Содержание
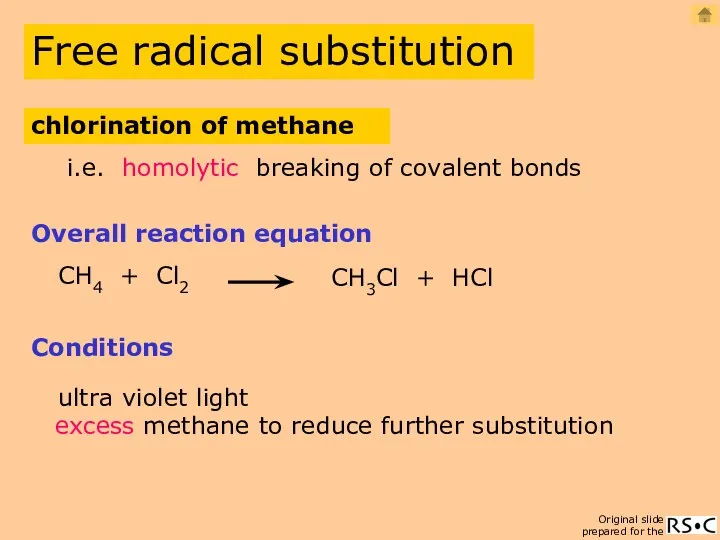
- 2. CH4 + Cl2 CH3Cl + HCl Overall reaction equation Conditions ultra violet light excess methane i.e.
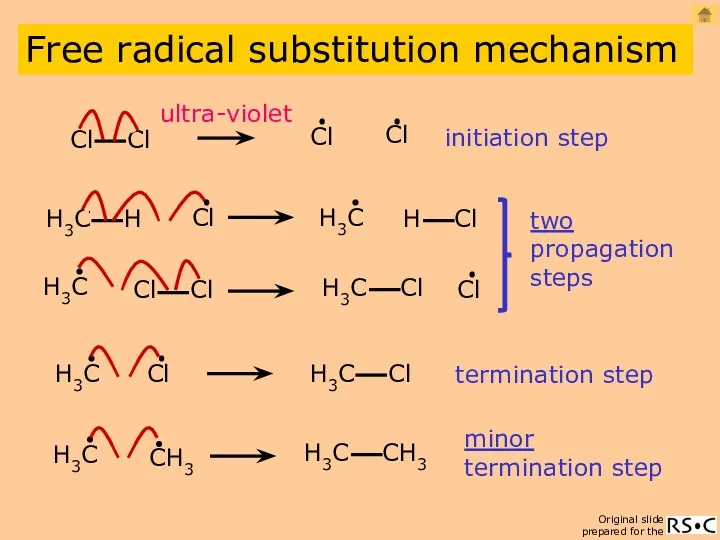
- 3. initiation step two propagation steps termination step ultra-violet minor termination step Free radical substitution mechanism
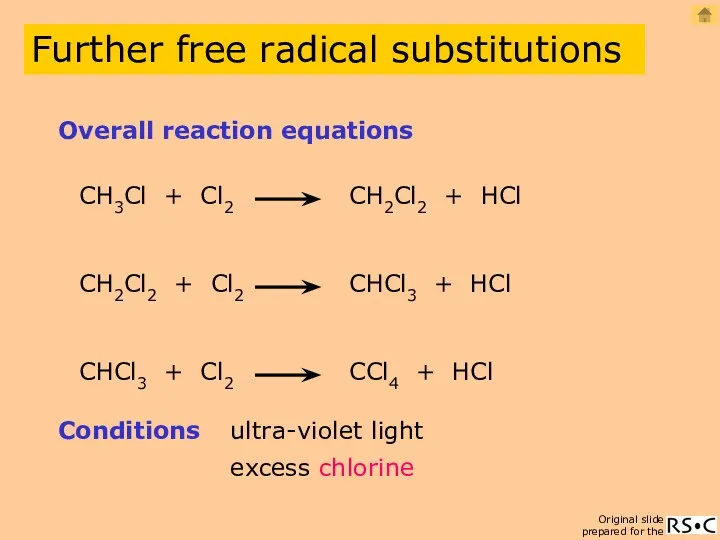
- 4. CH3Cl + Cl2 CH2Cl2 + HCl Overall reaction equations Conditions ultra-violet light CH2Cl2 + Cl2 CHCl3
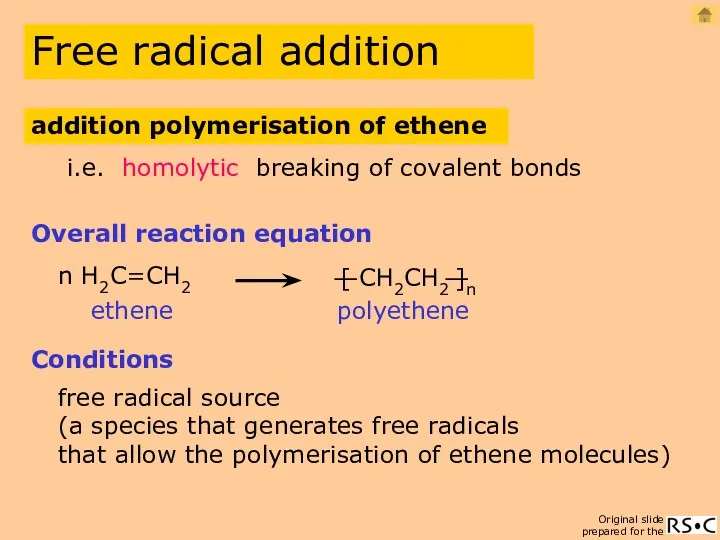
- 5. n H2C=CH2 Overall reaction equation polyethene free radical source i.e. homolytic breaking of covalent bonds (a
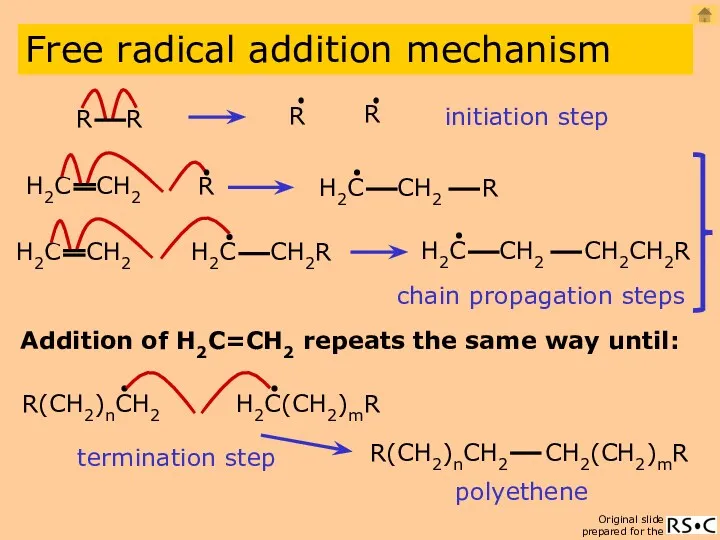
- 6. initiation step Addition of H2C=CH2 repeats the same way until: polyethene Free radical addition mechanism chain
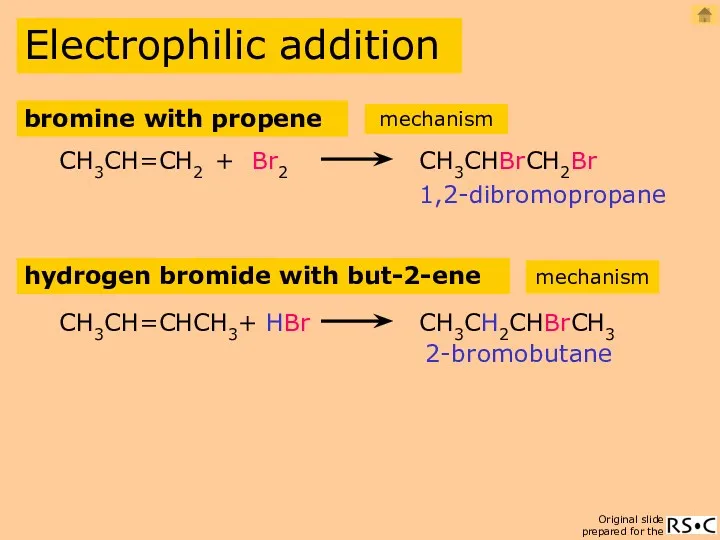
