Содержание
- 2. Principle : Determine the Hemoglobin content through destruction of RBC to get the Hb out by
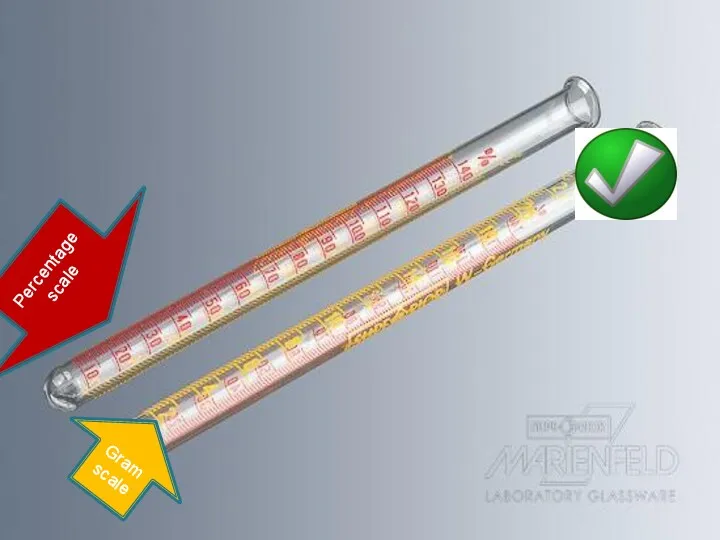
- 3. Haemometer HCL Capillary tube Dropper Tools 1 Two standard tube 2 one Graduated tube Percentage scale
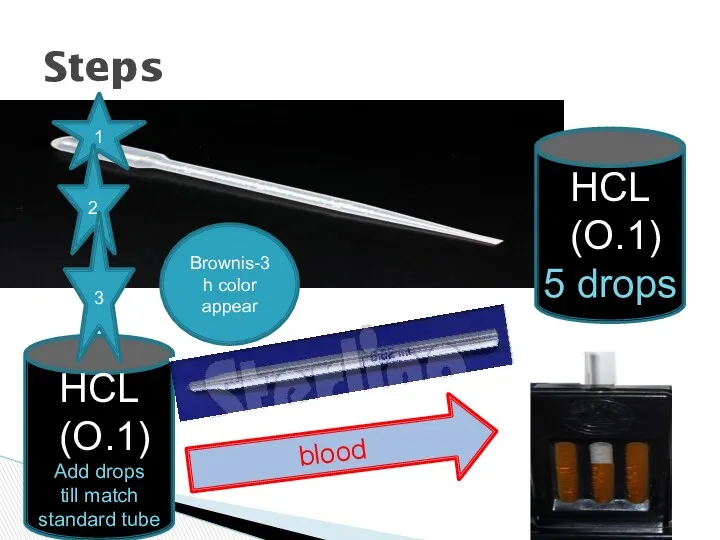
- 4. Steps HCL (O.1) Add drops till match standard tube 1 2 blood 3-Brownish color appear 3
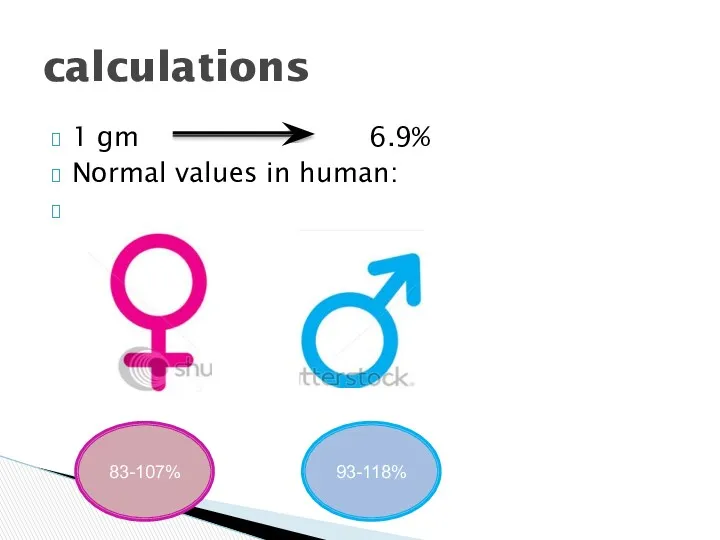
- 5. 1 gm 6.9% Normal values in human: calculations 83-107% 93-118%
- 6. Foreign RBC may clump together in the form of large aggregates agglutination. That agglutinated RBC are
