Содержание
- 3. Group 7 – the halogens The elements in group 7 of the periodic table, on the
- 4. Why are they called the ‘halogens’? Halogens are very reactive non metals. They are all toxic
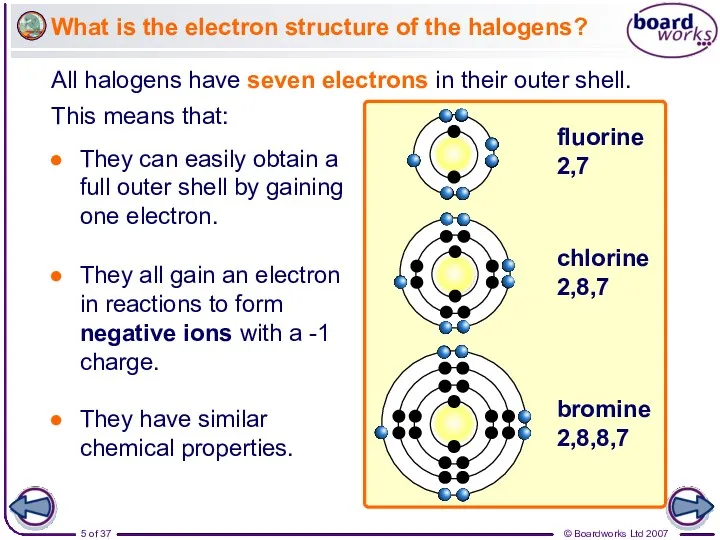
- 5. All halogens have seven electrons in their outer shell. What is the electron structure of the
- 6. How do halogen molecules exist? All halogen atoms require one more electron to obtain a full
- 8. poisonous and smelly. brittle and crumbly when solid What are the general properties of the halogens?
- 9. What is the physical state of the halogens? The melting and boiling points of the halogens
- 10. Halogen vapours Bromine and iodine are not gaseous, but have low boiling points. This means that
- 12. How do the halogens react with metals? The reactivity of halogens means that they readily react
- 13. What are halides? When halogens react with another substance, they become negative ions, as they are
- 14. Equations of halogens and iron When a halogen reacts with iron it forms an iron halide:
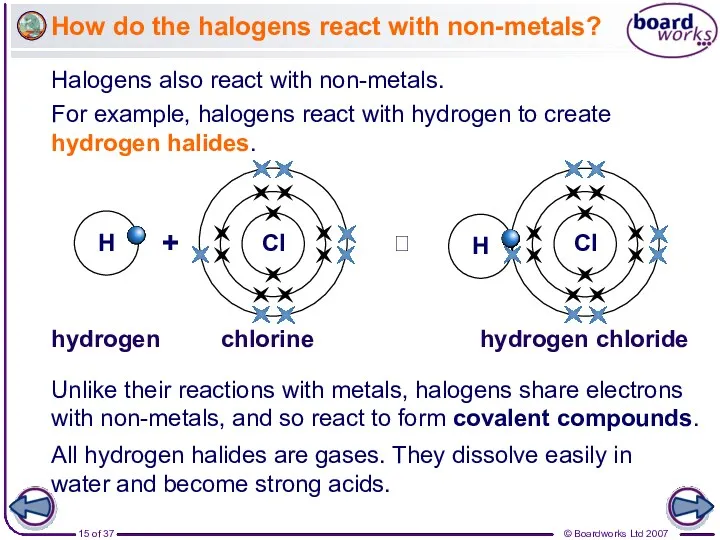
- 15. How do the halogens react with non-metals? Halogens also react with non-metals. For example, halogens react
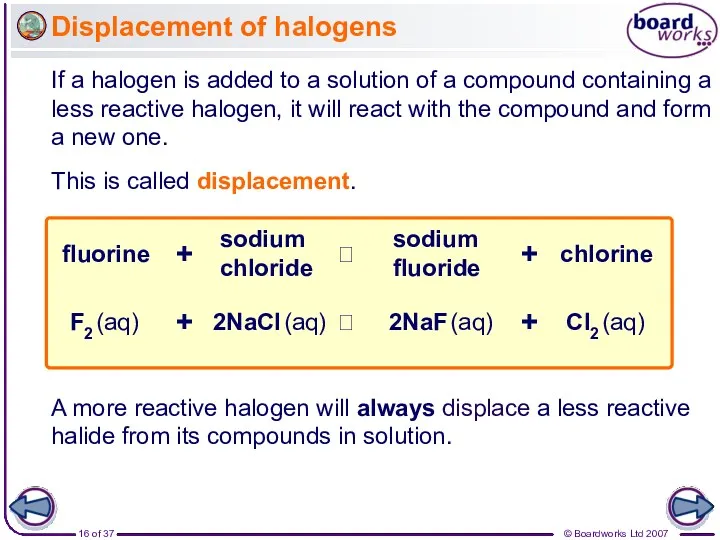
- 16. Displacement of halogens If a halogen is added to a solution of a compound containing a
- 17. Displacement of halogens Why will a halogen always displace a less reactive halogen?
