Содержание
- 2. Adjusting Entries
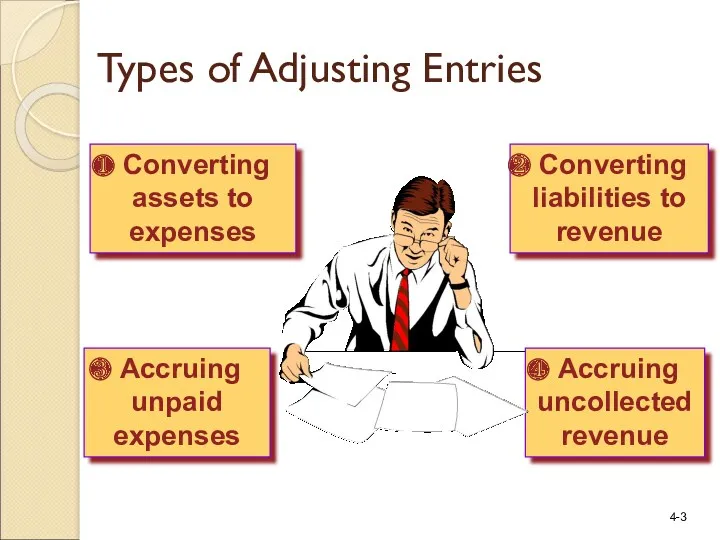
- 3. Accruing unpaid expenses Converting liabilities to revenue Accruing uncollected revenue Types of Adjusting Entries Converting assets
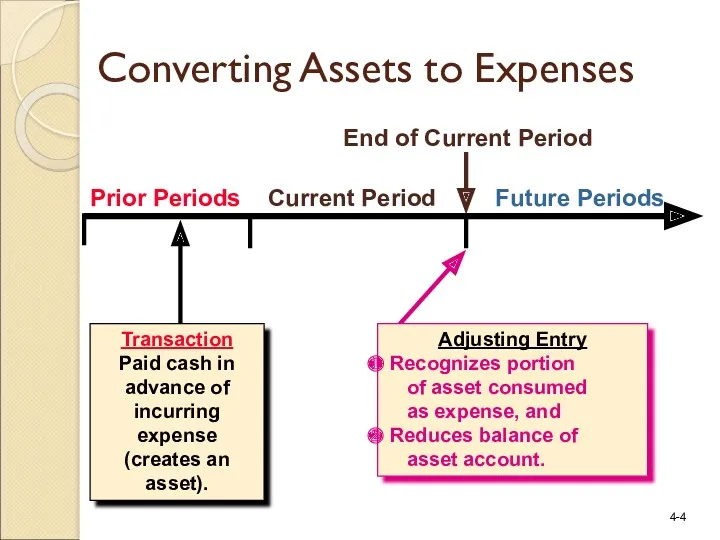
- 4. Prior Periods Current Period Future Periods Transaction Paid cash in advance of incurring expense (creates an
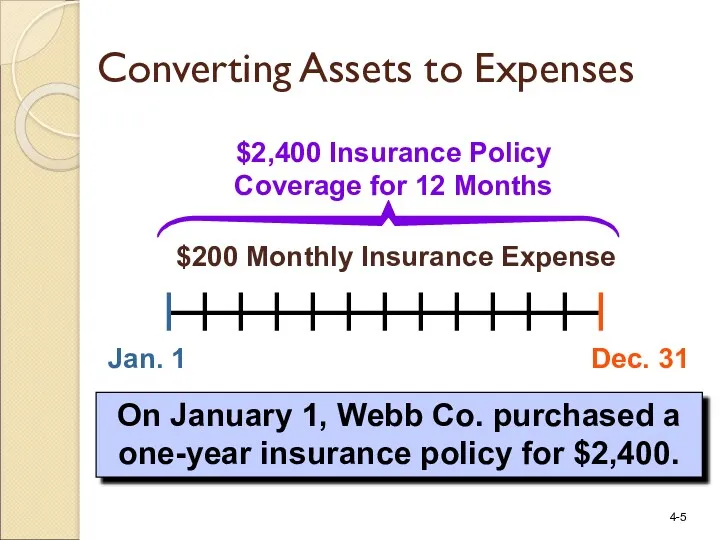
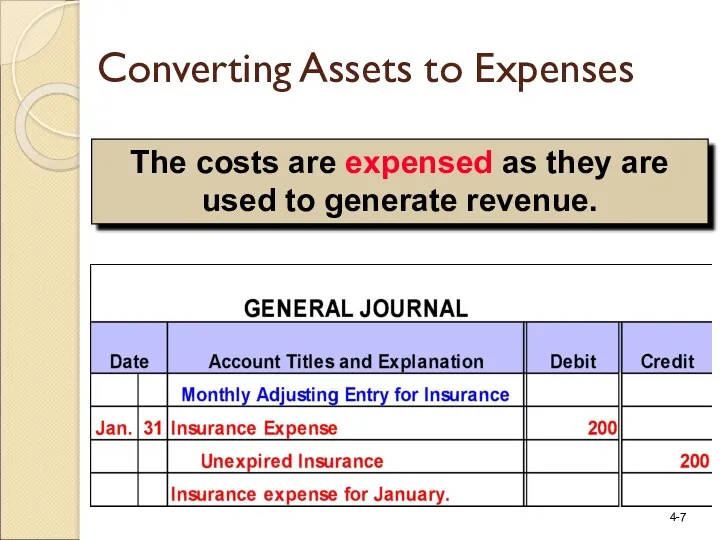
- 5. Jan. 1 Dec. 31 $2,400 Insurance Policy Coverage for 12 Months $200 Monthly Insurance Expense On
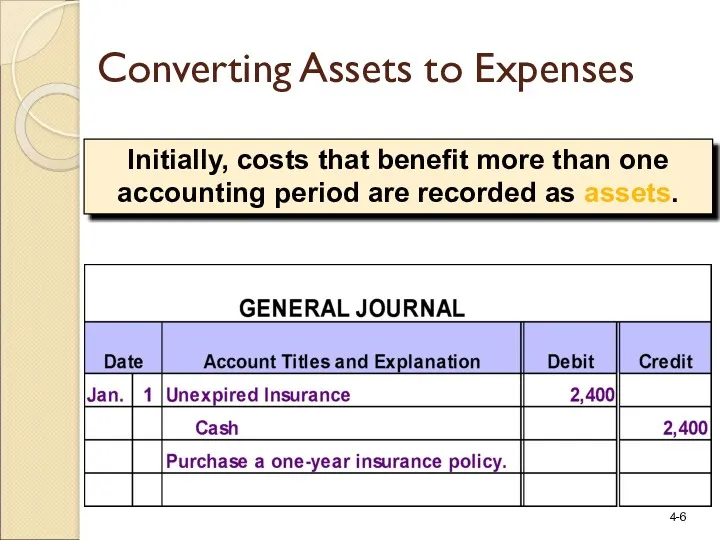