- 7. Electrophilic addition CH3CH=CH2 + Br2 CH3CHBrCH2Br bromine with propene hydrogen bromide with but-2-ene CH3CH=CHCH3 + HBr
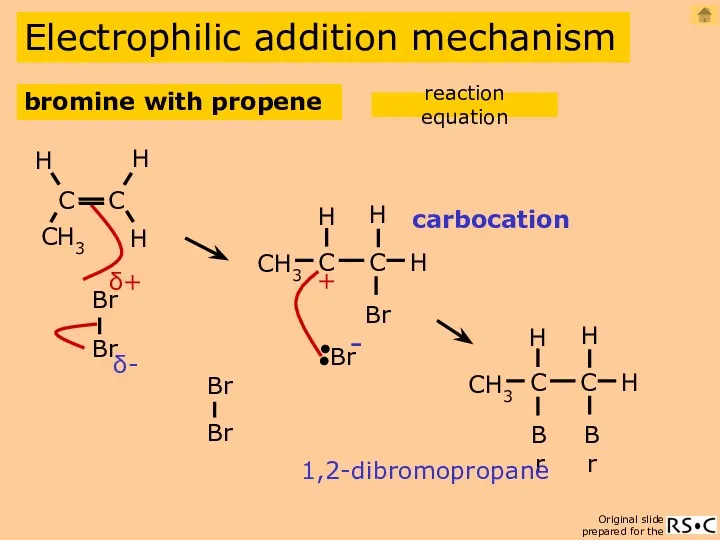
- 8. Electrophilic addition mechanism carbocation 1,2-dibromopropane bromine with propene reaction equation
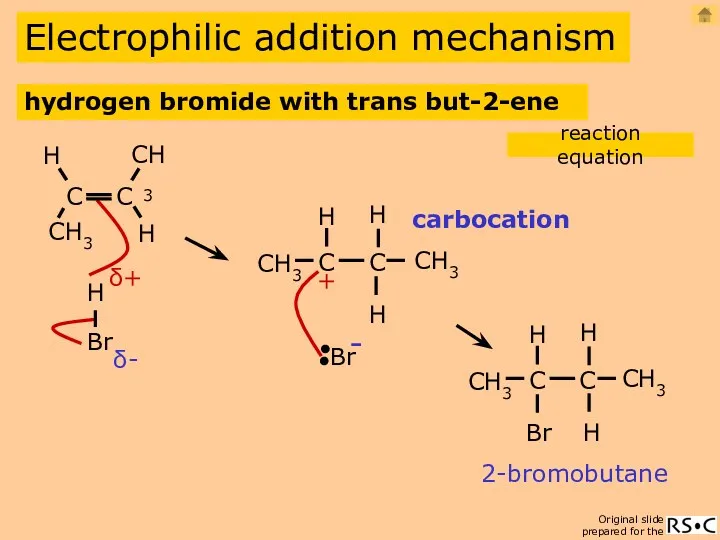
- 9. Electrophilic addition mechanism carbocation 2-bromobutane hydrogen bromide with trans but-2-ene reaction equation
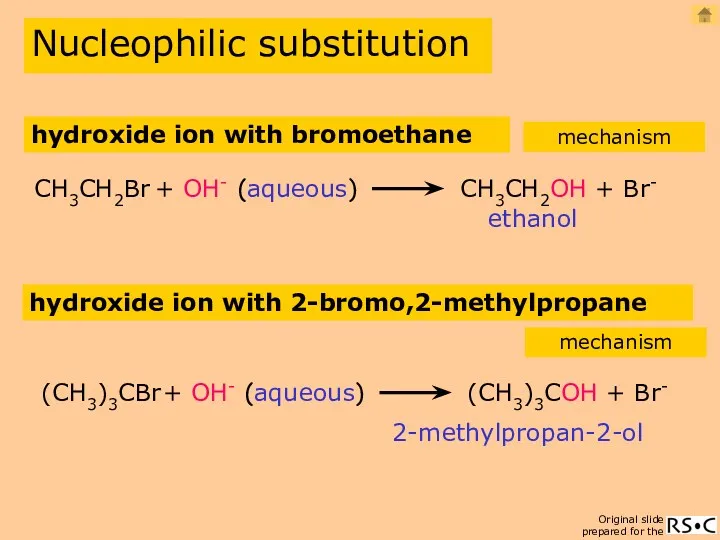
- 10. hydroxide ion with bromoethane ethanol CH3CH2Br + OH- CH3CH2OH + Br- (aqueous) Nucleophilic substitution mechanism hydroxide
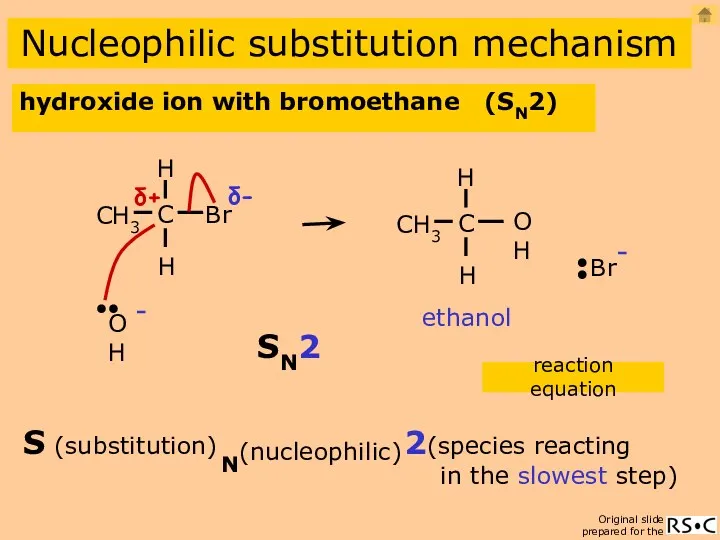
- 11. hydroxide ion with bromoethane (SN2) Nucleophilic substitution mechanism ethanol reaction equation 2(species reacting in the slowest
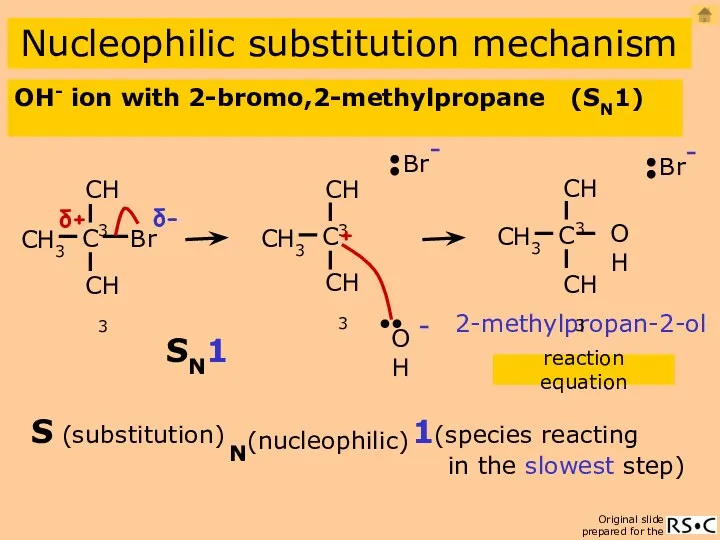