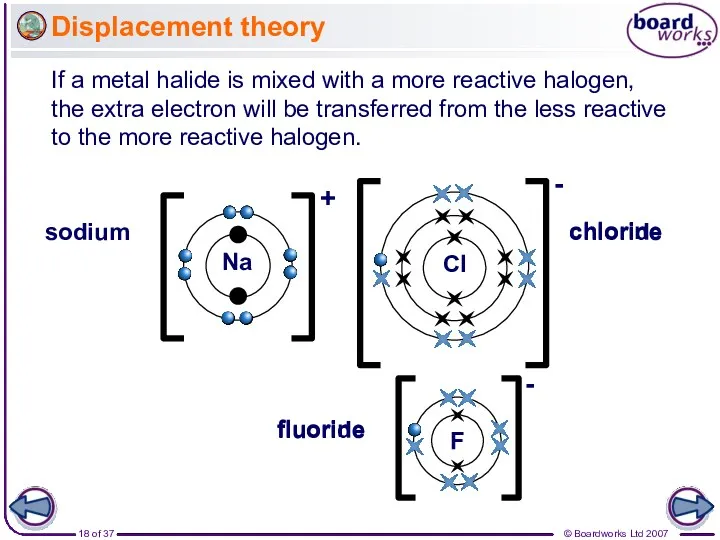
- 18. Displacement theory If a metal halide is mixed with a more reactive halogen, the extra electron
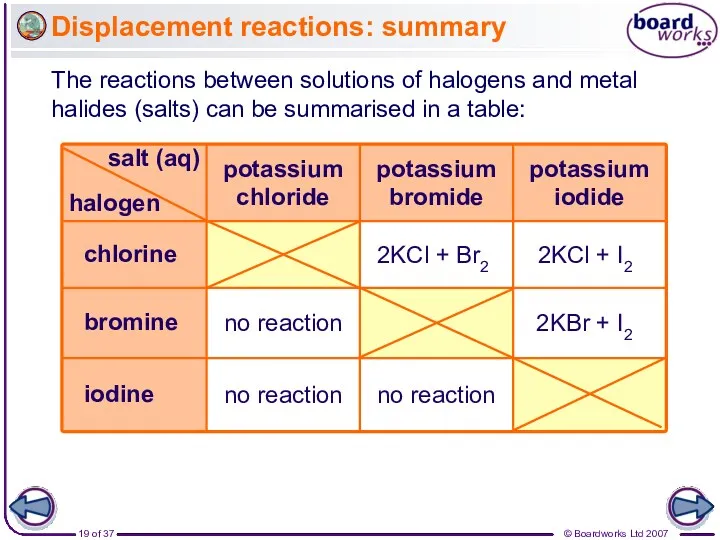
- 19. Displacement reactions: summary The reactions between solutions of halogens and metal halides (salts) can be summarised
- 21. What are the uses of halogens?
- 23. Скачать презентацию















 Кислородсодержащие органические соединения
Кислородсодержащие органические соединения Соединения щелочных металлов
Соединения щелочных металлов Об изучении окислительно-восстановительных реакций в школьном курсе химии. Степени окисления атомов и формулы веществ
Об изучении окислительно-восстановительных реакций в школьном курсе химии. Степени окисления атомов и формулы веществ Відносна молекулярна маса речовини, її обчислення за хімічною формулою
Відносна молекулярна маса речовини, її обчислення за хімічною формулою Алканы
Алканы Химические свойства основных классов неорганических веществ
Химические свойства основных классов неорганических веществ Дистиляттағы цианидтер, алифаттық қатардағы галоген туындылары, хлороформ, хлоралгидрат, төртхлорлы көміртек
Дистиляттағы цианидтер, алифаттық қатардағы галоген туындылары, хлороформ, хлоралгидрат, төртхлорлы көміртек Углеводородное сырье: способы переработки
Углеводородное сырье: способы переработки Предельные углеводороды
Предельные углеводороды Комплесные соединения
Комплесные соединения Мұнай. Мұнайдың шығу тарихы
Мұнай. Мұнайдың шығу тарихы Лекция 1. Периодический закон и периодическая система химических элементов. Индустрия красоты
Лекция 1. Периодический закон и периодическая система химических элементов. Индустрия красоты Салыстырмалы тығыздығы мен элементтердің массалық үлестері бойынша газ күйіндегі заттардың молекулалық формулаларын табу
Салыстырмалы тығыздығы мен элементтердің массалық үлестері бойынша газ күйіндегі заттардың молекулалық формулаларын табу Алкалоидтар түсінігі. Никотин, кофеин,морфин, хинин туралы түсініктер
Алкалоидтар түсінігі. Никотин, кофеин,морфин, хинин туралы түсініктер Неметаллические материалы, используемые в машино- и приборостроении
Неметаллические материалы, используемые в машино- и приборостроении Спирти. 3агальна характеристика спиртів
Спирти. 3агальна характеристика спиртів Алюминий и его соединения
Алюминий и его соединения Метаболизм нуклеиновых кислот
Метаболизм нуклеиновых кислот Азотистые гетероциклические соединения
Азотистые гетероциклические соединения Формы минералов и их агрегатов
Формы минералов и их агрегатов Химические свойства металлов
Химические свойства металлов Що ховається за цифрами? Харчові домішки
Що ховається за цифрами? Харчові домішки Адсорбция-фазалар бөлу беттерінде жүретін бір компоненттің екінші компонентке сіңуі
Адсорбция-фазалар бөлу беттерінде жүретін бір компоненттің екінші компонентке сіңуі Угарный газ
Угарный газ Контрольная работа по дисциплине Физическая химия. Раздел: Электрохимия
Контрольная работа по дисциплине Физическая химия. Раздел: Электрохимия Адсорбция. Разделение однородных и неоднородных смесей
Адсорбция. Разделение однородных и неоднородных смесей Ферум та його сполуки
Ферум та його сполуки Аминокислоты. Белки
Аминокислоты. Белки