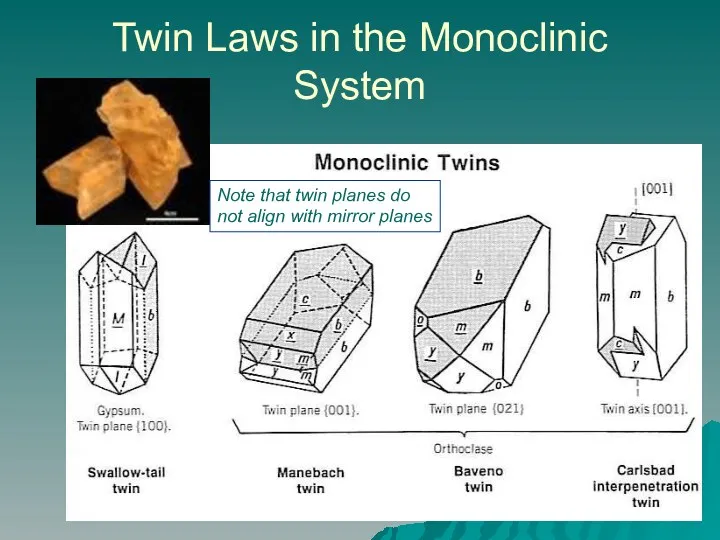
- 12. Twin Laws in the Monoclinic System Note that twin planes do not align with mirror planes
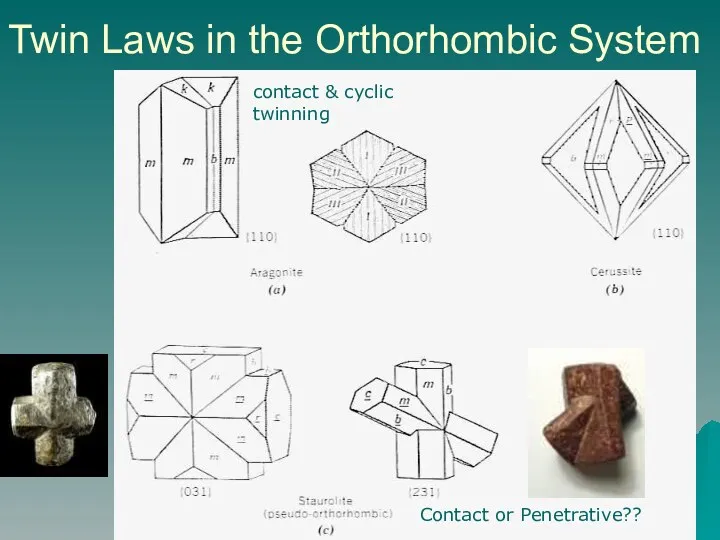
- 13. Twin Laws in the Orthorhombic System contact & cyclic twinning Contact or Penetrative??
