Содержание
- 2. Chapter 1 Financial Statements and Business Decisions
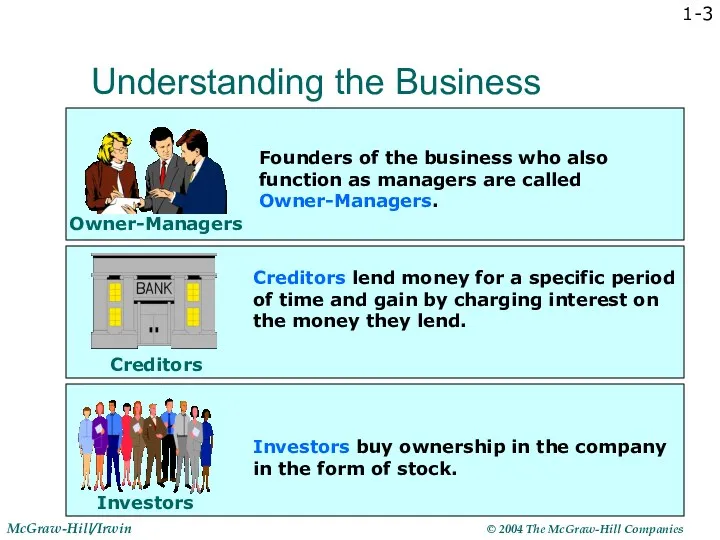
- 3. 1- Understanding the Business
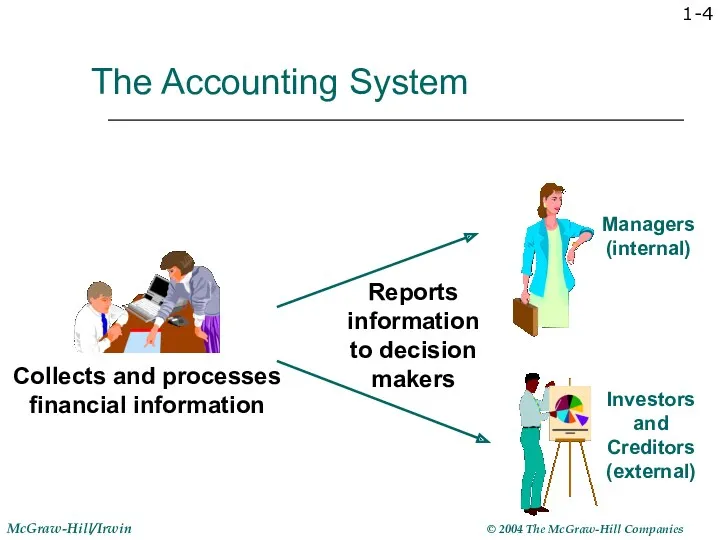
- 4. 1- The Accounting System
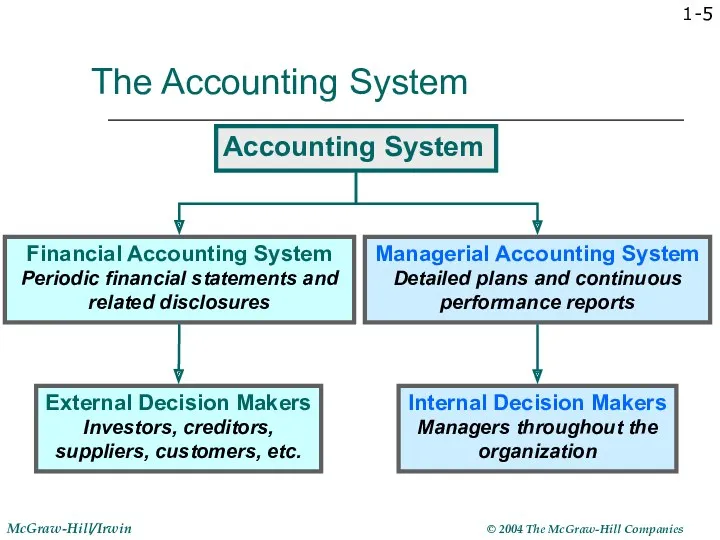
- 5. 1- The Accounting System Accounting System
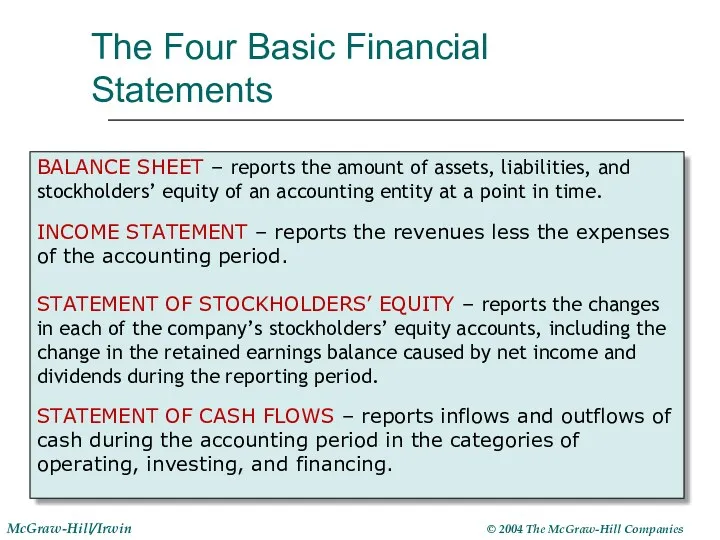
- 6. The Four Basic Financial Statements BALANCE SHEET – reports the amount of assets, liabilities, and stockholders’
- 7. 1- The Four Basic Financial Statements Companies can prepare financial statements at the end of the
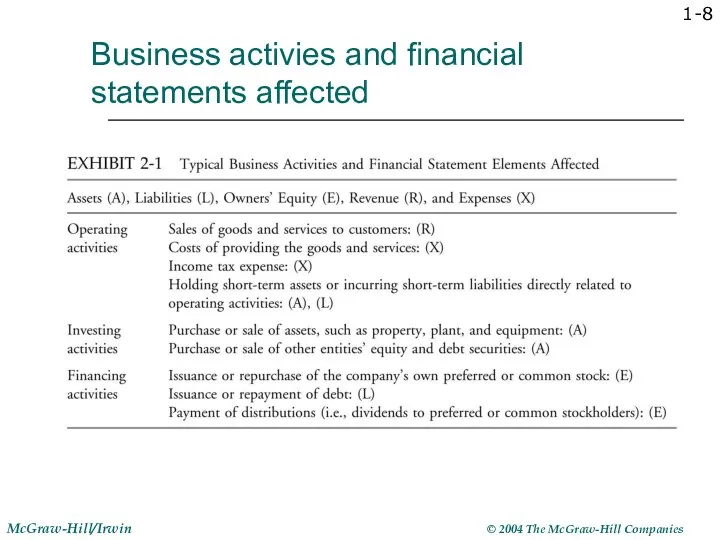
- 8. Business activies and financial statements affected 1-
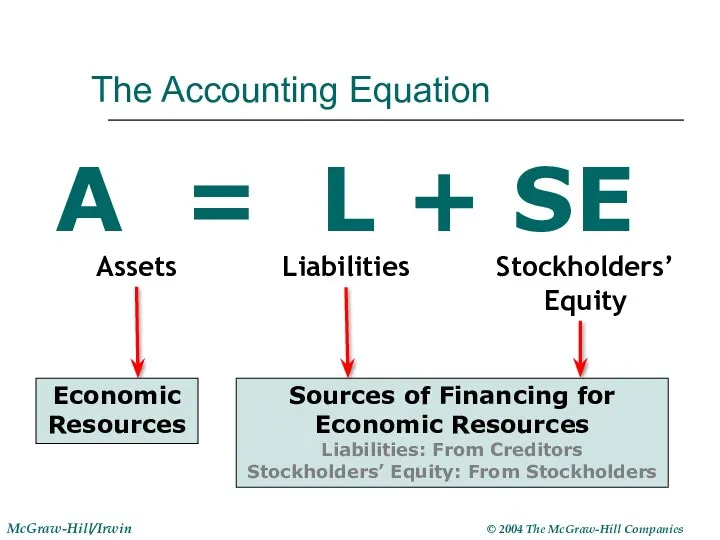
- 9. The Accounting Equation A = L + SE Assets Liabilities Stockholders’ Equity Economic Resources Sources of
