Содержание
- 2. Plan
- 3. Alkylation is the introduction of an alkyl substituent into the molecule of an organic compound. Typical
- 4. Butane-butylene fraction (BBF) must be purified from sulfur compounds, which are mainly represented by mercaptans. The
- 5. The alkylation reaction of isobutane with olefins is accompanied by the release of a large amount
- 7. Скачать презентацию
Plan
Plan
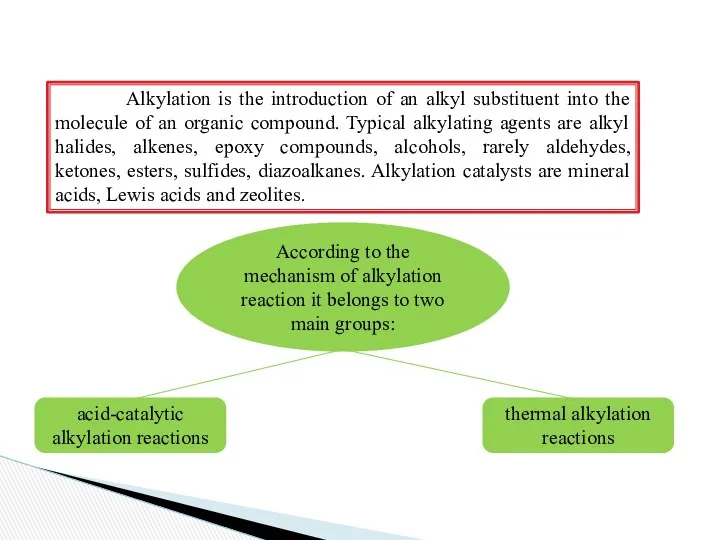
Alkylation is the introduction of an alkyl substituent into the
Alkylation is the introduction of an alkyl substituent into the
According to the mechanism of alkylation reaction it belongs to two main groups:
acid-catalytic alkylation reactions
thermal alkylation reactions
Butane-butylene fraction (BBF) must be purified from sulfur compounds, which
Butane-butylene fraction (BBF) must be purified from sulfur compounds, which
THE RAW MATERIAL OF ALKYLATION
The alkylation reaction of isobutane with olefins is accompanied by the
The alkylation reaction of isobutane with olefins is accompanied by the
heat removal through the heat exchange surface located inside the reactor, in this case closed cooling cycles are used with the use of special refrigerants - ammonia, propane
heat removal by evaporation in the reaction space of the components involved in the reaction, for example, isobutane, in this case, the heat transfer surface is not needed, which greatly simplifies the design of the reactor.
Two methods of heat removal



 Природный газ
Природный газ Plastic is one of the challenges of the 21st century
Plastic is one of the challenges of the 21st century Гідроліз солей
Гідроліз солей Обмен липидов-2
Обмен липидов-2 Пурины. Строение пурина
Пурины. Строение пурина Азотсодержащие соединения. Амины. Аминокислоты
Азотсодержащие соединения. Амины. Аминокислоты Оксосоединения. Основные понятия
Оксосоединения. Основные понятия Технические средства наноэлектроники. Эпитаксиальные методы получения наноструктур
Технические средства наноэлектроники. Эпитаксиальные методы получения наноструктур Применение гибридного биосорбента для очистки промышленных сточных вод от радиоактивных примесей
Применение гибридного биосорбента для очистки промышленных сточных вод от радиоактивных примесей Кислоты. Определение и классификация
Кислоты. Определение и классификация Тотығу түрлері.Липидтердің пероксидті тотығуы (ЛПТ), антиоксиданттар
Тотығу түрлері.Липидтердің пероксидті тотығуы (ЛПТ), антиоксиданттар Вода. Химические и физические свойства
Вода. Химические и физические свойства Природные источники углеводородов
Природные источники углеводородов Сформировать понятие о химическом составе пищи
Сформировать понятие о химическом составе пищи Дисахариди. Амінокислоти. Пептиди
Дисахариди. Амінокислоти. Пептиди Гидроочистка нефти и газа
Гидроочистка нефти и газа Химическая связь. Валентность элементов в ковалентных соединениях. Степень окисления элементов
Химическая связь. Валентность элементов в ковалентных соединениях. Степень окисления элементов Жири як представники естерів. Класифікація жирів, їхні хімічні властивості
Жири як представники естерів. Класифікація жирів, їхні хімічні властивості Электролитическая диссоциация
Электролитическая диссоциация Коррозия металлов и способы защиты от неё
Коррозия металлов и способы защиты от неё Строение и свойства циклоалканов
Строение и свойства циклоалканов Основания (3)
Основания (3) Щелочные породы среднего состава
Щелочные породы среднего состава Классы неорганических веществ (лекция № 4)
Классы неорганических веществ (лекция № 4) Соли-электролиты
Соли-электролиты Товары бытовой химии
Товары бытовой химии Основные понятия и законы химии
Основные понятия и законы химии Амфотерные оксиды и гидроксиды
Амфотерные оксиды и гидроксиды