Содержание
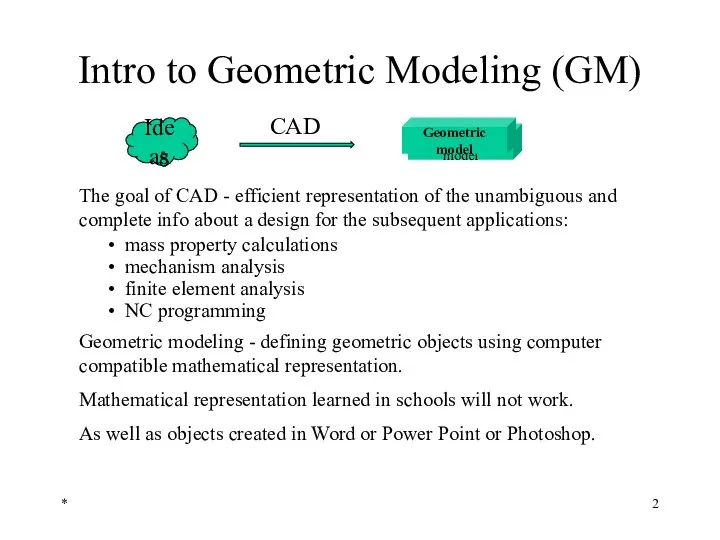
- 2. * Intro to Geometric Modeling (GM) The goal of CAD - efficient representation of the unambiguous
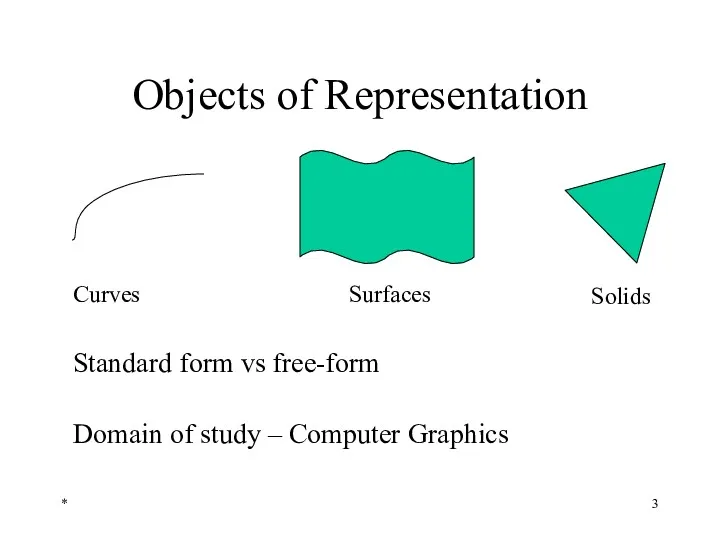
- 3. Objects of Representation * Standard form vs free-form Domain of study – Computer Graphics
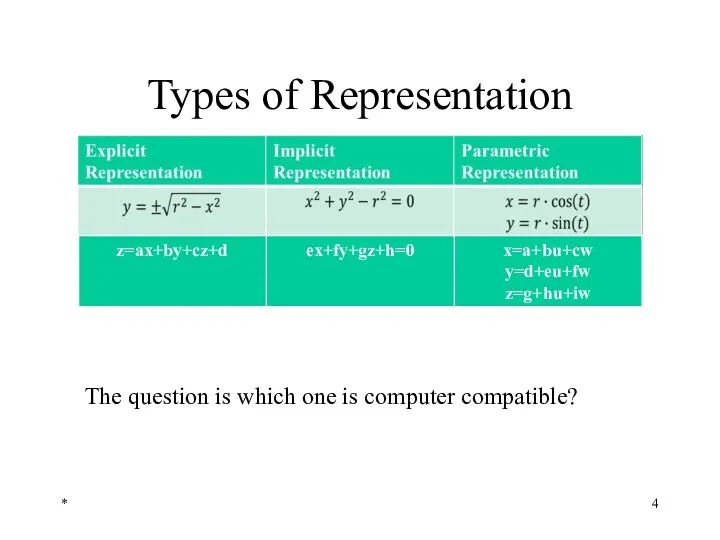
- 4. Types of Representation * The question is which one is computer compatible?