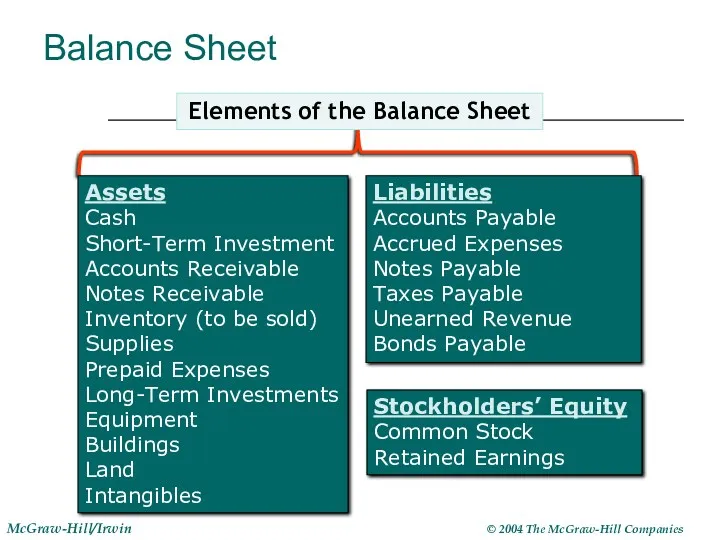
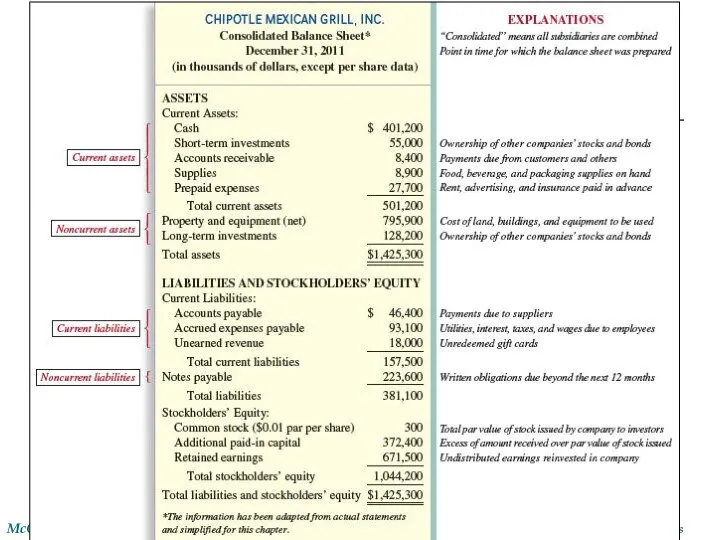
- 10. Balance Sheet Assets Cash Short-Term Investment Accounts Receivable Notes Receivable Inventory (to be sold) Supplies Prepaid
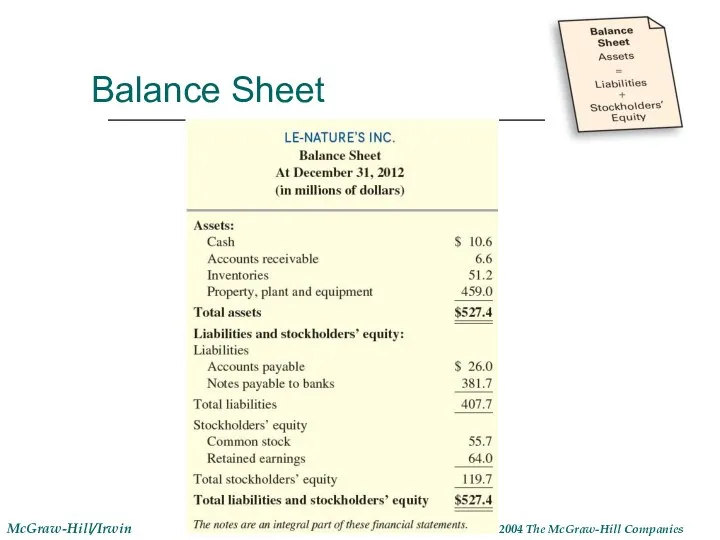
- 11. Balance Sheet
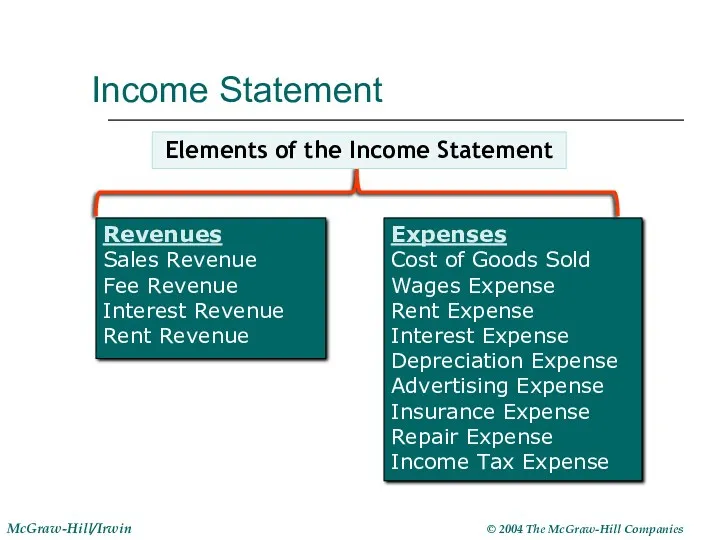
- 13. Income Statement Revenues Sales Revenue Fee Revenue Interest Revenue Rent Revenue Expenses Cost of Goods Sold
- 14. Income Statement
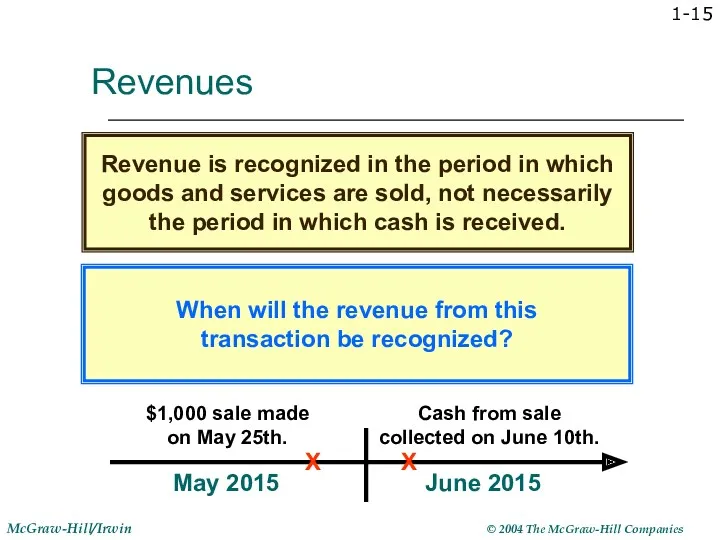
- 15. 1- Revenues When will the revenue from this transaction be recognized? Revenue is recognized in the
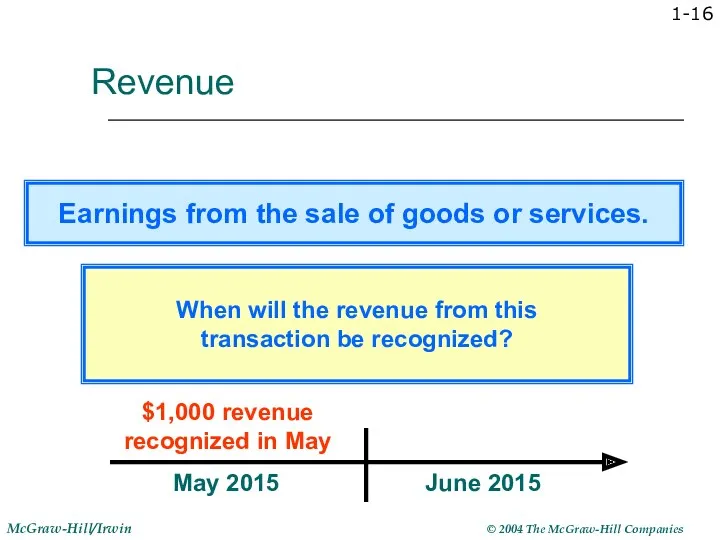
- 16. 1- Revenue May 2015 $1,000 revenue recognized in May June 2015 When will the revenue from
