Содержание
- 2. Main ideas What is navigation? What is navigation used for? ILS ; VOR/DME
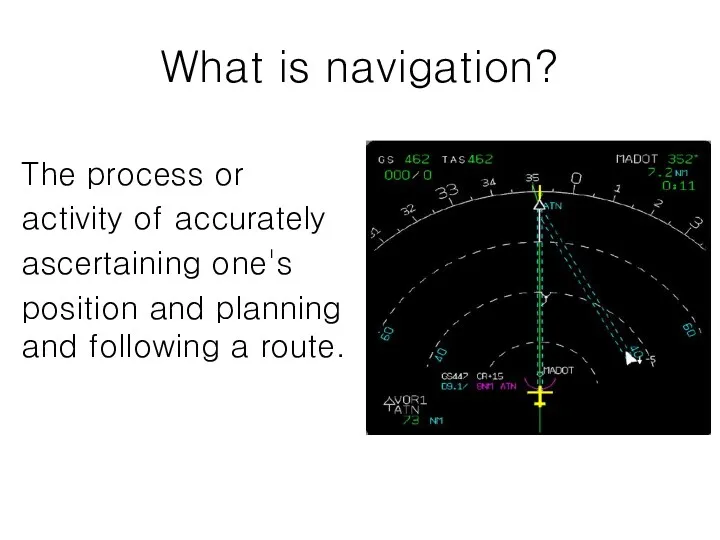
- 3. What is navigation? The process or activity of accurately ascertaining one's position and planning and following
- 4. What is navigation used for? Navigation is the art and science of determining the position of
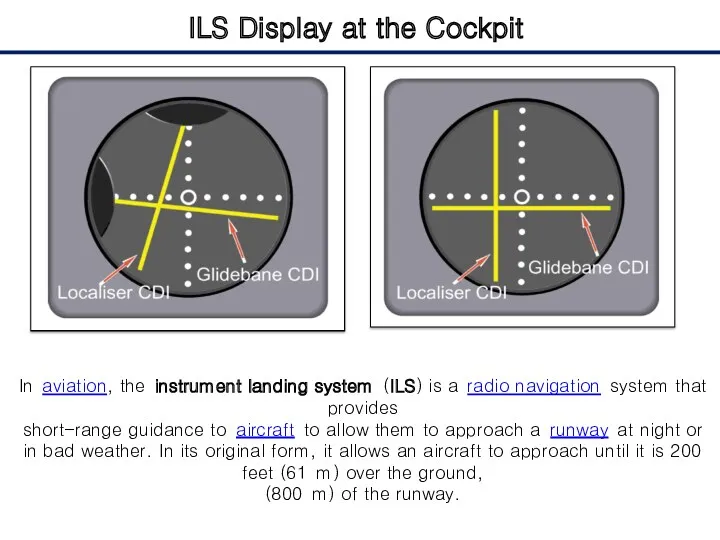
- 5. ILS Display at the Cockpit In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a radio navigation
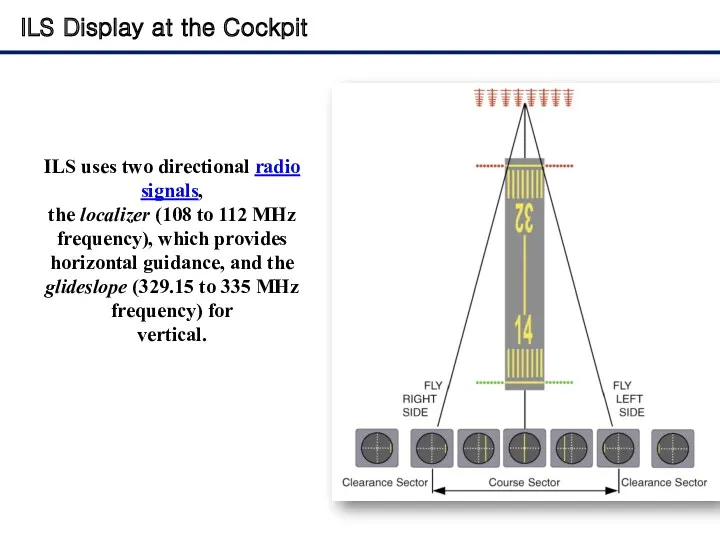
- 6. ILS Display at the Cockpit ILS uses two directional radio signals, the localizer (108 to 112
- 7. ILS Display at the Cockpit
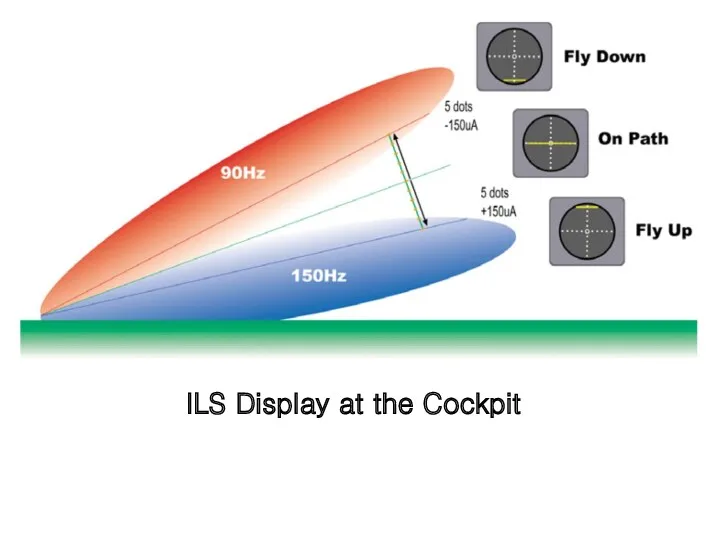
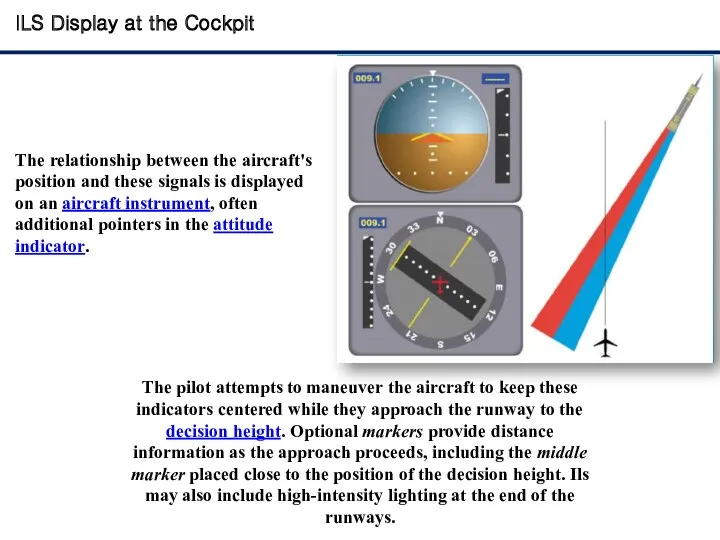
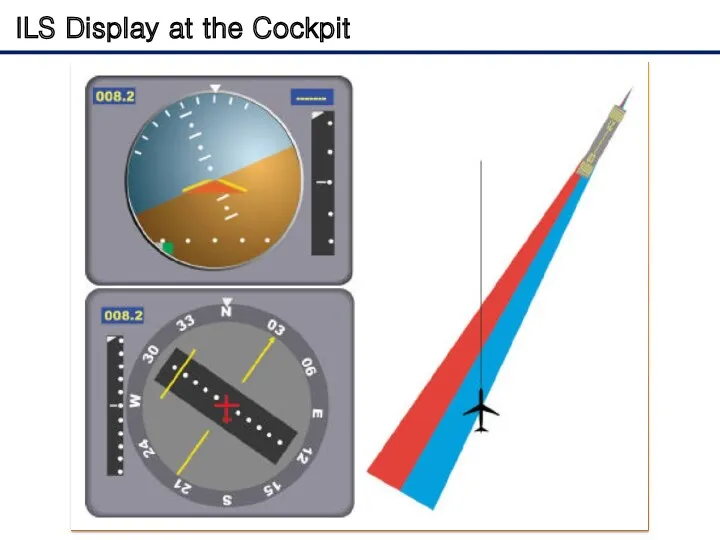
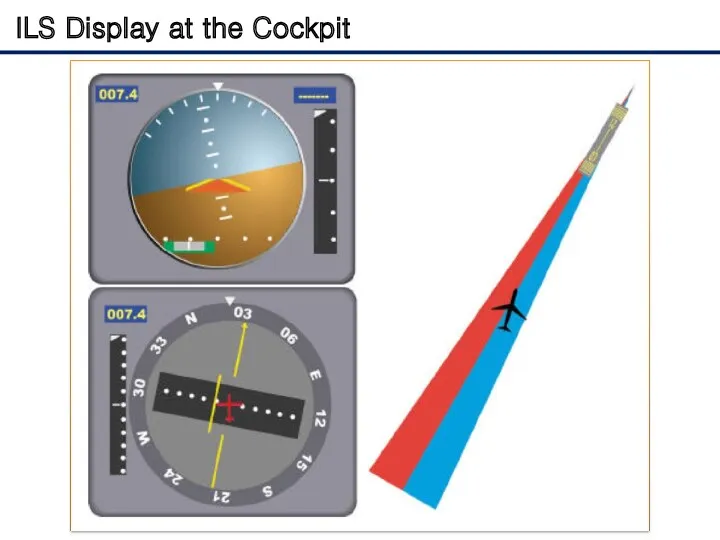
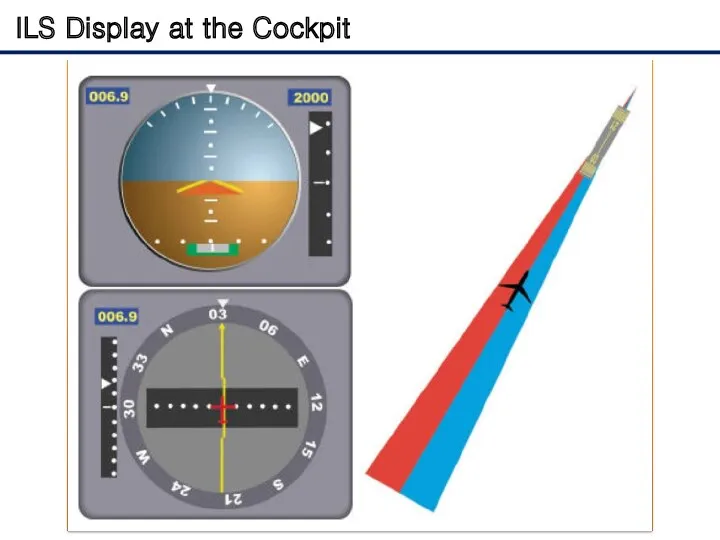
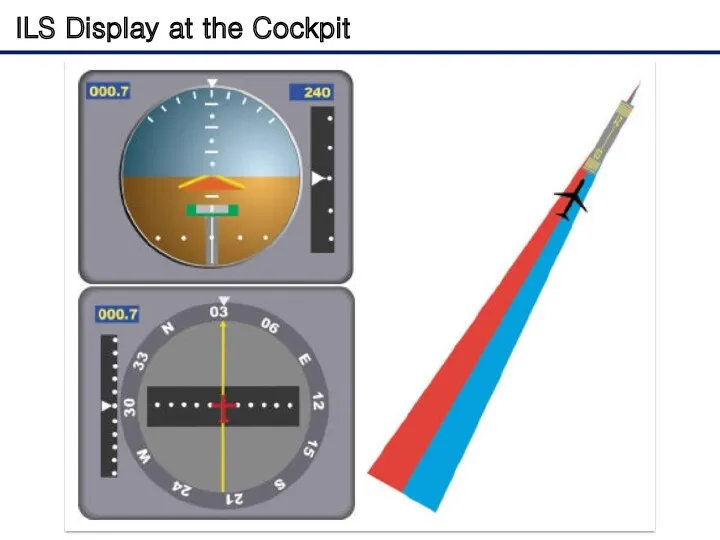
- 8. ILS Display at the Cockpit The relationship between the aircraft's position and these signals is displayed