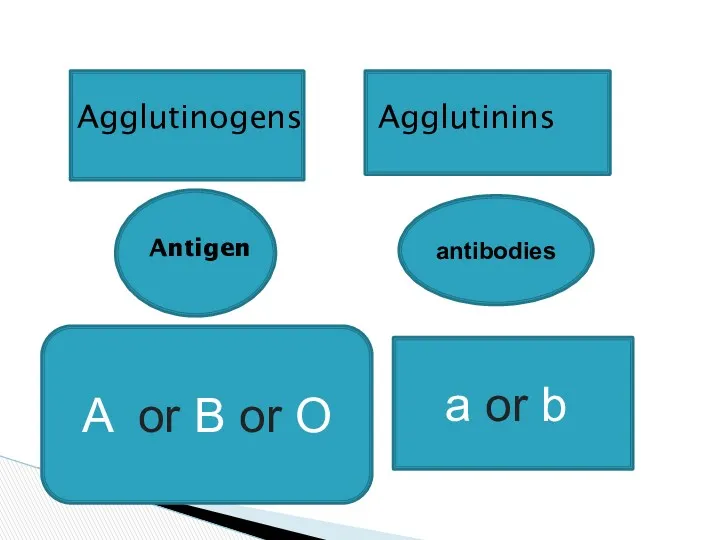
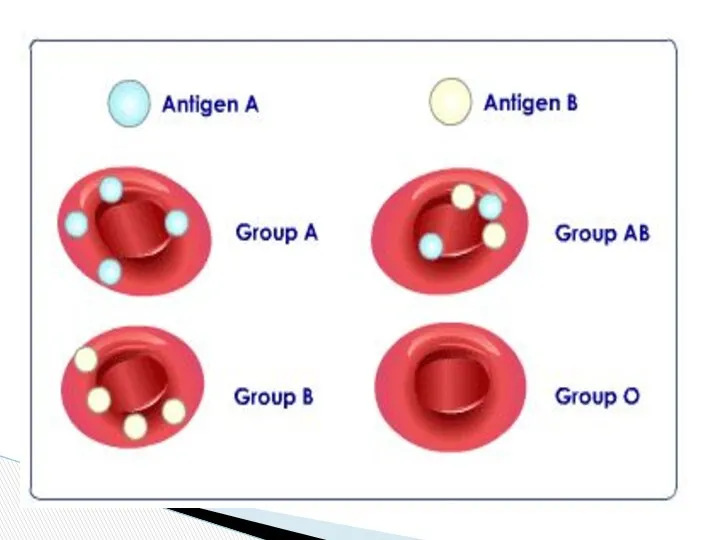
- 7. Agglutinogens Agglutinins Antigen antibodies A or B or O a or b
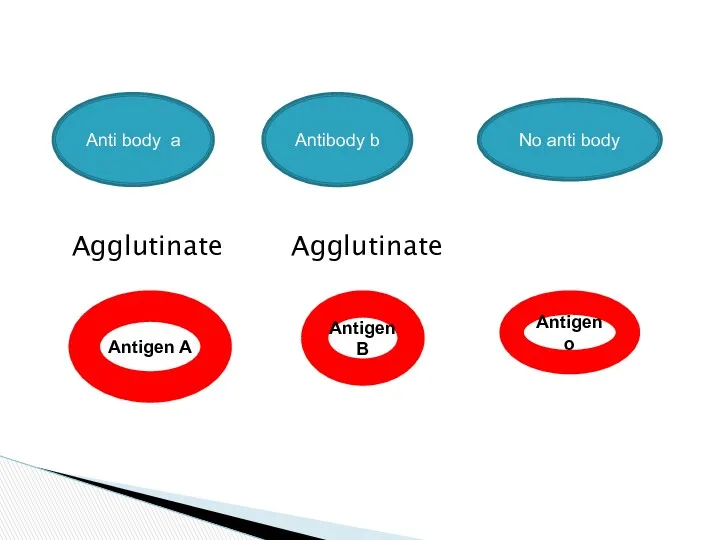
- 8. Agglutinate Agglutinate Anti body a Antibody b No anti body Antigen A Antigen o AntigenB
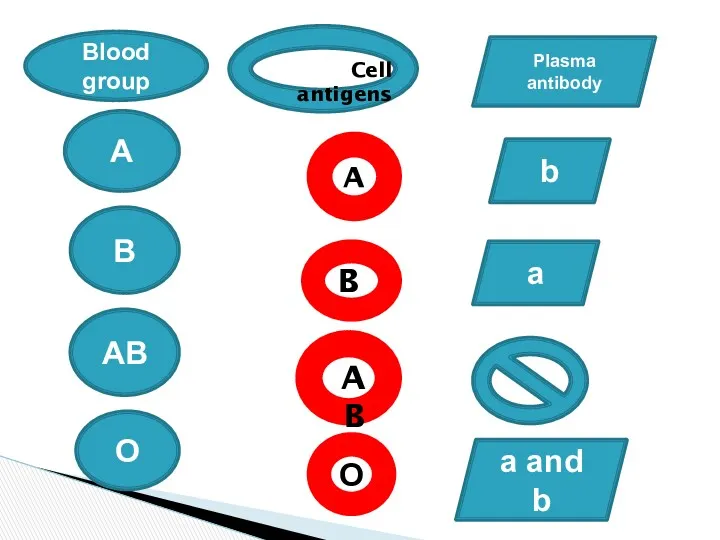
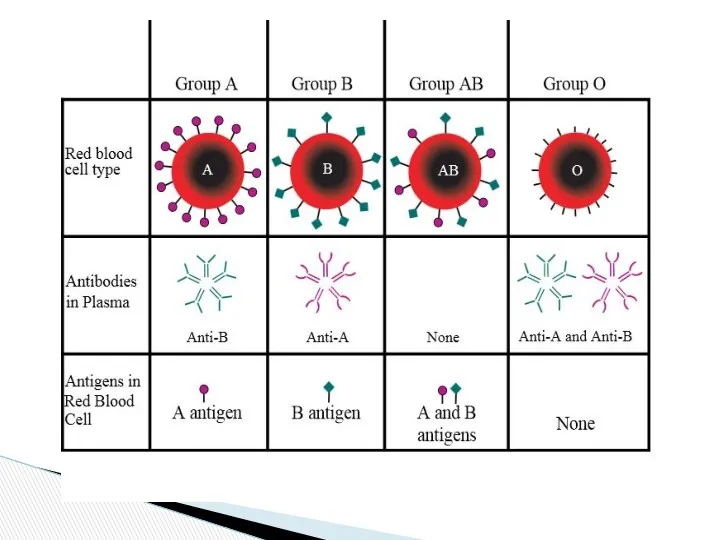
- 9. If the RBC have antigen A the corresponding plasma must have antibody b and not a
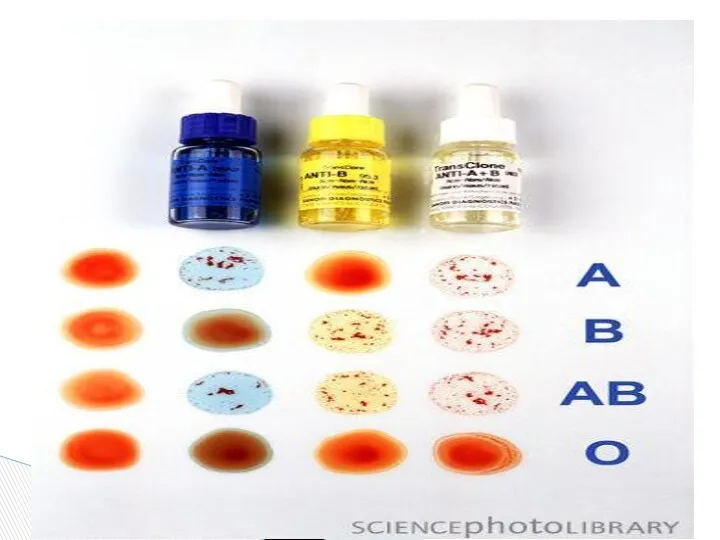
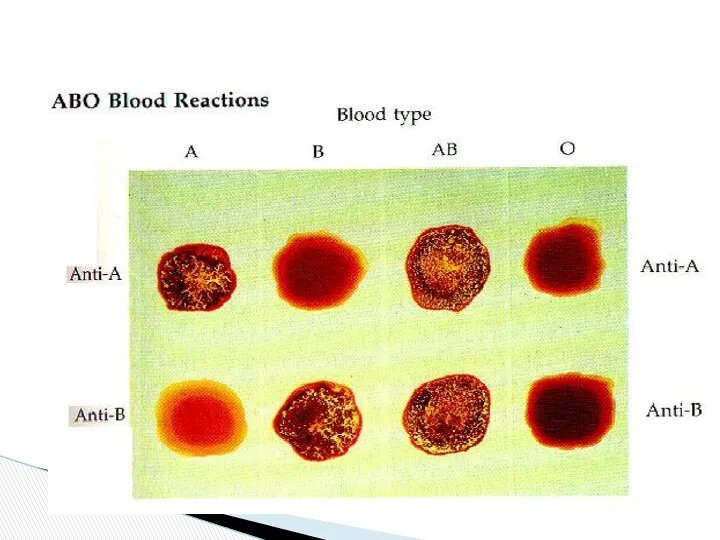
- 10. A Blood group B AB O O b a a and b Cell antigens A B
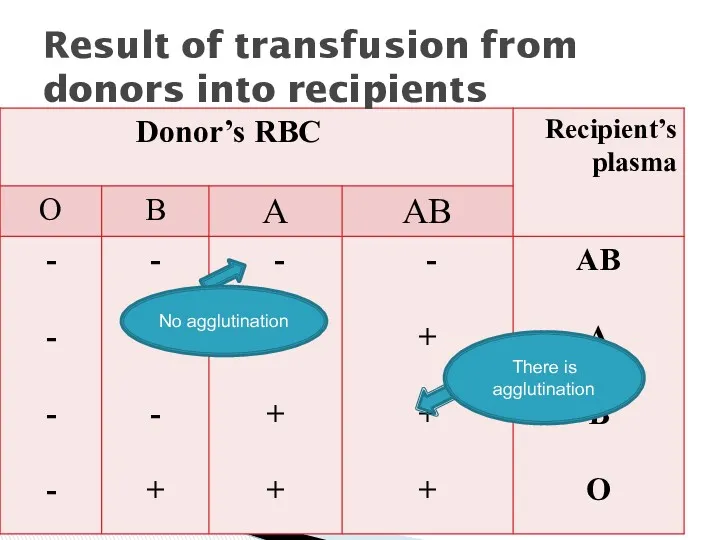