- 6. Initially, costs that benefit more than one accounting period are recorded as assets. Converting Assets to
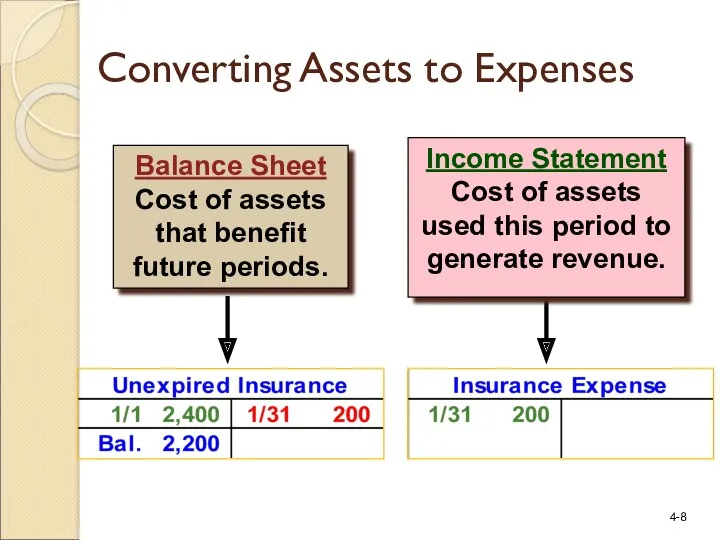
- 7. The costs are expensed as they are used to generate revenue. Converting Assets to Expenses
- 8. Income Statement Cost of assets used this period to generate revenue. Balance Sheet Cost of assets
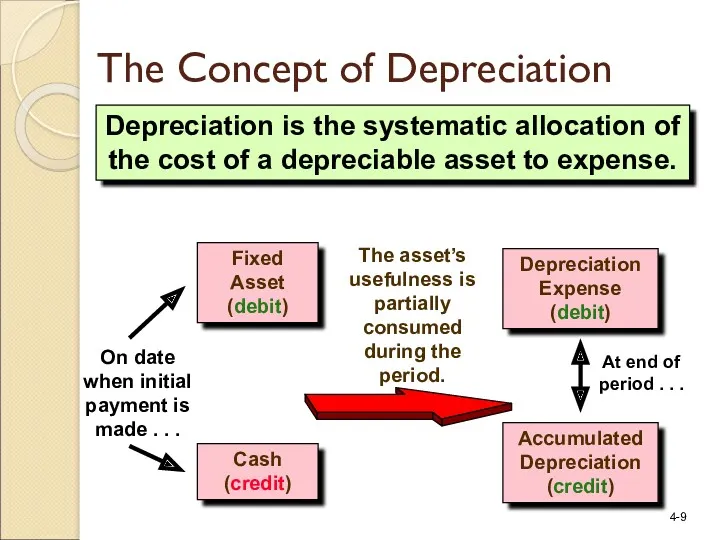
- 9. The Concept of Depreciation Depreciation is the systematic allocation of the cost of a depreciable asset
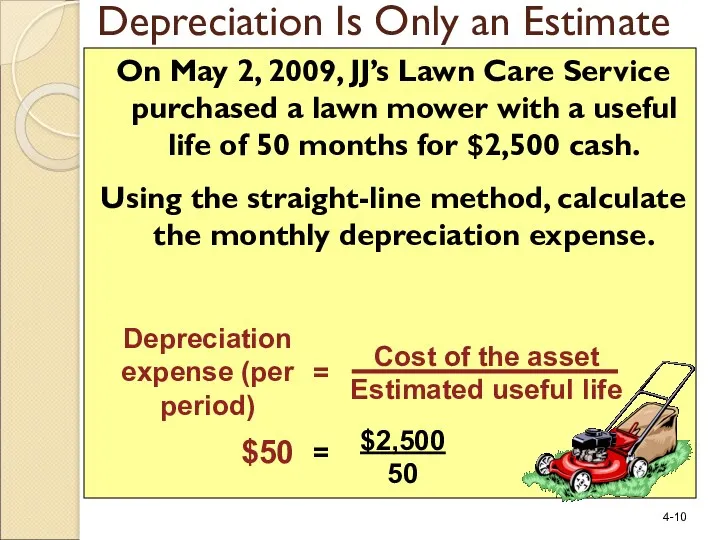
- 10. On May 2, 2009, JJ’s Lawn Care Service purchased a lawn mower with a useful life