- 12. OH- ion with 2-bromo,2-methylpropane (SN1) Nucleophilic substitution mechanism 2-methylpropan-2-ol reaction equation 1(species reacting in the slowest
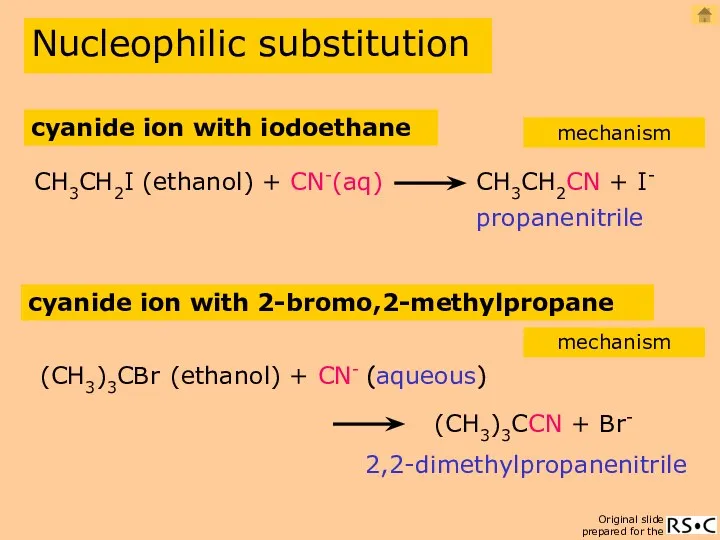
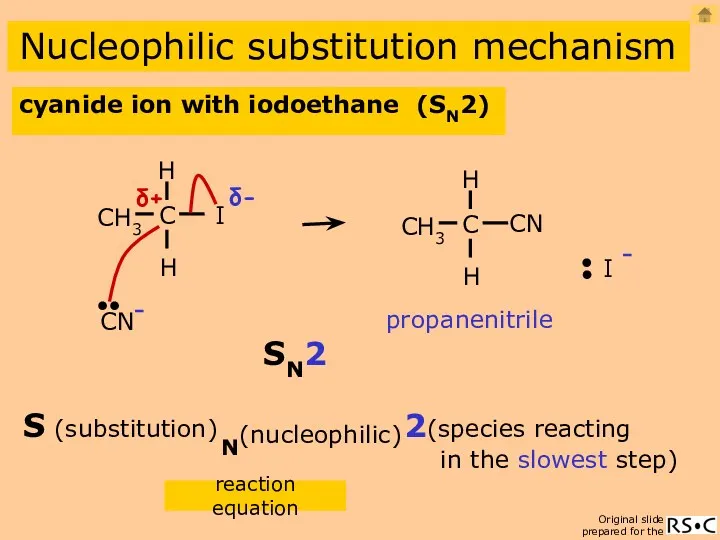
- 13. Nucleophilic substitution propanenitrile CH3CH2I (ethanol) + CN-(aq) CH3CH2CN + I- cyanide ion with iodoethane mechanism cyanide
- 14. cyanide ion with iodoethane (SN2) Nucleophilic substitution mechanism propanenitrile reaction equation 2(species reacting in the slowest
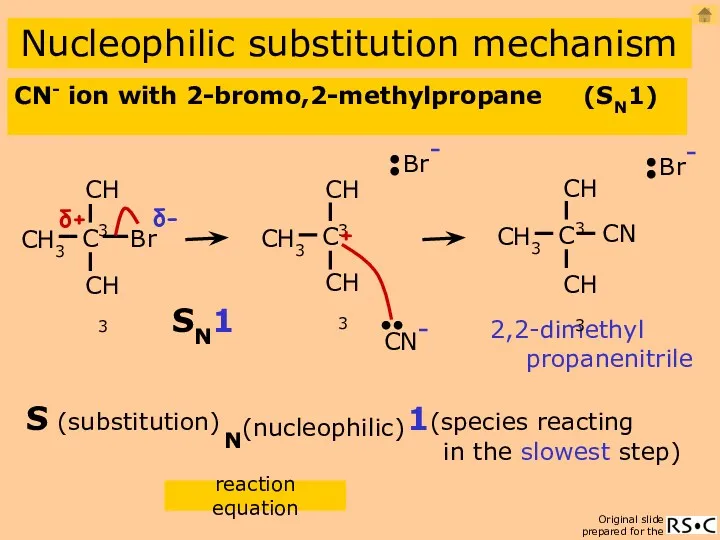
- 15. CN- ion with 2-bromo,2-methylpropane (SN1) Nucleophilic substitution mechanism 2,2-dimethyl propanenitrile 1(species reacting in the slowest step)
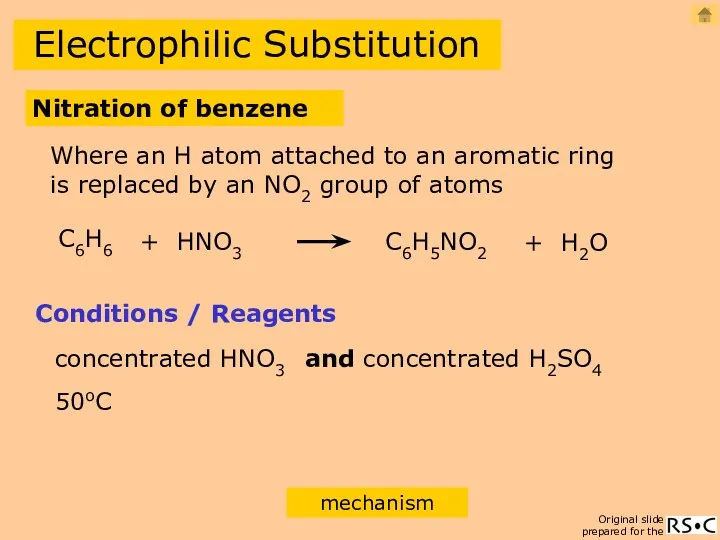
- 16. Electrophilic Substitution Nitration of benzene C6H6 + HNO3 C6H5NO2 + H2O Conditions / Reagents concentrated HNO3