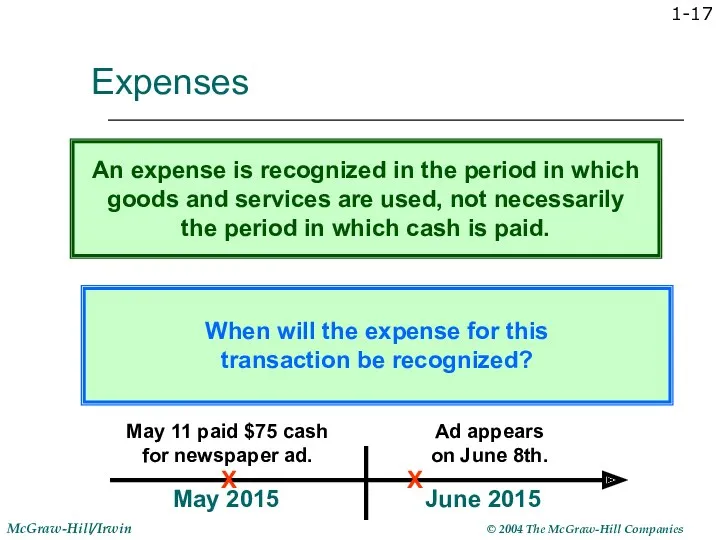
- 17. 1- Expenses When will the expense for this transaction be recognized? An expense is recognized in
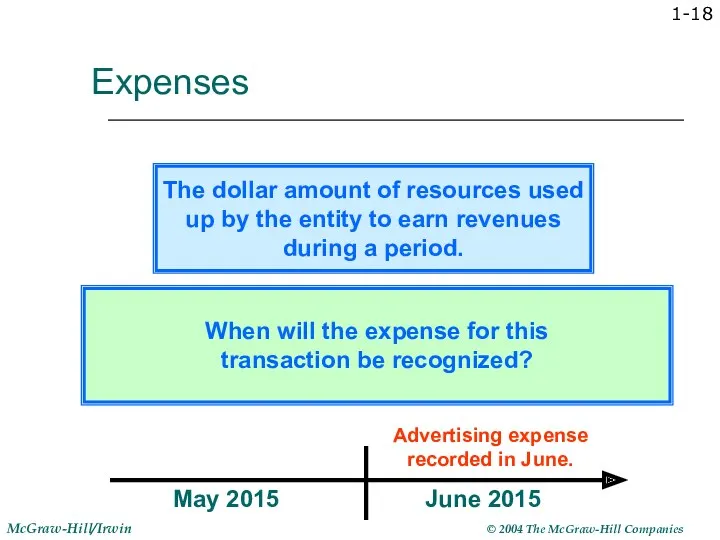
- 18. 1- Expenses May 2015 June 2015 Advertising expense recorded in June. The dollar amount of resources
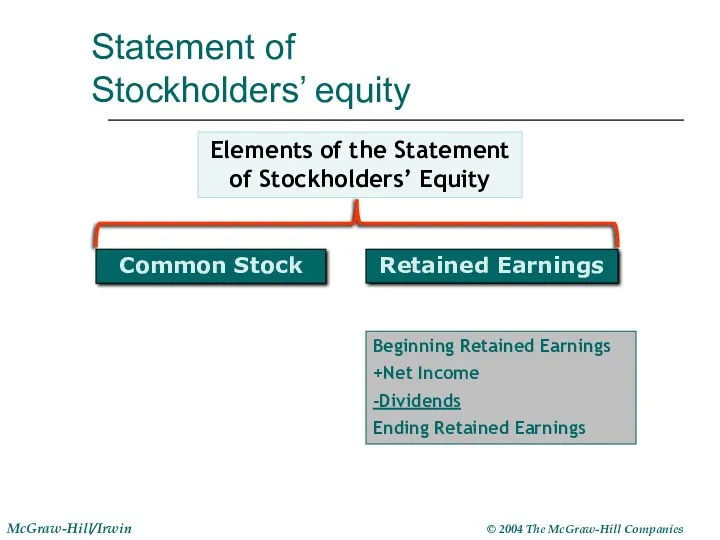
- 19. Statement of Stockholders’ equity Common Stock Retained Earnings Elements of the Statement of Stockholders’ Equity Beginning
- 20. Statement of Stockholders’ equity
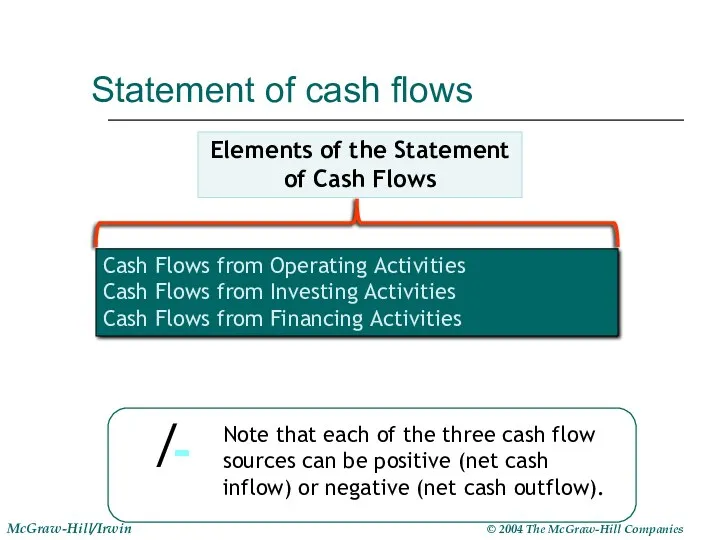
- 21. 1- Statement of Cash Flows Because revenues reported do not always equal cash collected. . .
- 22. Cash Flows from Operating Activities Cash Flows from Investing Activities Cash Flows from Financing Activities Statement