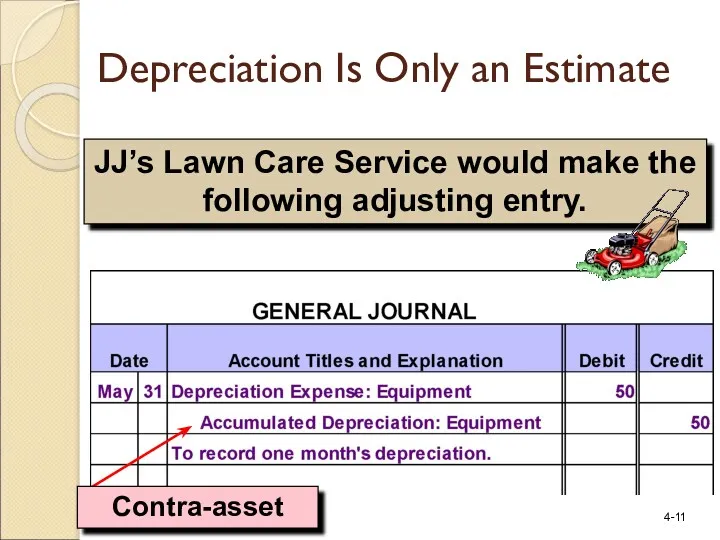
- 11. JJ’s Lawn Care Service would make the following adjusting entry. Depreciation Is Only an Estimate
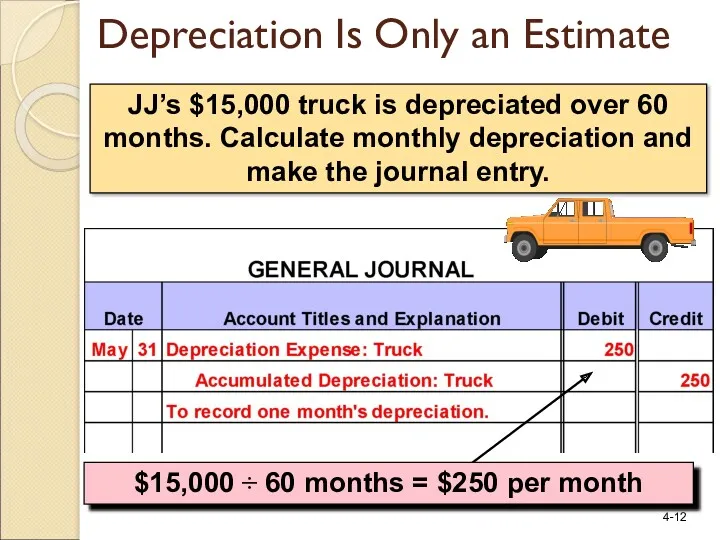
- 12. JJ’s $15,000 truck is depreciated over 60 months. Calculate monthly depreciation and make the journal entry.
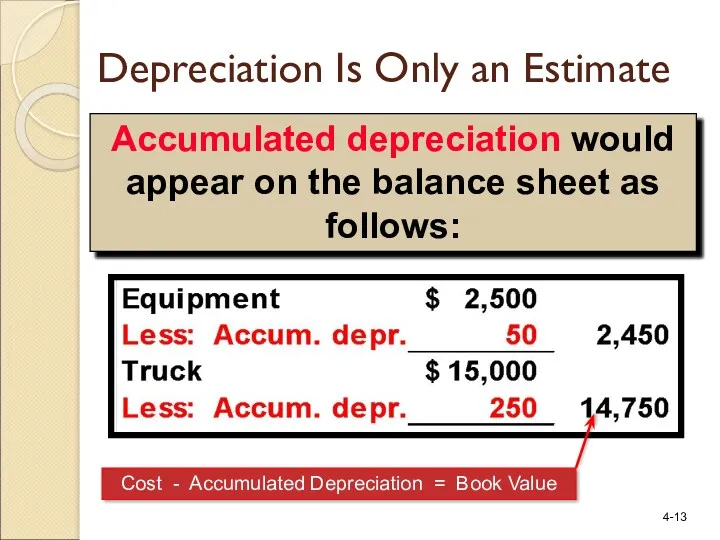
- 13. Accumulated depreciation would appear on the balance sheet as follows: Depreciation Is Only an Estimate Cost
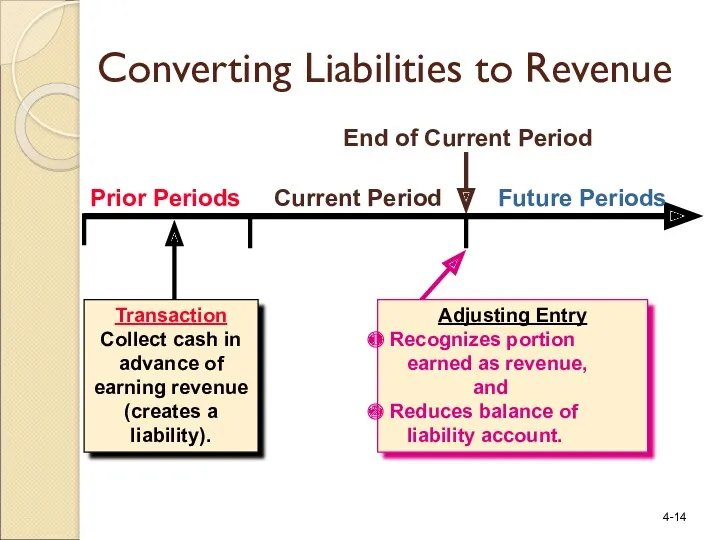
- 14. Prior Periods Current Period Future Periods Transaction Collect cash in advance of earning revenue (creates a