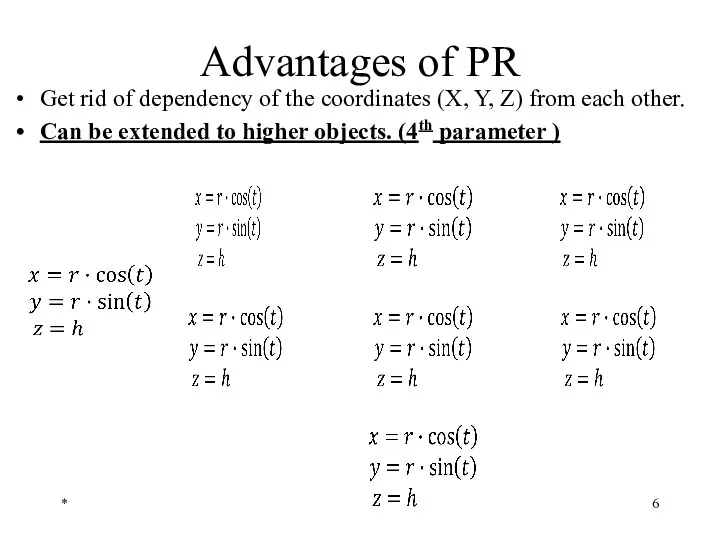
- 5. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
- 6. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
- 7. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
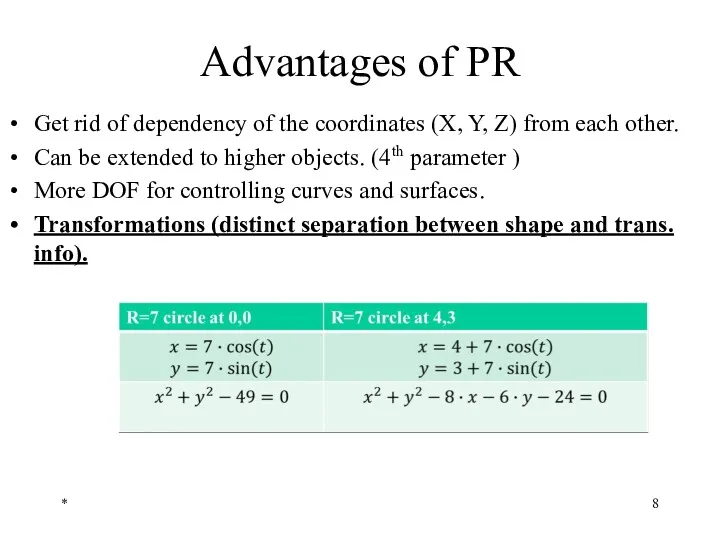
- 8. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
- 9. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
- 10. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
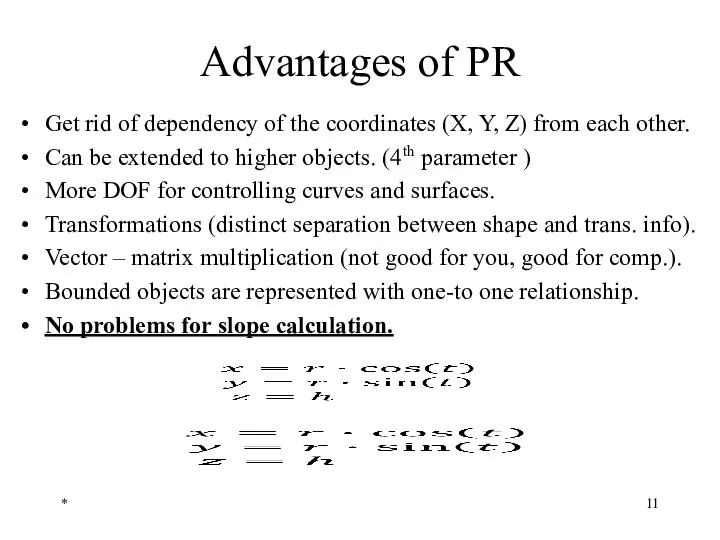
- 11. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
- 12. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y, Z) from each other.