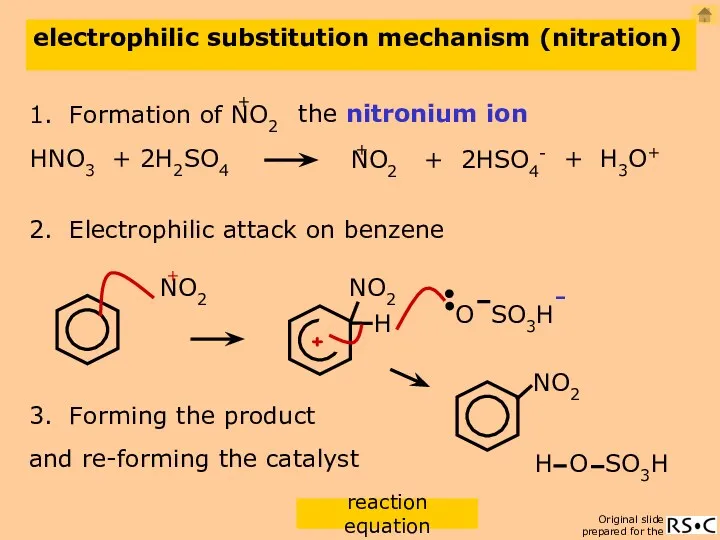
- 17. electrophilic substitution mechanism (nitration) 2. Electrophilic attack on benzene 3. Forming the product the nitronium ion
- 18. Bromination of benzene C6H6 + Br2 C6H5Br + HBr Conditions / Reagents Br2 and anhydrous AlBr3
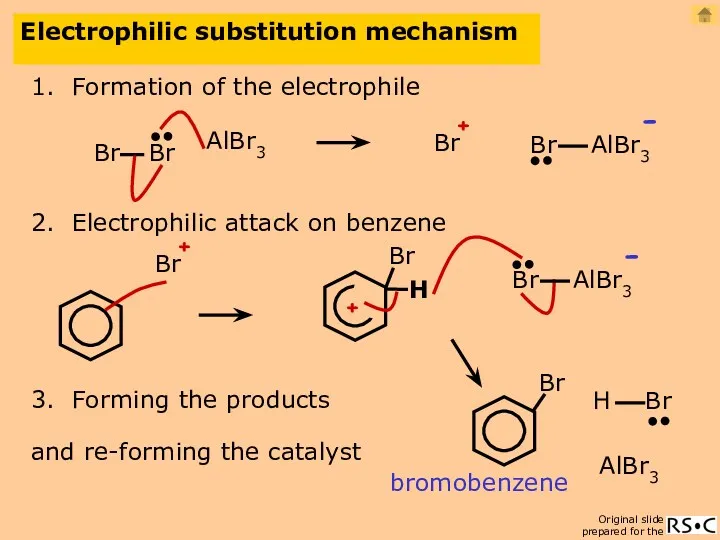
- 19. Electrophilic substitution mechanism 1. Formation of the electrophile AlBr3 2. Electrophilic attack on benzene 3. Forming
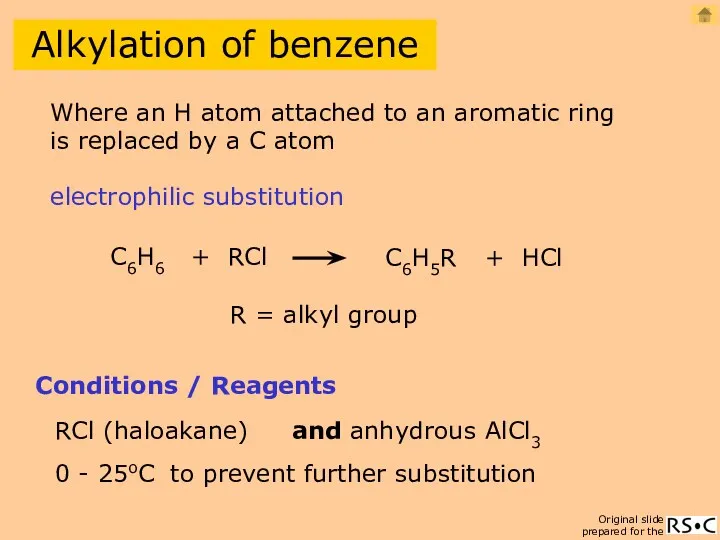
- 20. Alkylation of benzene C6H6 + RCl C6H5R + HCl Conditions / Reagents RCl (haloakane) and anhydrous
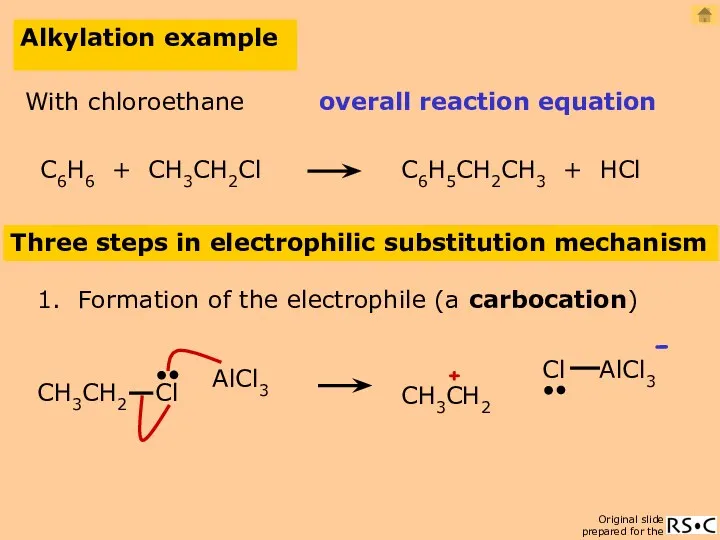
- 21. Alkylation example Three steps in electrophilic substitution mechanism 1. Formation of the electrophile (a carbocation) AlCl3
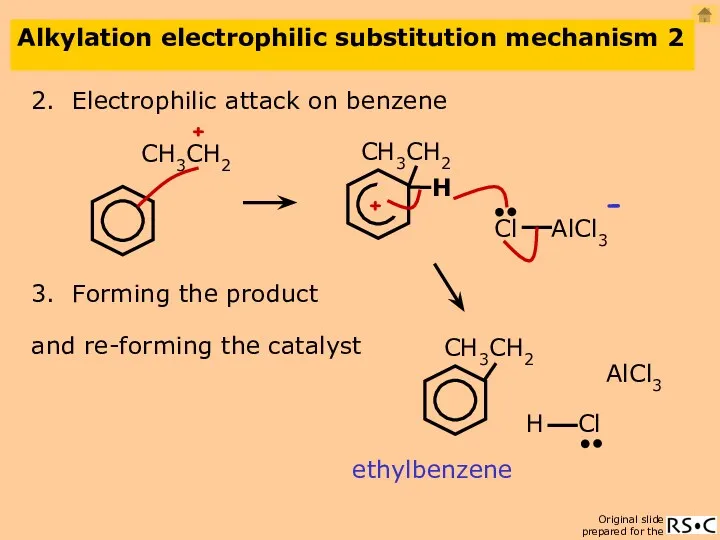