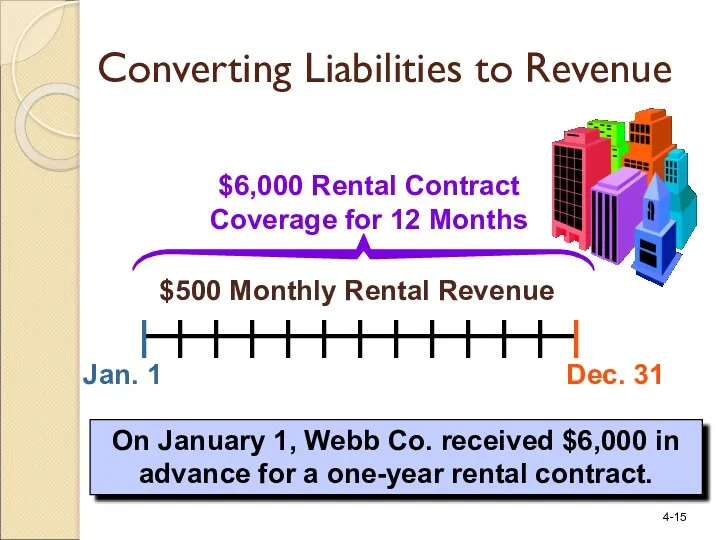
- 15. Jan. 1 Dec. 31 $6,000 Rental Contract Coverage for 12 Months $500 Monthly Rental Revenue On
- 16. Initially, revenues that benefit more than one accounting period are recorded as liabilities. Converting Liabilities to
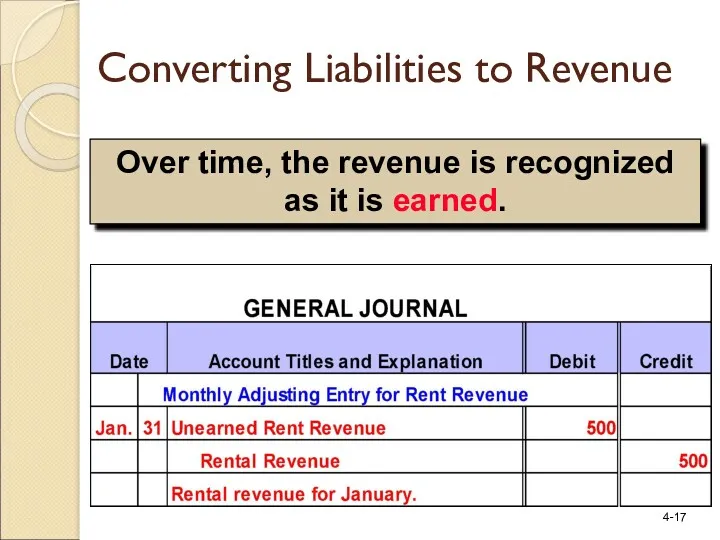
- 17. Over time, the revenue is recognized as it is earned. Converting Liabilities to Revenue
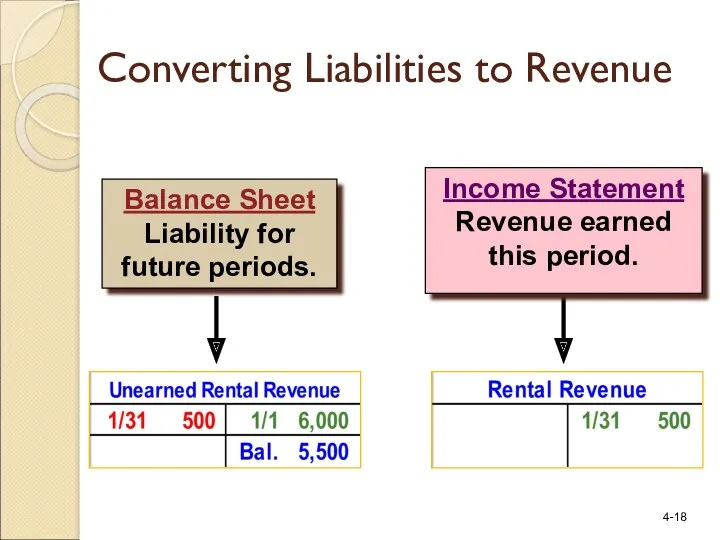
- 18. Income Statement Revenue earned this period. Balance Sheet Liability for future periods. Converting Liabilities to Revenue
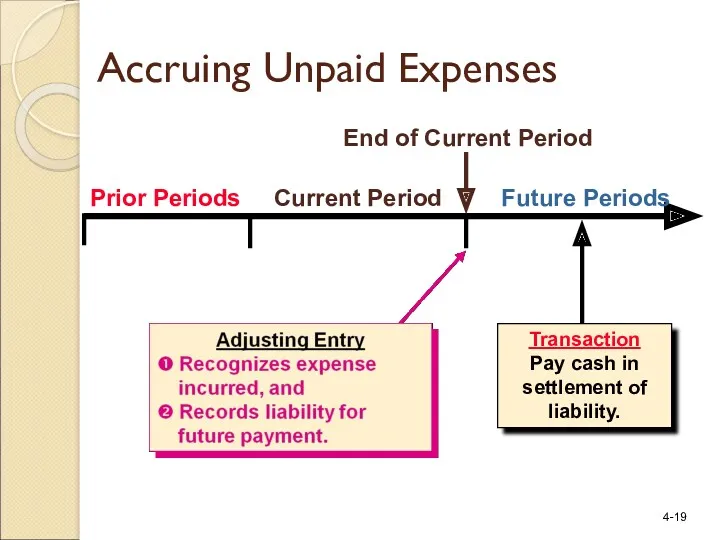