- 13. Result of transfusion from donors into recipients No agglutination There is agglutination
- 15. Group AB is called universal recipient , and group O is known as universal donor
- 16. Is that the RBC of the donor which may agglutinate inside the body of the recipient
- 17. Diluted by the recipient plasma Neutralized by the free water soluble antigens present in the recipient’s
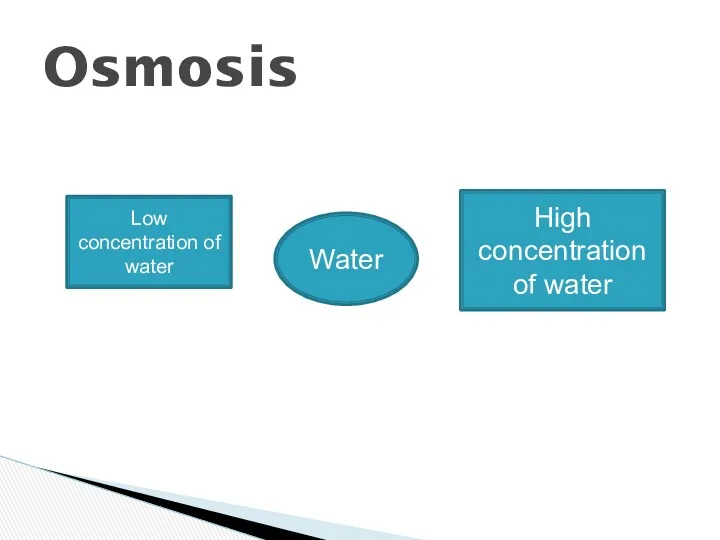
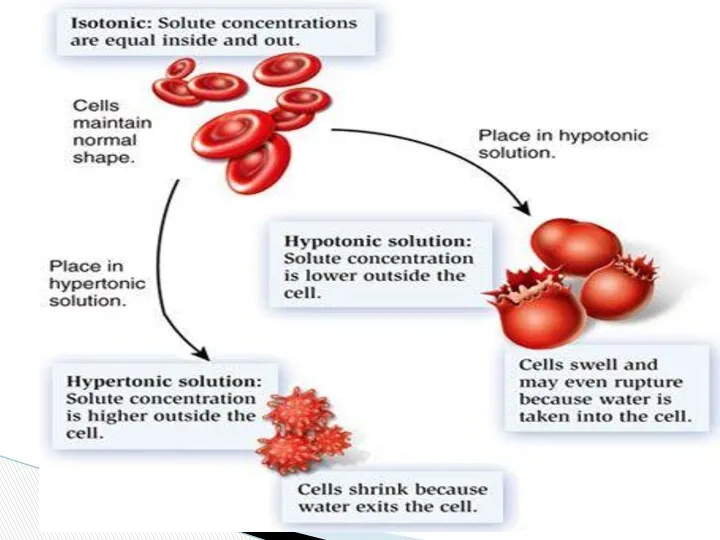
- 18. Osmotic behavior of blood
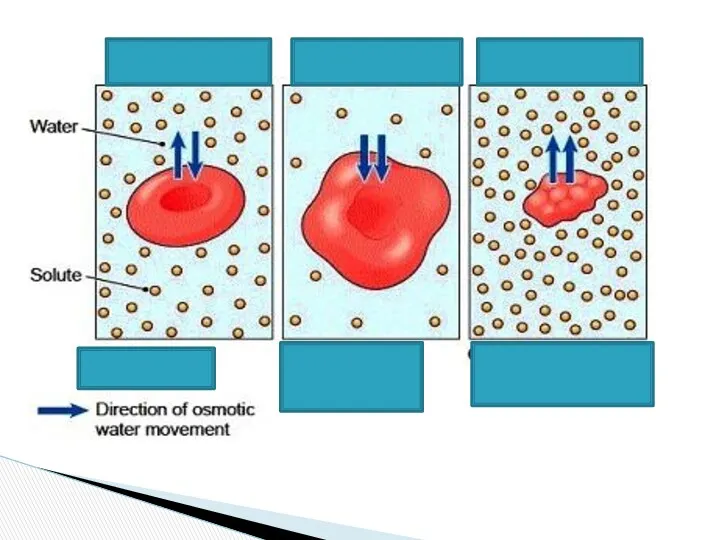
- 19. Osmosis Water Low concentration of water High concentration of water