- 22. Alkylation electrophilic substitution mechanism 2 2. Electrophilic attack on benzene ethylbenzene 3. Forming the product AlCl3
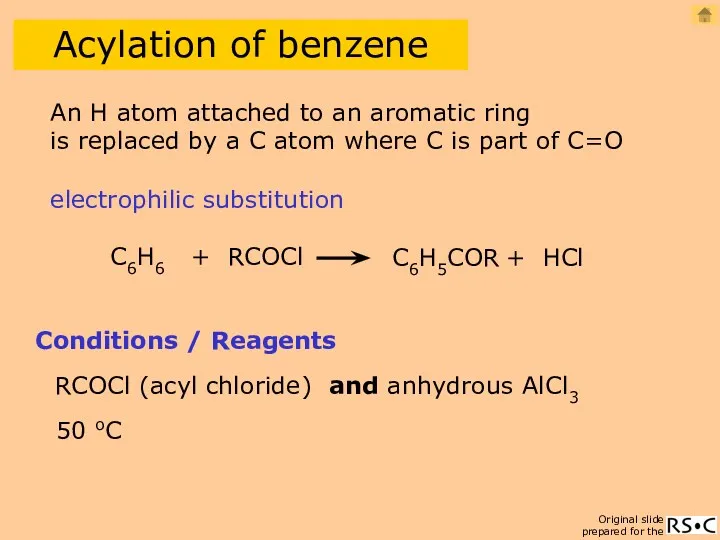
- 23. Acylation of benzene C6H6 + RCOCl C6H5COR + HCl Conditions / Reagents RCOCl (acyl chloride) and
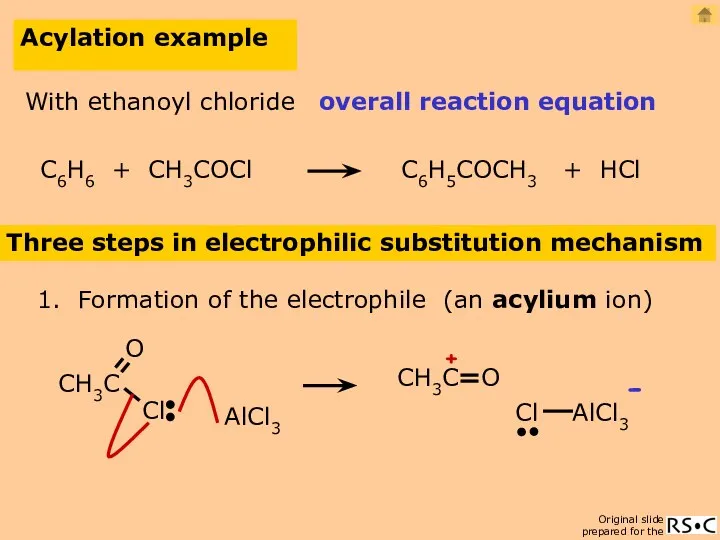
- 24. Acylation example Three steps in electrophilic substitution mechanism 1. Formation of the electrophile (an acylium ion)
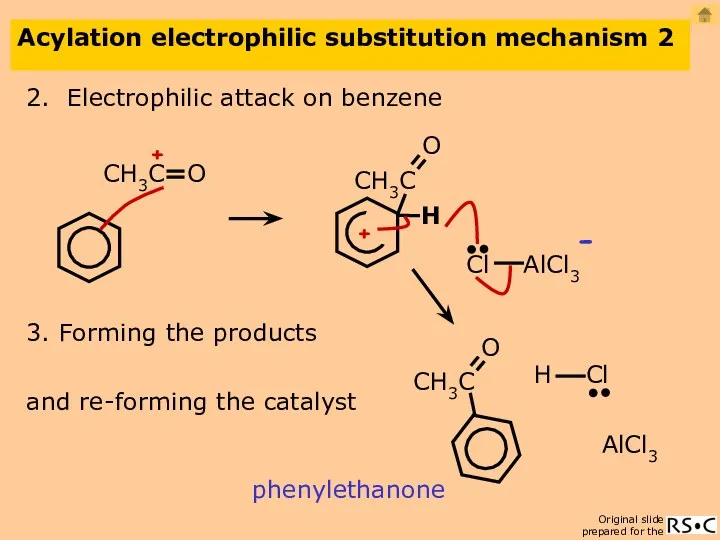
- 25. Acylation electrophilic substitution mechanism 2 2. Electrophilic attack on benzene phenylethanone AlCl3 3. Forming the products
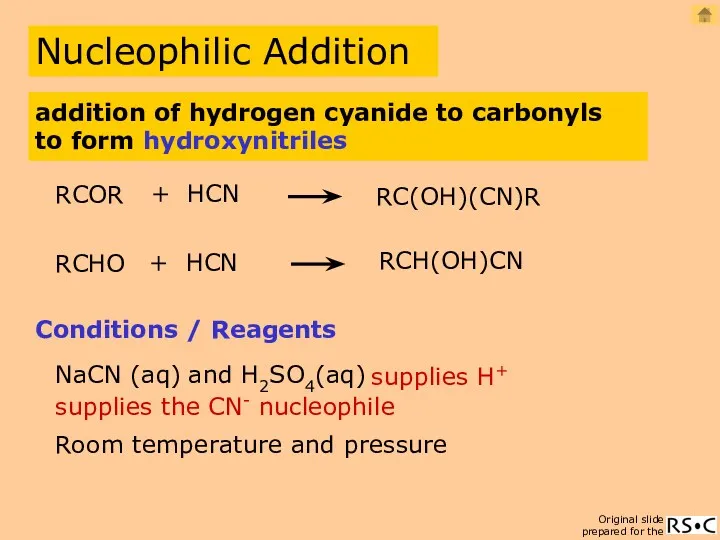
- 26. Nucleophilic Addition RCHO + HCN RCH(OH)CN Conditions / Reagents NaCN (aq) and H2SO4(aq) Room temperature and
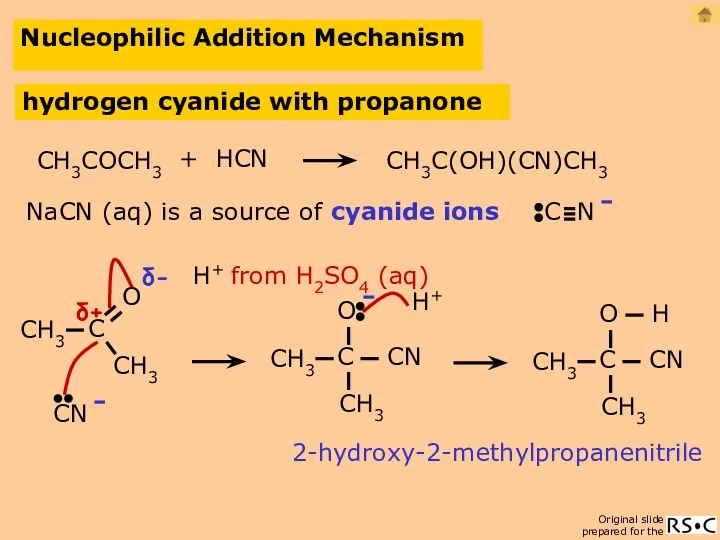
- 27. Nucleophilic Addition Mechanism hydrogen cyanide with propanone H+ NaCN (aq) is a source of cyanide ions