- 9. ILS Display at the Cockpit
- 10. ILS Display at the Cockpit
- 11. ILS Display at the Cockpit
- 12. ILS Display at the Cockpit
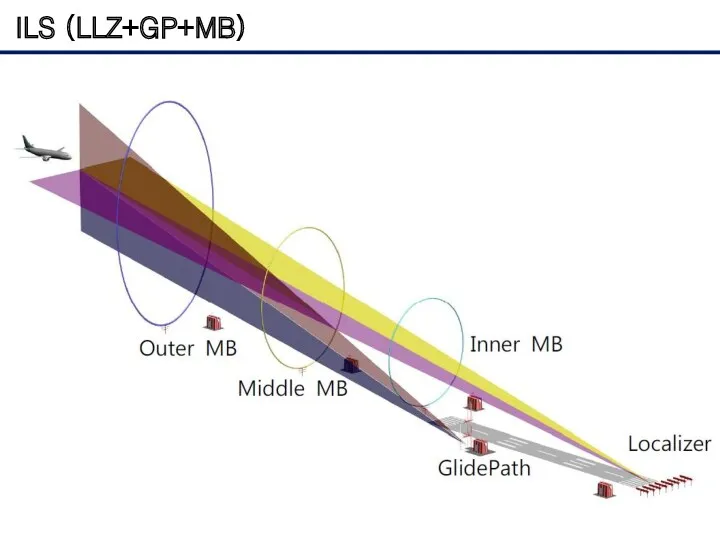
- 13. ILS (LLZ+GP+MB)
- 14. LLZ Antenna Array An instrument landing system operates as a ground-based instrument approach system that provides
- 15. GP Antenna Array
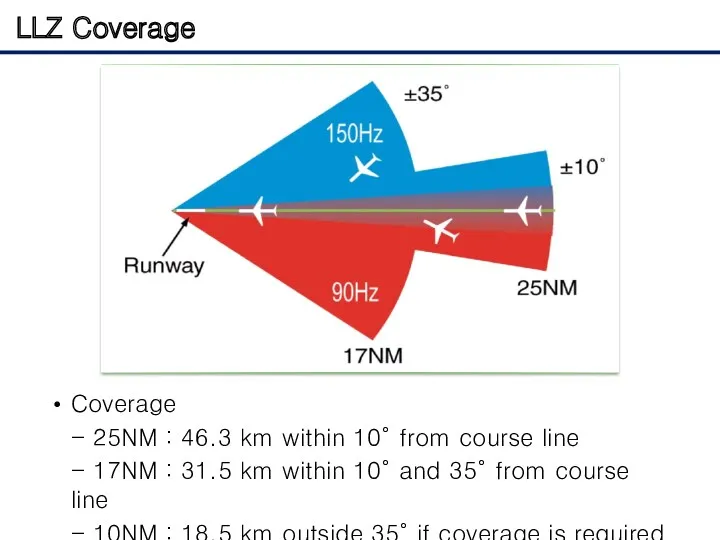
- 16. LLZ Coverage Coverage - 25NM : 46.3 km within 10° from course line - 17NM :
- 17. DVOR/DME In radio navigation, a VOR/DME is a radio beacon that combines a VHF omnidirectional range
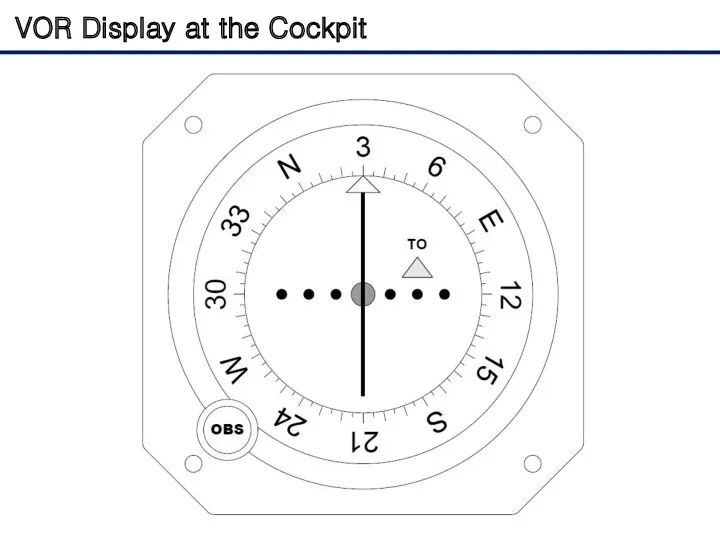
- 18. VOR Display at the Cockpit
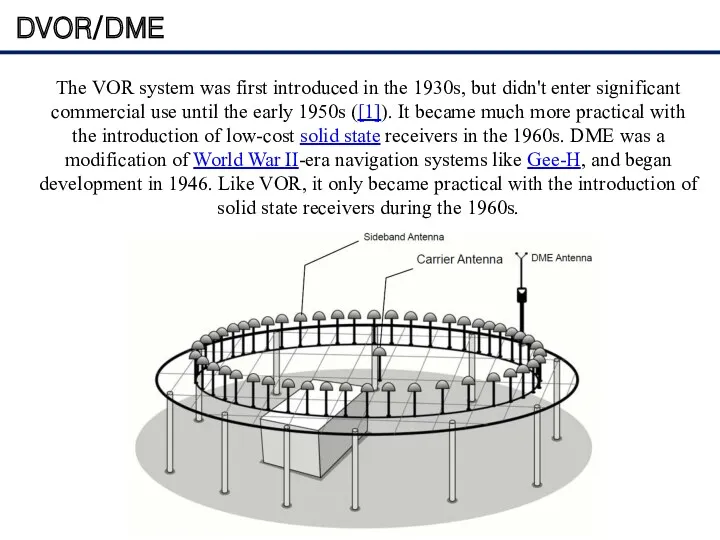
- 19. DVOR/DME The VOR system was first introduced in the 1930s, but didn't enter significant commercial use
- 20. DVOR Antenna Array
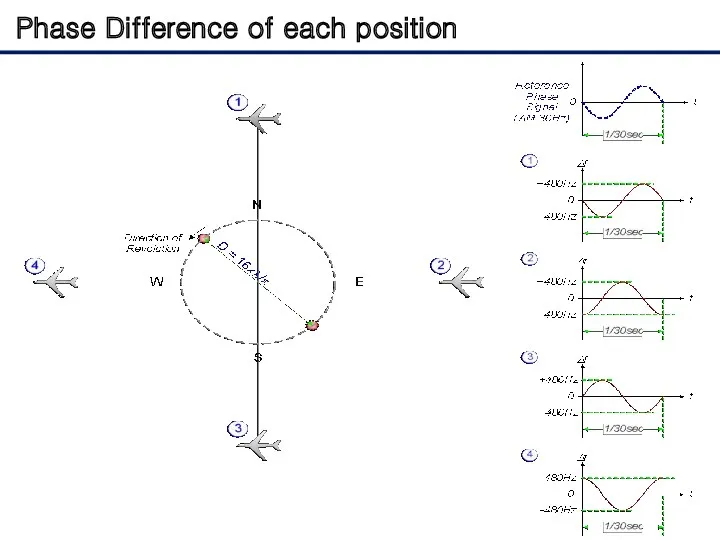
- 21. Phase Difference of each position
- 22. DME Antenna
- 24. Скачать презентацию







 Технология объектно-ориентированного проектирования ИС (разработки программного обеспечения) – Rational Unified Process (RUP)