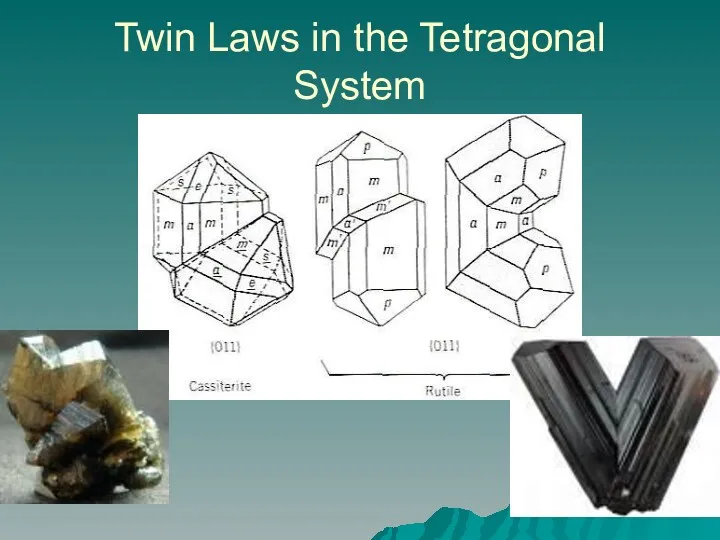
- 14. Twin Laws in the Tetragonal System
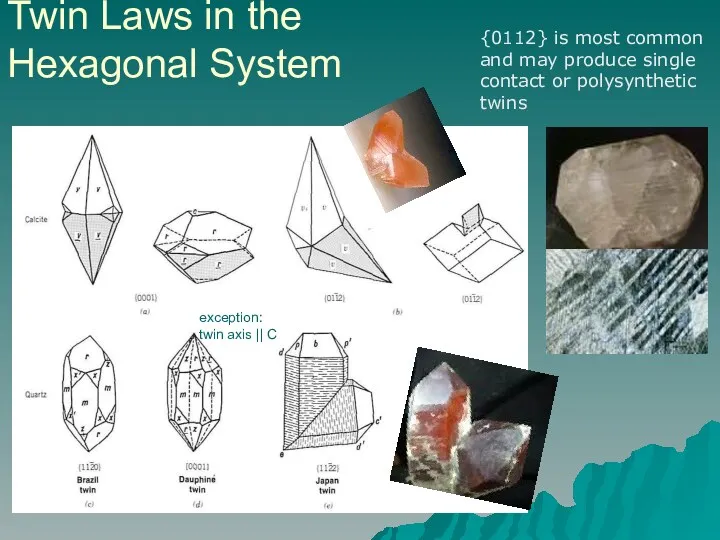
- 15. Twin Laws in the Hexagonal System {0112} is most common and may produce single contact or
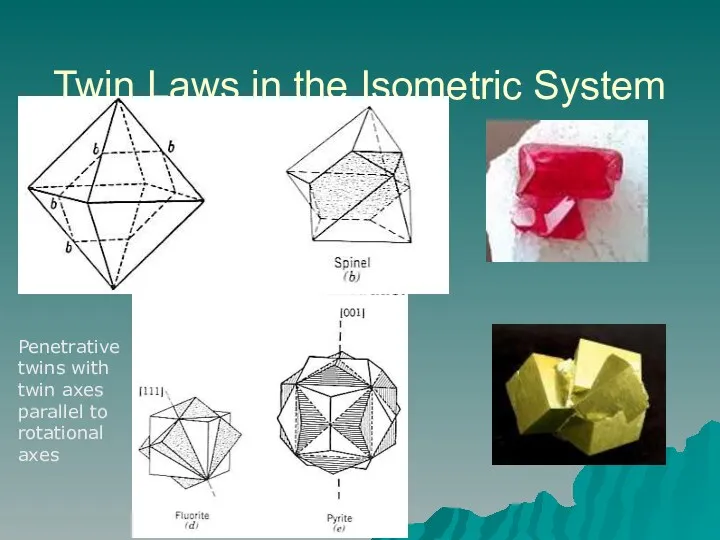
- 16. Twin Laws in the Isometric System Penetrative twins with twin axes parallel to rotational axes
- 18. Скачать презентацию

 Цветные металлы и сплавы
Цветные металлы и сплавы Атыраудағы химиялық өндіріс кәсіп орындары
Атыраудағы химиялық өндіріс кәсіп орындары Гидролиз неорганических солей
Гидролиз неорганических солей Химия в быту
Химия в быту Предмет органической химии
Предмет органической химии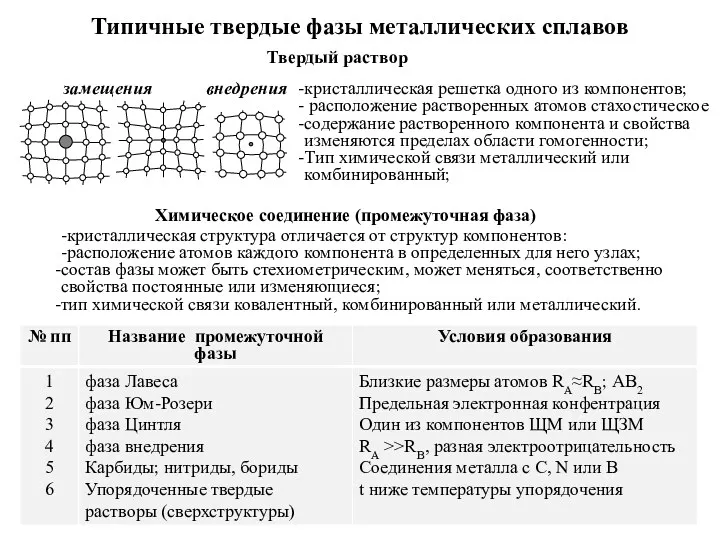 Типичные твердые фазы металлических сплавов
Типичные твердые фазы металлических сплавов Топливный элемент
Топливный элемент kremniy
kremniy Алюминий. Строение и свойства атома
Алюминий. Строение и свойства атома Простые вещества металлы
Простые вещества металлы Кислые породы умеренно-щелочного ряда
Кислые породы умеренно-щелочного ряда Why use plastics
Why use plastics Получение наночастиц в сверхкритическом флюиде
Получение наночастиц в сверхкритическом флюиде 20230330_metodicheskaya_razrabotka_ovr_v_organicheskoy_himii