- 28. Advice
- 30. Скачать презентацию


 Отримання кисню. Властивості кисню
Отримання кисню. Властивості кисню Соли. Определение солей
Соли. Определение солей Смещение химического равновесия
Смещение химического равновесия Общая химия
Общая химия Циклоалканы
Циклоалканы Химическая кинетика и катализ
Химическая кинетика и катализ Solutions and solubilities
Solutions and solubilities Искусственные каменные материалы
Искусственные каменные материалы Строение атома
Строение атома Сапалық талдау. Сапалық аналитикалық реакциялар
Сапалық талдау. Сапалық аналитикалық реакциялар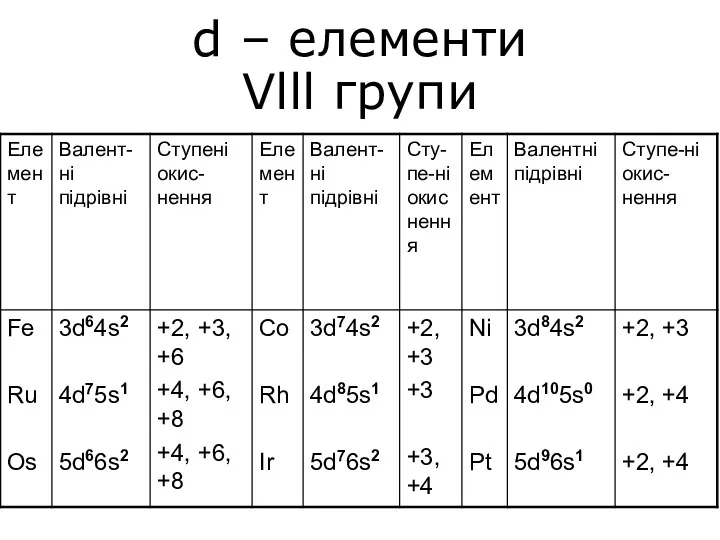 d – елементи Vlll групи
d – елементи Vlll групи Высокомолекулярные соединения (ВМС) или полимеры
Высокомолекулярные соединения (ВМС) или полимеры Реакции ионного обмена. Ионное произведение воды. Водородный показатель. Индикаторы