- 19. Prior Periods Current Period Future Periods Transaction Pay cash in settlement of liability. End of Current
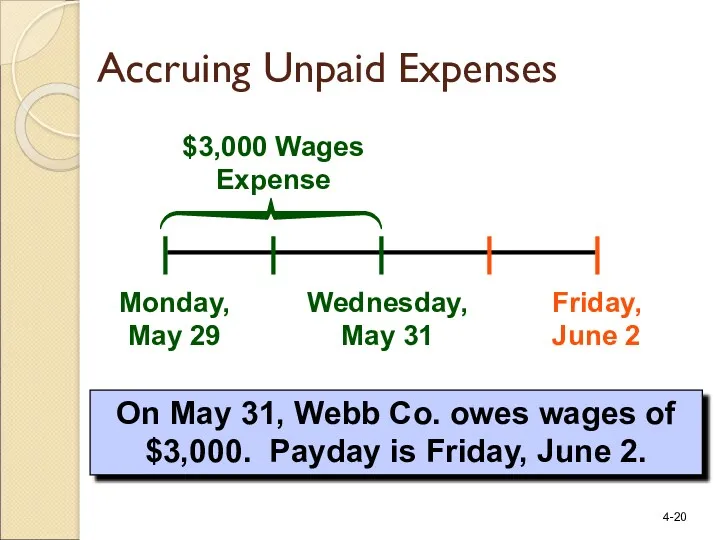
- 20. Monday, May 29 Friday, June 2 $3,000 Wages Expense On May 31, Webb Co. owes wages
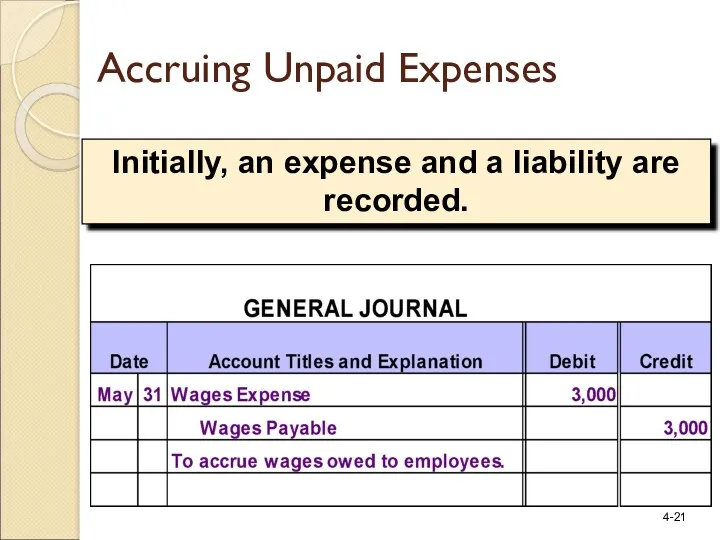
- 21. Initially, an expense and a liability are recorded. Accruing Unpaid Expenses
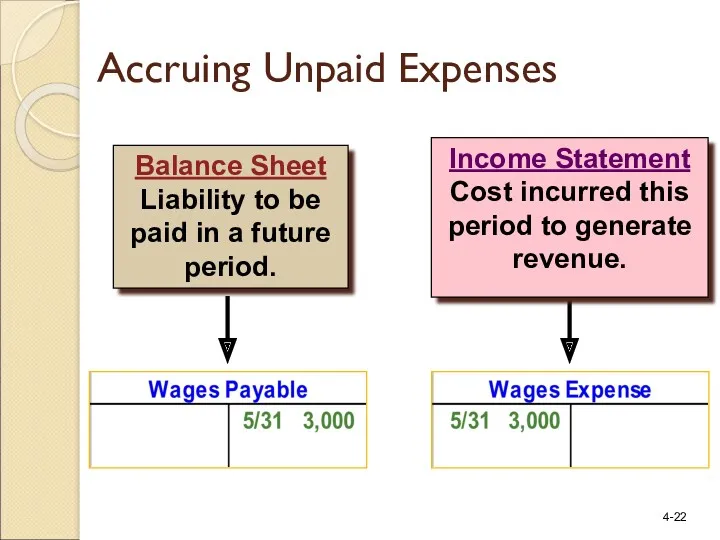
- 22. Income Statement Cost incurred this period to generate revenue. Balance Sheet Liability to be paid in
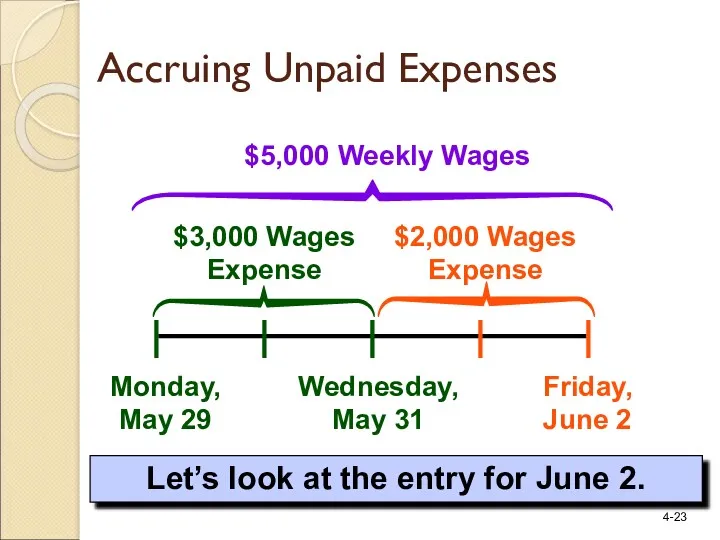
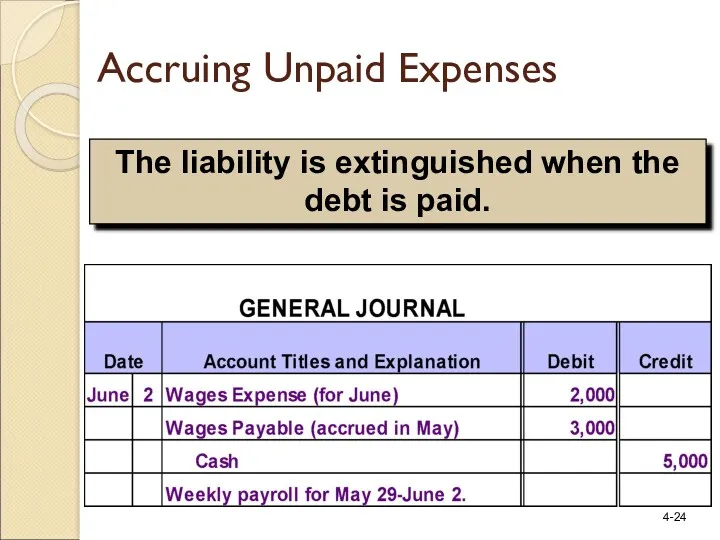
- 23. Monday, May 29 Friday, June 2 $5,000 Weekly Wages Let’s look at the entry for June