20230330_metodicheskaya_razrabotka_ovr_v_organicheskoy_himii Периодический закон и периодическая система химических элементов Д.И. Менделеева
Периодический закон и периодическая система химических элементов Д.И. Менделеева Молярный объём газов
Молярный объём газов 20230316_otkrytyy_urok_v_8_kl_geneticheskaya_svyaz.docx
20230316_otkrytyy_urok_v_8_kl_geneticheskaya_svyaz.docx 20230306_oni_byli_pervymi
20230306_oni_byli_pervymi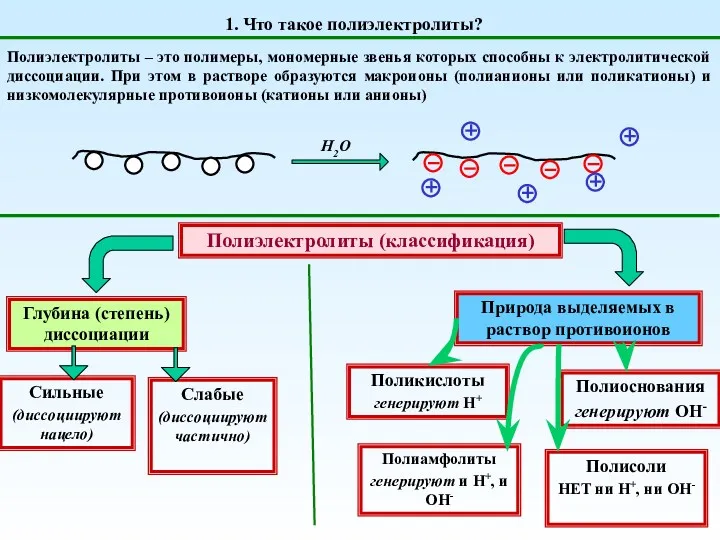 Полиэлектролиты. (Тема 3)
Полиэлектролиты. (Тема 3) Классификация химических реакций
Классификация химических реакций Катионная полимеризация (Лекция 6)
Катионная полимеризация (Лекция 6) Удивительные свойства воды
Удивительные свойства воды Гель-хроматография. Бумажная хроматография
Гель-хроматография. Бумажная хроматография Гомологический ряд алканов. Изомерия и номенклатура
Гомологический ряд алканов. Изомерия и номенклатура Топливо. Виды топлива. Химический состав топлива. Основные характеристики топлива. Марки топлива
Топливо. Виды топлива. Химический состав топлива. Основные характеристики топлива. Марки топлива Азот. Строение атома и молекулы
Азот. Строение атома и молекулы Удобрения. 9 класс
Удобрения. 9 класс Поверхностные явления. Адсорбция
Поверхностные явления. Адсорбция