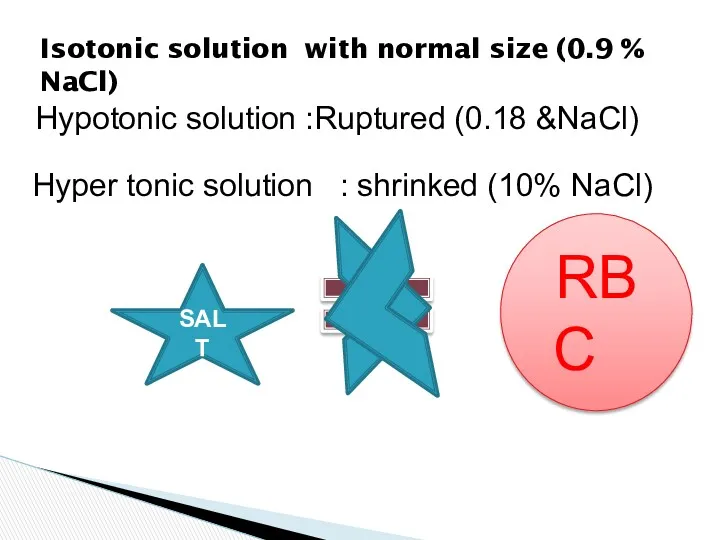
- 20. Isotonic solution with normal size (0.9 % NaCl) SALT RBC Salt Hyper tonic solution : shrinked
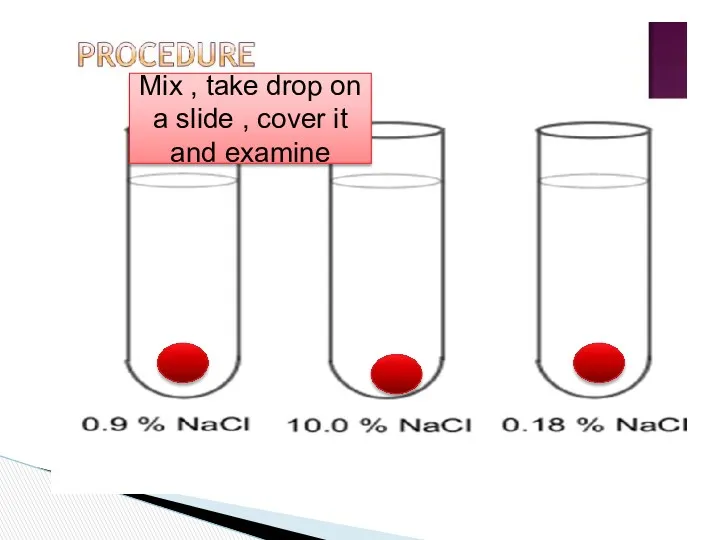
- 22. Tools: A-3 test tubes B- slides C-cover D-dropper
- 23. 2-add 10 ml of each solution Mix , take drop on a slide , cover it
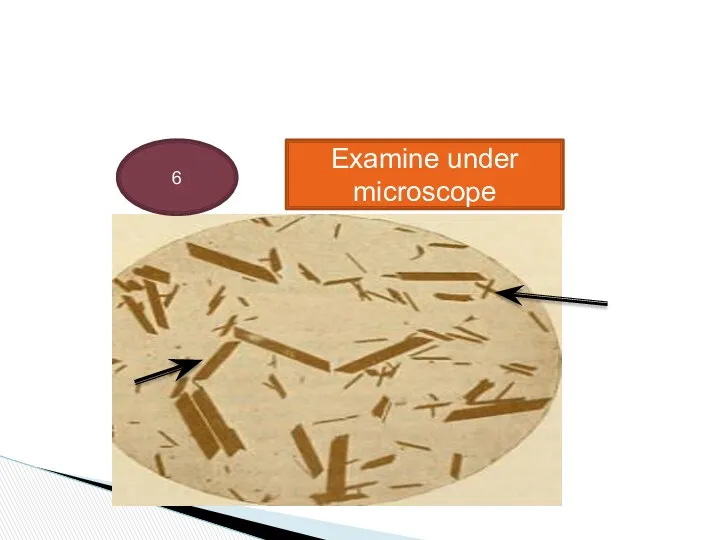
- 25. Haemin crystal
- 26. Aim : This test is used for knowing of any red liquid is blood or not
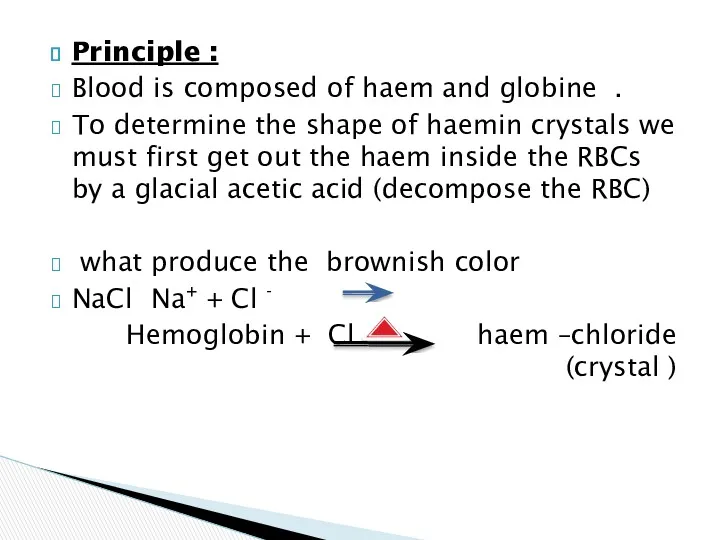
- 27. Principle : Blood is composed of haem and globine . To determine the shape of haemin
- 28. Procedure 1 2 3 mix