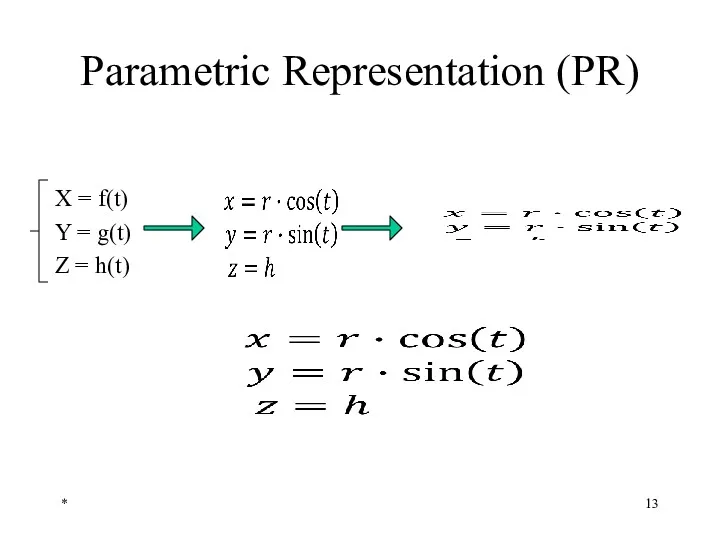
- 13. Parametric Representation (PR) X = f(t) Y = g(t) Z = h(t) *
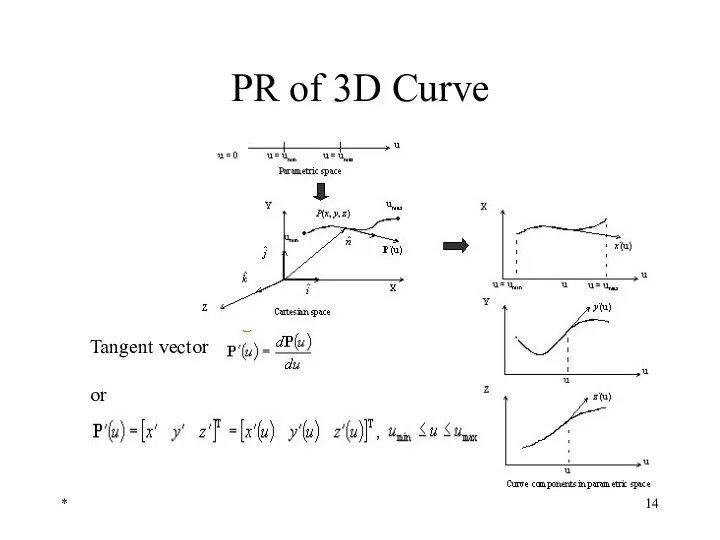
- 14. * PR of 3D Curve Tangent vector or
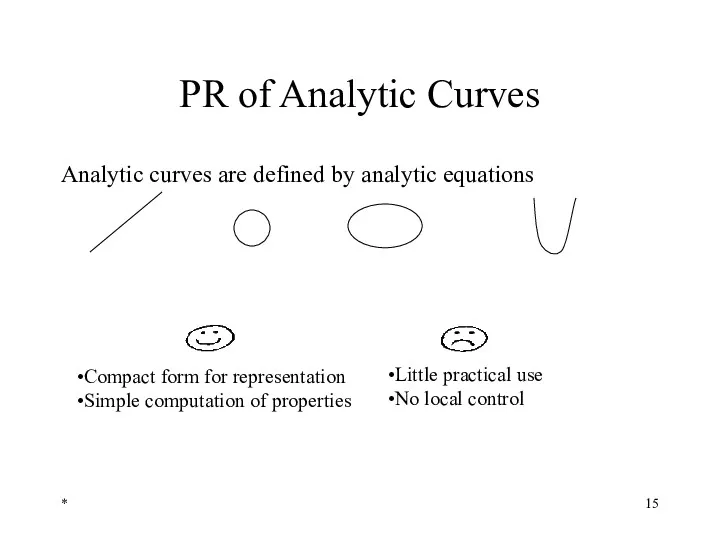
- 15. * PR of Analytic Curves Analytic curves are defined by analytic equations Compact form for representation
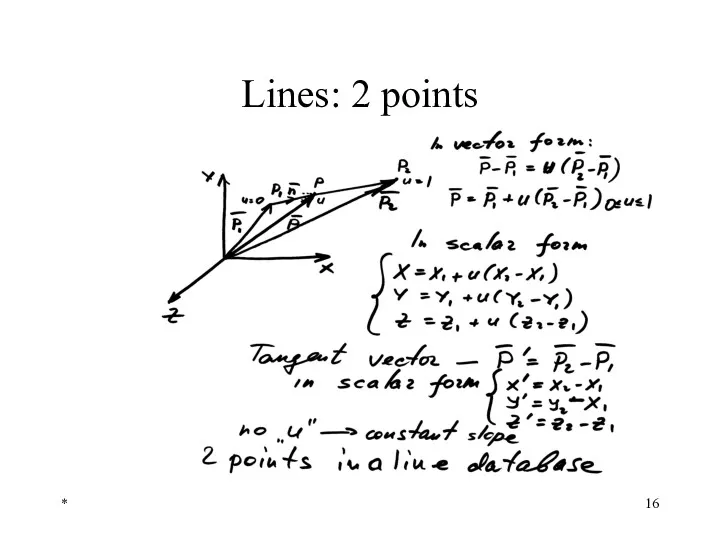
- 16. * Lines: 2 points
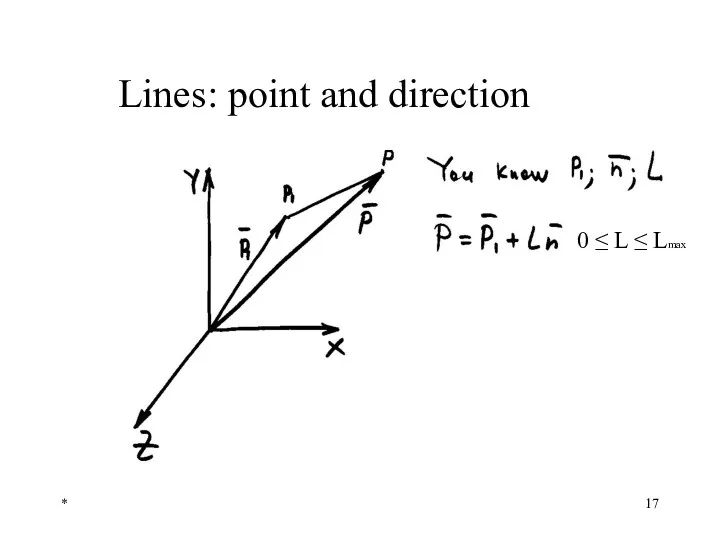
- 17. * Lines: point and direction n
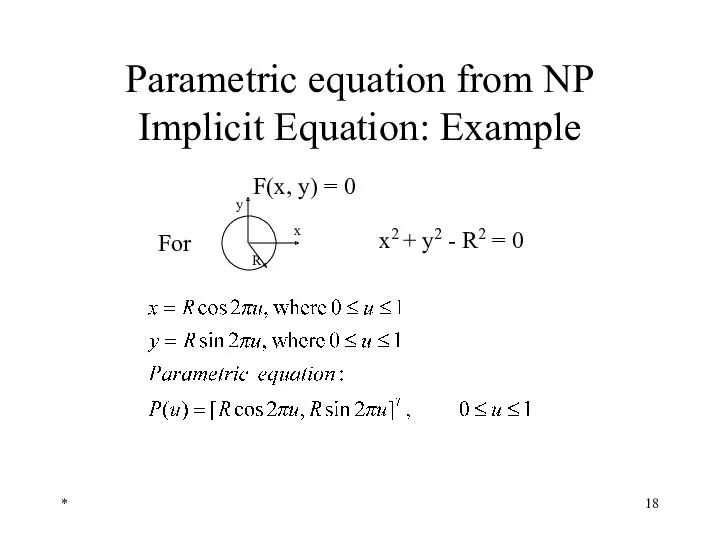