- 23. Statement of Cash Flows
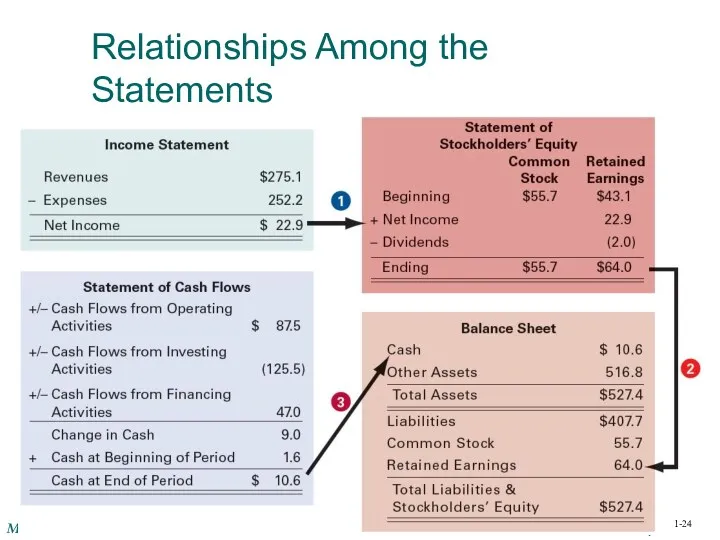
- 24. Relationships Among the Statements 1-
- 25. 1- Notes Notes provide supplemental information about the financial condition of a company. Three basic types
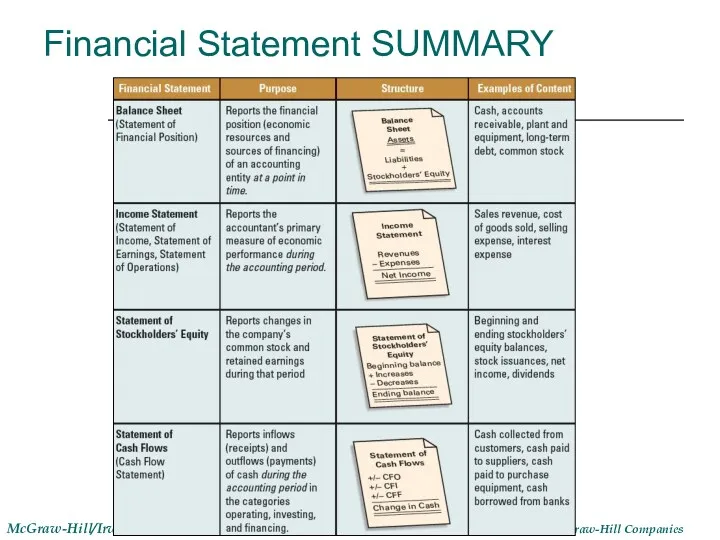
- 26. Financial Statement SUMMARY
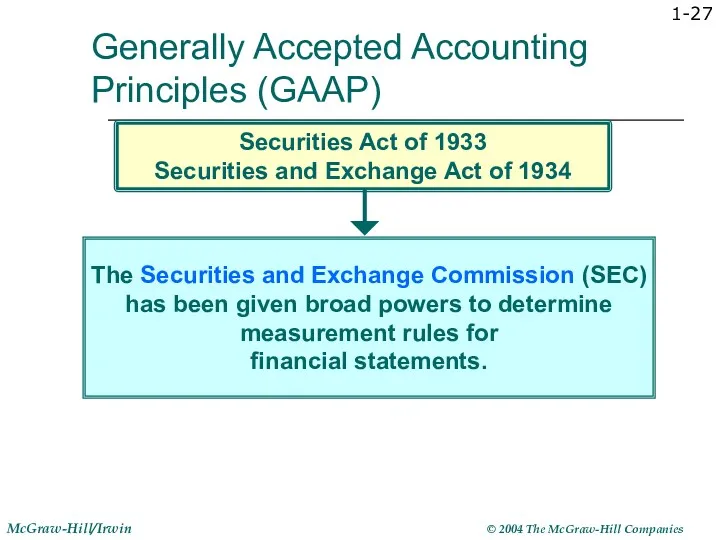
- 27. 1- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been given broad powers to determine measurement rules
- 28. 1- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) Currently, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is recognized as
- 29. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles Companies incur the cost of preparing the financial statements and bear the