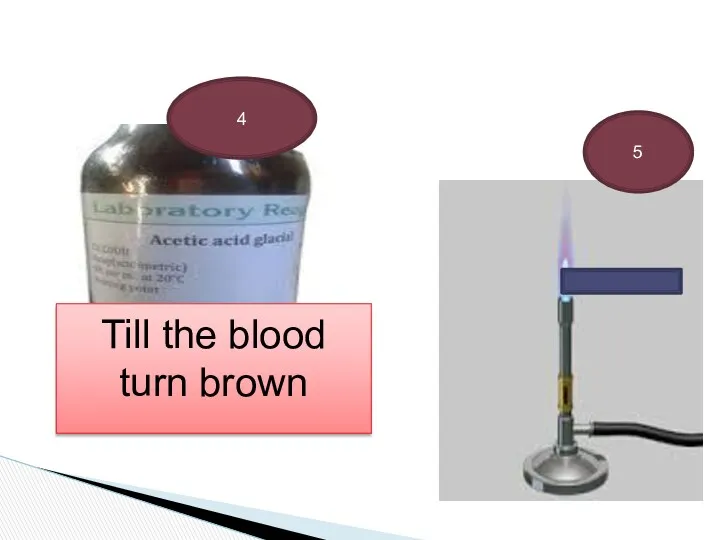
- 29. 4 Till the blood turn brown 5
- 30. 6 Examine under microscope
- 31. We can also find different type of crystal Do you know what is that ???? Salt
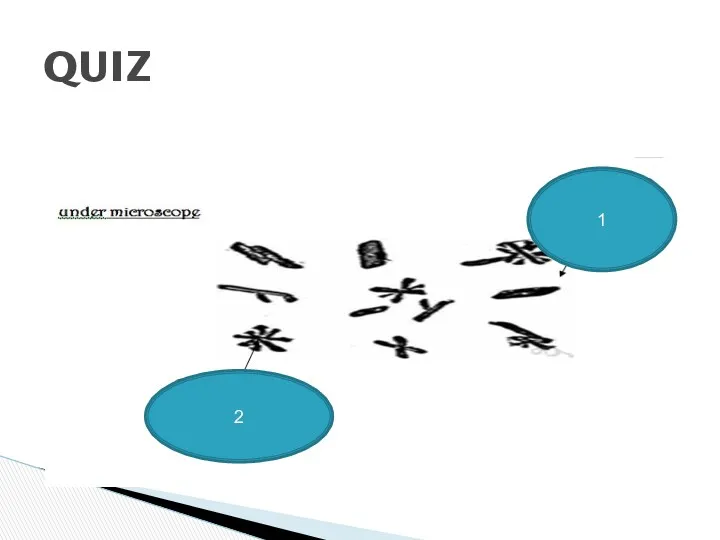
- 32. QUIZ 1 2
- 34. Скачать презентацию











 Термопластичные полимеры
Термопластичные полимеры Оксиды. Названия оксидов
Оксиды. Названия оксидов Основы коррозии и защиты металлов. Химическая коррозия
Основы коррозии и защиты металлов. Химическая коррозия Углеводы. Урок по химии для 9 класса
Углеводы. Урок по химии для 9 класса Определите положение в ПСХЭ элементов