- 24. The liability is extinguished when the debt is paid. Accruing Unpaid Expenses
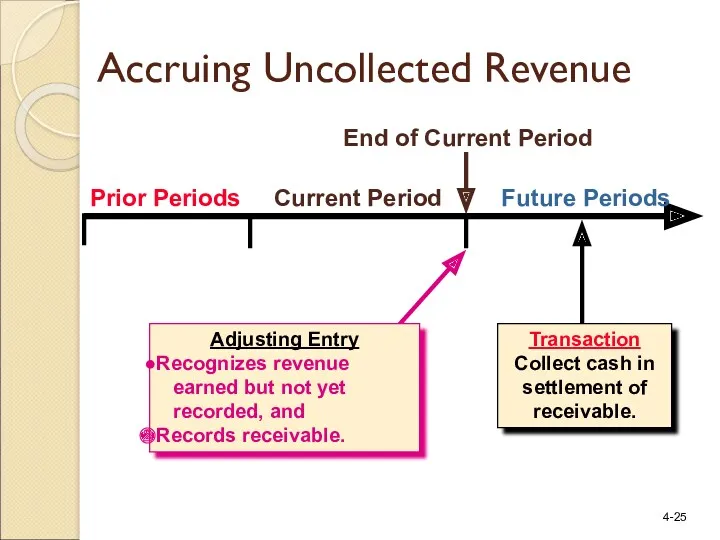
- 25. Prior Periods Current Period Future Periods Transaction Collect cash in settlement of receivable. End of Current
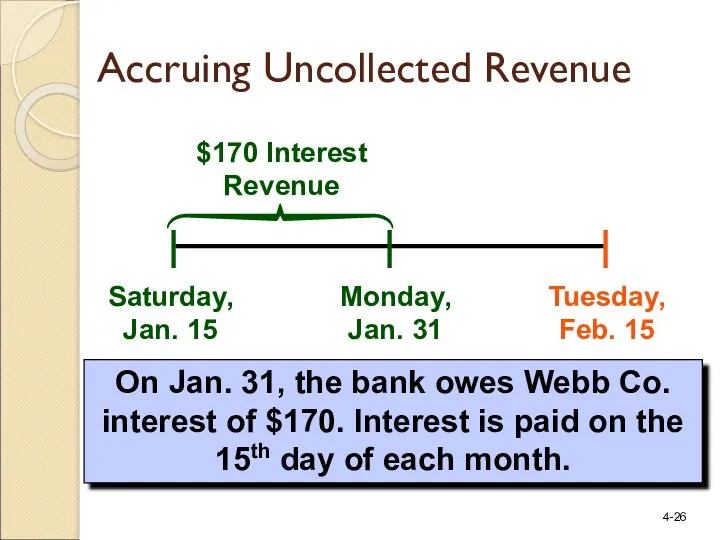
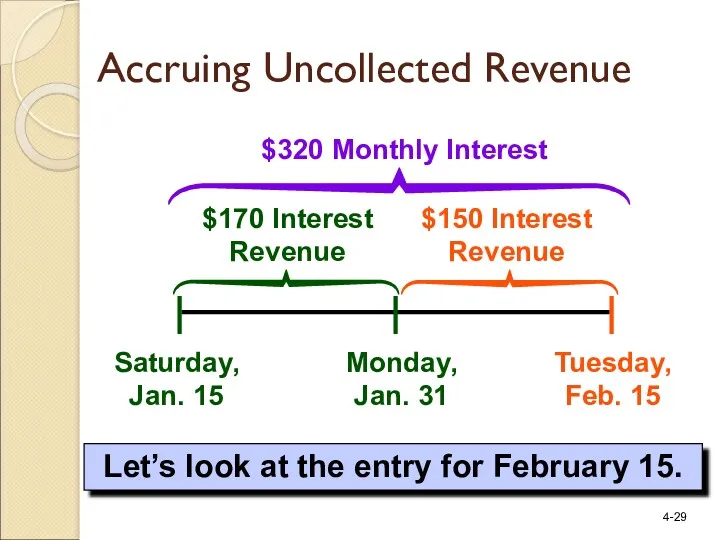
- 26. Saturday, Jan. 15 Tuesday, Feb. 15 $170 Interest Revenue On Jan. 31, the bank owes Webb
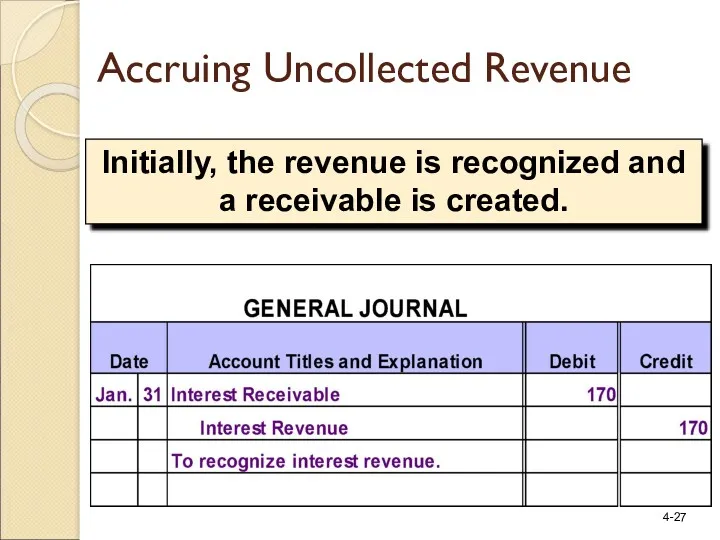
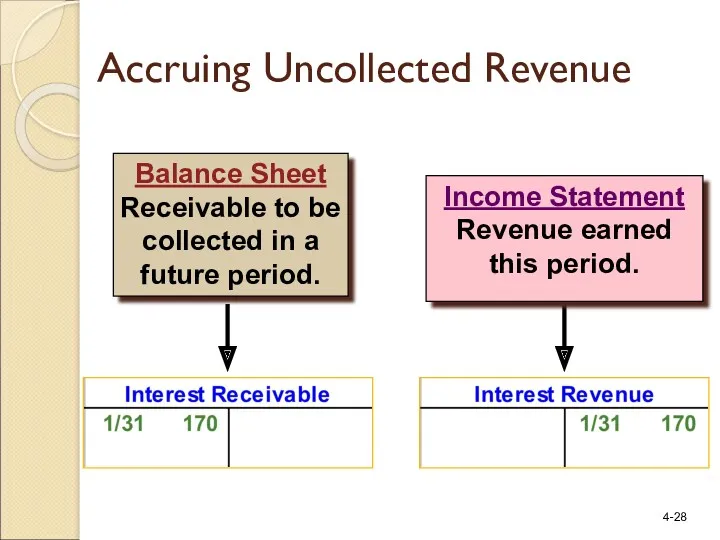
- 27. Initially, the revenue is recognized and a receivable is created. Accruing Uncollected Revenue