- 18. * Parametric equation from NP Implicit Equation: Example x2 + y2 - R2 = 0 F(x,
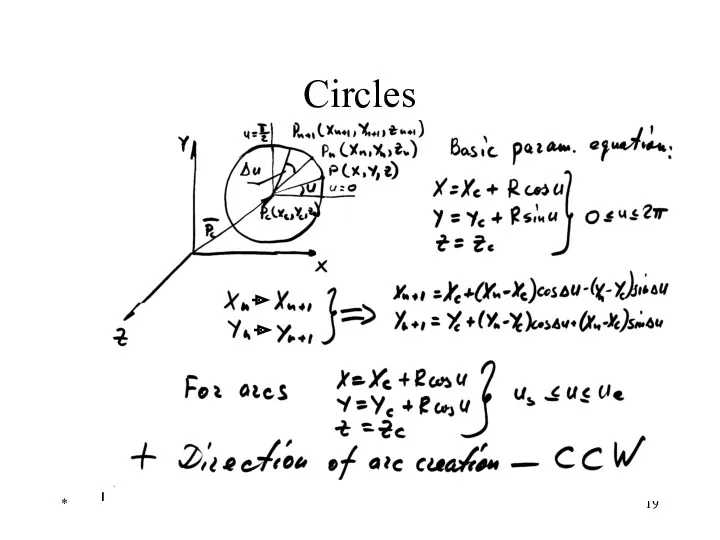
- 19. * Circles
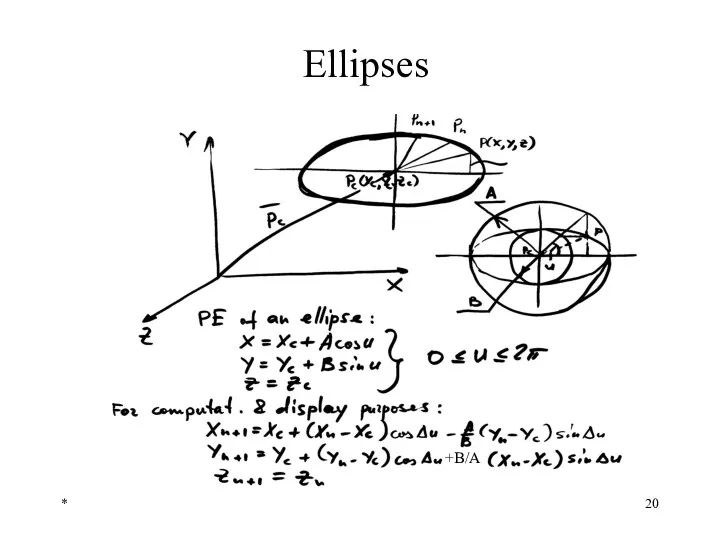
- 20. * Ellipses +B/A
- 22. Скачать презентацию





 Порівняння раціональних чисел. Математика. 6 клас
Порівняння раціональних чисел. Математика. 6 клас Угол между скрещивающимися прямыми
Угол между скрещивающимися прямыми Урок математики Решение задач
Урок математики Решение задач урок математики
урок математики Точечные перфокарты.