- 30. Since 2002, there has been substantial movement toward the adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
- 32. Скачать презентацию










 Капитан Грантов. Основы грантрайтинга
Капитан Грантов. Основы грантрайтинга Structuring. Transaction Framework
Structuring. Transaction Framework История денег
История денег Организация и совершенствование финансового менеджмента на предприятии
Организация и совершенствование финансового менеджмента на предприятии Bank of England
Bank of England Доходы, расходы и прибыль организации
Доходы, расходы и прибыль организации Ақша қаражаттар қозғалысы
Ақша қаражаттар қозғалысы Порядок работы с должниками ООО ТЭК-Энерго
Порядок работы с должниками ООО ТЭК-Энерго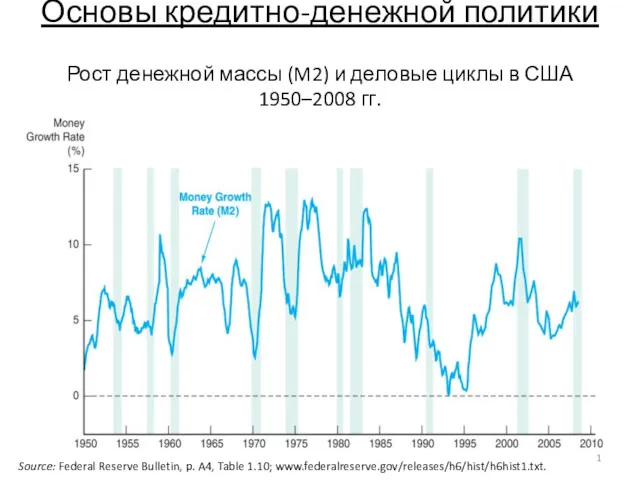 Основы кредитно-денежной политики