Технология объектно-ориентированного проектирования ИС (разработки программного обеспечения) – Rational Unified Process (RUP) Объектно-ориентированное программирование. Практические работы Pascal ABC
Объектно-ориентированное программирование. Практические работы Pascal ABC Программа Figma
Программа Figma Руководство пользователя для онлайн-курса ГПА
Руководство пользователя для онлайн-курса ГПА Интерактивная презентация для цикла уроков в 10 классе Создание Веб-сайта. Язык HTML. ;2.
Интерактивная презентация для цикла уроков в 10 классе Создание Веб-сайта. Язык HTML. ;2. Экскурсия по виртуальному музею Компьютерной графики (Office 2007)
Экскурсия по виртуальному музею Компьютерной графики (Office 2007) Линии связи
Линии связи Компьютерные технологии интеллектуальной поддержки управленческих решений
Компьютерные технологии интеллектуальной поддержки управленческих решений Управление ремонтами и обслуживанием оборудования. Решение на основе 1С:Предприятие 8
Управление ремонтами и обслуживанием оборудования. Решение на основе 1С:Предприятие 8 Functions are objects. Main concepts behind Python functions
Functions are objects. Main concepts behind Python functions Training Manual
Training Manual Стиснення та архівування даних
Стиснення та архівування даних Розробка клієнтського програмного забезпечення для корпоративних додатків на платформі Java
Розробка клієнтського програмного забезпечення для корпоративних додатків на платформі Java Welcome. Anti-virus
Welcome. Anti-virus Системы счисления. Позиционные и непозиционные системы
Системы счисления. Позиционные и непозиционные системы Стандартизация программного обеспечения
Стандартизация программного обеспечения Решения для электронного правительства и электронизация государственных услуг — БАРС Груп
Решения для электронного правительства и электронизация государственных услуг — БАРС Груп Моделирование и формализация
Моделирование и формализация Управление в логистических информационных системах (Информационные системы планирования и управления ресурсами предприятия)
Управление в логистических информационных системах (Информационные системы планирования и управления ресурсами предприятия) Работа с VirtualBox, установка рабочих станций и подготовка для включения в одноранговую сеть
Работа с VirtualBox, установка рабочих станций и подготовка для включения в одноранговую сеть Lazarus. Порядок создания приложения
Lazarus. Порядок создания приложения Школьная газета АстраWork
Школьная газета АстраWork Робототехніка на основі Arduino
Робототехніка на основі Arduino Programming logic and design seventh edition. Chapter 5. Looping
Programming logic and design seventh edition. Chapter 5. Looping Инструкция по заполнению регистрационной формы конференции
Инструкция по заполнению регистрационной формы конференции Метод PERT и управление проектами
Метод PERT и управление проектами Модели данных
Модели данных Технічні і програмні засоби КС реального часу. (Тема 10)
Технічні і програмні засоби КС реального часу. (Тема 10)