Точечные перфокарты. Итоговый тест по математике
Итоговый тест по математике Числовые последовательности
Числовые последовательности Уравнение окружности (9 класс)
Уравнение окружности (9 класс) Практическое применение знаний по математике, связанных с сельским хозяйством
Практическое применение знаний по математике, связанных с сельским хозяйством Урок математики в 1 классе на тему Приёмы сложения и вычитания, основанные на знании нумерации чисел
Урок математики в 1 классе на тему Приёмы сложения и вычитания, основанные на знании нумерации чисел Круглые числа. Состав числа 9. Сравнение выражений
Круглые числа. Состав числа 9. Сравнение выражений Урок Числа от 10 до 20
Урок Числа от 10 до 20 Вычитание чисел (часть 1)
Вычитание чисел (часть 1) Применение признаков равенства треугольников при решении задач
Применение признаков равенства треугольников при решении задач Метод максимального правдоподобия
Метод максимального правдоподобия Формирование УУД на различных этапах урока математики по ТДМ.
Формирование УУД на различных этапах урока математики по ТДМ. Преобразование графиков тригонометрических функций
Преобразование графиков тригонометрических функций Дифференциальные уравнения и их применение в медицинской практике
Дифференциальные уравнения и их применение в медицинской практике Второй признак равенства треугольников
Второй признак равенства треугольников Элементы матанализа. Применение производной при исследовании функции
Элементы матанализа. Применение производной при исследовании функции Таблица деления на 3
Таблица деления на 3 Функция её свойства и график
Функция её свойства и график Ряды динамики. Статистика
Ряды динамики. Статистика Vienkāršās formas
Vienkāršās formas Математический КВН
Математический КВН Вписані і центральні кути
Вписані і центральні кути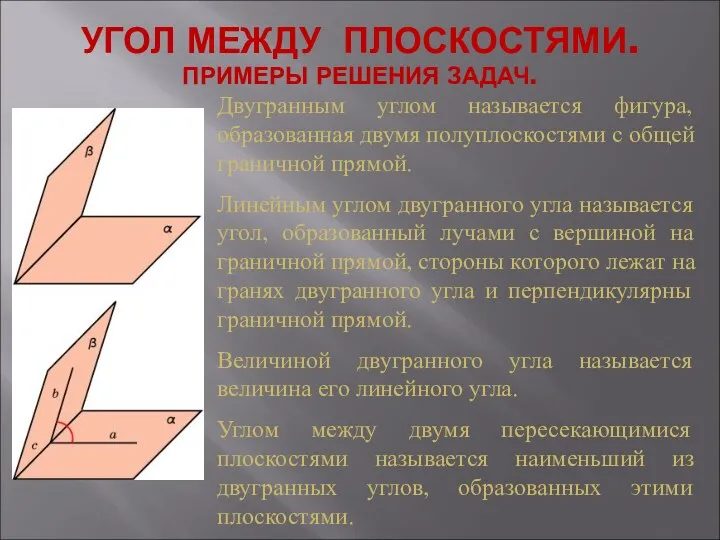 Угол между плоскостями. Примеры решения задач
Угол между плоскостями. Примеры решения задач Высота и скорость полета. (Тема 6)
Высота и скорость полета. (Тема 6)