Реакции ионного обмена. Ионное произведение воды. Водородный показатель. Индикаторы Сущность процесса электролитической диссоциации
Сущность процесса электролитической диссоциации Химические свойства карбоновых кислот
Химические свойства карбоновых кислот Растворы электролитов. Буферные растворы. Лекция 4
Растворы электролитов. Буферные растворы. Лекция 4 Виды коррозии
Виды коррозии Майлардың анықтамасы
Майлардың анықтамасы Алюміній. Загальна характеристика, властивості. Алюміній оксид, алюміній гідроксид, їх амфотерність
Алюміній. Загальна характеристика, властивості. Алюміній оксид, алюміній гідроксид, їх амфотерність Спектральные методы: инфракрасная спектроскопия. Люминесцентный анализ
Спектральные методы: инфракрасная спектроскопия. Люминесцентный анализ Существенные изменения в измерителях ЕГЭ по химии
Существенные изменения в измерителях ЕГЭ по химии Окислительные методы получения органических соединений
Окислительные методы получения органических соединений Амины. Понятие об аминах. Анилин как органическое основание
Амины. Понятие об аминах. Анилин как органическое основание Алкадиены (диены, диеновые углеводороды)
Алкадиены (диены, диеновые углеводороды)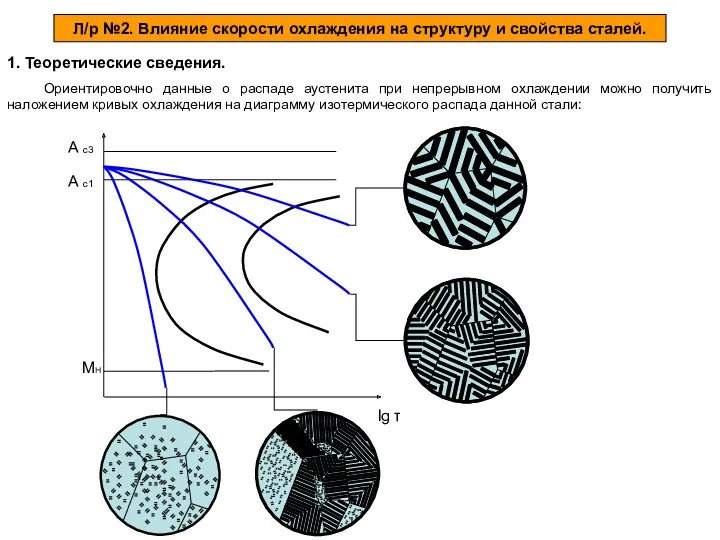 Влияние скорости охлаждения на структуру и свойства сталей
Влияние скорости охлаждения на структуру и свойства сталей Положение в периодической системе Менделеева водорода, лантаноидов, актиноидов и искусственно полученных элементов
Положение в периодической системе Менделеева водорода, лантаноидов, актиноидов и искусственно полученных элементов Алкины
Алкины Алкены. Этиленовые углеводороды, олефины
Алкены. Этиленовые углеводороды, олефины