Определите положение в ПСХЭ элементов Об изучении окислительно-восстановительных реакций в школьном курсе химии. Степени окисления атомов и формулы веществ
Об изучении окислительно-восстановительных реакций в школьном курсе химии. Степени окисления атомов и формулы веществ Химическая промышленность
Химическая промышленность Алканы.Определение. Общая формула класса углеводородов
Алканы.Определение. Общая формула класса углеводородов Донорно-акцепторний механізм утворення ковалентного зв’язку
Донорно-акцепторний механізм утворення ковалентного зв’язку Химический элемент фтор
Химический элемент фтор Аммиак
Аммиак ae2db93272ef42dba476a56bbc56b895
ae2db93272ef42dba476a56bbc56b895 Введение в органическую химию
Введение в органическую химию Цинковое покрытие
Цинковое покрытие Арены. Бензол. Урок химии. 10 класс
Арены. Бензол. Урок химии. 10 класс Влияние фтора на организм человека
Влияние фтора на организм человека Получение и применение алканов
Получение и применение алканов Медь, графит, алмаз
Медь, графит, алмаз Центрифугирование в цитологии
Центрифугирование в цитологии Застосування засобів захисту органів дихання від небезпечних хімічних речовин
Застосування засобів захисту органів дихання від небезпечних хімічних речовин Гидролиз солей