Основы кредитно-денежной политики Джерела фінансування інвестицій підприємства
Джерела фінансування інвестицій підприємства Разработка и внедрение электронных документов развитие
Разработка и внедрение электронных документов развитие Федеральный стандарт бухгалтерского учета для организаций государственного сектора События после отчетной даты
Федеральный стандарт бухгалтерского учета для организаций государственного сектора События после отчетной даты Учет денежных средств и расчетов. Кассовые операции. Учет труда и заработной платы в аптечной организации
Учет денежных средств и расчетов. Кассовые операции. Учет труда и заработной платы в аптечной организации Банковские услуги
Банковские услуги Финансовая система (тема 2)
Финансовая система (тема 2) Операції банків з обслуговування платіжного обігу. Безготівкові та готівкові розрахунки. Порядок відкриття рахунків в банках
Операції банків з обслуговування платіжного обігу. Безготівкові та готівкові розрахунки. Порядок відкриття рахунків в банках Bank RBK
Bank RBK Понятие и назначение финансов
Понятие и назначение финансов Стратегии ценообразования банковских услуг
Стратегии ценообразования банковских услуг Новая продуктовая линейка АО Микрофинансовая компания Пермского края при финансовой поддержке Правительства Пермского края
Новая продуктовая линейка АО Микрофинансовая компания Пермского края при финансовой поддержке Правительства Пермского края Объекты учета затрат в системе управленческого учета. (Лекция 3)