- 28. Income Statement Revenue earned this period. Balance Sheet Receivable to be collected in a future period.
- 29. Saturday, Jan. 15 Tuesday, Feb. 15 $320 Monthly Interest $170 Interest Revenue Let’s look at the
- 30. The receivable is collected in a future period. Accruing Uncollected Revenue
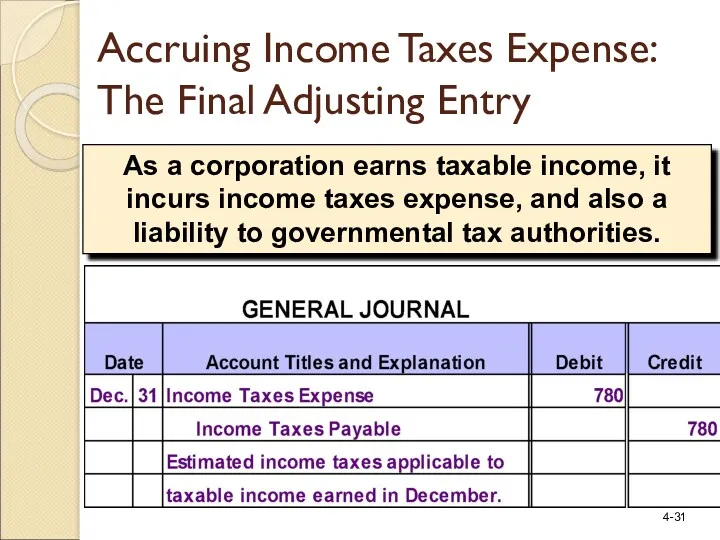
- 31. As a corporation earns taxable income, it incurs income taxes expense, and also a liability to
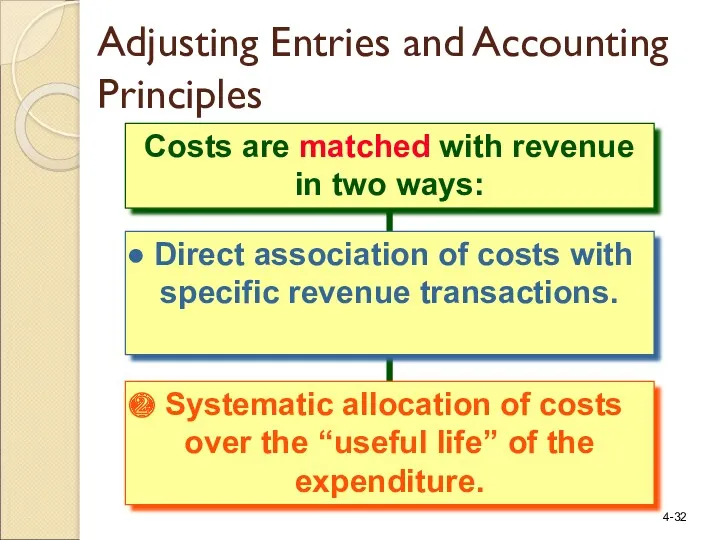
- 32. Costs are matched with revenue in two ways: Direct association of costs with specific revenue transactions.