Гидролиз солей Строение и свойства циклоалканов
Строение и свойства циклоалканов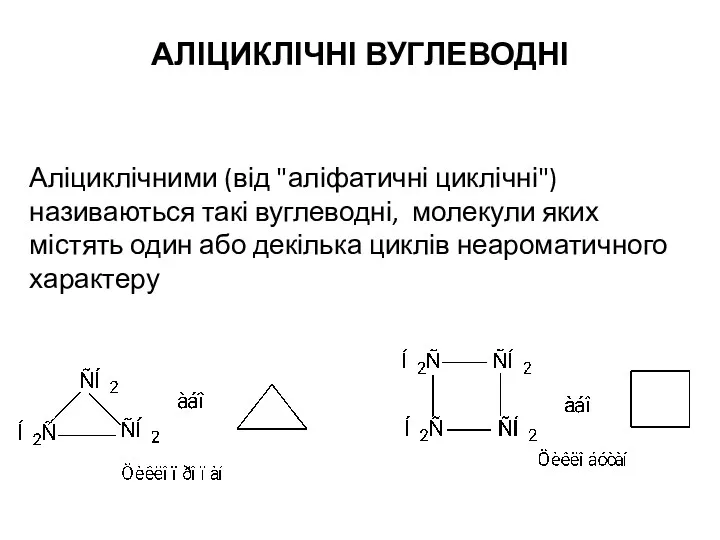 Аліциклічні вуглеводні
Аліциклічні вуглеводні Порівняльний аналіз методів відновлення свинцево-кислотних акумуляторів
Порівняльний аналіз методів відновлення свинцево-кислотних акумуляторів Процессы проявления и фиксирования
Процессы проявления и фиксирования Валентность элементов. Определение валентности по формулам
Валентность элементов. Определение валентности по формулам Графит
Графит Хімія у створенні нових матеріалів та побуті
Хімія у створенні нових матеріалів та побуті