Объекты учета затрат в системе управленческого учета. (Лекция 3) Дидактические игры по формированию основ финансовой грамотности у детей старшего дошкольного возраста
Дидактические игры по формированию основ финансовой грамотности у детей старшего дошкольного возраста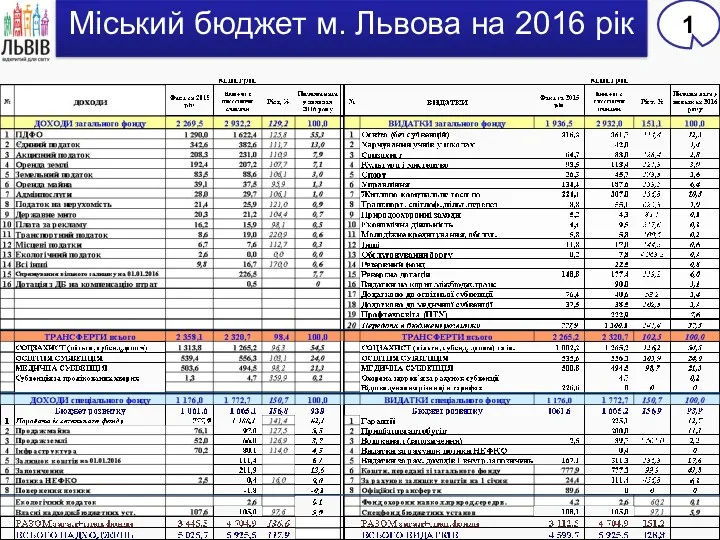 Міський бюджет м. Львова на 2016 рік
Міський бюджет м. Львова на 2016 рік Корректировка плана МТО ООО Таргин
Корректировка плана МТО ООО Таргин Надёжность и гарантии. Страховая компания Metlife Alico в Украине
Надёжность и гарантии. Страховая компания Metlife Alico в Украине Формирование бюджетов ОГВ и ОМСУ
Формирование бюджетов ОГВ и ОМСУ Всемирные (международные) экономические отношения
Всемирные (международные) экономические отношения Бухгалтерский баланс
Бухгалтерский баланс