- 33. An item is “material” if knowledge of the item might reasonably influence the decisions of users
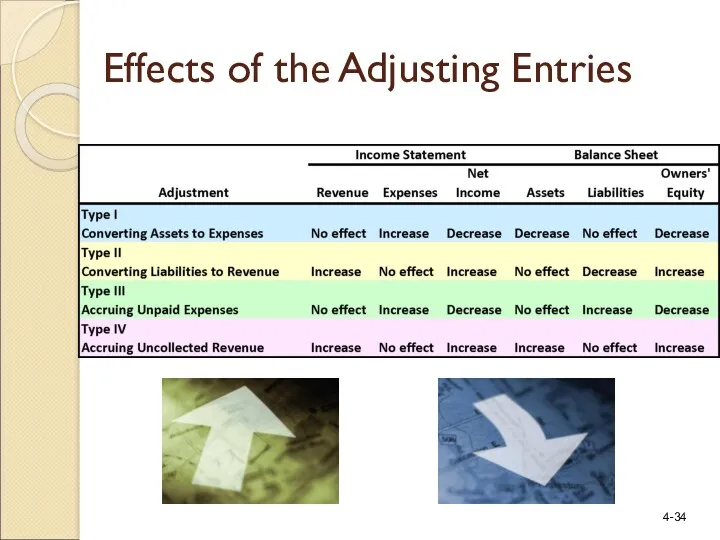
- 34. Effects of the Adjusting Entries
- 35. All balances are taken from the ledger accounts on May 31 after preparing the two depreciation
- 37. Скачать презентацию





 Теория бухгалтерского учёта
Теория бухгалтерского учёта Управление рисками валютных операций
Управление рисками валютных операций Производные ценные бумаги
Производные ценные бумаги Оборотные средства предприятия
Оборотные средства предприятия Характеристика бухгалтерского учета. Основы калькуляции и учета
Характеристика бухгалтерского учета. Основы калькуляции и учета Потоки платежей. Финансовая рента
Потоки платежей. Финансовая рента Денежно-кредитная система и монетарная политика государства
Денежно-кредитная система и монетарная политика государства Последовательность действий налоговых органов при камеральной налоговой проверке
Последовательность действий налоговых органов при камеральной налоговой проверке Государственные внебюджетные фонды
Государственные внебюджетные фонды Основы экономики. Задачи государства. Государственный бюджет
Основы экономики. Задачи государства. Государственный бюджет Управленческий учет для стратегических решений
Управленческий учет для стратегических решений Программа для моряков ПАО МТБ БАНК
Программа для моряков ПАО МТБ БАНК Почта России ЕАС ОПС
Почта России ЕАС ОПС Бюджетна система та бюджетний устрій
Бюджетна система та бюджетний устрій Понятие и структура правовой информации
Понятие и структура правовой информации Цель инвестиций. Активы и Пассивы
Цель инвестиций. Активы и Пассивы Содержание и организация финансового менеджмента на предприятии. (Лекция 1)
Содержание и организация финансового менеджмента на предприятии. (Лекция 1) Ақша және банк жүйесі
Ақша және банк жүйесі Организация кассовой работы в банках по обслуживанию юридических и физических лиц
Организация кассовой работы в банках по обслуживанию юридических и физических лиц Аналіз структури державних доходів України
Аналіз структури державних доходів України Ценовая политика. Сущность понятия
Ценовая политика. Сущность понятия Алгоритм получения родителями (законными представителями) частичной компенсации работающим гражданам стоимости путевок
Алгоритм получения родителями (законными представителями) частичной компенсации работающим гражданам стоимости путевок Страхование. Участники страхового рынка
Страхование. Участники страхового рынка Рынок недвижимости
Рынок недвижимости Памятка для плательщиков страховых взносов
Памятка для плательщиков страховых взносов Финансовый рычаг и структура капитала. Принятие решений о структуре капитала
Финансовый рычаг и структура капитала. Принятие решений о структуре капитала Основы теории стоимости денег во времени
Основы теории стоимости денег во времени Добро пожаловать в Компанию iCredit
Добро пожаловать в Компанию iCredit